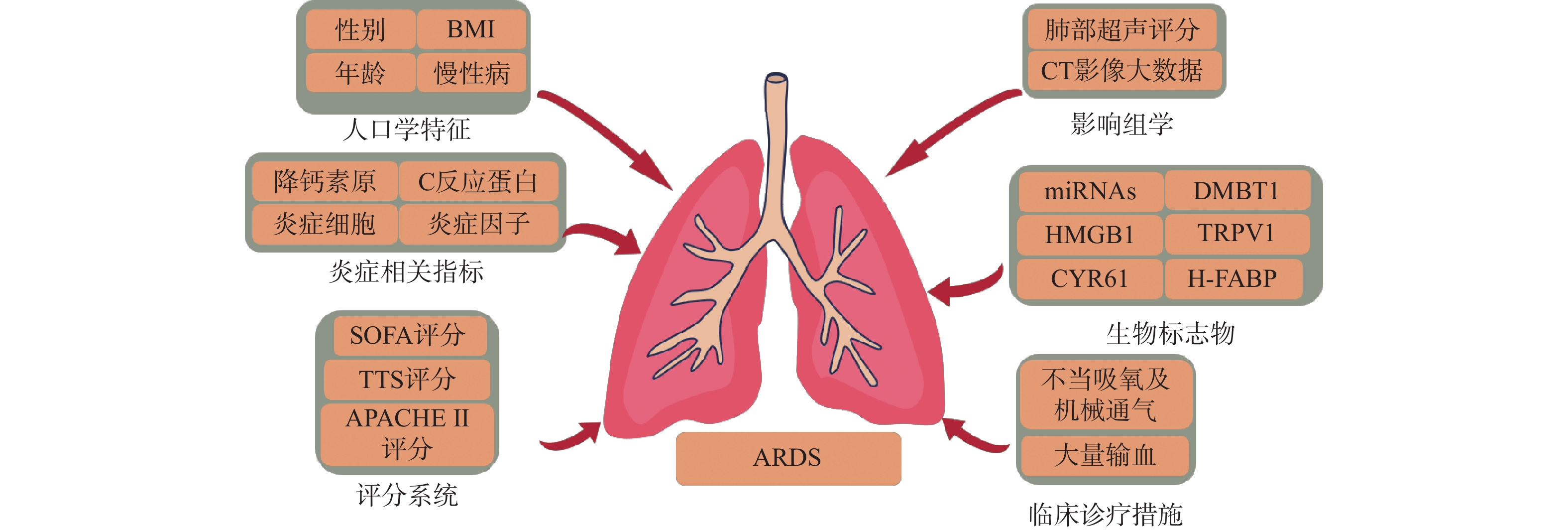
|
[1]
|
Meyer N J,Gattinoni L,Calfee C S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Lancet,2021,398(10300):622-637. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00439-6
|
|
[2]
|
Feng J,Liu L,He Y,et al. Novel insights into the pathogenesis of virus-induced ARDS: Review on the central role of the epithelial-endothelial barrier[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol,2021,17(9):991-1001. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2021.1951233
|
|
[3]
|
Ranieri V M,Rubenfeld G D,Thompson B T,et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition[J]. JAMA,2012,307(23):2526-2533.
|
|
[4]
|
杜欣欣,潘鹏飞,于湘友. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征的定义: 昨天,今天,明天[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志,2023,32(8):1023-1027. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0282.2023.08.003
|
|
[5]
|
Matthay M A,Arabi Y,Arroliga A C,et al. A new global definition of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2024,209(1):37-47. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202303-0558WS
|
|
[6]
|
杨婧,周永方,王洁,等. 重症医学2020年度研究进展[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2021,33(2):131-138. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210126-00121
|
|
[7]
|
Boxhoorn L,Voermans R P,Bouwense S A,et al. Acute pancreatitis[J]. Lancet,2020,396(10252):726-734. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31310-6
|
|
[8]
|
Shah J,Rana S S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in acute pancreatitis[J]. Indian J Gastroenterol,2020,39(2):123-132. doi: 10.1007/s12664-020-01016-z
|
|
[9]
|
周游,路国涛,王丹,等. 急性胰腺炎并发急性呼吸窘迫综合征预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志,2022,20(3):231-234. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115667-20210422-
|
|
[10]
|
Bellani G,Laffey J G,Pham T,et al. Epidemiology,patterns of care,and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries[J]. JAMA,2016,315(8):788-800. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291
|
|
[11]
|
Liu L,Yang Y,Gao Z,et al. Practice of diagnosis and management of acute respiratory distress syndrome in mainland China: A cross-sectional study[J]. J Thorac Dis,2018,10(9):5394-5404. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.08.137
|
|
[12]
|
Li X,Ma X. Acute respiratory failure in COVID-19: Is it "typical" ARDS?[J]. Crit Care,2020,24(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-02911-9
|
|
[13]
|
陆钦菊,王进京,傅小云. COVID-19相关ARDS: 从病理、病理生理到临床管理[J]. 遵义医科大学学报,2021,44(4):545-549.
|
|
[14]
|
唐敏,李娜. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制及相关生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2022,32(5):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2022.05.001
|
|
[15]
|
周垒垒,张先明. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征的发病机制及临床前药物研究[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2020,32(3):378-381. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200107-00111
|
|
[16]
|
Xu W,Sun N N,Gao H N,et al. Risk factors analysis of COVID-19 patients with ARDS and prediction based on machine learning[J]. Sci Rep,2021,11(1):2933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82492-x
|
|
[17]
|
Wang A,Gao G,Wang S,et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19 patients in Beijing, China: A retrospective study[J]. Med Sci Monit,2020,26:e925974.
|
|
[18]
|
Wu C,Chen X,Cai Y,et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan,China[J]. JAMA Intern Med,2020,180(7):934-943. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
|
|
[19]
|
Reynolds D,Kashyap R,Wallace L,et al. Older adult patients are at lower risk of ards compared to younger patients at risk: Secondary analysis of a multicenter cohort study[J]. J Intensive Care Med,2020,35(1):42-47. doi: 10.1177/0885066619848357
|
|
[20]
|
Jha S,Garima,Singh J B,et al. Risk factors and clinical outcomes associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in pregnant and non-pregnant women diagnosed with COVID-19: A Comparative analysis[J]. Cureus,2023,15(5):e39514.
|
|
[21]
|
Tsai Y T,Ku H C,Maithreepala S D,et al. Higher risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome and risk factors among patients with COVID-19: A systematic review,meta-analysis and meta-regression[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health,2022,19(22):15125.
|
|
[22]
|
Chen N,Zhou M,Dong X,et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan,China: A descriptive study[J]. Lancet,2020,395(10223):507-513. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
|
|
[23]
|
张静. 生物标志物在急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者中的联合检测价值[J]. 河南大学学报(医学版),2023,42(1):54-61.
|
|
[24]
|
Sivapalan P,Bonnesen B,Jensen J U. Novel perspectives regarding the pathology,inflammation,and biomarkers of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,22(1):205.
|
|
[25]
|
李若寒,李佳媚,任佳佳,等. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征中炎症和凝血的交互作用[J]. 中国急救医学,2023,43(9):752-756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2023.09.015
|
|
[26]
|
季永华,钱文霞,钱宇杰. 血清ANGPTL4水平对急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者疾病严重程度和预后的预测价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2022,43(19):2327-2331. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2022.19.005
|
|
[27]
|
Hrenak J,Simko F. Renin-Angiotensin System: An important player in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. Int J Mol Sci,2020,21(21):8038.
|
|
[28]
|
李磅,王红嫚. HMGB1在ARDS后肺纤维化中的研究进展[J]. 遵义医科大学学报,2023,46(7):725-730.
|
|
[29]
|
舒小燚,范绍辉,徐宇,等. 高迁移率族蛋白B1在ARDS中的释放机制研究进展[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2021,33(7):889-893. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200421-00316
|
|
[30]
|
段松堂,卢威,喻巍,等. miRNA-574-5p和HMGB1在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的临床意义[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2023,44(24):3059-3062. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2023.24.023
|
|
[31]
|
Oz M,Lorke D E,Howarth F C. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1)-independent actions of capsaicin on cellular excitability and ion transport[J]. Med Res Rev,2023,43(4):1038-1067. doi: 10.1002/med.21945
|
|
[32]
|
席宏,沈杰,杨谦梓,等. 瞬时受体电位香草酸亚型1在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的作用及研究进展[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版),2024,44(5):641-646. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-8115.2024.05.013
|
|
[33]
|
黄佳骏,宋磊,朱美君. 血清CYR61、H-FABP在新生儿急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊断中的临床价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2024,45(10):1203-1206+1211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4130.2024.10.011
|
|
[34]
|
蒲清瑚,刘国跃,王洪亮,等. MicroRNAs与急性呼吸窘迫综合征关系的研究进展[J]. 遵义医学院学报,2016,39(5):535-538,546.
|
|
[35]
|
Martucci G,Arcadipane A,Tuzzolino F,et al. Identification of a circulating miRNA signature to stratify acute respiratory distress syndrome patients[J]. J Pers Med,2020,11(1):15.
|
|
[36]
|
邱小宇,王晓芝,黄潇. 循环微小RNA可作为ARDS生物标志物的研究进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志,2022,27(8):1256-1260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2022.08.026
|
|
[37]
|
葛晨,张一凡,贾红炜,等. 恶性脑肿瘤缺失蛋白1在脓毒症致急性呼吸窘迫综合征大鼠中的表达和作用[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2023,35(2):152-157. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220509-00460
|
|
[38]
|
叶忆如,苏珊珊,周颖,等. 内皮细胞特异性分子-1在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的作用研究进展[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2022,34(7):773-776. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210409-00534
|
|
[39]
|
胡泊,李晓东,李甜,等. 功能残气量与肺部超声评分的相关性及其对急性呼吸窘迫综合征俯卧位通气治疗的预测价值[J]. 中国急救医学,2021,41(1):46-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2021.01.009
|
|
[40]
|
吕茂华,曹励琪,李香祥,等. 肺部超声评分评估急性呼吸窘迫综合征严重程度的Meta分析[J]. 中国超声医学杂志,2022,38(10):1191-1194.
|
|
[41]
|
范浩浩,姜倩倩,邢文宇,等. 基于人工智能的自动肺部超声评分对ARDS患者血管外肺水评估的价值[J]. 中国急救医学,2023,43(1):24-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2023.01.006
|
|
[42]
|
Chen Y,Wang Y,Zhang Y,et al. A quantitative and radiomics approach to monitoring ARDS in COVID-19 patients based on chest CT: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Med Sci,2020,17(12):1773-1782. doi: 10.7150/ijms.48432
|
|
[43]
|
Stubblefield J,Hervert M,Causey J L,et al. Transfer learning with chest X-rays for ER patient classification[J]. Sci Rep,2020,10(1):20900. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78060-4
|
|
[44]
|
Gerard S E,Herrmann J,Kaczka D W,et al. Multi-resolution convolutional neural networks for fully automated segmentation of acutely injured lungs in multiple species[J]. Med Image Anal,2020,60:101592. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.101592
|
|
[45]
|
Reamaroon N,Sjoding M W,Derksen H,et al. Robust segmentation of lung in chest x-ray: Applications in analysis of acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. BMC Med Imaging,2020,20(1):116. doi: 10.1186/s12880-020-00514-y
|
|
[46]
|
杨杰,黄佳捷,刘宁,等. 影像组学和深度学习在急性呼吸窘迫综合征早期识别和预测中的应用[J]. 中国急救医学,2023,43(10):819-825. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2023.10.011
|
|
[47]
|
Carrié C,Rieu B,Benard A,et al. Early non-invasive ventilation and high-flow nasal oxygen therapy for preventing endotracheal intubation in hypoxemic blunt chest trauma patients: The OptiTHO randomized trial[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27(1): 163.
|
|
[48]
|
唐瑞,唐雯,王导新. 机器学习对创伤合并急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者院内死亡的预测价值[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2022,34(3):260-264. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211117-01741
|
|
[49]
|
赵峰,沈子渊,杨翠,等. LIPS评分联合APACHEⅡ评分和氧合指数预测ARDS发生模型的建立和验证[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2022,34(10):1048-1054. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220930-00883
|
|
[50]
|
Shi Y,Wang L,Yu S,et al. Risk factors for acute respiratory distress syndrome in sepsis patients: A retrospective study from a tertiary hospital in China[J]. BMC Pulm Med,2022,22(1):238. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02015-w
|
|
[51]
|
吴旭,宋元林,胡莉娟. 血清生物标志物对重症社区获得性肺炎患者发生急性呼吸窘迫综合征及28d预后的预测价值[J]. 中国临床医学,2023,30(4):599-604. doi: 10.12025/j.issn.1008-6358.2023.20230228
|
|
[52]
|
Ma X,Dong Z,Wang Y,et al. Risk factors analysis of thoracic trauma complicated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and observation of curative effect of lung-protective ventilation[J]. Front Surg,2021,8:826682.
|
|
[53]
|
Trillo-Alvarez C,Cartin-Ceba R,Kor D J,et al. Acute lung injury prediction score: derivation and validation in a population-based sample[J]. Eur Respir J,2011,37(3):604-609. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00036810
|
|
[54]
|
Gajic O,Dabbagh O,Park P K,et al. Early identification of patients at risk of acute lung injury: Evaluation of lung injury prediction score in a multicenter cohort study[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2011,183(4):462-470. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201004-0549OC
|
|
[55]
|
Xie J,Liu L,Yang Y,et al. A modified acute respiratory distress syndrome prediction score: A multicenter cohort study in China[J]. J Thorac Dis,2018,10(10):5764-5773. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.09.117
|
|
[56]
|
荆晨晨,孙淑青,秦德春. 急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者早期风险预测模型的建立[J]. 中华护理杂志,2020,55(9):1285-1291. doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2020.09.001
|
|
[57]
|
彭庆荣,杨丽萍,谢永鹏,等. EICU住院患者急性呼吸窘迫综合征发生风险列线图模型的构建及验证[J]. 国际呼吸杂志,2024,44(7):838-843. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn131368-20240226-00099
|
|
[58]
|
Greener J G,Kandathil S M,Moffat L,et al. A guide to machine learning for biologists[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2022,23(1):40-55. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00407-0
|
|
[59]
|
Song X,Liu X,Liu F,et al. Comparison of machine learning and logistic regression models in predicting acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Med Inform,2021,151:104484. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2021.104484
|
|
[60]
|
Jiang T,Gradus J L,Rosellini A J. Supervised machine learning: A brief primer[J]. Behav Ther,2020,51(5):675-687. doi: 10.1016/j.beth.2020.05.002
|
|
[61]
|
彭川,熊辉. 机器学习在急诊科诊疗中的应用研究进展[J]. 中国中西医结合急救杂志,2022,29(2):253-256. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9691.2022.02.028
|
|
[62]
|
Le S,Pellegrini E,Green-Saxena A,et al. Supervised machine learning for the early prediction of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)[J]. J Crit Care,2020,60:96-102. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.07.019
|
|
[63]
|
武俊伟,刘超,王雪,等. ICU住院患者重度急性呼吸窘迫综合征早期预测模型的构建[J]. 解放军医学院学报,2022,43(11):1146-1150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-5227.2022.11.008
|
|
[64]
|
莫继朋,贾中芝,汤艳,等. 基于人工神经网络建立社区获得性肺炎并发急性呼吸窘迫综合征的预测模型[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2022,34(4):367-372. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210927-01406
|
|
[65]
|
肖慧敏,刘坚,刘秀梅,等. 机器学习辅助急性呼吸窘迫综合征诊治的研究进展[J]. 中国急救医学,2023,43(1):64-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1949.2023.01.012
|
|
[66]
|
张伟俊,陈剑潇,皋源. 机器学习在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的应用进展[J]. 中华危重病急救医学,2023,35(6):662-664. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20221027-00944
|





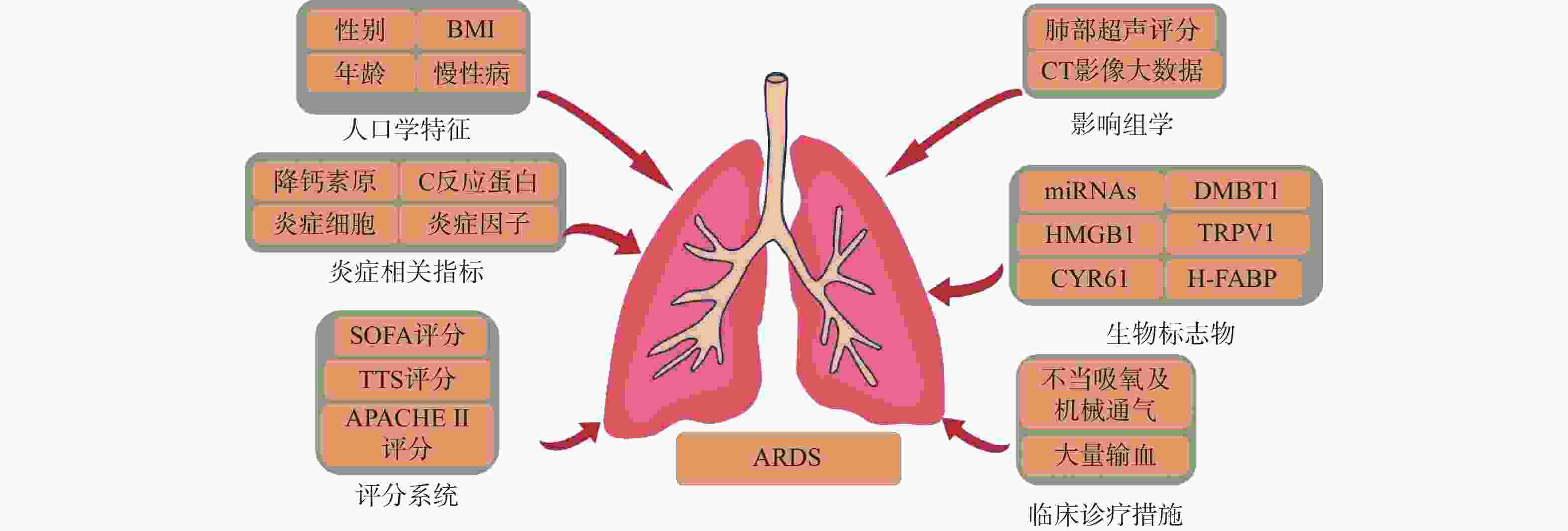
 下载:
下载: