HIF-2Α Promotes Osteoarthritis Progression by Regulating Articular Cartilage Deg-eneration Through Activation of CXCR4
-
摘要:
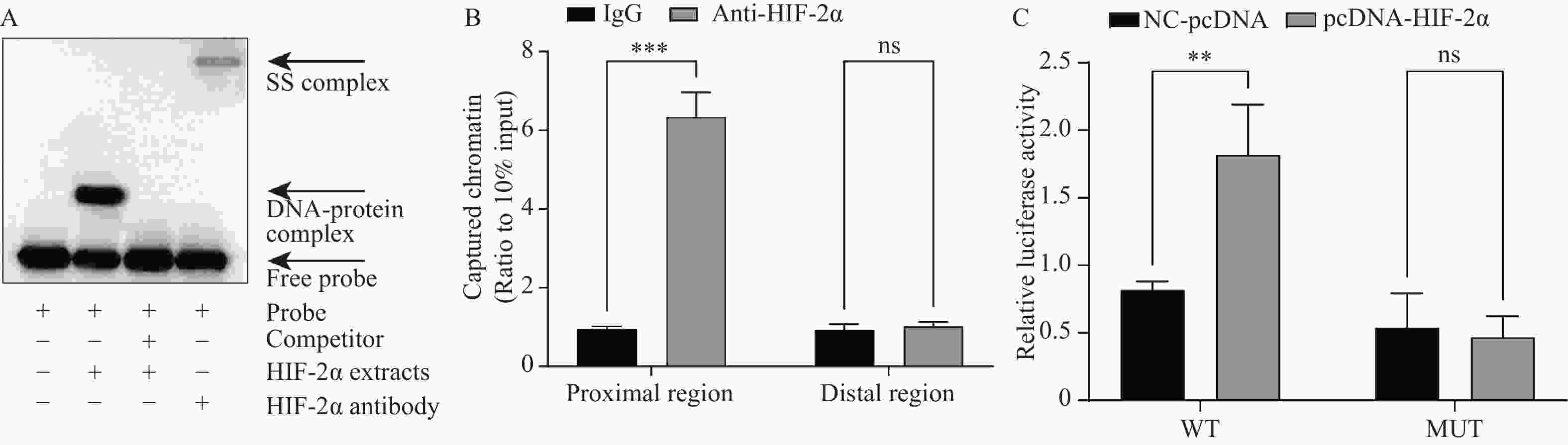
目的 探讨缺氧诱导因子2α(hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha,HIF-2α)/C-X-C趋化因子受体4型(C-X-C receptor 4,CXCR4)通路调节骨关节炎(osteoarthritis,OA)的分子机制。 方法 用C57BL/6 雄性小鼠原代软骨细胞构建软骨退变细胞模型。将pcDNA、pcDNA-HIF-2α、si-NC、si-HIF-2α和si-CXCR4质粒并转染至细胞中,用RT-qPCR、Western blot和免疫荧光检测HIF-2α、CXCR4、MMP-3,Collagen II和aggrecan的表达水平。流式细胞术评估细胞凋亡,ELISA检测炎症因子PGE2、IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α的表达。通过EMSA、CHIP和双荧光素酶报告验证HIF-2α和CXCR4的相互作用。 结果 HIF-2α在低氧环境下通过上调软骨细胞内MMP-3的表达和炎症因子PGE2、IL-6、IL-1β和TNF-α的分泌(P < 0.05),下调Collagen II和aggrecan表达(P < 0.001),促进了软骨细胞凋亡。HIF-2α与CXCR4的启动子结合,调控其转录表达。HIF-2α通过激活CXCR4在低氧环境下促进OA的进展;而敲低CXCR4后,抑制了HIF-2α对软骨细胞炎症、降解和凋亡的促进作用,缓解OA的进展。 结论 HIF-2α/CXCR4轴可以有效介导软骨细胞炎症反应、基质降解和凋亡。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the specific molecular mechanisms by which the hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha (HIF-2α)/C-X-C chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) pathway regulates the progression of osteoarthritis (OA). Method A cartilage degeneration cell model was established using primary chondrocytes from male C57BL/6 mice. Co-transfected cells with pcDNA, pcDNA-HIF-2α, si-NC, si-HIF-2α, and si-CXCR4 plasmids. Detected expression levels of HIF-2α, CXCR4, MMP-3, Collagen II, and aggrecan via RT-qPCR, Western blot, and immunofluorescence. Flow cytometry assessed apoptosis, while ELISA measured levels of inflammatory mediators PGE2, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α. EMSA, ChIP, and dual luciferase assays validated the interaction between HIF-2α and CXCR4. Results HIF-2α promoted chondrocyte apoptosis under hypoxic conditions by upregulating MMP-3 expression and secretion of inflammatory mediators PGE2, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α (P < 0.05) while downregulating Collagen II and aggrecan expression (P < 0.001). HIF-2α binds to the CXCR4 promoter to regulate its transcriptional expression. HIF-2α promotes OA progression under hypoxia by activating CXCR4. Knockdown of CXCR4 inhibited HIF-2α's promotion of chondrocyte inflammation, degradation, and apoptosis, thereby alleviating OA progression. Conclusion The HIF-2α/CXCR4 axis effectively mediates chondrocyte inflammation, matrix degradation, and apoptosis. -
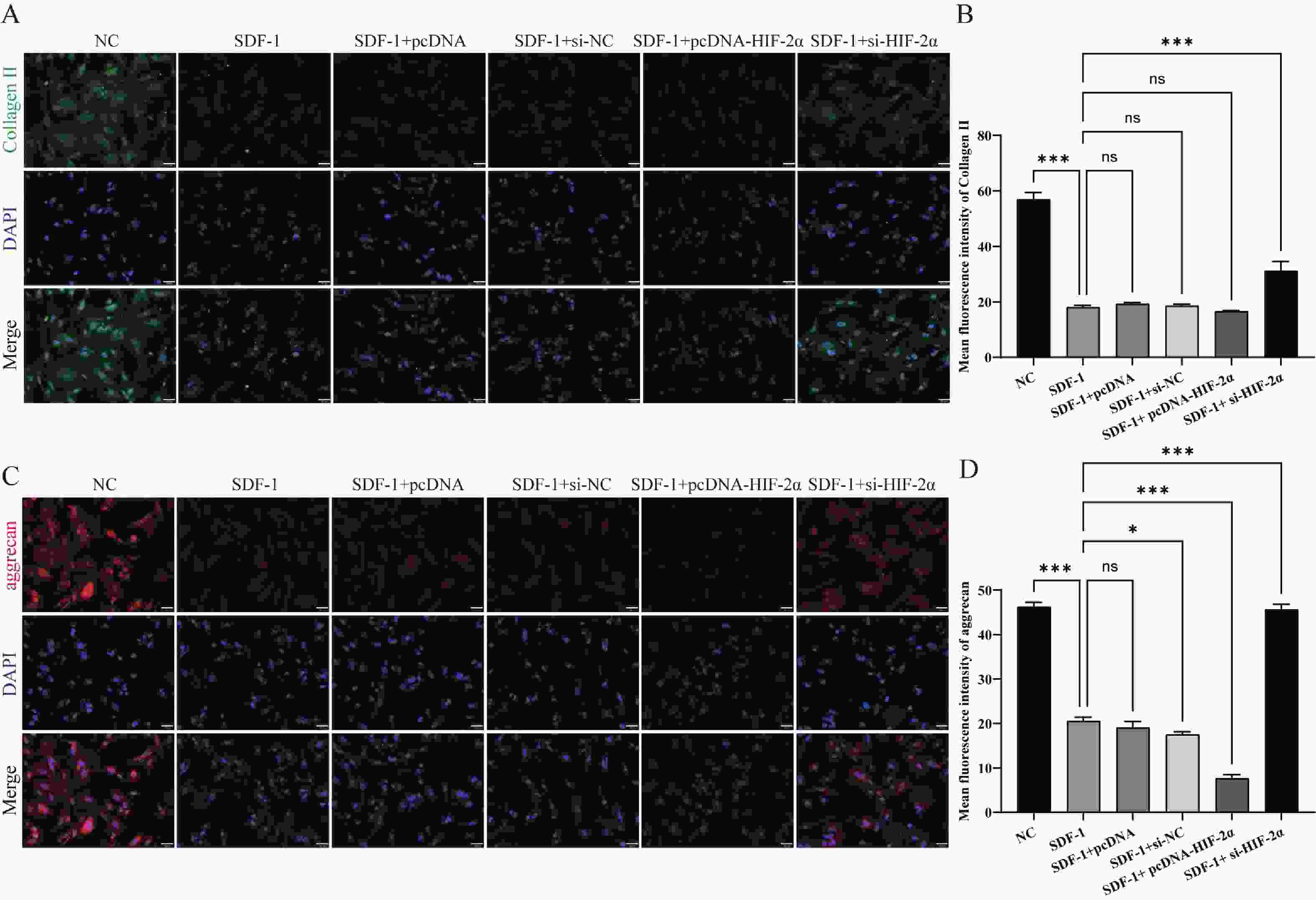
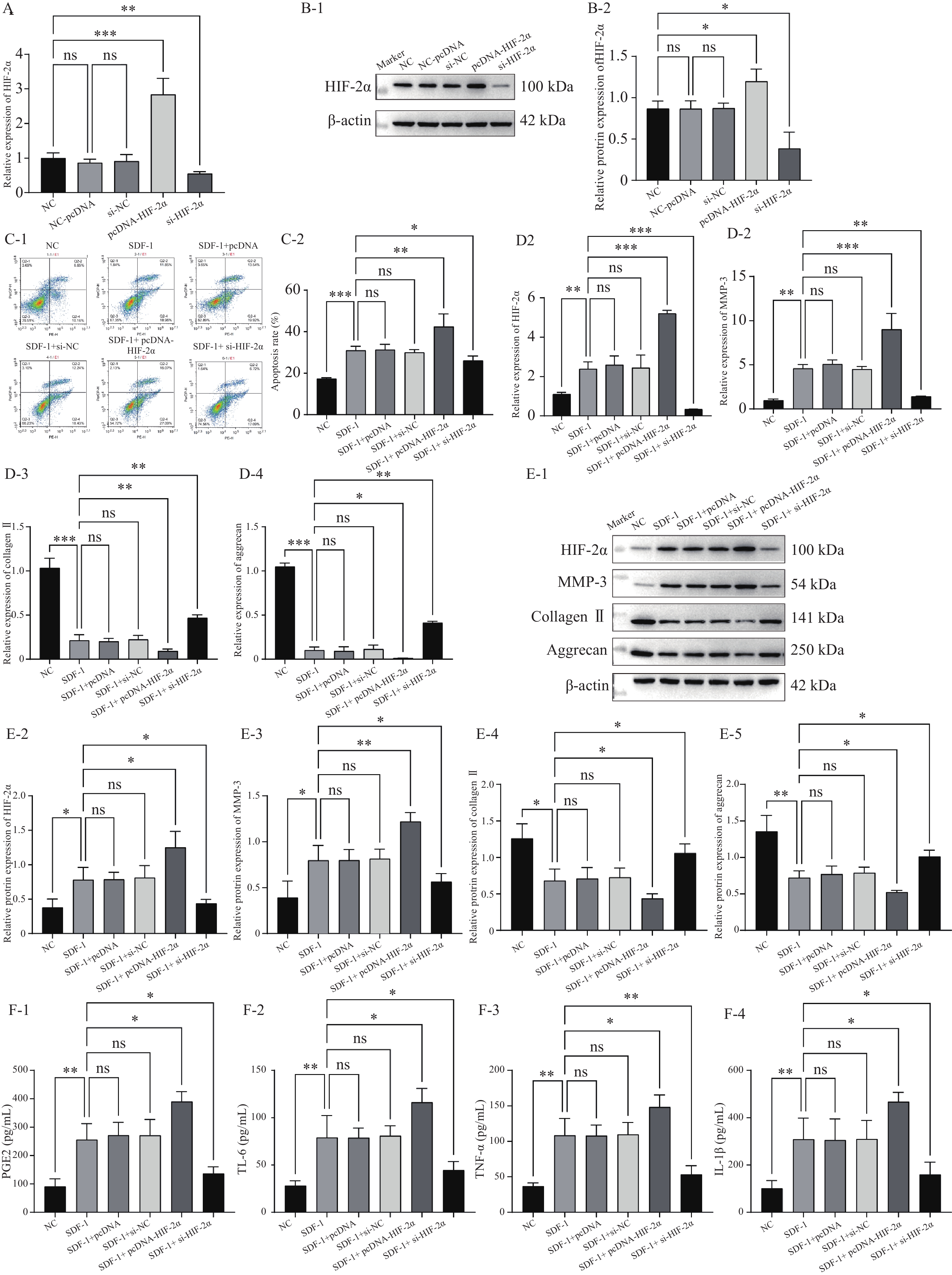
图 1 HIF-2α在低氧环境下诱发并加速OA的进展($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
A:RT-qPCR检测转染效率;B:Western blot检测转染效率;C:流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡;D:RT-qPCR检测HIF-2α,MMP-3,Collagen II,aggrecan的表达水平;E:Western blot检测HIF-2α,MMP-3,Collagen II,aggrecan的蛋白表达水平;F:ELISA检测PGE2,IL-6,TNF-α,IL-1β的含量;nsP > 0.05,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。
Figure 1. HIF-2α induces and accelerates the progression of OA in a hypoxic environment ($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
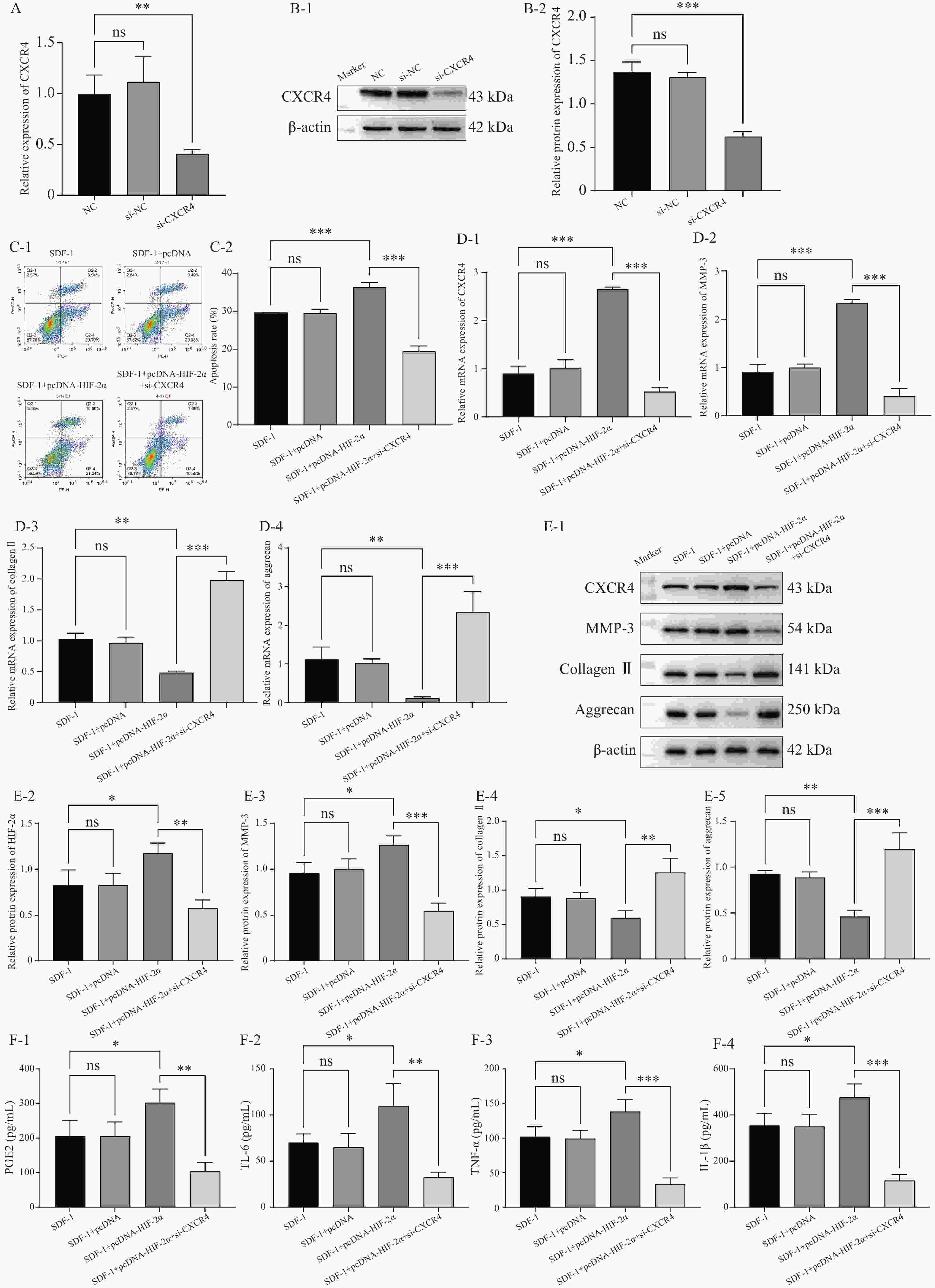
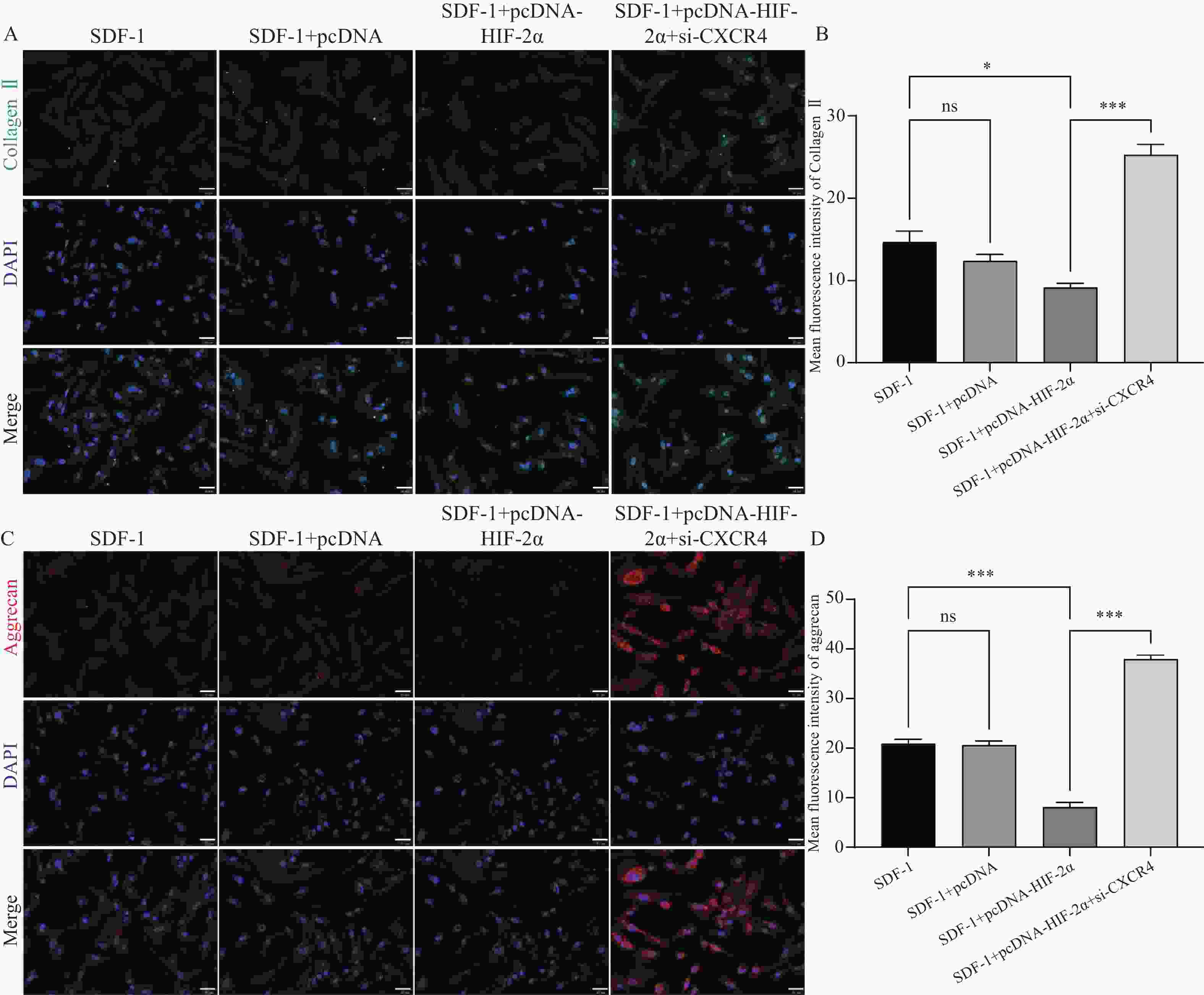
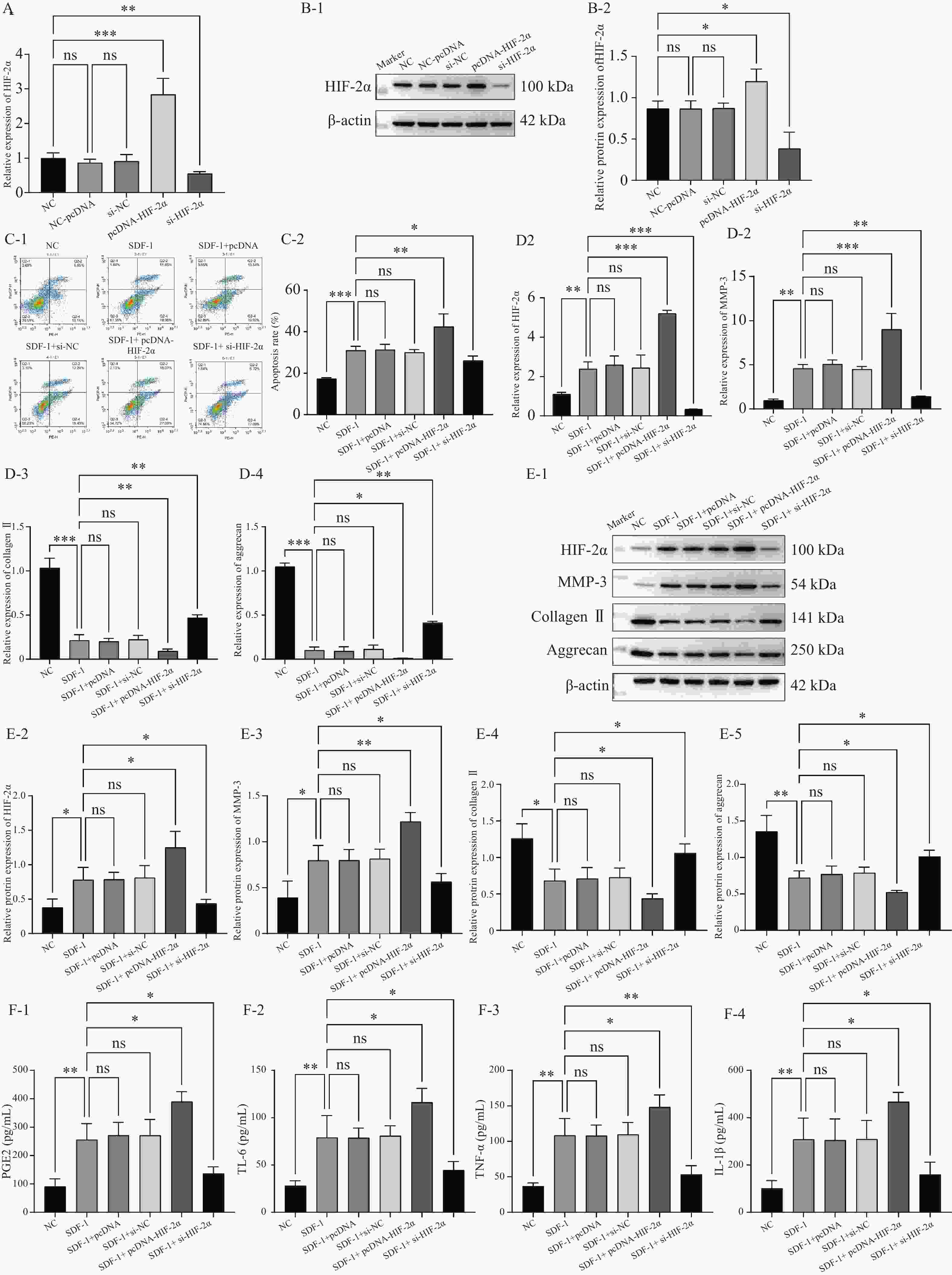
图 4 HIF-2α通过激活CXCR4在低氧环境下促进OA的进展($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
A:RT-qPCR检测转染效率;B:Western blot检测转染效率;C:流式细胞术检测细胞凋亡;D:RT-qPCR检测CXCR4,MMP-3,Collagen II,aggrecan的表达水平;E:Western blot检测CXCR4,MMP-3,Collagen II,aggrecan的蛋白表达水平;F:ELISA检测PGE2,IL-6,TNF-α,IL-1β的含量。nsP > 0.05,*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。
Figure 4. HIF-2α promotes OA progression through activation of CXCR4 in a hypoxic environment ($ \bar x \pm s $,n = 3)
表 1 PCR引物序列
Table 1. PCR primer sequences
基因 引物 序列(5′-3′) 引物长度(bp) HIF-2α Forward 5′-CCACCGAGCGTGACTTCT-3′ 18 Reverse 5′-CATAGGCAGAGCGTCCAA-3′ 19 MMP-3 Forward 5′-CCACAGACTTGTCCCGTTTC-3′ 20 Reverse 5′-TCGTGCCCTCGTATAGCC-3′ 18 Collagen II Forward 5′-ACTGGTGGAGCAGCAAGAGC-3′ 21 Reverse 5′-GCGATGTCAATAATGGGAAGG-3′ 22 aggrecan Forward 5′-CGGGAAGGTTGCTATGGT-3′ 18 Reverse 5′-CCTGTCTGGTTGGCGTGT-3′ 18 CXCR4 Forward 5′-CCAGCCCTCCTCCTGACTA-3′ 20 Reverse 5′-ATCCTTGCTTGATGACCC-3′ 18 β-actin Forward 5′-CATTGTTACCAACTGGGACG-3′ 21 Reverse 5′-AGGATGGCGTGAGGGAGA-3′ 18 -
[1] Shen K, Zhou H, Zuo Q, et al. GATD3A-deficiency-induced mitochondrial dysfunction facilitates senescence of fibroblast-like synoviocytes and osteoarthritis progression[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 10-23. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44064-7 [2] 宋洋. Nrf2-CHI3L1信号轴对创伤性骨关节炎的作用机制及基因治疗研究[D]. 2023. [3] Wang L J, Zeng N, Yan Z P, et al. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis following ACL injury[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2020, 22(1): 57. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02156-5 [4] Zhang C, Zhao R, Dong Z, et al. IHH-GLI-1-HIF-2α signalling influences hypertrophic chondrocytes to exacerbate osteoarthritis progression[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2024, 49: 207-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2024.09.008 [5] Li W, Wu N, Wang J, et al. Role of HIF-2α/NF-κB pathway in mechanical stress-induced temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis[J]. Oral Dis, 2022, 28(8): 2239-2247. doi: 10.1111/odi.13986 [6] Ye T, He F, Lu L, et al. The effect of oestrogen on mandibular condylar cartilage via hypoxia-inducible factor-2α during osteoarthritis development[J]. Bone, 2020, 130: 115-123. [7] Ito Y, Matsuzaki T, Ayabe F, et al. Both microRNA-455-5p and -3p repress hypoxia-inducible factor-2α expression and coordinately regulate cartilage homeostasis[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 41-48. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20292-z [8] Hiraide T, Tsuda N, Momoi M, et al. CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway as a novel therapeutic target for RNF213-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 26604. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77388-5 [9] Singh D D, Yadav D K, Shin D. Targeting the CXCR4/CXCL12 Axis to overcome drug resistance in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cells, 2025, 14(18): 01. [10] Zheng H, Fang J, Lu W, et al. TCF12 regulates the TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathway to accelerate the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting CXCR4[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2024, 44: 35-46. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2023.11.006 [11] Yang T, Li C, Li Y, et al. MicroRNA-146a-5p alleviates the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by inhibiting SDF-1/CXCR4-induced chondrocyte autophagy[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 117: 109938. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.109938 [12] Jia D, Li Y, Han R, et al. miR‑146a‑5p expression is upregulated by the CXCR4 antagonist TN14003 and attenuates SDF-1induced cartilage degradation[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(5): 4388-4400. [13] Xiang Y, Li Y, Yang L, et al. miR-142-5p as a CXCR4-Targeted MicroRNA Attenuates SDF-1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage degradation via inactivating MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Biochem Res Int, 2020, 2020: 4508108. [14] 唐超, 魏伟生, 蒋永颂, 等. miR-21-5p靶向TNFAIP3对大鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞损伤的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志, 2023, 12(1): 45-52. [15] Jia Y, Yan Q, Zheng Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 mediated RPRD1B stability facilitates fatty acid metabolism and lymph node metastasis via c-Jun/c-Fos/SREBP1 axis in gastric cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 287. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02449-4 [16] Mumby S, Perros F, Grynblat J, et al. Differential responses of pulmonary vascular cells from PAH patients and controls to TNFα and the effect of the BET inhibitor JQ1[J]. Respir Res, 2023, 24(1): 193. doi: 10.1186/s12931-023-02499-y [17] Li C, Li W, Pu G, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-338-3p-modified adipose stem cells inhibited inflammation injury of chondrocytes via targeting RUNX2 in osteoarthritis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2022, 17(1): 567. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03437-2 [18] Tu T C, Nagano M, Yamashita T, et al. A chemokine receptor, CXCR4, which is regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor 2α, is crucial for functional endothelial progenitor cells migration to ischemic tissue and wound repair[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2016, 25(3): 266-276. doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0290 [19] Qian Y, Chu G, Zhang L, et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomal miR-26b-5p regulates macrophage polarization and chondrocyte hypertrophy by targeting TLR3 and COL10A1 to alleviate osteoarthritis[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 72. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02336-4 [20] Fang G, Wen X, Jiang Z, et al. FUNDC1/PFKP-mediated mitophagy induced by KD025 ameliorates cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis[J]. Mol Ther, 2023, 31(12): 3594-3612. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.10.016 [21] Chen J, Chen N, Zhang T, et al. Rongjin niantong fang ameliorates cartilage degeneration by regulating the SDF-1/CXCR4-p38MAPK signalling pathway[J]. Pharm Biol, 2022, 60(1): 2253-2265. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2143533 [22] Zhang X A, Kong H. Mechanism of HIFs in osteoarthritis[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1168799. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1168799 [23] Yang J, Shin Y, Kim H J, et al. Prokineticin 2 is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction in mouse[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2023, 25(1): 236. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03206-4 [24] Zhou K, He S, Yu H, et al. Inhibition of syndecan-4 reduces cartilage degradation in murine models of osteoarthritis through the downregulation of HIF-2α by miR-96-5p[J]. Lab Invest, 2021, 101(8): 1060-1070. doi: 10.1038/s41374-021-00595-5 [25] 汪航. 靶向HIF-2α延缓骨关节炎关节软骨退变作用的研究[D]. 山西医科大学, 2023. [26] Zhou Y, Ming J, Deng M, et al. Chemically modified curcumin (CMC2.24) alleviates osteoarthritis progression by restoring cartilage homeostasis and inhibiting chondrocyte apoptosis via the NF-κB/HIF-2α axis[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2020, 98(10): 1479-1491. doi: 10.1007/s00109-020-01972-1 [27] Cho C, Kang L J, Jang D, et al. Cirsium japonicum var. maackii and apigenin block Hif-2α-induced osteoarthritic cartilage destruction[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(8): 5369-5379. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14418 [28] Qin H, Zhao X, Hu Y J, et al. Inhibition of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis to alleviate abnormal bone formation and angiogenesis could improve the subchondral bone microenvironment in osteoarthritis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 8852574. doi: 10.1155/2021/8852574 [29] Wang G, Li Y, Meng X, et al. The study of targeted blocking SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway with three antagonists on MMPs, type II collagen, and aggrecan levels in articular cartilage of guinea pigs[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2020, 15(1): 195. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-01646-1 [30] Yang K, Xie Q, Liao J, et al. Shang-ke-huang-shui and coptisine alleviate osteoarthritis in the knee of monosodium iodoacetate-induced rats through inhibiting CXCR4 signaling[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116476. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116476 [31] Tang X, He J, Hao Y. Histone demethylase PHF8 protected against chondrocyte injury and alleviated posttraumatic osteoarthritis by epigenetically enhancing WWP2 expression[J]. Hum Exp Toxicol, 2024, 43: 9603271241292165. [32] 黄少烁. 黄芪甲苷通过SDF-1/CXCR4信号通路对骨性关节炎作用机制的实验研究[D]. 山东中医药大学: 2023. [33] 许颖捷, 贾梦莹, 龚忠诚. 异常流体剪切力通过NF-κB及MIF/CXCR4-NLRP3信号通路促进关节细胞焦亡的作用及机制研究[C]. 第20次全国颞下颌关节病学及HE学研讨会暨第七届亚洲颞下颌关节学术大会, 2023: 3. [34] Cheng B, Ma X, Zhou Y, et al. Recent progress in the development of hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) modulators: Inhibitors, agonists, and degraders (2009-2024)[J]. Eur J Med Chem, 2024, 275: 116645. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.116645 [35] Kuo Y C, Au H K, Hsu J L, et al. IGF-1R promotes symmetric self-renewal and migration of alkaline phosphatase(+) germ stem cells through HIF-2α-OCT4/CXCR4 Loop under Hypoxia[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2018, 10(2): 524-537. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2017.12.003 -





 下载:
下载: