Study on the Regulatory Mechanism of Inhibiting miR-153-3p to Delay Intervertebral Disc Degeneration via Nrf2 Regulation
-
摘要:
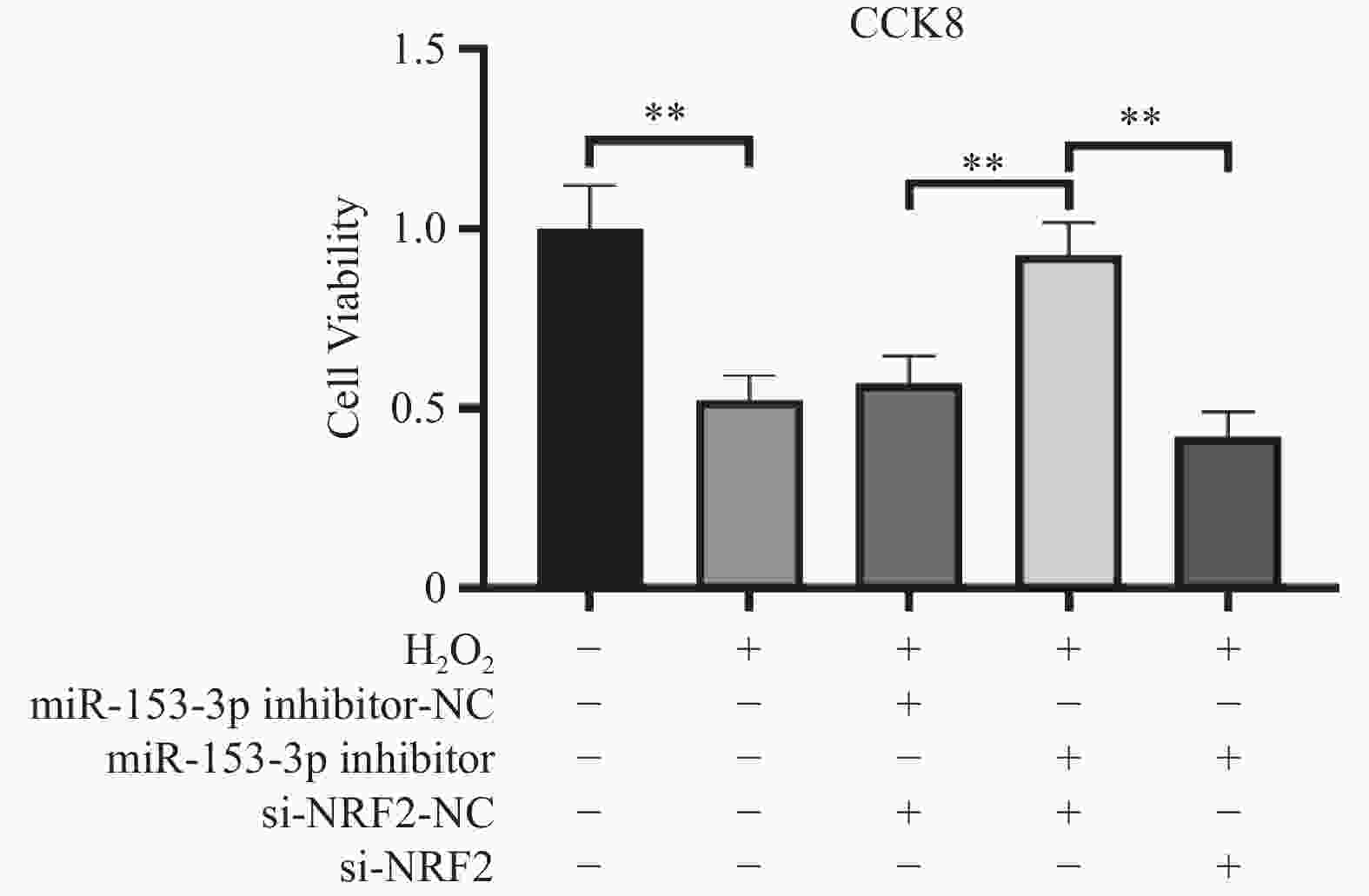
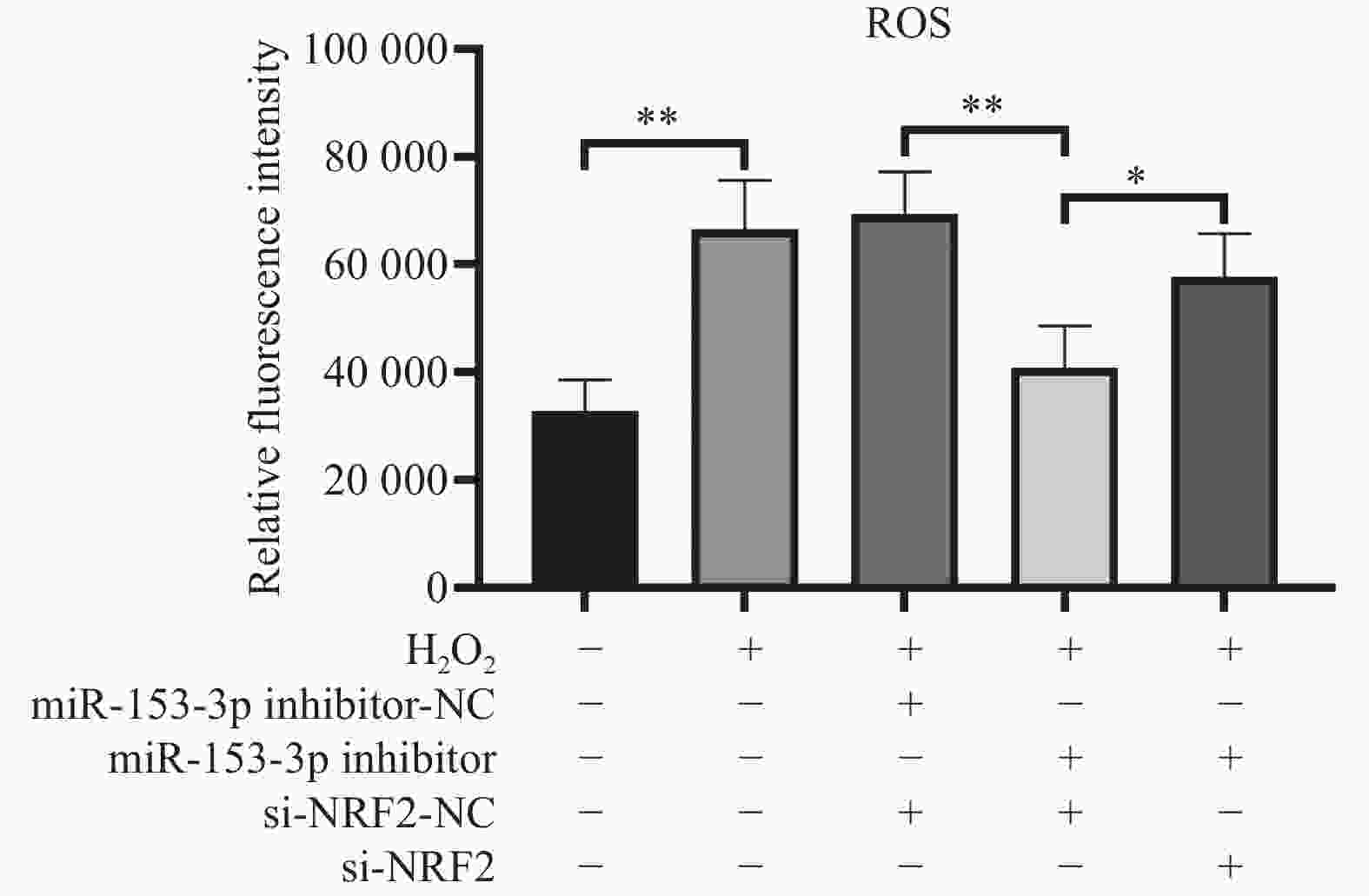
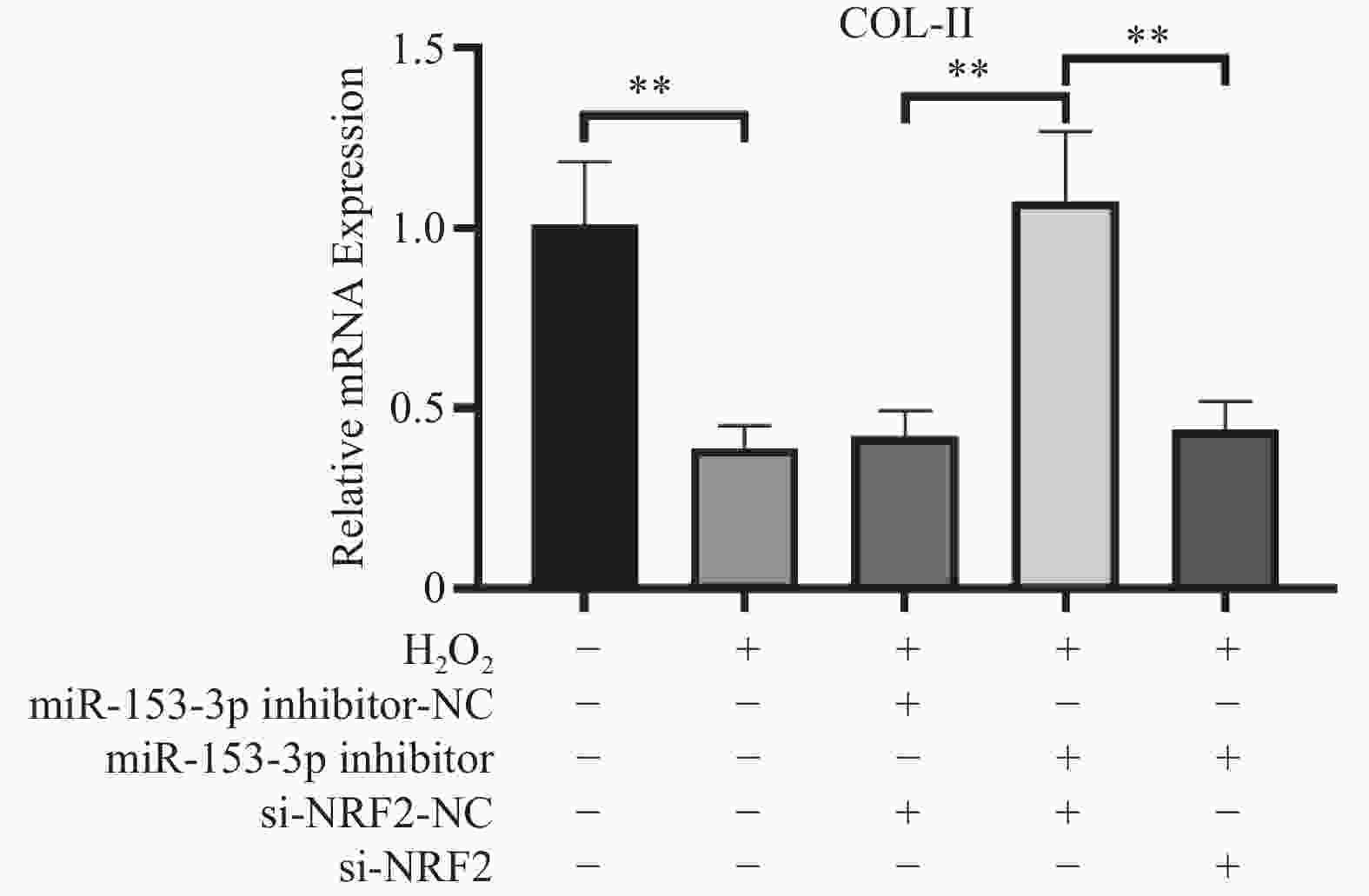
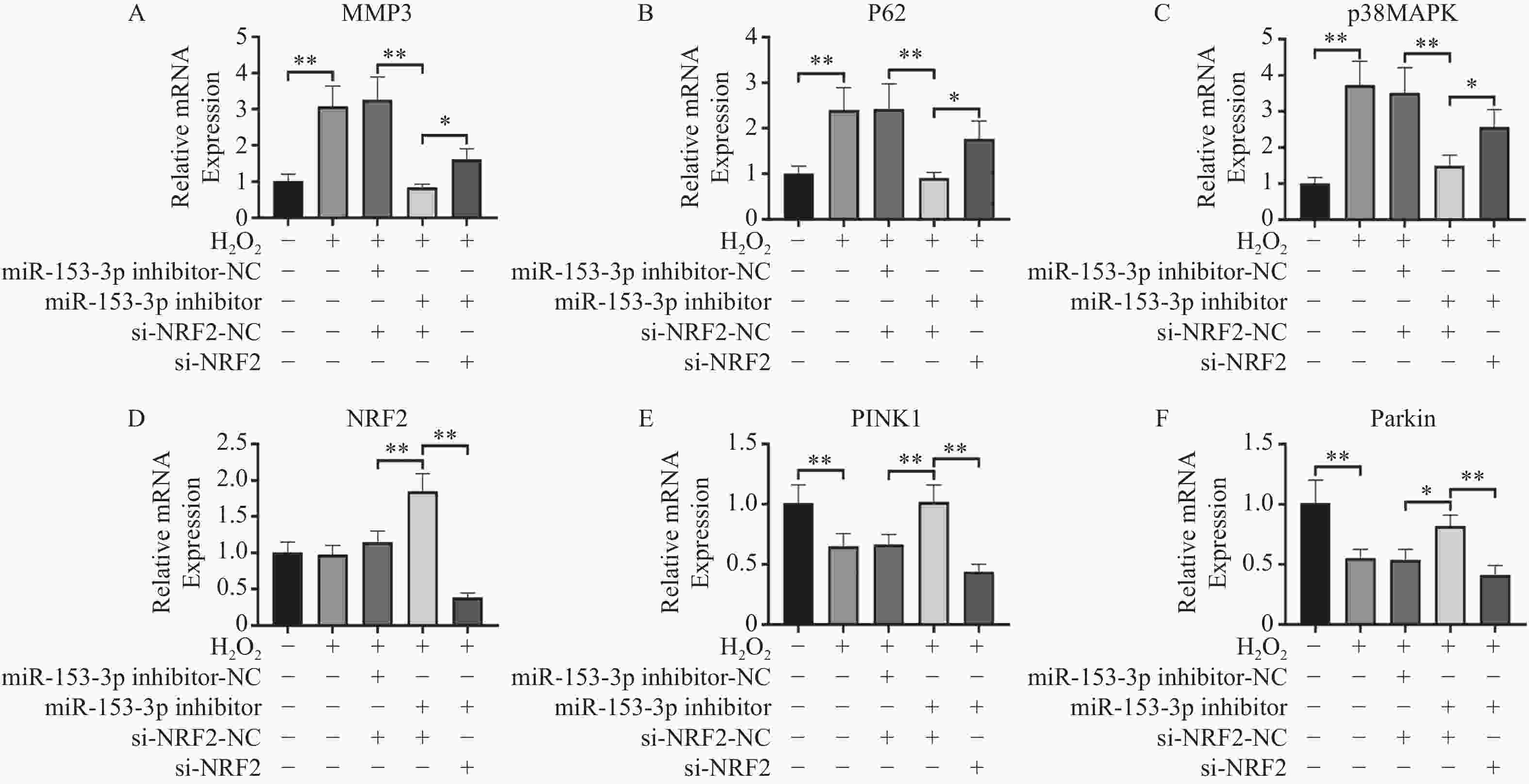
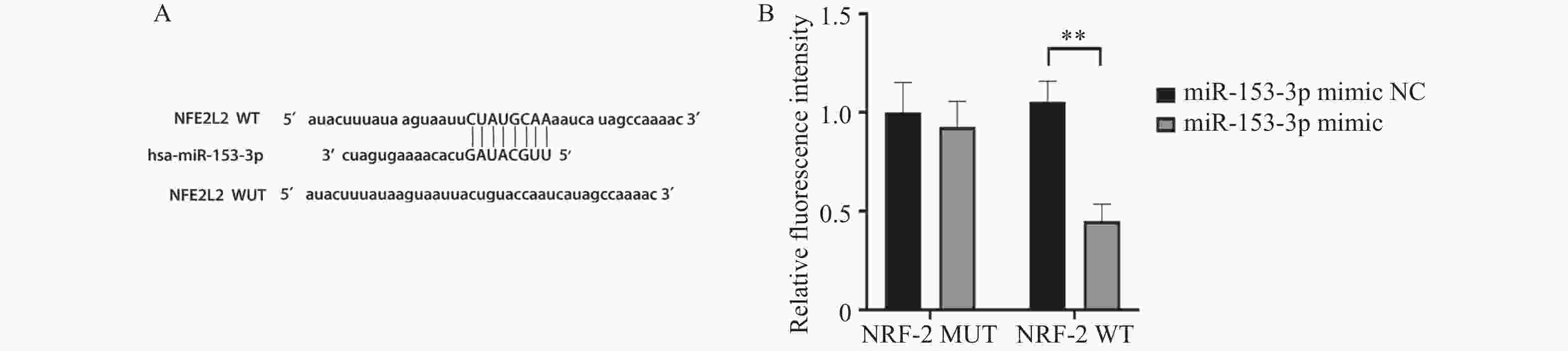
目的 探讨人髓核细胞中miR-153-3p及Nrf2表达与椎间盘退变的相关机制。 方法 以H2O2构建髓核细胞氧化损伤模型,将miR-153-3p inhibitor-NC、si-Nrf2-NC 、miR-153-3p inhibitor、si-Nrf2分组转染至髓核细胞,利用RT-qPCR和Western blot实验检测转染效率,采用CCK-8法检测细胞活力,流式细胞仪检测细胞内活性氧ROS 水平、线粒体膜电位下降的比值;RT-qPCR检测Nrf2、MMP-3、Col-Ⅱ、PINK1、Parkin、p62、p38 MAPK的表达量,双荧光素酶报告实验测量荧光素酶活性。 结果 (1)经H2O2处理的HNPCs细胞活力下降及线粒体膜电位降低、ROS水平提高、Col-Ⅱ表达减少,MMP-3、P62、p38 MAPK表达均升高,PINK1、Parkin表达均降低(P < 0.05),Nrf2无明显变化(P > 0.05)。(2)抑制经H2O2处理的髓核细胞miR-153-3p表达,其细胞活力及线粒体膜电位提高、ROS水平下降、Col-Ⅱ表达增加, MMP-3、P62、p38 MAPK表达均降低;而PINK1、Parkin及Nrf2表达均升高(P < 0.05)。(3)抑制经H2O2处理的髓核细胞miR-153-3p表达,同时沉默Nrf2表达,可见细胞活力及线粒体膜电位下降、ROS水平升高、Col-Ⅱ表达减少,且其MMP-3、P62、p38 MAPK表达升高;Nrf2、PINK1、Parkin 表达降低(P < 0.05)。(4)双荧光素酶活性分析显示miR-153-3p与 Nrf2间存在结合位点和结合关系,关系呈负相关(P < 0.05)。 结论 抑制miR-153-3p表达可缓解H2O2诱导的髓核细胞退变和纤维化,激活受损髓核细胞自噬、延缓髓核细胞凋亡,这一作用与Nrf2调控PINK1/Parkin途径、p38 MAPK炎性反应通路相关。 -
关键词:
- 椎间盘退变 /
- 人髓核细胞 /
- miR-153-3p /
- Nrf2
Abstract:Objective To investigate the correlation mechanism between miR-153-3p and Nrf2 expression in human nucleus pulposus cells and intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD). Methods The oxidative damage model of nucleus pulposus cells was duplicated induced by H2O2. MiR-153-3p inhibitor-NC, si-NRF2-NC, miR-153-3p inhibitor, and si-NRF2 were transfected into nucleus pulposus cells according to the grouping require. The transfection efficiency was detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot. The cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay, when the intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and the ratio of mitochondrial membrane potential decline were measured by flow cytometry, RT-qPCR was used to detect the expression levels of Nrf2, MMP-3, Col II, PINK1, Parkin, P62, and p38 MAPK. And dual luciferase reporter assay was used to measure luciferase activity. Results (1) HNPCs treated with H2O2 showed a decrease in HNPCs cell viability, a reduction in mitochondrial membrane potential, an increase in ROS levels, and a decrease in Col II expression (P < 0.05). And the expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK increased, while the expression of PINK1 and Parkin decreased. There was no significant change in Nrf2(P > 0.05). (2) Inhibition of miR-153-3p expression in nucleus pulposus cells treated with H2O2 led to increased cell viability, elevated mitochondrial membrane potential, reduced ROS levels, and enhanced Col-II expression, accompanied by decreased expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK, while simultaneously increasing the expression of PINK1, Parkin, and Nrf2 (P < 0.05). (3) When miR-153-3p expression was inhibited and Nrf2 expression was silenced in nucleus pulposus cells treated with H2O2, a notable decline in cell viability and mitochondrial membrane potential was observed, along with a marked increase in ROS levels. Additionally, Col-II expression decreased, whereas the expression of MMP-3, P62, and p38 MAPK increased. However, the expression of Nrf2, PINK1, and Parkin decreased (P < 0.05). (4) Dual-luciferase assay analysis revealed binding sites and a binding relationship between miR-153-3p and Nrf2, indicating a negative correlation between miR-153-3p and Nrf2 (P < 0.05). Conclusion Inhibition of miR-153-3p expression can alleviate H2O2 induced degeneration and fibrosis of nucleus pulposus cells, activate autophagy of damaged nucleus pulposus cells, and delay apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells. This effect is related to the PINK1/Parkin pathway and p38 MAPK inflammatory response pathway regulated by Nrf2. -
Key words:
- Intervertebral disc degeneration /
- Human nucleus pulposus cells /
- miR-153-3p /
- Nrf2
-
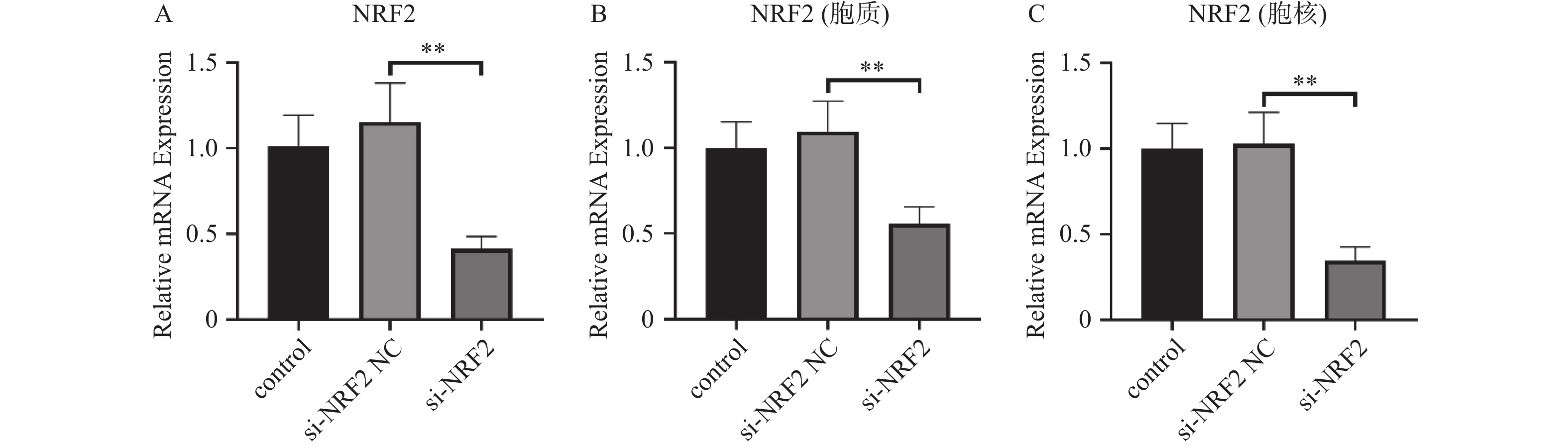
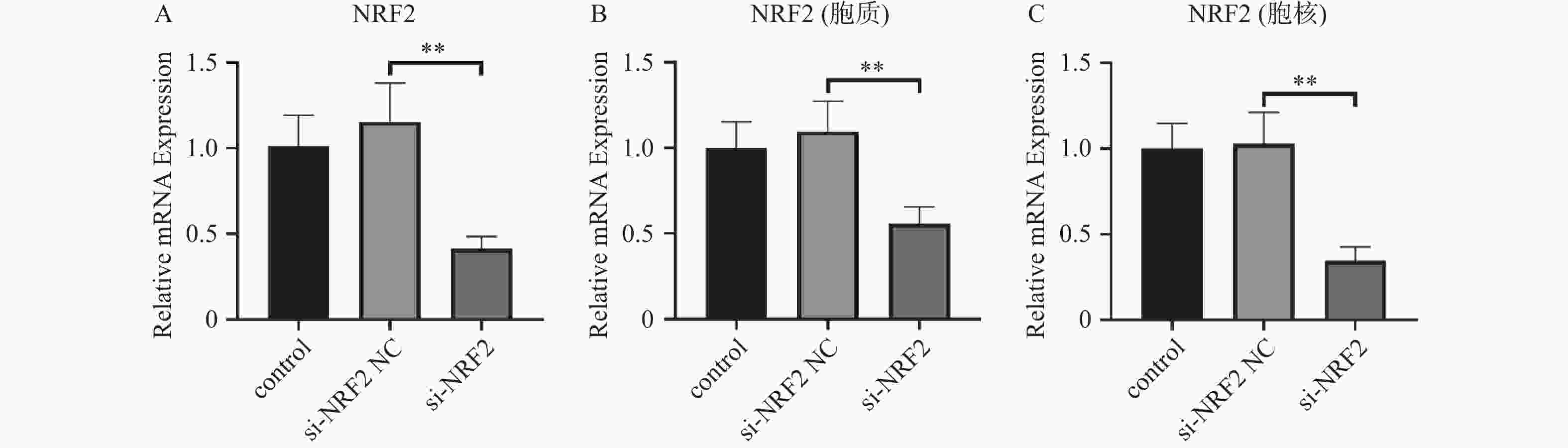
图 5 RT-qPCR检测各组Nrf2、MMP-3、PINK1、Parkin、p62、p38 MAPK的相对表达量($ \bar x \pm s$,n = 3)
A:各组MMP3表达;B:各组p62表达;C:各组p38MAPK表达;D:各组Nrf2表达E:各组PINK1表达;F:各组Parkin表达;*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01;+:阳性标本处理;-:阴性标本处理。
Figure 5. RT-qPCR detection of relative expression levels of Nrf2,MMP-3,PINK1,Parkin,p62,p38 MAPK in each group($ \bar x \pm s$,n = 3)
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. primer sequence
基因 引物序列 产物长度/bp 序列号 PINK1 F TTGCCCCTAACACGAGGAAC 95 NM_032409.3 R ACGTGCTGACCCATGTTGAT Parkin F GACAGCAGGAAGGACTCACC 123 XM_011535863.1 R GCTGCACTGTACCCTGAGTT P62 F ACTGCTCCAACCTCATCTGC 96 NM_001193357.2 Homo R TAAGCTGAAGCCCTGTGTCC p38 MAPK F ATGCGTCTGACAGGAACACC 108 NM_001315.3 Homo R CGCAAAGTTCATCTTCGGCA Nrf2 F GCCAACTACTCCCAGGTTGC 122 NM_006164.5 Homo R AACGTAGCCGAAGAAACCTCA MMP-3 F AGCCAACTGTGATCCTGCTT 102 NM_002422.5 Homo R TTCCTGAGGGATTTGCGCC Col-Ⅱ F AGGACTCTGCACTGAATGGC 106 NM_001844.5 Homo R TCTGCCCAGTTCAGGTCTCT β-actin F GTCATTCCAAATATGAGATGCGT 121 NM_001101.5 R GCTATCACCTCCCCTGTGTG 表 2 流式检测各组线粒体膜电位($\bar x \pm s$,n = 3)
Table 2. Flow cytometry detection of mitochondrial membrane potential in each group($\bar x \pm s$,n = 3)
分组 线粒体膜电位下降比例 ①对照组 16.13 ± 1.65 ②H2O2组 7.84 ± 0.95#▲ ③H2O2 + miR-153-3p inhibitor-NC + si-Nrf2-NC 8.63 ± 0.79#▲ ④H2O2 + miR-153-3p inhibitor +
si-Nrf2-NC15.03 ± 1.72 ⑤H2O2 + miR-153-3p inhibitor +
siRNA-Nrf26.03 ± 0.76△#▲ F 39.713 P <0.01* *P < 0.05;与③组比较,△P < 0.05;与①组比较,#P < 0.05;与④组比较,▲P < 0.05。 -
[1] 张嘉军,刘勇,许德荣,郭建伟,王华聪. 椎间盘退变的机制及其治疗综述[J]. 临床医学进展,2020,10(10):2302-2310. [2] 王延海,张雷明,冯艳艳. 大黄素改善高糖条件中人肾小球血管内皮细胞炎症、氧化应激及凋亡作用的研究[J]. 中国临床药理学杂,2023,39(10):1422-1426. [3] 杨召,苑珍珍. 炎性因子在中医药治疗椎间盘退变中的机制研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2021,29(24):2246-2248. [4] 李敬超. 红景天苷通过Nrf2/ARE信号通路缓解椎间盘退变的研究 [D]. 天津:天津医科大学,2020. [5] 寇裕,顾勇,陈亮. 黑磷调控氧化应激-炎症级联效应延缓椎间盘退变的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(15):2338-2345. [6] 庾珊,肖林,龚东平,等. miR-153-3p对于腰退行性病变调节机制的初步探讨[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(8):53-58. [7] Ebrahimi S O,Reiisi S,Shareef S. miRNAs,oxidative stress,and cancer: A comprehensive and updated review.[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2020,235(11):8812-8825. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29724 [8] 郭静,吴琦,蔡旖斐,等. miR-153-3p调控神经突的生长[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2019,33(7):650-653. [9] 张丽霞,周露玙,许胜,等. MiR-153-3p调控异丙肾上腺素诱导的心肌肥大机制研究[J]. 转化医学杂志,2019,8(4):199-202+212. [10] 崔文洁,袁杰清,施海,等. lncRNA KTN1-AS1调节miR-153-3p/NFAT5轴对非小细胞肺癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭的影响[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2023,33(2):22-30. [11] 张曹,何亚琴,钱海权,等. miR-153-3p通过靶向FZD3调控胃癌SGC7901细胞的增殖、侵袭与迁移[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2021,28(9):885-892. [12] 孙蕾,王华,姜珏,等. miR-153-3p靶向下调Rho相关螺旋蛋白激酶1(ROCK1)基因抑制乳腺癌细胞增殖及迁移[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2020,36(2):138-144. [13] 黄兆琦,许卫,黄炯华,等. 下调miR-153-3p可促进Nrf2表达从而减轻H2O2诱导的H9C2细胞损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(7):1249-1254. [14] Zou X,Zhang X,Han S,et al. Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications of matrix metalloproteinases in intervertebral disc degeneration: A comprehensive review[J]. Biochimie,2023,214(PtB):27-48. [15] 周树良,徐良,钱学峰,等. 椎间盘退变程度与髓核中miRNA-142-3p、混合谱系激酶3及白细胞介素1β的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(2):165-171. [16] D'Arcy M S. Cell death: a review of the major forms of apoptosis,necrosis and autophagy[J]. Cell Biology International,2019,43(6):582-592. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11137 [17] 庞延,卢健棋,唐梅玲,等. 强心汤对慢性心力衰竭模型大鼠梗死心肌区组织活性氧及PINK1/parkin介导的线粒体自噬的影响[J]. 中医杂志,2023,64(7):722-728. [18] Picca A,Faitg J,Auwerx J,et al. Mitophagy in human health,ageing and disease.[J]. Nature Metabolism,2023,5(12):2047-2061. doi: 10.1038/s42255-023-00930-8 [19] 潘世鸿,刘瑞端. 线粒体自噬与椎间盘退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2024,28(36):5872-5876. [20] Quinn P M J,Moreira P I,Ambrosio A F,et al. PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation[J]. Acta Neuropathologica Communications,2020,8(1):189. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01062-w [21] Jahanian S,Pareja-Cajiao M,Gransee H M,et al. Autophagy markers LC3 and p62 in aging lumbar motor neurons[J]. Experimental Gerontology,2024,194:112483. [22] 魏思灿,林天来,黄玲,等. 槲皮素通过PINK1/parkin通路激活线粒体自噬减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2020,36(12):2251-2257. [23] Song C,Zhang A,Zhang M,et al. Nrf2/PINK1-mediated mitophagy induction alleviates sodium fluoride-induced hepatic injury by improving mitochondrial function,oxidative stress,and inflammation[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2023,252:114646. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114646 [24] Han Y,Li X,Yan M,et al. Oxidative damage induces apoptosis and promotes calcification in disc cartilage endplate cell through ROS/MAPK/NF-κB pathway: Implications for disc degeneration[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2019,516(3):1026-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.03.111 [25] Shi Z W,Zhu L,Song Z R,et al. Roles of p38 MAPK signalling in intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Cell Prolif,2023,56(8):e13438. -





 下载:
下载: