MiR-196b Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Lung Adenocarcinoma by Targeting ERG
-
摘要:
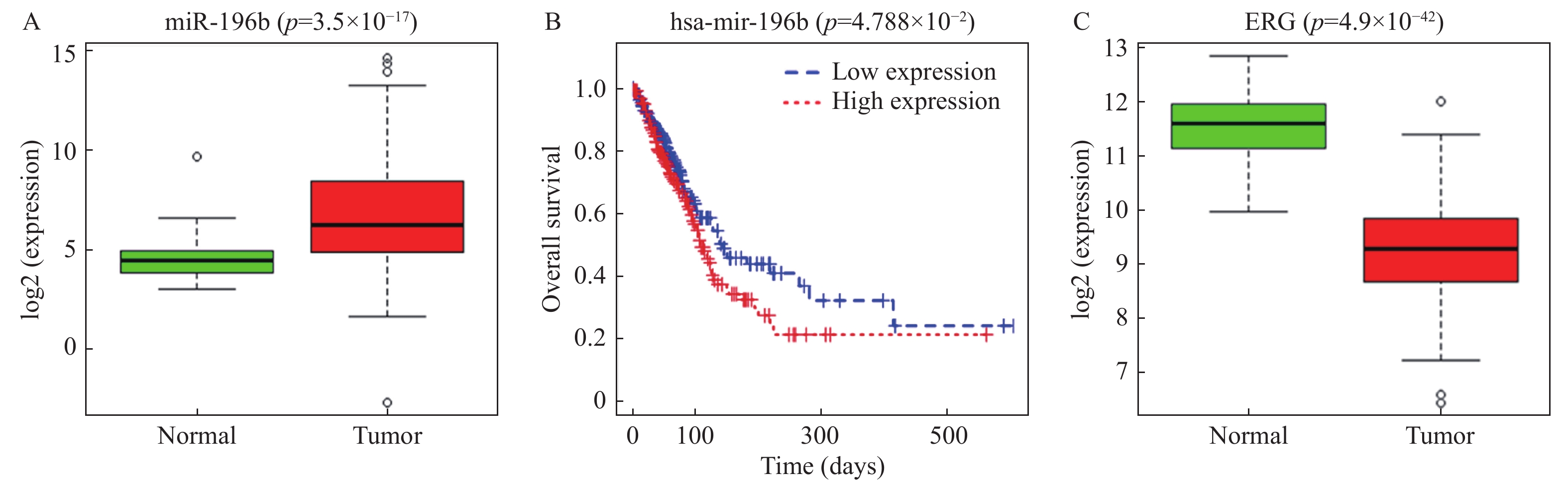
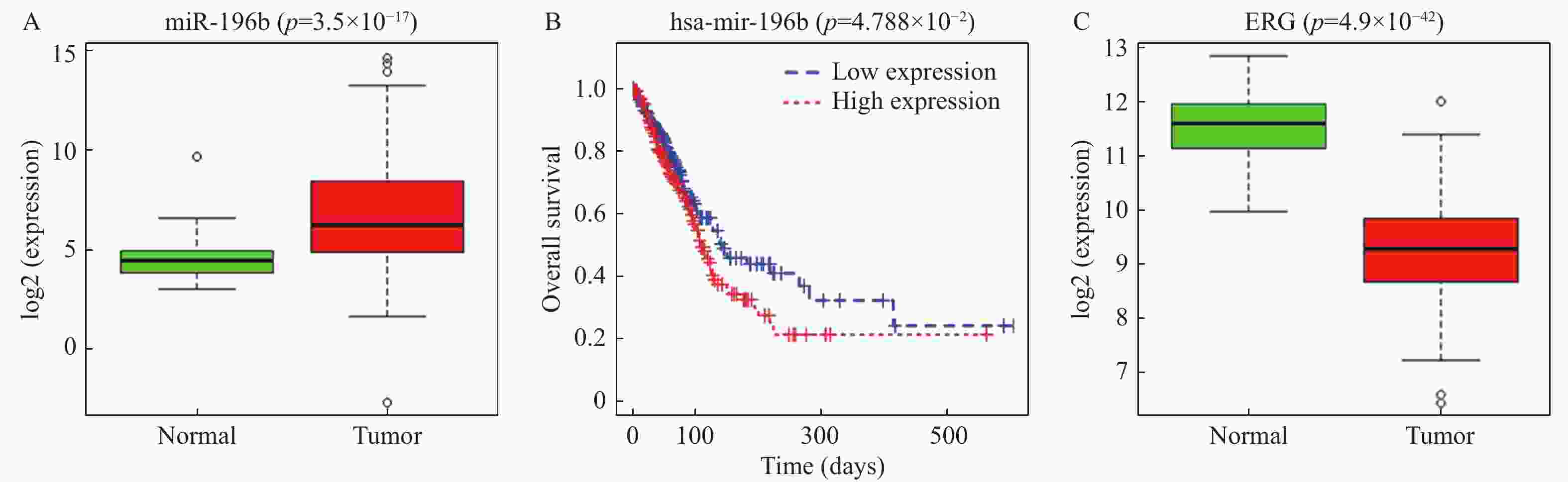
目的 探究miR-196b影响肺腺癌(lung adenocarcinoma,LUAD)进展的机制。 方法 通过TCGA数据库分析miR-196b在LUAD组织中的表达水平,利用TargetScan预测其下游靶基因并用双荧光素酶实验进行验证,qRT-PCR检测miR-196b和ETS相关基因(ETS-related gene,ERG)在LUAD细胞系中的表达情况,MTT、划痕愈合和Transwell实验分别检测不同处理后LUAD细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力的变化情况。 结果 miR-196b在LUAD中高表达(P = 3.50e-17)并靶向负调控ERG,过表达miR-196b能够促进LUAD细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭(P < 0.05),回复实验证实miR-196b/ERG调控轴能够影响LUAD细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭( P < 0.05)。 结论 miR-196b靶向ERG促进LUAD进展的分子机制,对开发LUAD新的临床治疗方法具有潜在意义。 Abstract:Objective To explore the mechanisms of miR-196b affecting the progression of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Methods The expression level of miR-196b in LUAD tissues was analyzed through TCGA database. TargetScan was used to predict its downstream target genes, and dual-luciferase assay was performed to validate the predictions. qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of miR-196b and ETS-related gene (ERG) in LUAD cell lines. MTT, scratch healing, and Transwell assays were used to respectively assess the changes in proliferation, migration, and invasion abilities of LUAD cells after different treatments. Results miR-196b was highly expressed in LUAD (P = 3.50e-17) and negatively regulated ERG. Overexpression of miR-196b promoted proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells (P < 0.05). Rescue experiments confirmed that miR-196b/ERG regulatory axis can affect the proliferation, migration, and invasion of LUAD cells ( P < 0.05). Conclusion The molecular mechanism of miR-196b targeting ERG in promoting the progression of LUAD has potential significance for the development of new clinical treatment methods for LUAD. -
Key words:
- miR-196b /
- ERG /
- Lung adenocarcinoma /
- Proliferation /
- Migration
-
图 4 miR-196b的靶点检测及不同处理组细胞中ERG 的表达情况
A:通过TargetScan数据库预测miR-196b和ERG的靶向结合位点;B:双荧光素酶法检测miR-196b与ERG的靶向结合关系;C:采用qRT-PCR和Western blot检测各细胞系中ERG mRNA和蛋白的表达;D:采用qRT-PCR和Western blot检测不同处理组ERG mRNA和蛋白的表达。与NC组或BEAS-2B组做比较,*P < 0.05。
Figure 4. Target detection of miR-196b and expression of ERG in cells of different treatment groups
图 5 miR-196b能靶向下调ERG促进肺腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力
A:采用qRT-PCR和Western blot检测不同处理组大鼠ERG mRNA和蛋白的表达;B:MTT实验检测不同处理组的细胞增殖能力;C:划痕愈合实验检测不同处理组细胞迁移能力;D:Transwell实验检测不同处理组细胞的迁移和侵袭能力(100×)。NC-mimic、NC-inhibitor、oe-NC和si-NC分别表示miR-196b过表达、miR-196b沉默、ERG过表达和ERG沉默对照组,miR-mimic和miR-inhibitor分别表示miR-196b过表达和沉默组,oe-ERG和si-ERG分别表示ERG过表达组和沉默组;miR-mimic/inhibitor + oe/si-NC与NC组比较,miR-mimic/inhibitor + oe/si-NC组与miR-mimic/inhibitor + oe/si-ERG组比较,*P < 0.05,。
Figure 5. miR-196b can target down regulate ERG to promote the proliferation,migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells
表 1 研究使用的细胞系及培养基
Table 1. Cell lines and media used in the study
细胞系 编号 培养基 BEAS-2B BNCC338205 DMEM-H PC-9 BNCC340767 HCC-78 BNCC338064 RPMI-1640 H1395 BNCC255519 Calu-3 BNCC338514 表 2 引物序列表
Table 2. Primer Sequence Table
基因 引物序列(5′→ 3′) miR-196b Forward primer: GTACCACTTTATCCCGTTCACCA
Reverse primer:ATCTCGAGGCAGGGAGAGAGGAATAAU6 Forward primer: GCCCATCTTGACCCGAAT Reverse primer: AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT ERG Forward primer:GAGTGGGCGGTGAAAGAATA Reverse primer: GGAGATGTGAGAGAAGAGTG GAPDH Forward primer:CTCCTCCTGTTCGACAGTCAGC Reverse primer:CCCAATACGACCAAATCCGTT -
[1] Luo C,Lei M,Zhang Y,et al. Systematic construction and validation of an immune prognostic model for lung adenocarcinoma[J]. J Cell Mol Med,2020,24(2):1233-1244. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14719 [2] Seguin L,Durandy M,Feral C C. Lung adenocarcinoma tumor origin: A Guide for personalized medicine[J]. Cancers (Basel),2022,14(7):1759. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071759 [3] Siegel R L,Miller K D,Jemal A. Cancer statistics,2016[J]. CA Cancer J Clin,2016,66(1):7-30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332 [4] Guo T,Li J,Zhang L,et al. Multidimensional communication of microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in lung cancer[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2019,145(1):31-48. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2767-5 [5] Xin H,Wang C,Chi Y,et al. MicroRNA-196b-5p promotes malignant progression of colorectal cancer by targeting ING5[J]. Cancer Cell Int,2020,20:119. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01200-3 [6] Shao L,Chen Z,Peng D,et al. Methylation of the HOXA10 promoter directs miR-196b-5p-dependent cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Res,2018,16(4):696-706. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0655 [7] Chen L,Tang H,Liu G,et al. MicroRNA-196b promotes gastric cancer progression by targeting ECRG4[J]. Anticancer Drugs,2021,32(2):127-137. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000998 [8] Wu X, Wu G, Zhang H, et al. MiR-196b promotes the invasion and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting AQP4 [J]. Technol Cancer Res Treat, 2021, 20: 1533033820985868. [9] Xu Q,Xu Z. miR-196b-5p promotes proliferation,migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells via targeting RSPO2[J]. Cancer Manag Res,2020,12:13393-13402. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S274171 [10] Li H,Feng C,Shi S. miR-196b promotes lung cancer cell migration and invasion through the targeting of GATA6[J]. Oncol Lett,2018,16(1):247-252. [11] Tharakan B,Hunter F A,Muthusamy S,et al. ETS-related gene activation preserves adherens junctions and permeability in microvascular endothelial cells[J]. Shock,2022,57(2):309-315. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001899 [12] Khosh Kish E,Choudhry M,Gamallat Y,et al. The expression of proto-oncogene ETS-related gene (ERG) plays a central role in the oncogenic mechanism involved in the development and progression of prostate cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(9):4772. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094772 [13] Lorenzoni M,De Felice D,Beccaceci G,et al. ETS-related gene (ERG) undermines genome stability in mouse prostate progenitors via Gsk3beta dependent Nkx3.1 degradation[J]. Cancer Lett,2022,534:215612. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215612 [14] He Y,Tao W,Shang C,et al. Xeroderma pigmentosum group D suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis of HepG2 cells by downregulating ERG expression via the PPARgamma pathway[J]. Int J Exp Pathol,2021,102(3):157-162. doi: 10.1111/iep.12396 [15] Robinson M D,McCarthy D J,Smyth G K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data[J]. Bioinformatics,2010,26(1):139-140. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp616 [16] Zhang B,Chen M,Jiang N,et al. A regulatory circuit of circ-MTO1/miR-17/QKI-5 inhibits the proliferation of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cancer Biol Ther,2019,20(8):1127-1135. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1598762 [17] Sheng K,Lu J,Zhao H. ELK1-induced upregulation of lncRNA HOXA10-AS promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression by increasing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2018,501(3):612-618. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.224 [18] 宋家美,刘洋,史涛,等. DATS调控VEGF信号轴改善URSA小鼠胎盘血管的形成[J]. 昆明医科大学学报.,2023,44(5):6-11. [19] 徐冬杏,唐波,朱国,等. Twist1调控Bmi1对胆囊癌细胞侵袭迁移的影响及其机制研究[J]. 昆明医科大学学报,2023,44(3):28-33. [20] Wei K,Ma Z,Yang F,et al. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes promote lung adenocarcinoma progression by delivering miR-942[J]. Cancer Lett,2022,526:205-216. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.10.045 [21] Xiong Y,Feng Y,Zhao J,et al. TFAP2A potentiates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by a novel miR-16 family/TFAP2A/PSG9/TGF-beta signaling pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis,2021,12(4):352. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03606-x [22] Lu J,Lin J,Zhou Y,et al. MiR-328-3p inhibits lung adenocarcinoma-genesis by downregulation PYCR1[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2021,550:99-106. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.02.029 [23] Zhang J,Yang W,Xiao Y,et al. MiR-125b inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human colon cancer SW480 cells via targeting STAT3[J]. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov,2022,17(2):187-194. doi: 10.2174/1574892816666210708165037 [24] Angeles AK,Heckmann D,Flosdorf N,et al. The ERG-regulated LINC00920 promotes prostate cancer cell survival via the 14-3-3epsilon-FOXO pathway[J]. Mol Cancer Res,2020,18(10):1545-1559. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0021 [25] Smolarz B,Durczynski A,Romanowicz H,et al. miRNAs in cancer (review of literature)[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2022,23(5):2805. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052805 [26] Singh A P,Luo H,Matur M,et al. A coordinated function of lncRNA HOTTIP and miRNA-196b underpinning leukemogenesis by targeting FAS signaling[J]. Oncogene,2022,41(5):718-731. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-02127-3 [27] Dioguardi M,Cantore S,Sovereto D,et al. Potential role of miR-196a and miR-196b as prognostic biomarkers of survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic review,meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis[J]. Life (Basel),2022,12(8):1269. doi: 10.3390/life12081269 [28] Adamo P,Ladomery M R. The oncogene ERG: A key factor in prostate cancer[J]. Oncogene,2016,35(4):403-414. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.109 [29] Kulda V,Topolcan O,Kucera R,et al. Prognostic significance of TMPRSS2-ERG fusion gene in prostate cancer[J]. Anticancer Res,2016,36(9):4787-4793. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.11037 [30] Hagglof C,Hammarsten P,Stromvall K,et al. TMPRSS2-ERG expression predicts prostate cancer survival and associates with stromal biomarkers[J]. PLoS One,2014,9(2):e86824. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086824 [31] Wei Y,Peng J,He S,et al. miR-223-5p targeting ERG inhibits prostate cancer cell proliferation and migration[J]. J Cancer,2020,11(15):4453-4463. doi: 10.7150/jca.44441 [32] Moh-Moh-Aung A,Fujisawa M,Ito S,et al. Decreased miR-200b-3p in cancer cells leads to angiogenesis in HCC by enhancing endothelial ERG expression[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):10418. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67425-4 [33] Yue C,Ma H,Zhou Y. Identification of prognostic gene signature associated with microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma[J]. PeerJ,2019,7:e8128. doi: 10.7717/peerj.8128 [34] Tang Q,Chen J,Di Z,et al. TM4SF1 promotes EMT and cancer stemness via the Wnt/beta-catenin/SOX2 pathway in colorectal cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2020,39(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01690-z [35] Gao C,Yao H,Liu H,et al. TM4SF1 is a potential target for anti-invasion and metastasis in ovarian cancer[J]. BMC Cancer,2019,19(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5417-7 [36] Peng X C,Zeng Z,Huang Y N,et al. Clinical significance of TM4SF1 as a tumor suppressor gene in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Med,2018,7(6):2592-2600. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1494 -





 下载:
下载: