Network Pharmacology-based Analysis of the Anti-atherosclerosis Mechanism of Scutellarin and Experimental Validation in Vivo
-
摘要:
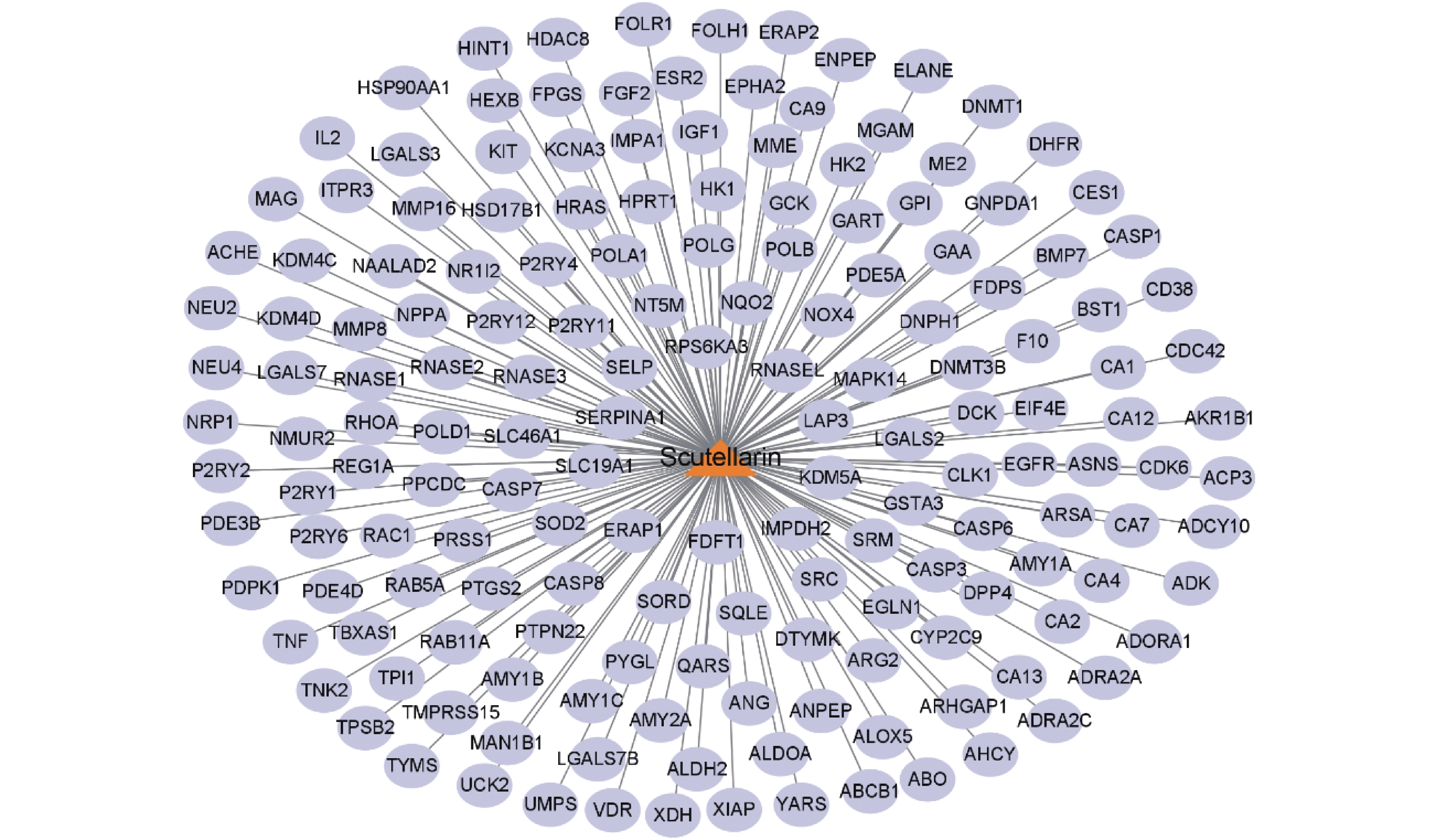
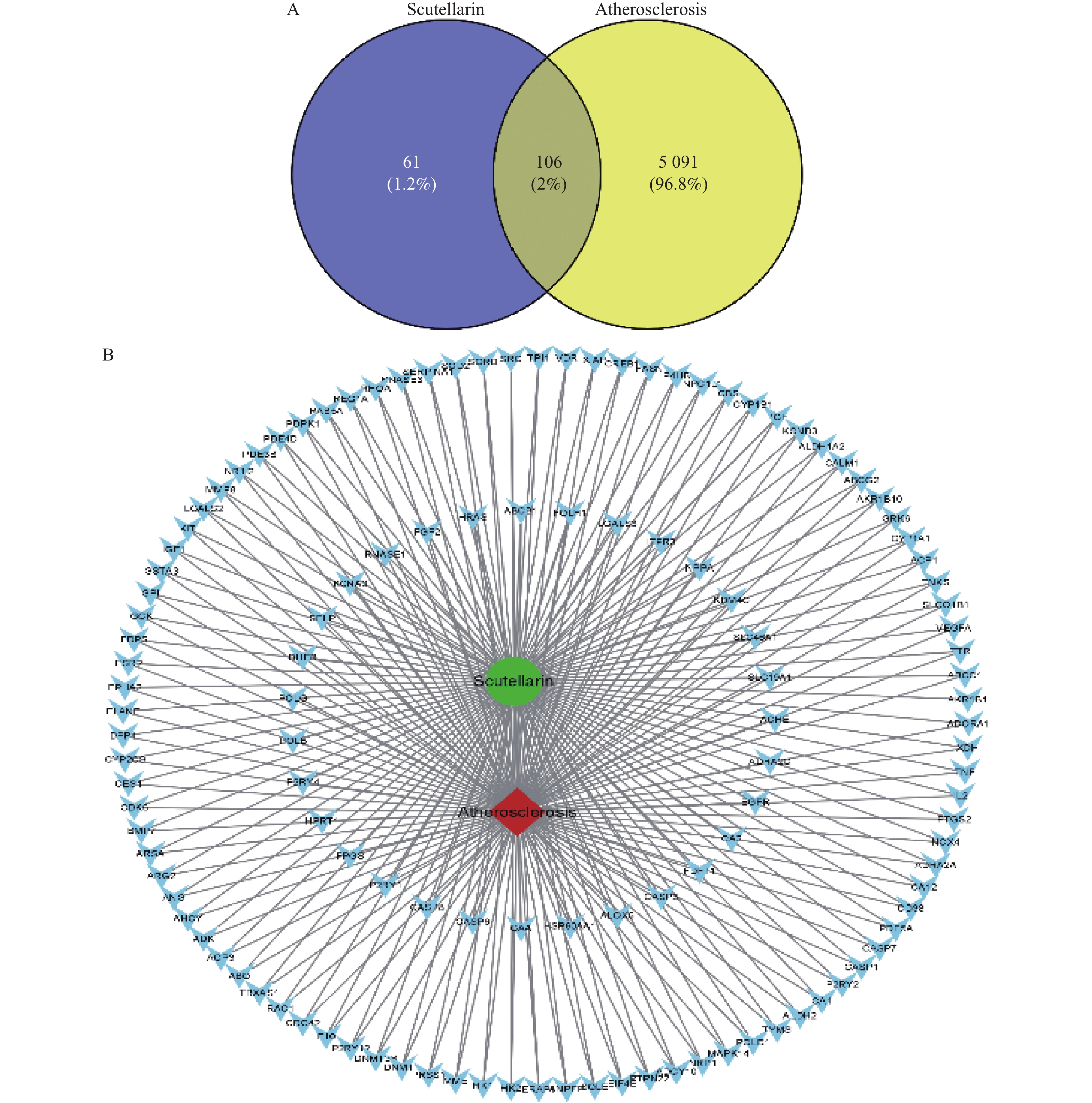
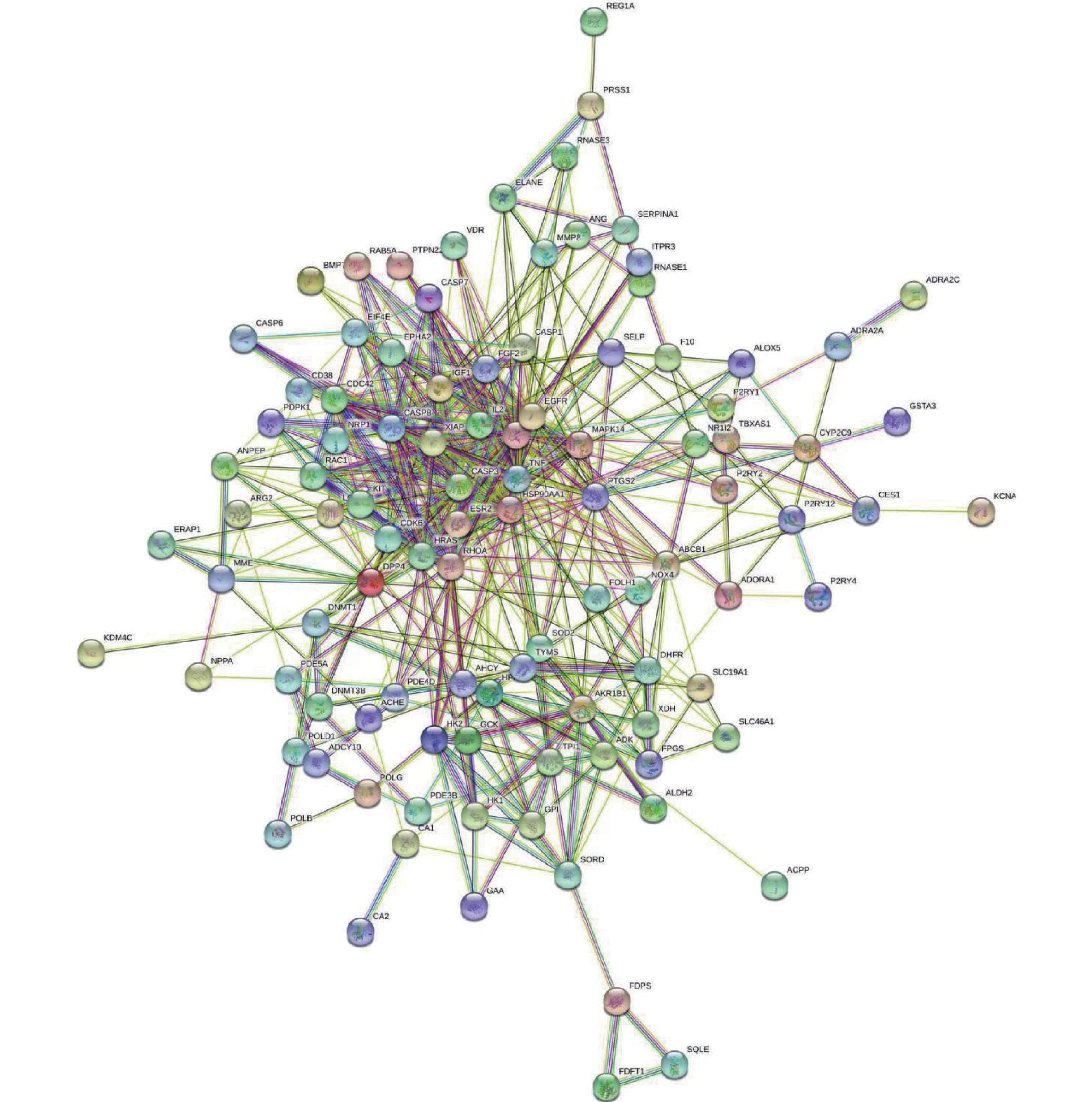
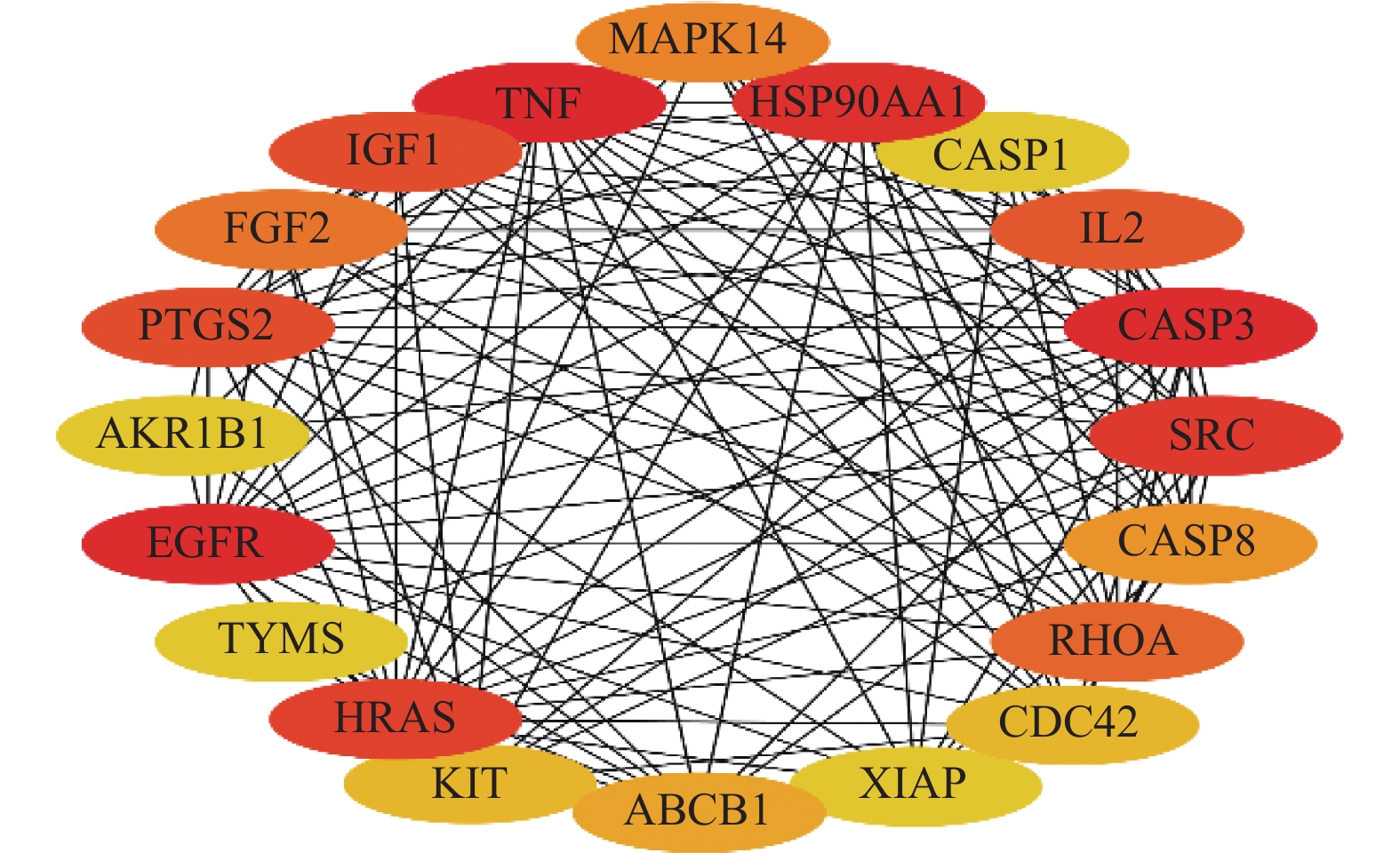
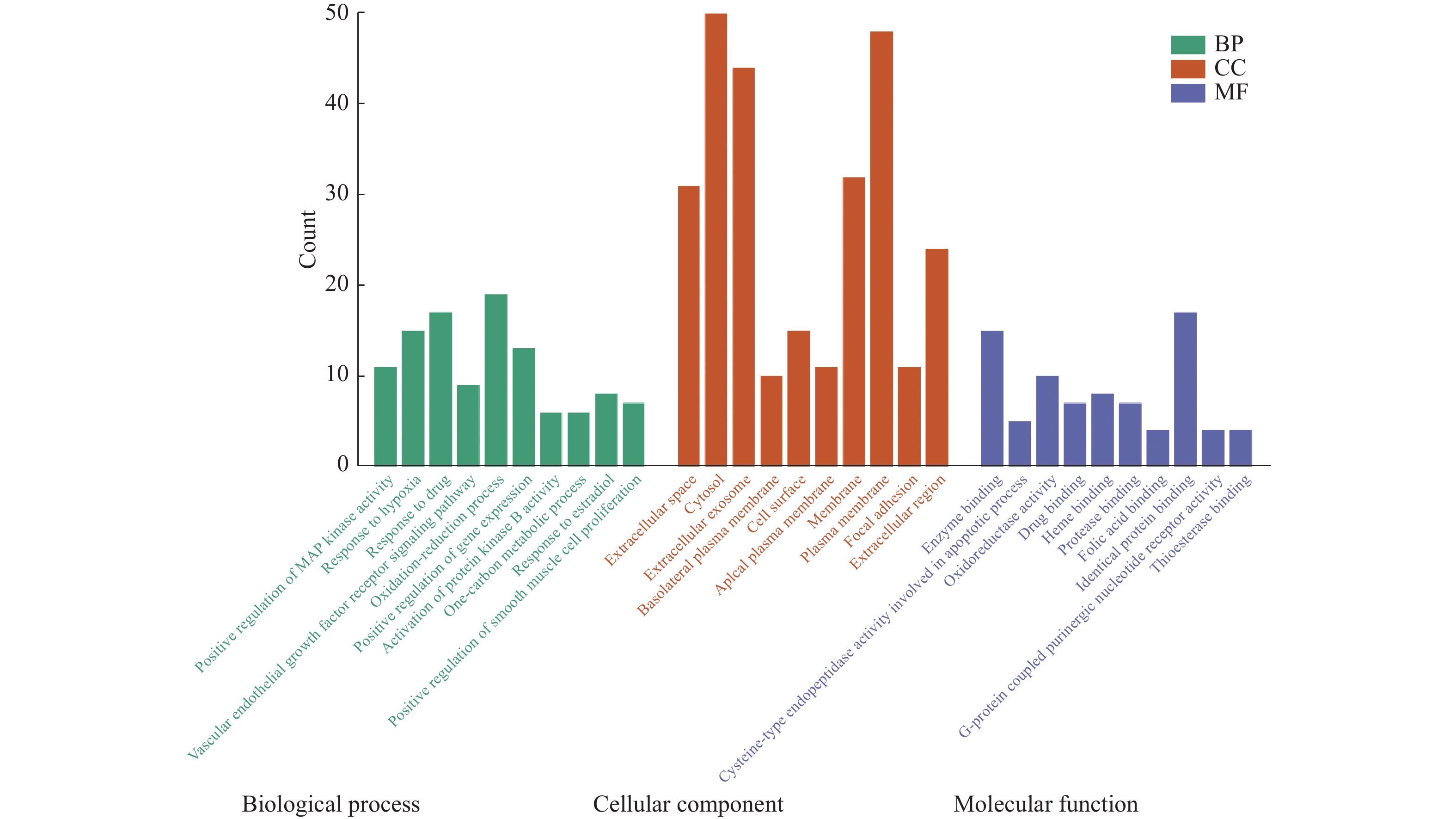
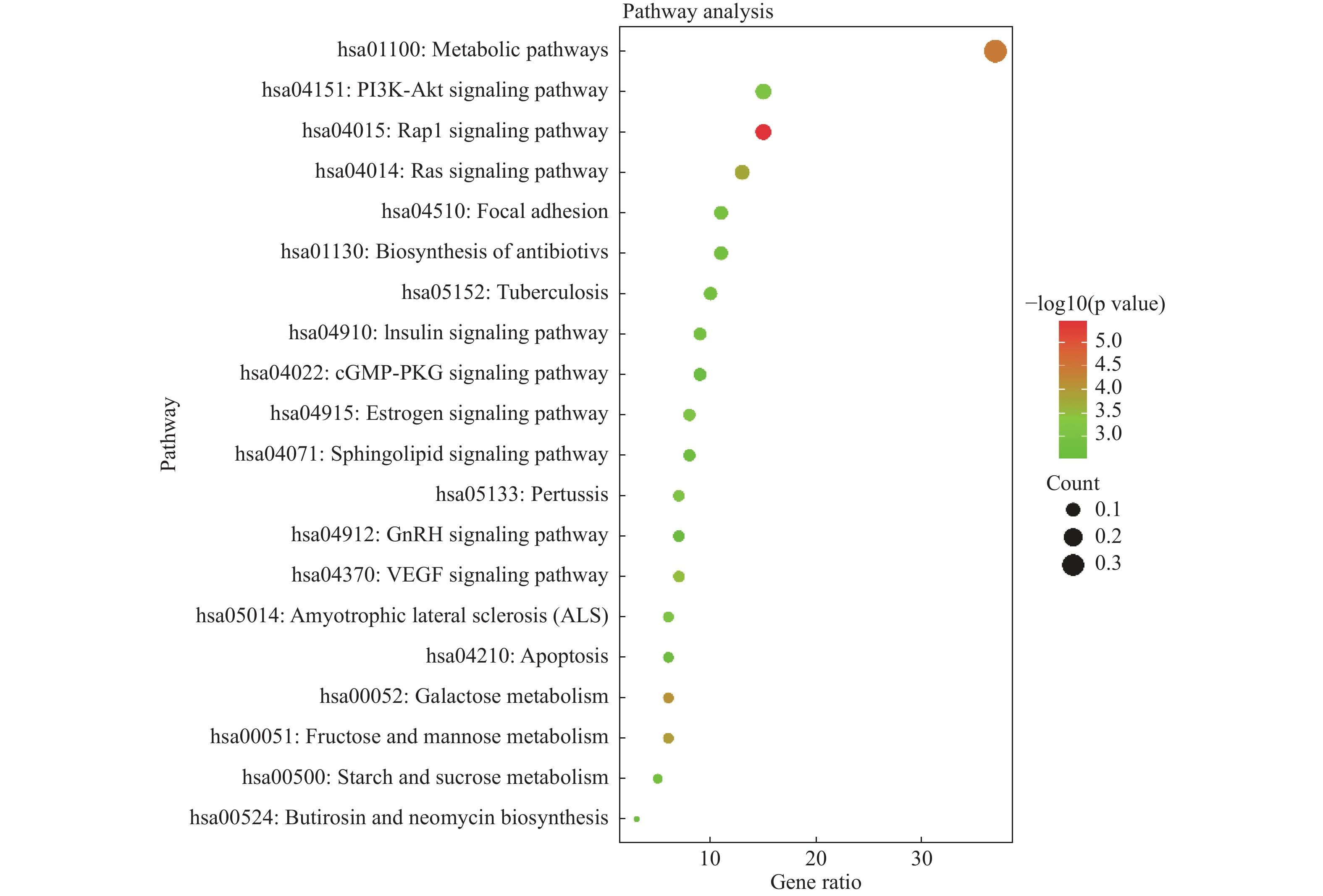
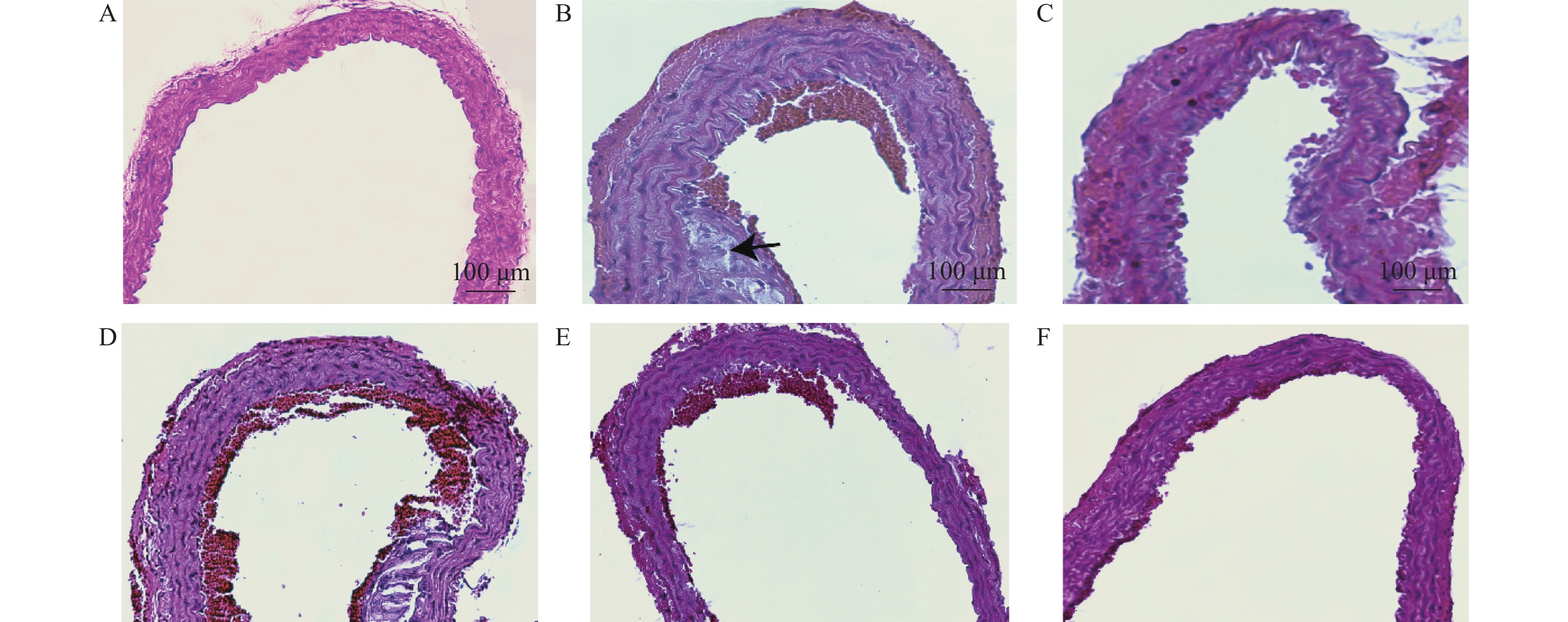
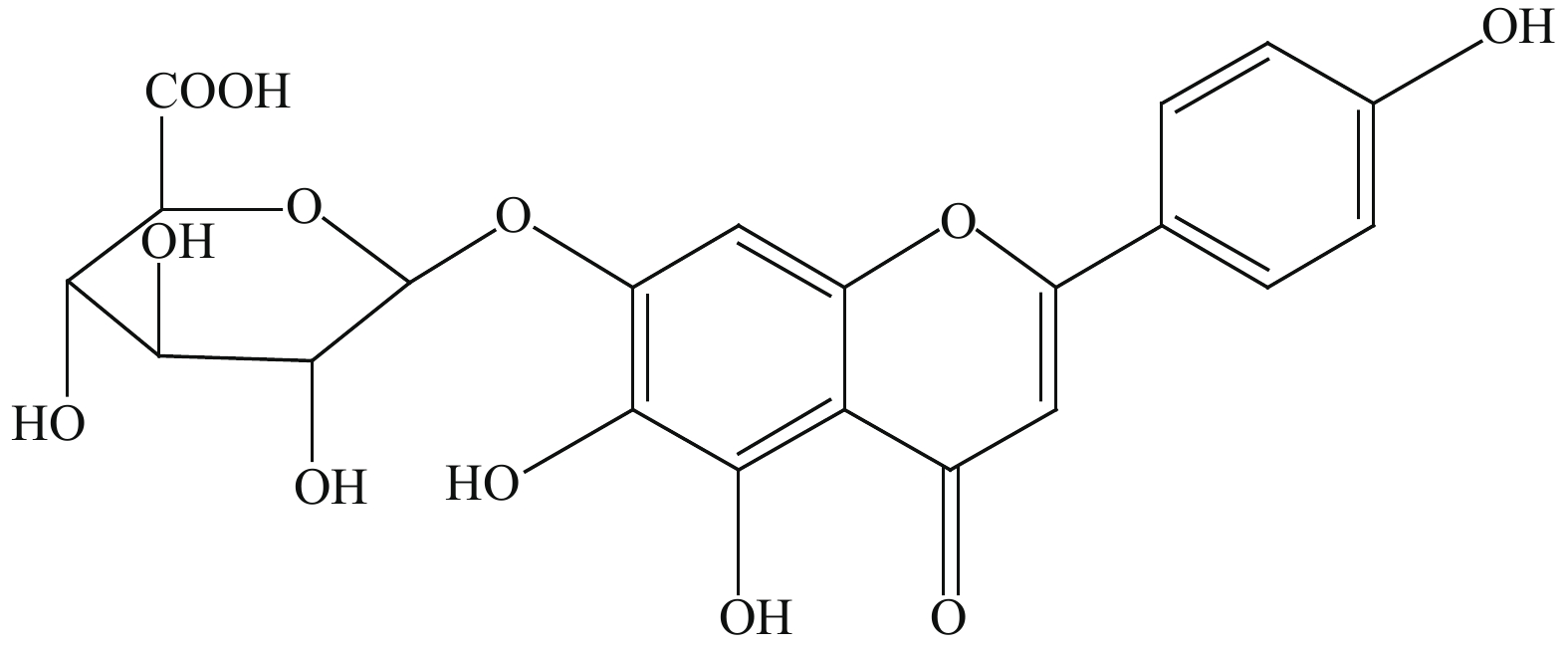
目的 基于网络药理学分析灯盏乙素(Scutellarin) 治疗动脉粥样硬化(atherosclerosis,AS) 潜在的分子生物学机制。 方法 通过PubChem数据库进行灯盏乙素潜在的靶点预测,运用Disgenet,CeneCards筛选与AS关联的靶基因,利用Cytoscape 3.9.0建立疾病-靶点-成份可视化网络,使用String构建蛋白互作网络图,利用David数据库进行GO及KECG的网络构建。另外,高脂喂养复制APOE-/-小鼠AS模型, 用不同浓度的灯盏乙素灌胃治疗,利用RT-PCR方法验证筛选所得核心通路的表达变化。 结果 (1)网络药理学预测结果:灯盏乙素治疗AS的核心靶点共有肿瘤坏死因子-α (TNF-α),AKT丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶(AKT serine/threonine kinase,MAPK),低密度脂蛋白受体(Low density lipoprotein receptor),载脂蛋白E(apolipoprotein E,APOE)等共106个。灯盏乙素调控PI3K/AKT信号通路(hsa04151)、Ras信号通路(hsa04014)、MAPK信号通路(hsa04010)(P < 0.05)等涉及细胞的增殖,炎症反应,氧化应激,及细胞凋亡等生物学过程来治疗AS;(2) 体内实验验证的结果:和模型组相比,灯盏乙素组呈浓度依耐性地下调PI3K、AKT、mTOR和Bcl-2 的mRNA表达,上调Bax和Caspase-3的mRNA表达,( P < 0.05)。另外,和模型组相比,灯盏乙素则呈浓度依耐性地下调小鼠血清TNF-α和IL-1β的含量( P < 0.05)。 结论 经过网络药理学筛选和RT-PCR验证,灯盏乙素通过调控PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路抑制APOE-/-小鼠AS模型炎症反应,促进细胞凋亡而治疗AS。 -
关键词:
- 网络药理学 /
- 灯盏乙素 /
- 动脉粥样硬化 /
- APOE-/- 小鼠AS模型 /
- PI3K/AKT/mTOR
Abstract:Objective To analyze the potential molecular biological mechanism of scutellarin for the treatment of atherosclerosis (AS) based on network pharmacology. Methods The PubChem database was used to predict the potential targets of scutellarin, and the Disgenet and CeneCards databases were used to predict and screen the genes related to atherosclerosis, and the Cytoscape 3.7.0 software was used to establish and construct the component-target-disease network visualization network. The GO and KECG pathways were analyzed using the David database. In addition, an APOE-/- mouse AS model was developed and treated with different concentrations of scutellarin, and the expression changes of the core targets were verified by RT-PCR. Results 1. Network pharmacological prediction results: the core targets of Scutellarin for AS treatment were tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 (MAPK), low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), apolipoprotein E (APOE), among other targets, with 106 in total. The key targets of Scutellarin are PI3K/AKT signaling pathway (hsa04151), Ras signaling pathway (hsa04014) and MAPK signaling pathway (hsa04010) (P < 0.05), which are involved in cell proliferation, inflammatory response, oxidative stress and apoptosis, to treat AS. 2. Results of in vivo experiments: compared with the model group, the mRNA expression of PI3K, AKT, mTOR and Bcl-2 was down-regulated and the mRNA expression of Bax and Caspase-3 was up-regulated in the Scutellarin group. In addition, compared with model group, Scutellarin down-regulated the contents of TNF-α and IL-1β in serum concentration-dependent (P < 0.05). Conclusion Through network pharmacology screening and RT-PCR verification, Scutellarin inhibits the process of inflammatory response in a mouse model of AS by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- Network pharmacology /
- Scutellarin /
- Atherosclerosis /
- APOE-/- mice AS model /
- PI3K\AKT\mTOR
-
肝内胆管癌是一种具有高度侵袭性的恶性肿瘤[1],预后差,近年来,其发病率逐年升高[2]。腺苷酸激酶4(Adenylate kinase4,AK4)是腺苷酸激酶家族的一员,其分子量为25kDa,别称为AK3L1。多项研究显示AK4促进恶性肿瘤的发生发展[3-5]。但其对肝内胆管癌的作用尚无报道。本实验通过小干扰RNA手段,就AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1增殖、迁移能力的影响作出探究。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 细胞系
本实验所用肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1购自上海誉驰生物科技有限公司,该细胞已通过中国科学院昆明动物研究所鉴定明确。该细胞作为肝内胆管癌细胞株之一,常用于肿瘤增殖、迁移的研究。
1.2 小干扰RNA(Small interfering RNA,siRNA)转染细胞
本实验采用siRNA技术以沉默AK4。siRNA购自上海市吉玛基因生物技术有限公司,共计构建6条si-RNA序列,序列设计见表1。本次实验分组为空白对照组(CON)、阴性对照组(siRNA-NC)、阳性对照组(siRNA-GAPDH)、实验组1(siRNA-AK4-1),实验组2(siRNA-AK4-2),实验组3(siRNA-AK4-3)。转染试剂采用上海市吉玛基因生物技术有限公司GP-transfect-Mate。采用免疫印迹法(Western Blot,WB)对实验组1、实验组 实验组3进行si-RNA筛选,其中空白对照组不添加siRNA,阴性对照组基因序列与目的基因序列无同源性,阳性对照组基因序列与内参GAPDH同源。各组间其余实验操作步骤(转染方法、WB、EdU、细胞划痕实验)均一致。
表 1 si-RNA序列Table 1. Sequence of si-RNA built by siRNA technology组别 序列 Antisense Negative control 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ 5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3′ GAPDH Positive control 5′-UGACCUCAACUACAUGGUUTT-3′ 5′-AACCAUGUAGUUGAGGUCATT-3′ siRNA-AK4-1 5′-GCGGAAGGGUAUAUAACCUTT-3′ 5′-AGGUUAUAUACCCUUCCGCCT-3′ siRNA-AK4-2 5′-CAGGCUAAGACAGUACAAATT-3′ 5′-UUUGUACUGUCUUAGCCUGTT-3′ siRNA-AK4-3 5′-CACCUAUUCAGUCCAAAGATT-3′ 5′-UCUUUGGACUGAAUAGGUGTT-3′ 转染前1 d将HUCCT1细胞接种至6孔板中,以次日细胞融合度达到60%~80%为宜,用无抗生素的完全培养基进行培养。转染:(1)转染试剂室温备用;(2)按照每孔200 µL无血清培养基(1640培养基)加5~8 µL转染试剂配置转染试剂混合物。静置5 min;(3)按照每孔200 µL无血清培养基(1640培养基)加150/pmol siRNA配置siRNA混合物。静置5 min;(4)将转染试剂混合物滴加到siRNA混合物中,混匀,静置20 min;(5)20 min后将混合液均匀加至6孔板各孔中;(6)各孔另外加入1 600 µL无抗生素完全培养基;(7)孔板放入细胞培养箱中培养48 h,使用免疫印迹检测转染效率。
1.3 免疫印迹实验检测转染效率及siRNA筛选
(1)裂解细胞:使用PMSF(品牌:Beyotime,货号:ST506-2 PMSF)与RIPA裂解液(强)品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0013B)按照200∶1配置细胞裂解液。于冰上充分裂解细胞;(2)测蛋白浓度:取裂解产物于4 ℃离心机12000 r/min,离心30 min。吸取86 µL上清液,使用BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0012 500次)测定蛋白浓度;(3)取80 µL上清液加20 µL SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液(品牌:Beyotime,货号:P0015L)沸水加热15 min;(4)电泳:配置12%下层胶,5%上层胶,蛋白上样量为2.5 µg,上层胶60 V恒压电泳,下层胶100 V恒压电泳;(5)转膜:甲醇浸泡PVDF膜,胶、膜放置妥当后以300 mA恒流条件下湿转发转膜,时间为30 min;(6)封闭:PVDF膜置于5%脱脂牛奶中封闭,缓慢摇晃,室温封闭2 h;(7):孵育一抗:兔单克隆抗体[EPR7678] to AK3L1抗体,(1∶7000,品牌:Abcam,货号:ab131327)。一抗孵育过夜,4 ℃;(8):孵育二抗:山羊抗兔IgG(H+L)(品牌:Proteintech,货号:SA00001-2,1∶10000),室温孵育2 h;(9)显影:ECL化学发光液孵育1 min后,于成像仪中曝光显影。
1.4 增殖EdU实验
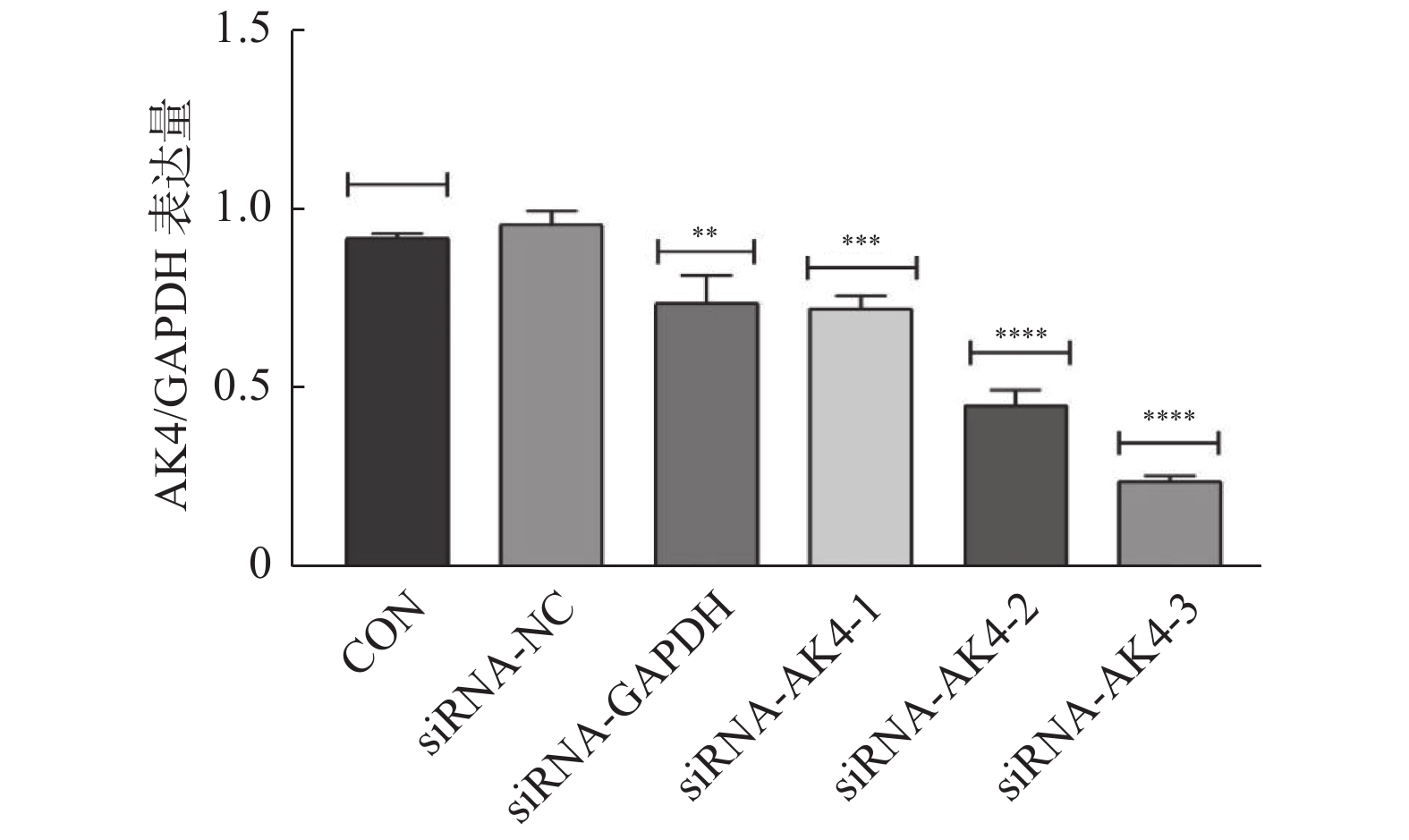
(1)转染细胞:6孔板培养细胞。免疫印迹实验已明确siRNA-AK4-3的沉默效果最好,故本次实验使用siRNA-NC及siRNA-AK4-3做细胞转染。分组亦同。转染完成24 h开始进行EdU实验。(2)工作液孵育:使用BeyoclickTM Edu-555配置2XEdU工作液后(品牌:Beyotime,货号:C0075s),与无抗生素完全培养基等体积加入六孔板中,孵育2 h。(3):固定、染色:每孔1 mL固定液固定15 min,洗涤后加入通透液孵育15 min,Click反应液孵育15 min,1X Hoechst 33342溶液孵育10 min。(4):荧光检测:洗涤液清洗后于倒置荧光显微镜观察。
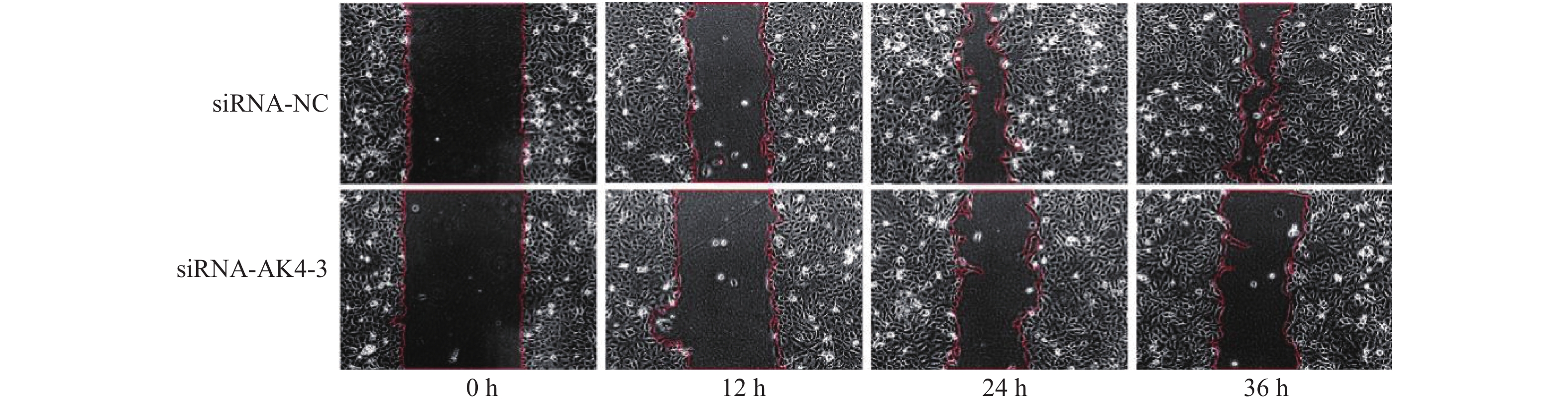
1.5 细胞划痕实验
(1)转染细胞:6孔板培养细胞。本次实验分组为siRNA-NC及siRNA-AK4-3。转染完成24 h开始细胞划痕实验。(2)画线:使用直尺于6孔板背面作横行画线。(3)划痕:待细胞融合度为95%~100%时,使用200 µL枪头沿直尺作垂直于画线的划痕。(4)冲洗:使用PBS冲洗孔板3次,动作轻柔,吸净PBS后,加入无血清1640培养液。(5)拍照:每孔以“十”字交叉处上下为定点,于0 h,12 h,24 h,36 h拍照,对比不同时间下各组细胞迁移能力,并进行统计分析。
1.6 统计学处理
数据分析使用GraphPad Prism 8及SPSS 26统计软件,计量资料采用(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),计数资料用t检验,3组及多组计量资料采用单因素方差分析。所有检验取两端。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
2.1 siRNA转染效率及筛选
免疫印迹法检测各组后量化结果分别为:空白对照组(CON):(0.9±0.01,)阴性对照组(siRNA-NC):(0.92±0.01),阳性对照组(siRNA-GAPDH):(0.95±0.04),实验组1(siRNA-AK4-1):(0.74±0.08),实验组2(siRNA-AK4-2):(0.45±0.04),实验组3(siRNA-AK4-3):(0.24±0.02)。免疫印迹结果显示各组内参齐,沉默效果较好,其中阳性对照组对GAPDH的沉默效果显著。各siRNA组中siRNA-AK4-3对AK4的沉默效果最好,见图1,2。因此,后期实验使用siRNA-NC作为对照组,siRNA-AK4-3作为实验组。
2.2 增殖EdU实验
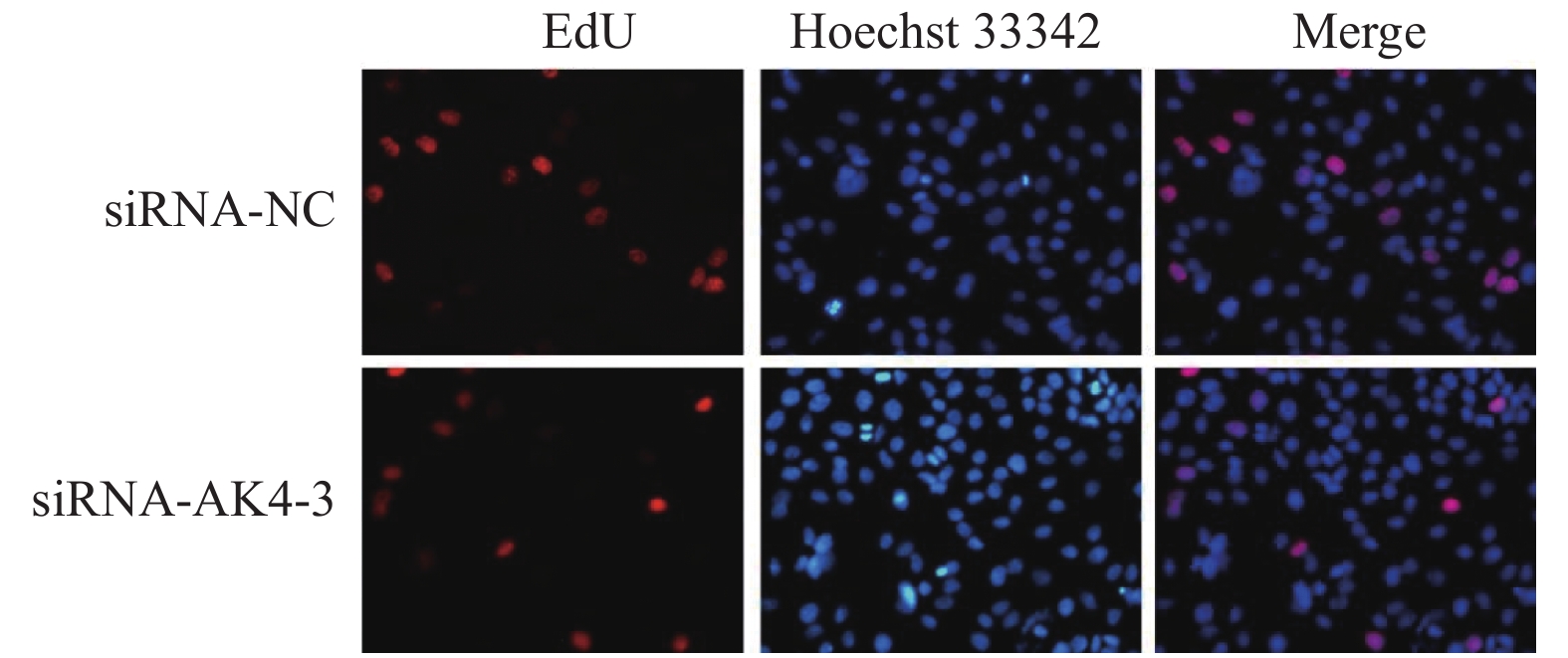
Edu实验结果显示:siRNA-NC组增殖细胞(15.9±4.4)/视野,细胞总数(110.9±22.4)/视野。siRNA-AK4-3组增殖细胞数目(12.8±5.0)/视野,细胞总数(116.7±22.1)/视野。两组增殖比率有差异,差异有统计学意义。siRNA-NC组增殖细胞多于siRNA-AK4-3组,AK4促进细胞增殖,见图3,4。
图3中EdU中增殖的HUCCT1细胞被标记为红色荧光,Hoechst 33342中蓝色荧光标记的为视野下所有活细胞,Merge图由EdU和Hoechst 33342图像合并后得到。
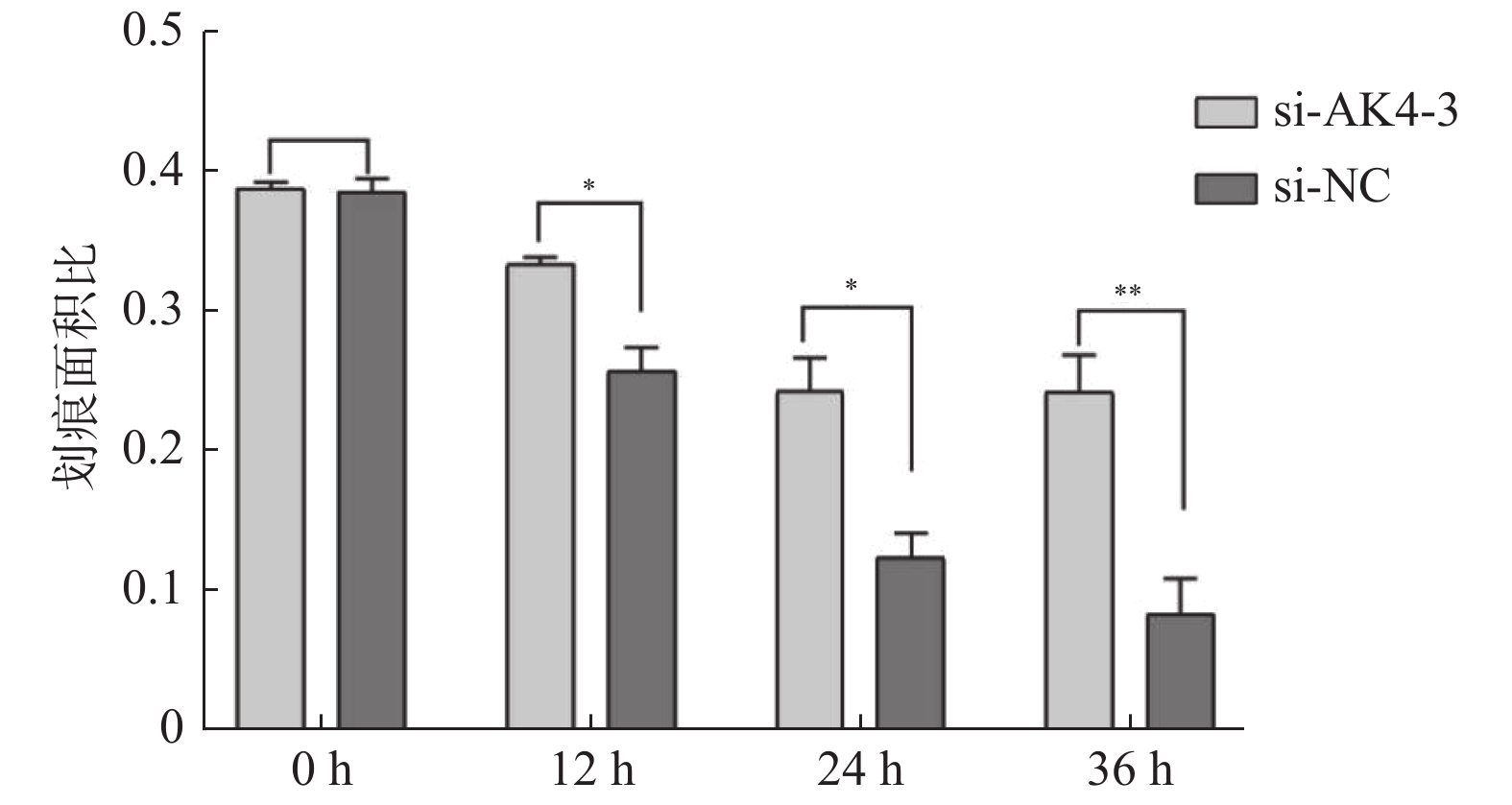
2.3 细胞划痕实验
划痕实验取划痕面积/视野总面积,各组面积比见表2,差异有统计学意义,见图5,6。siRNA-NC组细胞迁移面积较siRNA-AK4-3组更大,AK4促进细胞迁移。
表 2 划痕面积比Table 2. Scratch area ratio项目 0 h 12 h 24 h 36 h siRNA-NC 0.39 ± 0.01 0.26 ± 0.017 0.12 ± 0.017 0.08 ± 0.026 siRNA-AK4-3 0.39 ± 0.005 0.33 ± 0.001 0.24 ± 0.024 0.24 ± 0.027 3. 讨论
肝内胆管癌的手术治疗是极其重要的,目前全球范围内术后其平均无瘤生存时间( DFS) 为12 ~ 36 个月[6-7],但胆管癌起病隐匿,多数患者在发现疾病时已属晚期[8],据报道,肝内胆管癌的根治切除率为30%~40% ,其他肝胆恶性肿瘤均比此数据高[1,9]。肝内胆管癌的辅助化疗(吉西他滨联合铂类)在一定程度上实现肿瘤将期,从而获得手术机会[10-12],但其中位生存期仍然不到1 a时间[13-15]。根据Andrew X Zhu的RCT临床研究,靶向药物Ivosidenib使得患者有10.3个月的中位生存期,而安慰剂组仅有7.5个月[16],Abou-Alfa GK等学者也通过RCT实验研究了Ivosidenib在胆管癌中的作用,其结果是实验组的无病生存期为2.7个月(95% CI:1.6~4.2),而安慰剂组的无病生存期为1.4个月(95% CI:1.4~1.6)[17]。A Demols也在胆管癌的靶向治疗上进行了RCT研究,他研究了靶向药Regorafenib对胆管癌作用,最终得出实验组无病生存期为3.0个月(95% CI:2.3~4.9),而对照组无病生存期为1.5个月(95% CI:1.2~2.0),然而实验组的总生存时间和对照组的总生存时间并无统计学差异[18]。可以看出,靶向药能提高患者生存时间,但有研究显示部分靶向药并不能显著提升患者的总生存率[18, 19]。因此需寻找一个更有效的作用靶点。
1944年,美国学者Kalckar在实验中首次发现了肌苷酸[20]。在随后的科学实践中,更名为腺苷酸激酶AK。AK4定位于细胞线粒体基质内,在肝脏、心脏、脑、肾脏、胃肠道组织中富于表达[21],AK4在细胞能量代谢方面表现出特异性[22],因此他与肿瘤应该存在相关性。2012年由台湾地区学者Yi-Hua Jan完成了首例AK4与癌症关系论证的研究:体外试验中shRNA沉默肺癌细胞CL1-5和A549中的AK4后,两株细胞的侵袭能力下降约50%,从而证实AK4促进肺癌细胞的侵袭[3]。连云港市的学者MinMin HUANG在研究中显示AK4在人浆液性卵巢癌组织中高表达。在体内试验中,AK4敲低组的肿瘤体积明显减小,肿瘤重量明显减轻。这些试验均显示AK4促进了人浆液性卵巢癌的发生发展[4]。Jie Zhang等在Her-2阳性乳腺癌中的研究显示AK4的表达水平与肿瘤TNM分期(P = 0∶017)和淋巴结转移(P = 0∶046) 显著相关。体外试验中,MTT法、细胞划痕实验和Transwell试验都显示敲低AK4组的癌细胞增值、迁移、侵袭能力减弱。体外试验也显示敲低了AK4的肿瘤组织体积减小,重量减轻[5]。此后AK4与肿瘤的研究未曾断绝,田华等学者通过免疫组化等方法证实了AK4在肺腺癌中高表达[23]。李辰运的研究显示AK4在胰腺导管腺癌中高表达,并且与肿瘤分期、淋巴结转移、神经受侵、脉管内瘤栓有相关性(P < 0.05)[24]。李绍军等也证实AK4在食管鳞状细胞中高表达[25],夏林等也通过免疫组化的方式证实了AK4在胃癌中高表达[26],尽管我国的多数学者都明确了AK4在大多数肿瘤中的表达,但是很遗憾,仅有少数人通过体内、体外实验论证AK4对相关癌症的影响,无法将他们的研究进一步转化为临床制定治疗方案的依据。
本实验首次论证AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1增殖、迁移的影响。首先予siRNA沉默AK4的表达,再通过EdU检测细胞增殖能力,细胞划痕实验检测细胞迁移能力。本次实验的结论与前人的研究结论相似,即AK4促进肝内胆管癌细胞HUCCT1的增殖、迁移。本实验的不足在于,笔者尚未完成AK4对肝内胆管癌细胞其他生物学能力的影响,如EMT、侵袭等等。因此,笔者接下来即将完成其他细胞生物学行为实验,并且探究在机制方面的变化以及通过体内实验验证结论。本实验结论将为肝内胆管癌的临床分子靶向治疗提供基础实验数据,采用生物医学工程技术干预肝内胆管癌组织中AK4的表达,将有助于肿瘤的综合治疗。
-
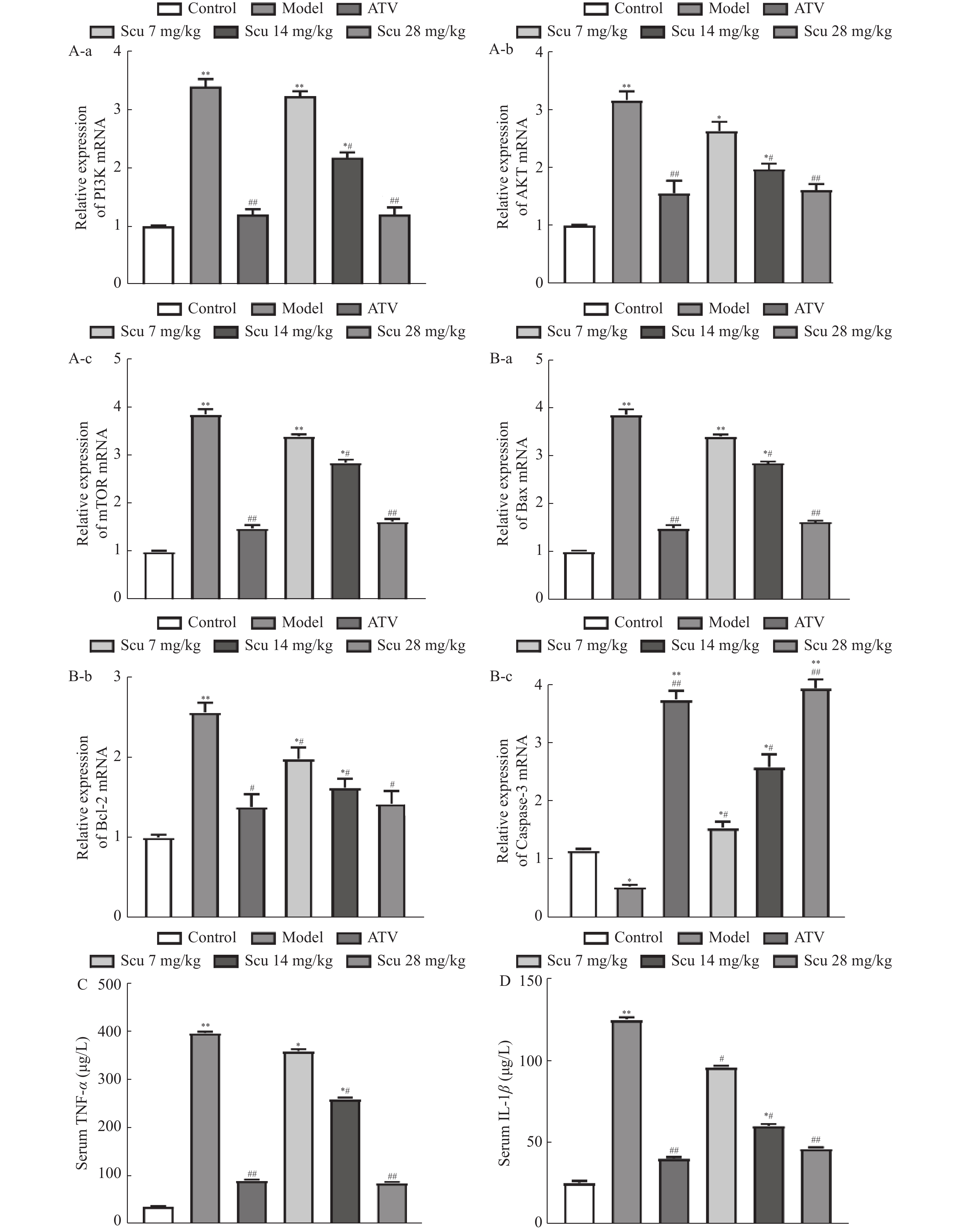
图 9 灯盏乙素对PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路及炎症因子的影响[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),n = 6)]A-a:PI3K的mRNA 表达;A-b:AKT的mRNA 表达;A-c:mTOR的mRNA 表达。B-a:Bax的mRNA 表达;B-b:Bcl-2的mRNA 表达;B-c:Caspase-3的mRNA 表达。C: 小鼠血清TNF-α的含量。D:小鼠血清IL-1β的含量。与空白对照组相比较,*P < 0.05,** P < 0.01;与模型组比较,#P < 0.05,#P < 0.01。
Figure 9. Effects of Scutellarin on PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway-related genes and inflammatory factors[(
$\bar x \pm s $ ),n = 6)]表 1 实验涉及的部分数据库
Table 1. Main databases involved in the experiment
名称 网址 用途 Pubchem https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 化合物相关信息下载 Swiss http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/ 药物相关靶点检索 Pharm mapper http://www.lilab-ecust.cn/pharmmapper/ 药物相关靶点检索 Genecards https://www.genecards.org/ 疾病相关靶点检索 Disgenet https://www.disgenet.org/ 疾病相关靶点检索 Venny https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/ 疾病-药物靶点交集图 Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ 靶点名称翻译 David https://david.ncifcrf.gov/ KEGG、GO分析 String https://string-db.org/ 蛋白质相互作用网络 微生信平台 http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/ 数据处理 Cytoscape v3.9.0软件 https://cytoscape.org/ 数据处理及绘图 表 2 引物序列
Table 2. The primer sequence
引物名称 长度(bp) 引物序列5′→3′ PI3K 20 Forward primer:CTTATGTCCTTGGCATTGGT Reverse primer:CAAAGTCTATGTGGAAGAGCTG AKT1 20 Forward primer:TCACCCAGTGACAACTCAG Reverse primer:AAACTCGTTCATGGTCACAC Bcl-2 19 Forward primer:TGACTGAGTACCTGAACCG Reverse primer:TAGTTCCACAAAGGCATCC Bax 19 Forward primer:CTGCAGAGGATGATTGCTG Reverse primer:GTCTGCAAACATGTCAGCT Caspase-3 21 Forward primer:AACTCTTCATCATTCAGGCCT Reverse primer:CCATATCATCGTCAGTTCCAC β-actin 20 Forward primer:CTTCCTGGGTATGGAATCCT Reverse primer:TCTTTACGGATGTCAACGTC mTOR 20 Forward primer:GCAGATTTGCCAACTATCTTCGG Reverse primer:CAGCGGTAAAAGTGTCCCCTG -
[1] Sun J J,Yin X W,Liu H H,et al. Rapamycin inhibits ox-LDL-induced inflammation in human endothelial cells in vitro by inhibiting the mTORC2/PKC/c-Fos pathway[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin,2018,39(3):336-344. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.102 [2] Troidl K,Schubert C,Vlacil A K,et al. The lipopeptide MALP-2 promotes collateral growth[J]. Cells,2020,9(4):997. doi: 10.3390/cells9040997 [3] Xi J Y,Rong Z. Scutellarin ameliorates high glucose-induced vascular endothelial cells injury by activating PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy[J]. J Ethnopharmacol,2021,271:113855. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113855 [4] Keeter,W C,Ma S,Stahr N,et al. Atherosclerosis and multi-organ-associated pathologies[J]. Semin Immunopathol,2022,44(3):363-374. doi: 10.1007/s00281-022-00914-y [5] Wu M F,Xu K Z,Guo YG,et al. Lipoprotein(a) and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease:Current understanding and future perspectives[J]. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther,2019,33(6):739-748. doi: 10.1007/s10557-019-06906-9 [6] Panes O,Gonzalez C,Hidalgo P,et al. Platelet tissue factor activity and membrane cholesterol are increased in hypercholesterolemia and normalized by rosuvastatin,but not by atorvastatin.[J]. Atherosclerosis,2017,257:164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.12.019 [7] Lee Y P,Cho Y,Kim E J,et al. Reduced expression of pyruvate kinase in kidney proximal tubule cells is a potential mechanism of pravastatin altered glucose metabolism[J]. Sci Rep,2019,9(1):5318. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-39461-2 [8] Ott B R,Daiello L A,Dahabreh I J,et al. Do statins impair cognition? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. J Gen Intern Med,2015,30(3):348-358. doi: 10.1007/s11606-014-3115-3 [9] Mo J,Yang R H,Li F,et al. Scutellarin protects against vascular endothelial dysfunction and prevents atherosclerosis via antioxidation[J]. Phytomedicine,2018,42:66-74. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.021 [10] Zhou S,Ai Z,Li W,et al. Deciphering the pharmacological mechanisms of taohe-chengqi decoction extract against renal fibrosis through integrating network pharmacology and experimental validation In vitro and in vivo[J]. Front Pharmacol,2020,11(1):425. [11] 何信用,王俊岩,宋囡,等. 基于网络药理学的葛根素治疗动脉粥样硬化潜在分子机制研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2020,38(9):116-120. doi: 10.13193/j.issn.1673-7717.2020.09.029 [12] Fernandez-Hernando C,Jozsef L,Jenkins D,et al. Absence of akt1 reduces vascular smooth muscle cell migration and survival and induces features of plaque vulnerability and cardiac dysfunction during atherosclerosis[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2009,29(12):2033-2040. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.196394 [13] 李敏静,郭莉,陈晔,等. 血府逐瘀汤含药血清对低氧诱导的大鼠肺动脉平滑肌细胞增殖及PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志,2020,40(7):836-841. [14] 张莉,白林英,母凯茜,等. 灯盏乙素对小型猪动脉粥样硬化模型颈总动脉斑块组织中基质金属蛋白酶-1、2、9 表达的影响[J]. 中药药理与临床,2020,36(6):91-97. [15] Ashino T,Yamamoto M,Yoshida T,et al. Redox-sensitive transcription factor Nrf2 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell migration and neointimal hyperplasia[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol,2013,33(4):760-768. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300614 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-






 下载:
下载:
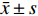

 下载:
下载: