Study on the Mechanism of Trim47 in Acute Lung Injury via TAB1/I κB Inflammatory Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
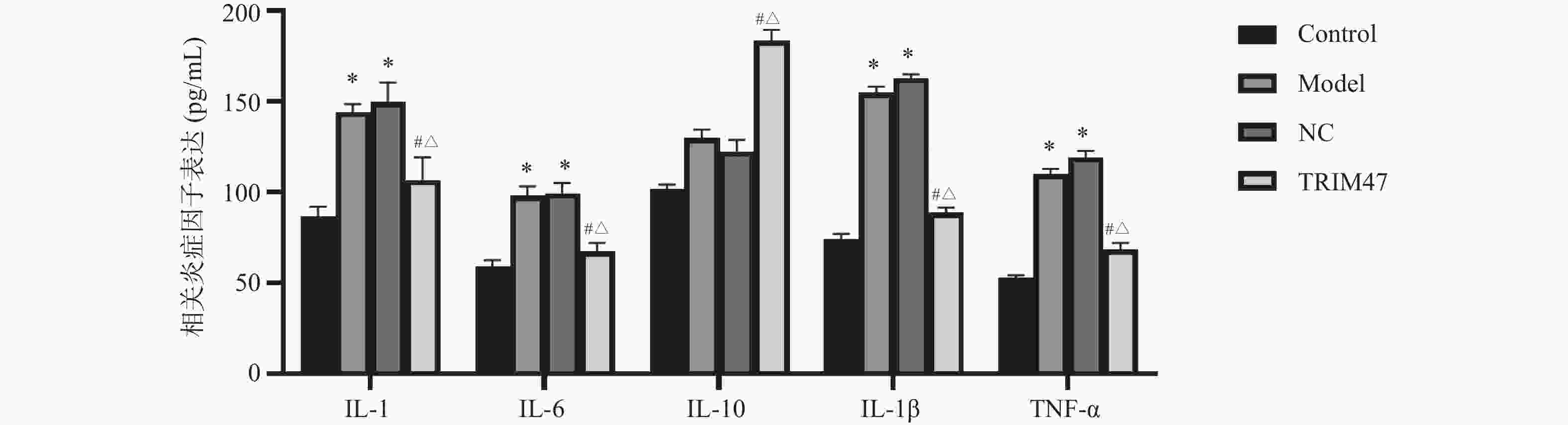
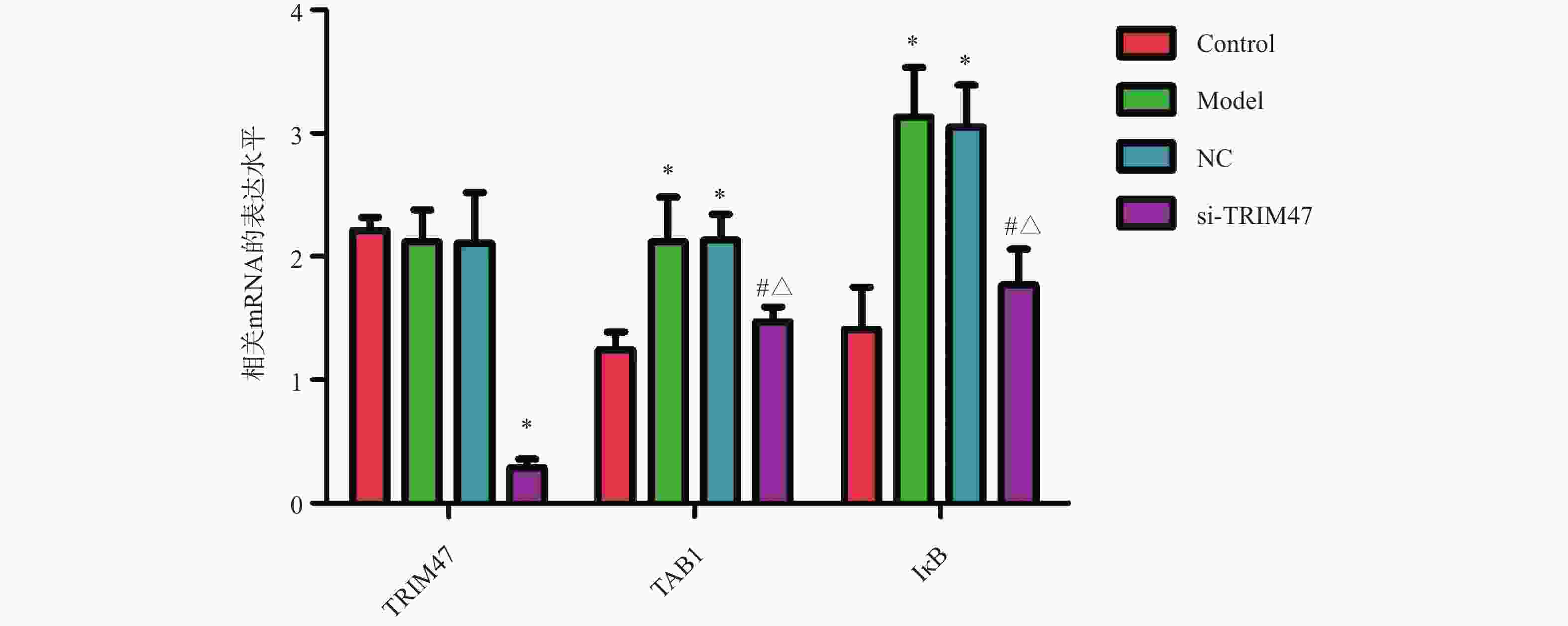
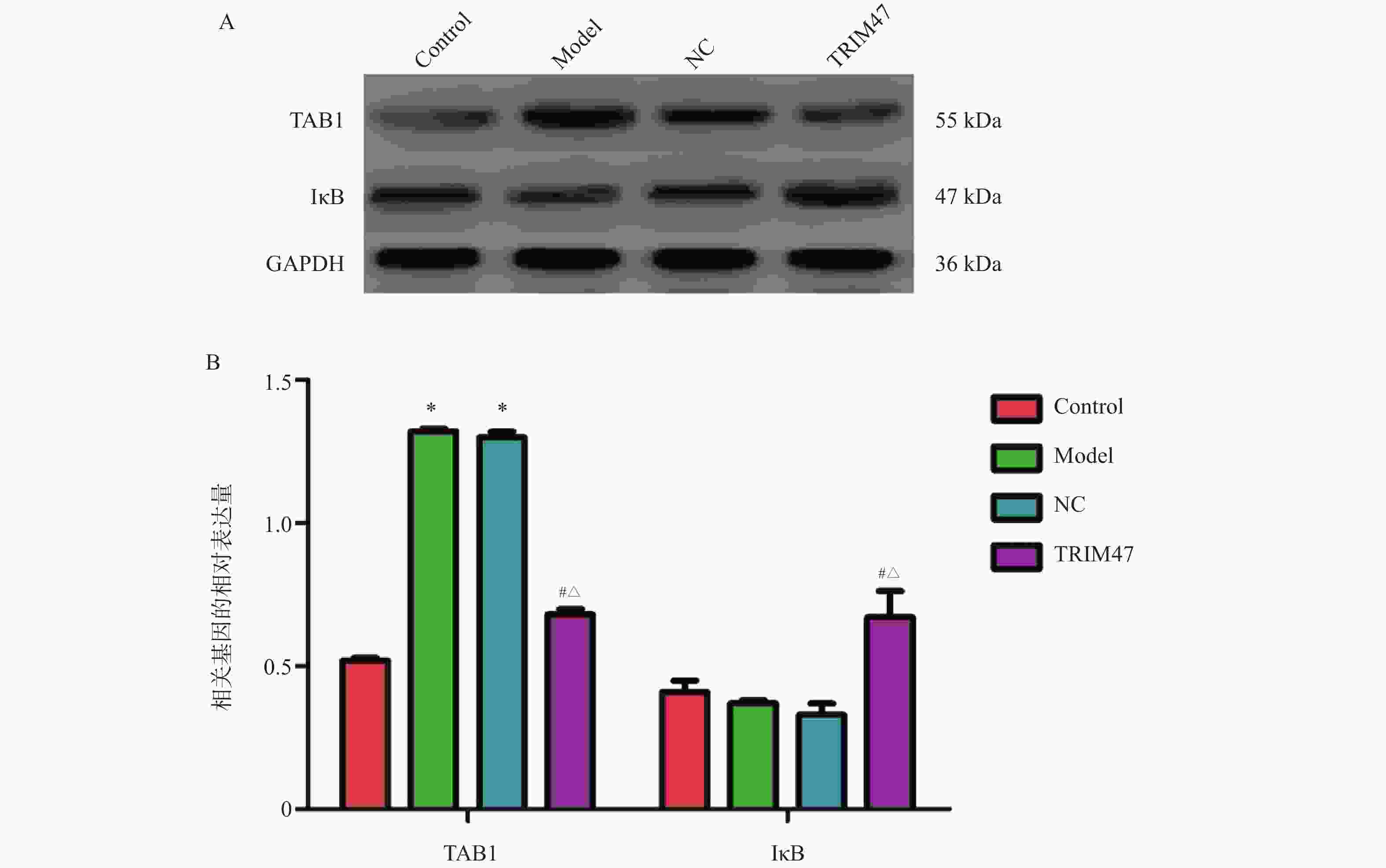
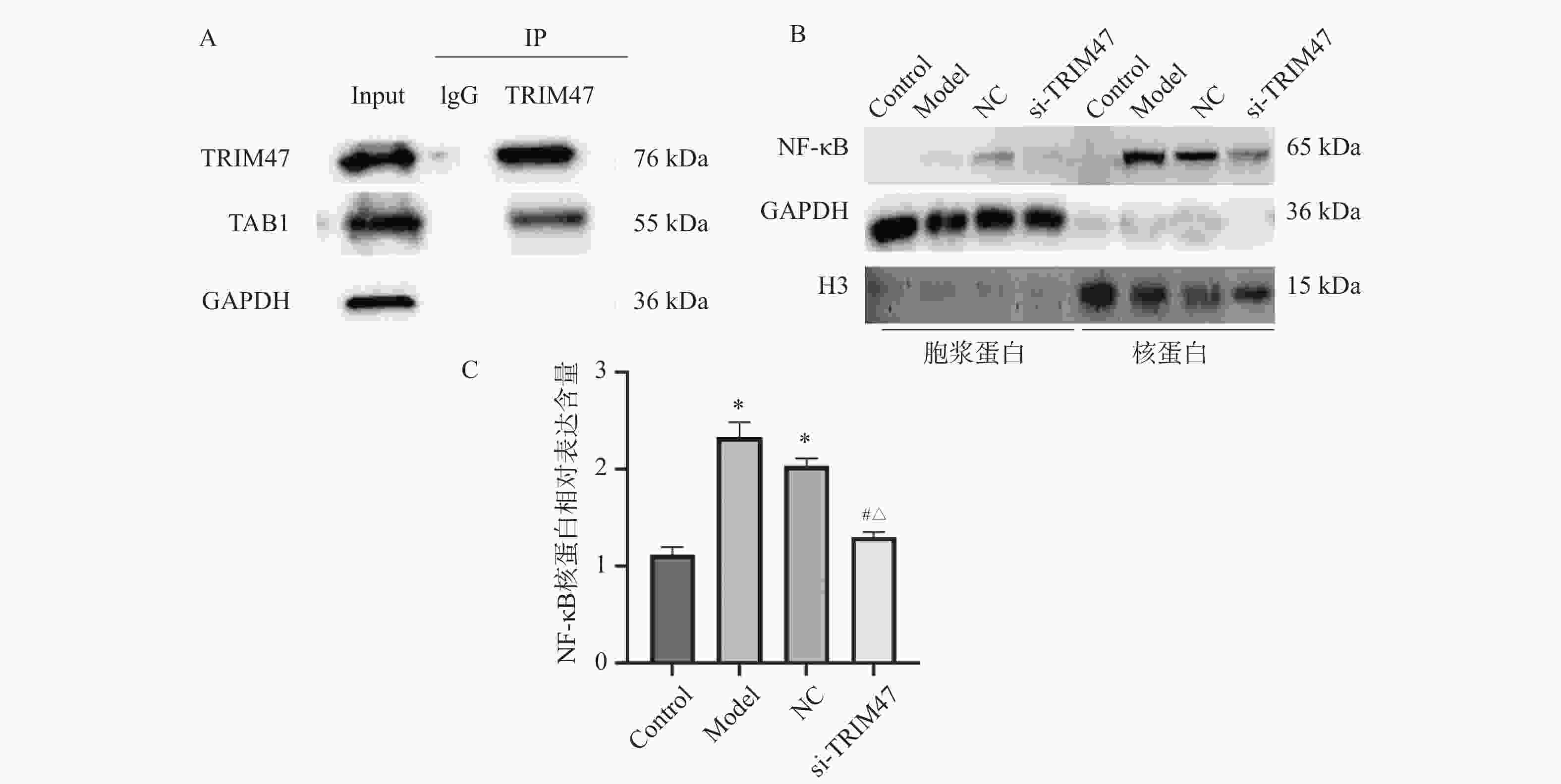
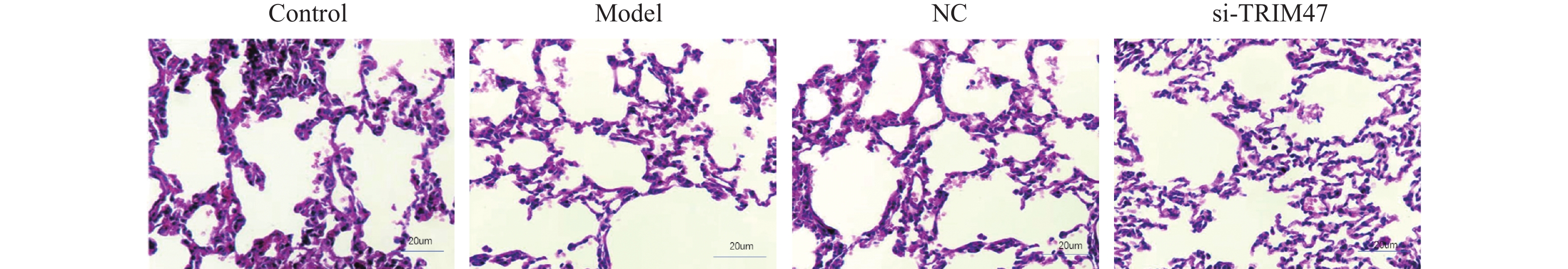
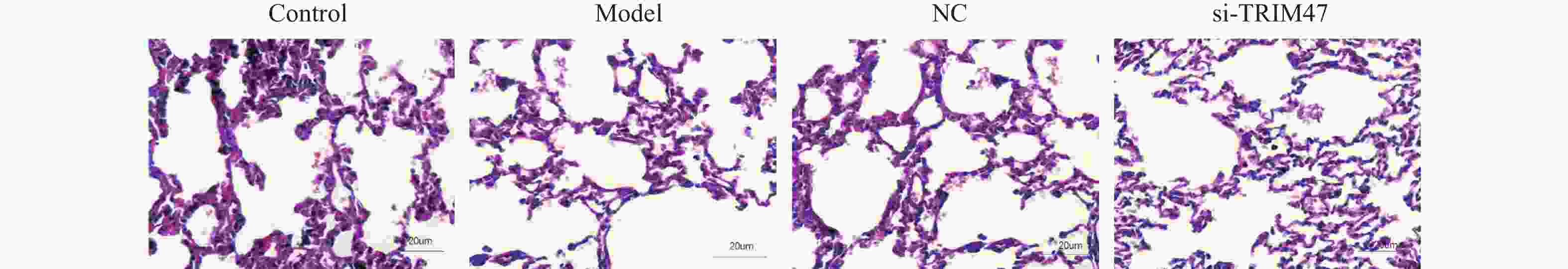
目的 探讨Tripartite结构蛋白47(tripartite motif containing 47,TRIM47)对急性肺损伤急性肺损伤(acute lung injury,ALI)大鼠模型肺组织的影响以及对转化生长因子β激活激酶1(TGF-beta activated kinase 1,TAB1)/核因子κB抑制蛋白(inhibitor of NF-κB,IκB)调控机制。 方法 构建SD大鼠ALI模型,模型组、空载体组(NC)组及si-TRIM47组诱导建立大鼠ALI模型,NC组与si-TRIM47组于建模后经尾静脉分别注射NC质粒及靶向TRIM47的siRNA干扰质粒(si-TRIM47)。干预1周后,通过苏木精-伊红(HE)染色观察各组肺组织病理学改变,ELISA检测外周血白细胞介素(Interleukin,IL)-1、IL-6、IL-10、IL-1β、肿瘤坏死因子(tumor necrosis factor,TNF-α)的表达水平,qPCR测定肺组织中TAB1及IκB的mRNA相对表达量,Western blot分析肺组织中TAB1与IκB蛋白表达水平,同时检测NF-κB入核情况;CO-IP检测TRIM47和TAB1蛋白结合情况。 结果 HE染色结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组和NC组的组织炎性细胞浸润程度升高(P < 0.05);与模型组和NC组相比,si-TRIM47组的病理病变程度则相对较轻。ELISA检测结果显示,与对照组相比,模型组IL-1、IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α升高(P < 0.01)。与模型组和NC组相比,si-TRIM47组大鼠的IL-1、IL-6、IL-1β、TNF-α降低,而IL-10升高(P < 0.01);qPCR和Western blot结果表明,与对照组相比,模型组、NC组大鼠TAB1和核蛋白NF-κB升高、IκB表达水平降低(P < 0.01);与模型组和NC组相比,si-TRIM47组TAB1降低和核蛋白NF-κB降低、IκB表达水平升高(P < 0.01)。此外,CO-IP实验显示,TRIM47促进TAB1蛋白表达。 结论 si-TRIM47可能通过抑制炎症因子释放及TAB1信号通路的激活,对ALI大鼠发挥保护作用。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect of tripartite motif containing 47 (TRIM47) on lung tissue of acute lung injury rat model and its effect on the molecular mechanism regulating transforming growth factor Transforming growth factor beta activated kinase 1 binding protein 1(TAB1) / inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB). Methods The ALI model was constructed in SD rats, the model group, empty carrier (NC)group and si-TRIM47 group were induced to establish a rat ALI model. The NC group and si-TRIM47 group were injected with NC plasmid and siRNA interference plasmid targeting TRIM47 (si-TRIM47) via tail vein after modeling. One week after the intervention, pathological changes in the lung tissues of each group were observed via hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Levels of peripheral blood interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, IL-10, IL-1β, and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF-α)were detected by ELISA. The relative mRNA expression levels of TAB1 and IκB in lung tissues were measured using quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Protein expression levels of TAB1 and IκB in lung tissues were analyzed by Western blot, while nuclear translocation of NF-κB was simultaneously detected. The protein interaction between TRIM47 and TAB1 was examined by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP). Results In histopathological observations, compared with the control group, the model group and NC group exhibited increased inflammatory cell infiltration, whereas the si-TRIM47 group showed relatively milder pathological lesions compared to both the model and NC groups. ELISA results indicated that, compared with the control group, the model group had elevated levels of IL-1, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α (P < 0.01); in contrast, compared with the model group and NC group, the si-TRIM47 group demonstrated reduced levels of IL-1, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α but increased IL-10 (P < 0.01) group and NC group, the si-TRIM47 group demonstrated reduced levels of IL-1, IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α but increased IL-10 (P < 0.01). Furthermore, qPCR and Western blot results revealed that, compared with the control group, TAB1 and nuclear NF-κB protein levels were elevated while IκB expression was markedly reduced in the model and NC groups(P < 0.01); conversely, the si-TRIM47 group exhibited decreased TAB1 and nuclear NF-κB protein alongside increased IκB expression compared to the model and NC groups (P < 0.01). Additionally, the CO-IP assay confirmed that TRIM47 promoted TAB1 protein expression. Conclusion si-TRIM47 may exert a protective effect against ALI in rats by inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors and the activation of the TAB1 signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- Si-trim47 /
- Acute lung injury /
- Inflammatory factors /
- TAB1 signaling path
-
表 1 qPCR检测中不同基因的引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences of different genes in qPCR detection
基因 引物序列(5'-3') 引物长度(bp) TAB1 Forward:5′- CGACGCGTTGGCGGCGCAGAGGAGGAGCTTGC -3′ 23 Reverse:5′- ACGCGTCGAC TACCCTGGGGTCAGGCTGCCCAGGA -3' IκB Forward:5′- TGAAAAACTGGATGTCCCTGTATG -3′ 22 Reverse:5′- GGCCCATTTCCCGCCCCCTGGCAT -3′ GAPDH Forward:5'- GTACGACTCACTATAGGGA -3′
Reverse:5'- AGGTCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGT -3′20 -
[1] Li Y, Cao Y, Xiao J, et al. Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 inhibits ferroptosis and alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2020, 27(9): 2635-2650. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0528-x [2] He Y Q, Zhou C C, Yu L Y, et al. Natural product derived phytochemicals in managing acute lung injury by multiple mechanisms[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 163: 105224. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105224 [3] Tang J, Xu L, Zeng Y, et al. Effect of gut microbiota on LPS-induced acute lung injury by regulating the TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 91: 107272. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107272 [4] Xiao K, He W, Guan W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells reverse EMT process through blocking the activation of NF-κB and Hedgehog pathways in LPS-induced acute lung injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(10): 863. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03034-3 [5] liu C, Yin Z, Feng T, et al. An integrated network pharmacology and RNA-Seq approach for exploring the preventive effect of Lonicerae japonicae Flos on LPS-induced acute lung injury[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2021, 264: 113364. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113364 [6] Hu Y Z, Li X, Han R, et al. Molecular identification and expression analysis of TAB1 from orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides)[J]. Dev Comp Immunol, 2019, 90: 152-156. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2018.09.014 [7] Guesmi F, Prasad S, Tyagi A K, et al. Antinflammatory and anticancer effects of terpenes from oily fractions of Teucruim Alopecurus, blocker of IκBα kinase, through downregulation of NF-κB activation, potentiation of apoptosis and suppression of NF-κB-regulated gene expression[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 95: 1876-1885. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.09.115 [8] Sokolova O, Kähne T, Bryan K, et al. Interactome analysis of transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1 inHelicobacter pylori-infected cells revealed novel regulators tripartite motif 28 and CDC37[J]. Oncotarget, 2018, 9(18): 14366-14381. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24544 [9] Li L, Zhang S, Wei L, et al. Anti-fibrotic effect of melittin on TRIM47 expression in human embryonic lung fibroblast through regulating TRIM47 pathway[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 256: 117893. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117893 [10] Zhan W, Zhang H, Su Y, et al. TRIM47 promotes HDM-induced bronchial epithelial pyroptosis by regulating NEMO ubiquitination to activate NF-κB/NLRP3 signaling[J]. Cell Biol Int, 2024, 48(8): 1138-1147. doi: 10.1002/cbin.12186 [11] Qiao Q, Liu X, Yang T, et al. Nanomedicine for acute respiratory distress syndrome: The latest application, targeting strategy, and rational design[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2021, 11(10): 3060-3091. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.023 [12] Huang C Y, Deng J S, Huang W C, et al. Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by hispolon in mice, through regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 pathways, and suppressing oxidative stress-mediated ER stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(6): 1742. doi: 10.3390/nu12061742 [13] Wei S, Zhao Q, Zheng K, et al. GFAT1-linked TAB1 glutamylation sustains p38 MAPK activation and promotes lung cancer cell survival under glucose starvation[J]. Cell Discov, 2022, 8: 77. [14] Kumazoe M, Ogawa F, Hikida A, et al. Plant miRNA osa-miR172d-5p suppressed lung fibrosis by targeting Tab1[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 2128. [14] Kumazoe M, Ogawa F, Hikida A, et al. Plant miRNA Osa-miR172d-5p suppressed lung fibrosis by targeting Tab1[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13: 2128. [15] Dong Z, Li B, Wang X. MicroRNA-889 plays a suppressive role in cell proliferation and invasion by directly targeting TAB1 in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Mol Med Report, 2019, 20(1): 261-269. [16] 王瑞哲, 寇育乐, 贺宏伟. 肺肠合治法对LPS诱导急性肺损伤大鼠NF-κB炎症通路和巨噬细胞极化的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2022, 28(8): 93-100. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20211804 [17] Wu D, Zhang H, Wu Q, et al. Sestrin 2 protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by inducing mitophagy in alveolar macrophages[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 267: 118941. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118941 [18] Qian Y, Wang Z, Lin H, et al. TRIM47 is a novel endothelial activation factor that aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice via K63-linked ubiquitination of TRAF2[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 148. [19] Hou L, Zhang J, Liu Y, et al. MitoQ alleviates LPS-mediated acute lung injury through regulating Nrf2/Drp1 pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2021, 165: 219-228. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.01.045 [20] Hu Q, Zhang S, Yang Y, et al. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis and treatment of acute lung injury[J]. Mil Med Res, 2022, 9(1): 61. doi: 10.1186/s40779-022-00417-9 [21] Ju M, Liu B, He H, et al. MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice via inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Cycle, 2018, 17(16): 2001-2018. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1509635 [22] Mussbacher M, Salzmann M, Brostjan C, et al. Cell type-specific roles of NF-κB linking inflammation and thrombosis[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 85. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00085 -





 下载:
下载: