Infection Mechanism and Detection of Occult Hepatitis B Virus in Voluntary Blood Donors
-
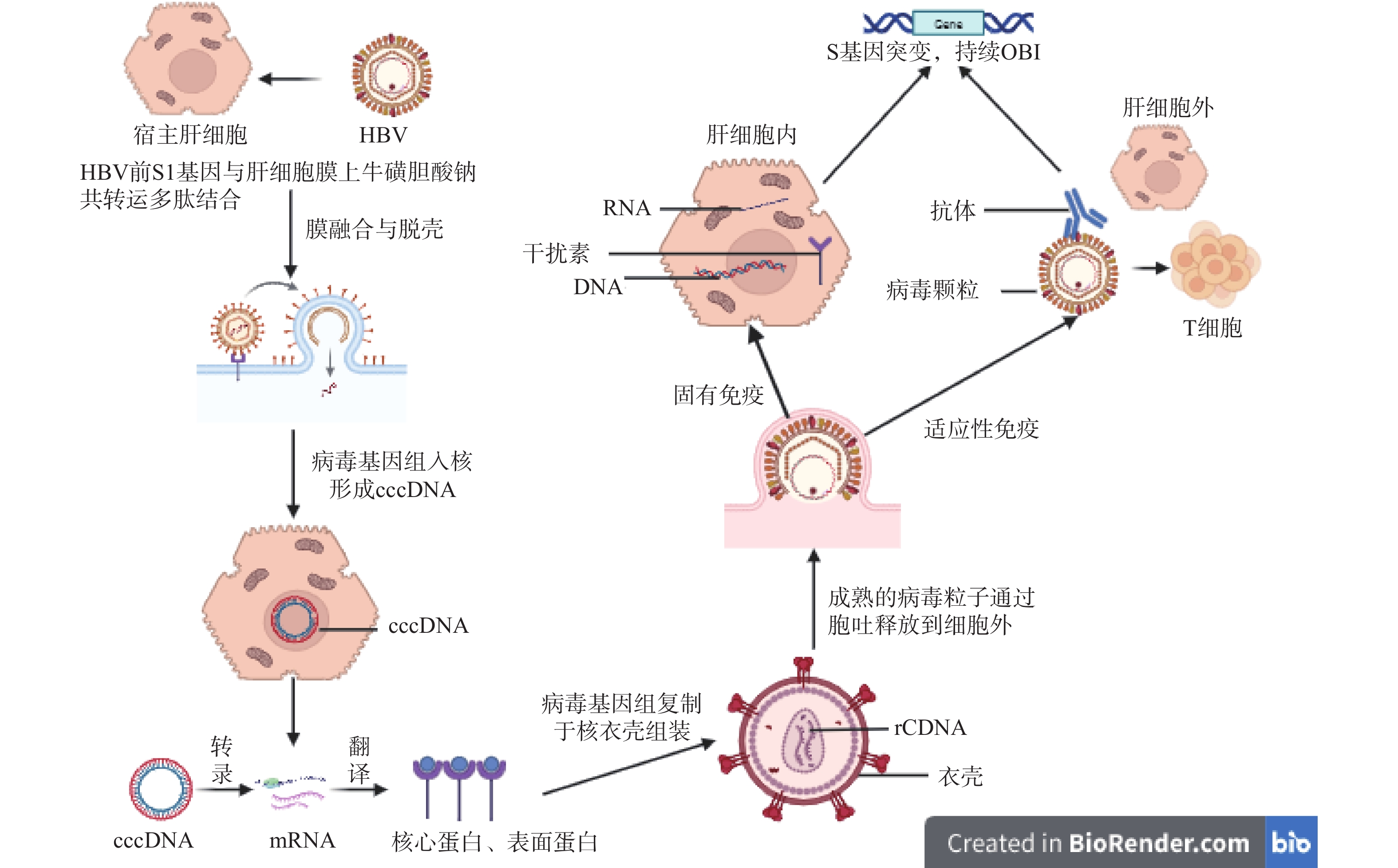
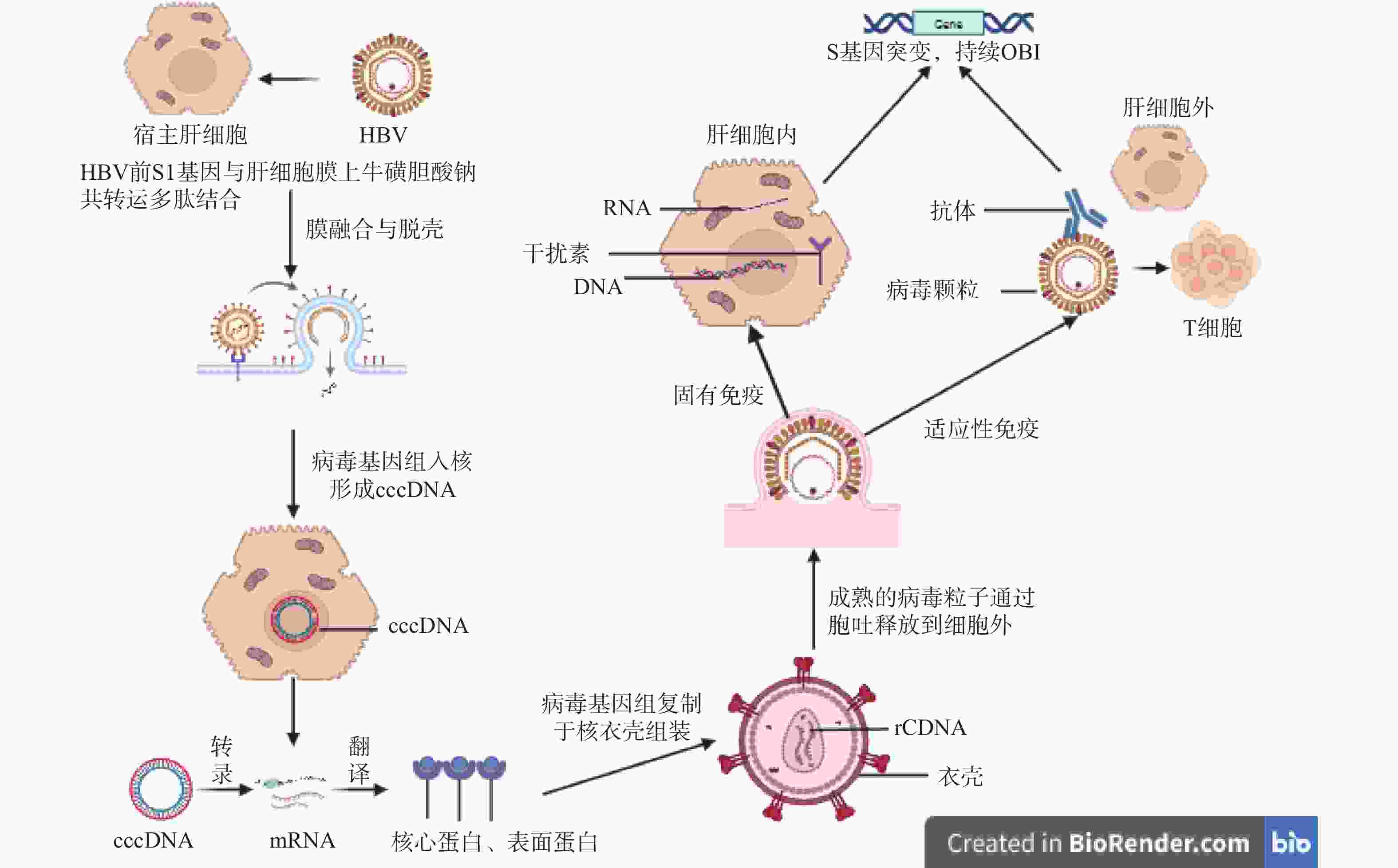
摘要: 发生输血后肝炎(post transfusion hepatitis,PTH)的风险主要来自于输入HBsAg阴性的HBV感染血液,即血清学窗口期(window period,WP)和隐匿性HBV感染(occult HBV infection,OBI)。其中,OBI是一种低病毒复制的HBV,因此成为了乙肝病毒感染防治的难点,也是输血后肝炎的重要传染源之一。虽然通过核酸检测技术(nucleic acid test,NAT)能一定程度上减少输血后肝炎发生,但有部分OBI感染者在献血者中存在,是HBV经血传播的潜在风险。本文主要对OBI的概念、血清学特征、基因组特征、发生机制、流行病学特点和检测策略进展进行概述。Abstract: The risk of post-transfusion hepatitis (PTH) primarily stems from blood transfusion containing HBV-infected blood that is HBsAg-negative, specifically during the serological window period (WP) and occult HBV infection (OBI). OBI is a low viral replication form of HBV, making it a challenge in hepatitis B virus infection prevention and control, and a significant transmission source of post-transfusion hepatitis. Although nucleic acid testing (NAT) can reduce the occurrence of post-transfusion hepatitis to some extent, some OBI-infected individuals exist among blood donors, representing a potential risk of HBV transmission through blood. This article primarily provides an overview of OBI's concept, serological characteristics, genomic features, pathogenesis mechanisms, epidemiological characteristics, and advances in detection strategies.
-
表 1 不同NAT检测技术性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of different NAT detection technologies
维度 灵敏度 检测速度 检测优势 成本效益 血液筛查 TMA 高 快(等温) RNA病毒 较高 单样本检测 PCR 受限于试剂 较慢(热循环) DNA病毒,RNA需逆转录 适合常规筛查 混样检测 -
[1] Raimondo G, Pollicino T, Cacciola I, et al. Occult hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2007, 46(1): 160-170. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2006.10.007 [2] Cacciola I, Pollicino T, Squadrito G, et al. Occult hepatitis B virus infection in patients with chronic hepatitis C liver disease[J]. N Engl J Med, 1999, 341(1): 22-26. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199907013410104 [3] 尤红, 王福生, 李太生, 等. 慢性乙型肝炎防治指南(2022年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2023, 26(3): 457-478. [4] Wei L, Chen M, Wang F, et al. Analysis of hepatitis B virus test results among blood donors in Chongqing, China[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2024, 24(1): 857. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09753-8 [5] 胡一钦, 黄纪红, 王敏, 等. 血液核酸筛查系统在不同检测筛查模式下的乙肝检测结果分析及评价[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2024, 37(9): 1030-1035. [6] Raimondo G, Locarnini S, Pollicino T, et al. Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection[J]. J Hepatol, 2019, 71(2): 397-408. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.03.034 [7] Song S H, Hwang S G. Occult hepatitis B virus infection: transmission and reactivation[J]. Korean J Gastroenterol, 2013, 62(3): 148-153. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.62.3.148 [8] Saitta C, Pollicino T, Raimondo G. Occult hepatitis B virus Infection: An update[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(7): 1504. doi: 10.3390/v14071504 [9] Vaillant A. HBsAg, Subviral particles, and their clearance in establishing a functional cure of chronic hepatitis B virus Infection[J]. ACS Infect Dis, 2021, 7(6): 1351-1368. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00638 [10] Fu M X, Faddy H M, Candotti D, et al. International review of blood donation screening for anti-HBc and occult hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Transfusion, 2024, 64(11): 2144-2156. doi: 10.1111/trf.18018 [11] Deng X, Guo X, Gu H, et al. Anti-HBc-nonreactive occult hepatitis B infections with HBV genotypes B and C in vaccinated immunocompetent adults[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2022, 29(11): 958-967. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13733 [12] Pisaturo M, Onorato L, Russo A, et al. An estimation of the prevalence of occult HBV infection in Western Europe and in Northern America: A meta-analysis[J]. J Viral Hepat, 2020, 27(4): 415-427. doi: 10.1111/jvh.13248 [13] 刘佳惠, 王贝, 周丽玲. 徐州地区献血者人群隐匿性乙型肝炎病毒感染现状及血清学特征分析[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2025, 38(3): 402-407. [14] Herrscher C, Roingeard P, Blanchard E. Hepatitis B virus entry into cells[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(6): 1486. doi: 10.3390/cells9061486 [15] Sun H, Chang L, Yan Y, et al. Hepatitis B virus pre-S region: clinical implications and applications [J]. Rev Med Virol, 2020. Epub ahead of print. [16] Thi Cam Huong N, Trung N Q, Luong B A, et al. Mutations in the HBV PreS/S gene related to hepatocellular carcinoma in Vietnamese chronic HBV-infected patients[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(4): e0266134. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266134 [17] Cakal B, Cavus B, Atasoy A, et al. Comparison of S gene mutations in patients with occult and chronic hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Virus Res, 2022, 318: 198855. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198855 [18] Kitab B, El Feydi A E, Afifi R, et al. Hepatitis B genotypes/subgenotypes and MHR variants among Moroccan chronic carriers[J]. J Infect, 2011, 63(1): 66-75. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2011.05.007 [19] Liu X, Chen S X, Liu H, et al. Host immunity and HBV S gene mutation in HBsAg-negative HBV-infected patients[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1211980. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1211980 [20] Kumar R. Review on hepatitis B virus precore/core promoter mutations and their correlation with genotypes and liver disease severity[J]. World J Hepatol, 2022, 14(4): 708-718. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.708 [21] Yu Y, Kass M A, Zhang M, et al. Deep mutational scanning of hepatitis B virus reveals a mechanism for cis-preferential reverse transcription [J]. Cell, 2024, 187(11): 2735-2745. e12. [22] Fernandes Da Silva C, Keeshan A, Cooper C. Hepatitis B virus genotypes influence clinical outcomes: A review[J]. Can Liver J, 2023, 6(3): 347-352. doi: 10.3138/canlivj-2023-0003 [23] Sekiba K, Miyake N, Miyakawa Y, et al. CRISPR-mediated proximity labeling unveils ABHD14B as a host factor to regulate HBV cccDNA transcriptional activity[J]. Hepatol Commun, 2025, 9(8): e0757. [24] Vyas A K, Banu S A, Rahangdale K, et al. Dissection the hepatitis B virus replication mechanisms and advances in In Vivo models: A comprehensive review [J]. Dig Dis, 2025: 1-31. [25] Venkatesan H, Mahesh J S, Venkataraman S. Decoding hepatitis B virus mutations that impact host-virus interactions and therapeutics [J]. J Biosci, 2025, 50. [26] Zhang J, Lou T, Zhu M, et al. Virus-host interaction mechanisms in interferon therapy for hepatitis B virus infection: Recent advances[J]. Front Immunol, 2025, 16: 1603544. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1603544 [27] Kostyusheva A, Brezgin S, Glebe D, et al. Host-cell interactions in HBV infection and pathogenesis: The emerging role of m6A modification[J]. Emerg Microbes Infect, 2021, 10(1): 2264-2275. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.2006580 [28] Salih A, Inoue S, Onwuzurike N. Rothmund-Thomson syndrome (RTS) with osteosarcoma due to RECQL4 mutation[J]. BMJ Case Rep, 2018, 2018: bcr2017222384. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2017-222384 [29] Lu L, Jin W, Wang L L. Aging in Rothmund-Thomson syndrome and related RECQL4 genetic disorders[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2017, 33: 30-35. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.06.002 [30] Lelie N, Bruhn R, Busch M, et al. Detection of different categories of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in a multi-regional study comparing the clinical sensitivity of hepatitis B surface antigen and HBV-DNA testing[J]. Transfusion, 2017, 57(1): 24-35. doi: 10.1111/trf.13819 [31] Candotti D, Lin C K, Belkhiri D, et al. Occult hepatitis B infection in blood donors from South East Asia: molecular characterisation and potential mechanisms of occurrence[J]. Gut, 2012, 61(12): 1744-1753. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301281 [32] 范加诚, 李青, 陈秀丽, 等. 献血者HBVs基因变异的生物信息学分析[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2024, 37(8): 933-939. [33] 晁春梅, 哏传香, 金正英, 等. 2015-2019年云南省献血者血清阳性隐匿性乙肝病毒感染流行病学特征[J]. 热带医学杂志, 2021, 21(5): 650-652+669. [34] 叶贤林, 李彤, 王若楠, 等. 计划免疫后出生献血者乙肝无症状慢性感染血清学与分子生物学特征分析[J]. 中国输血杂志, 2024, 37(1): 26-31. [35] Mak L Y, Wong D K, Pollicino T, et al. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance[J]. J Hepatol, 2020, 73(4): 952-964. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.042 [36] 吴诗阳, 孙加进, 杨州. 乙肝血清学检测研究进展[J]. 现代医学与健康研究电子杂志, 2023, 7(23): 134-137. [37] Lalana Garcés M, Ortiz Pastor O, Solé Enrech G, et al. Control of occult hepatitis B virus infection[J]. Adv Lab Med, 2022, 3(4): 321-341. [38] 王全慧, 潘彤, 樊晶. 隐匿性乙型肝炎病毒感染的输血传播风险及防范[J]. 检验医学与临床, 2024, 21(6): 838-841+861. [39] Pathak A, Panda D, Sharma M, et al. Blood donation Screening of transfusion-transmissible viral infection using two different nucleic acid testing (NAT) platforms: A single tertiary care oncology centre experience[J]. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus, 2023, 39(3): 456-463. doi: 10.1007/s12288-022-01598-y [40] Manso T, De Salazar A, Rodríguez-Velasco M, et al. Detection and quantification of HBV and HCV in plasma samples by means of different molecular assays: comparative study[J]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed), 2024, 42(1): 13-16. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2022.07.007 [41] Wu D, Feng F, Wang X, et al. The impact of nucleic acid testing to detect human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis B virus yields from a single blood center in China with 10-years review[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2022, 22(1): 279. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07279-5 [42] Abbasian S, Sharifi Z, Maghsudlu M. Prevalence of Hepatitis b virus infection among voluntary blood donors from the northeastern region of Iran: Genotyping, viral load characterization and drug resistance prediction[J]. Clin Lab, 2021, 67(1): 10.7754. [43] D'souza S, Al-Yasiri L, Chen A, et al. Development of low-cost in-house assays for quantitative detection of HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA to enhance hepatitis B virus diagnostics and antiviral screening in resource-limited settings[J]. Pathogens, 2025, 14(3): 258. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030258 [44] Bermúdez-Forero M I, García-Otálora M A. Nucleic acid testing in Colombian blood banks (2018-2024): Implementation, yield estimates and implications for safer transfusion policy [J]. Vox Sang, 2025, Epub ahead of print. [45] Liu Y, Ma Y. Clinical applications of metagenomics next-generation sequencing in infectious diseases[J]. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B, 2024, 25(6): 471-484. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300029 [46] Qi H, Lv J, Liao J, et al. Metagenomic insights into microalgae-bacterium-virus interactions and viral functions in phycosphere facing environmental fluctuations [J]. Water Res, 2025, 268(Pt A): 122676. [47] Slavov S N. Viral metagenomics for identification of emerging viruses in transfusion medicine[J]. Viruses, 2022, 14(11): 2448. doi: 10.3390/v14112448 [48] Rodino K G, Simner P J. Status check: next-generation sequencing for infectious-disease diagnostics[J]. J Clin Invest, 2024, 134(4): e178003. doi: 10.1172/JCI178003 [49] Schlaberg R, Chiu C Y, Miller S, et al. Validation of metagenomic next-generation sequencing tests for universal pathogen detection[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2017, 141(6): 776-786. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0539-RA [50] Simner P J, Miller S, Carroll K C. Understanding the promises and hurdles of metagenomic next-generation sequencing as a diagnostic tool for infectious diseases[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2018, 66(5): 778-788. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix881 [51] Guzman-Cole C, Huang A D. Nf-UnO-pipeline: A nextflow metagenomic co-assembly pipeline for novel pathogen detection of mNGS outbreak sets[J]. Bioinformatics, 2025, 41(8): btaf436. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaf436 [52] 赖伟兰, 谢丽明, 陈亚军. 基于高通量测序下低拷贝乙型肝炎病毒检测方法的应用分析[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2018, 39(23): 2937-2940. [53] Berg M G, Olivo A, Forberg K, et al. Advanced molecular surveillance approaches for characterization of blood borne hepatitis viruses[J]. PLoS One, 2020, 15(7): e0236046. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236046 [54] Zhang Y, Sun D, Fang Y, Et al. Uncommon pulmonary manifestation of hepatitis B virus: A case report of secondary organizing pneumonia[J]. BMC Infect Dis, 2025, 25(1): 645. doi: 10.1186/s12879-025-11049-4 [55] Gao D Q, Hu Y Q, Wang X, et al. Hepatitis B virus in cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with purulent bacterial meningitis detected by multiplex-PCR: A case report[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2022, 10(5): 1697-1701. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i5.1697 [56] Stramer S L. Current perspectives in transfusion-transmitted infectious diseases: Emerging and re-emerging infections[J]. ISBT Sci Ser, 2014, 9(1): 30-36. doi: 10.1111/voxs.12070 [57] Mengyi Z, Yuhui L, Zhan G, et al. Plasma metagenomics reveals regional variations of emerging and re-emerging pathogens in Chinese blood donors with an emphasis on human parvovirus B19[J]. One Health, 2023, 17: 100602. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2023.100602 [58] Towner J S, Sealy T K, Khristova M L, et al. Newly discovered ebola virus associated with hemorrhagic fever outbreak in Uganda[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2008, 4(11): e1000212. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000212 [59] Mishra N, Pereira M, Rhodes R H, et al. Identification of a novel polyomavirus in a pancreatic transplant recipient with retinal blindness and vasculitic myopathy[J]. J Infect Dis, 2014, 210(10): 1595-1599. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiu250 [60] Zheng N, Yu H L, Zhang B J, et al. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing-based characterization of the viral spectrum in clinical pulmonary and peripheral blood samples of patients[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2025, 15: 1562965. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1562965 -





 下载:
下载: