Galangin Inhibits the Migration and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Hela Cells Through Hippo/YAP Pathway
-
摘要:
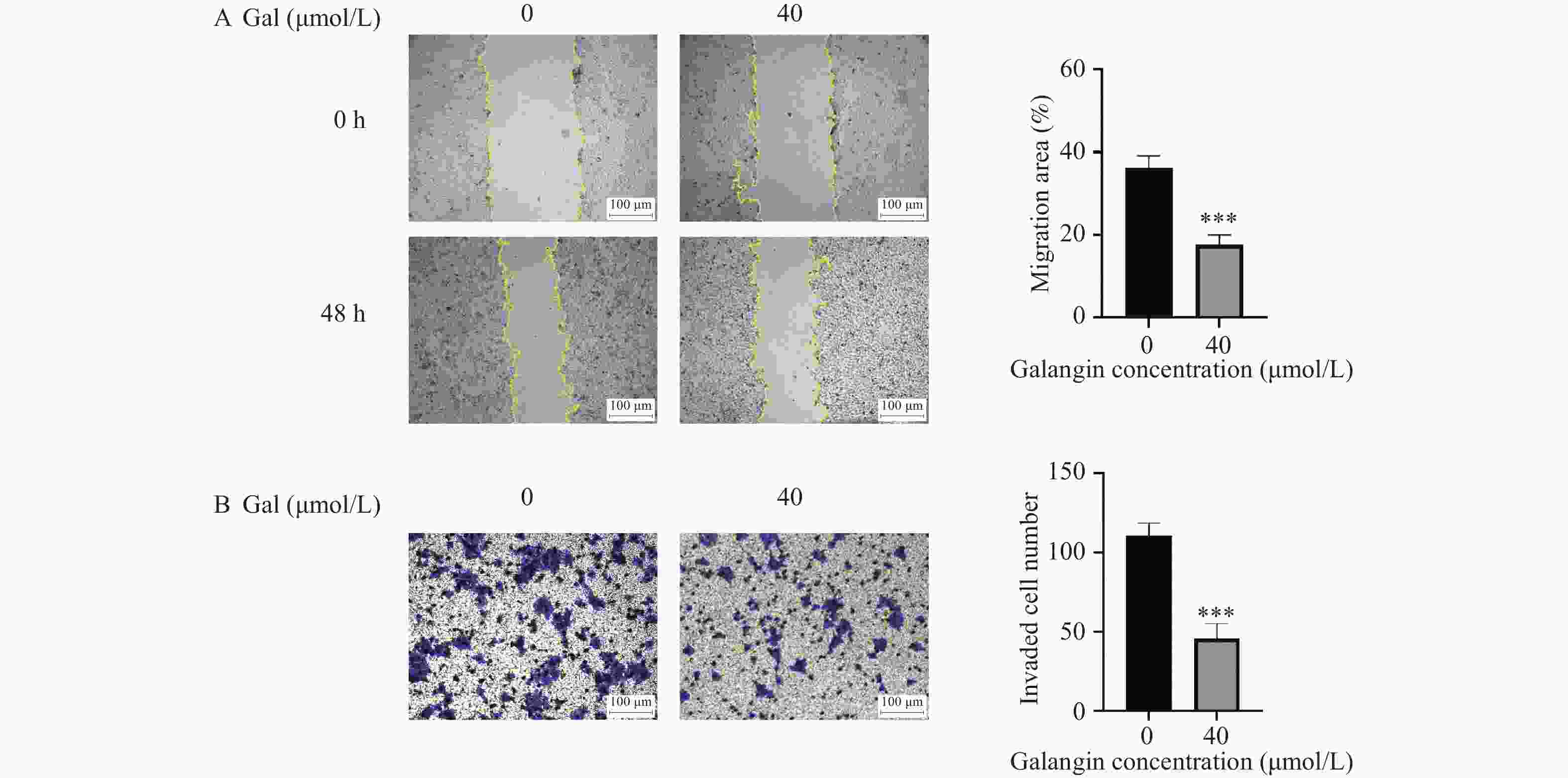
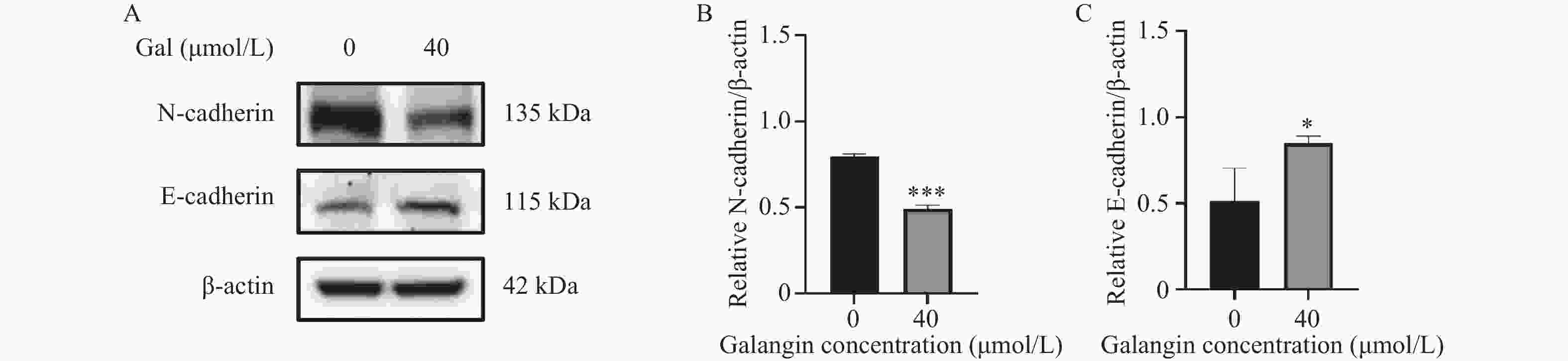
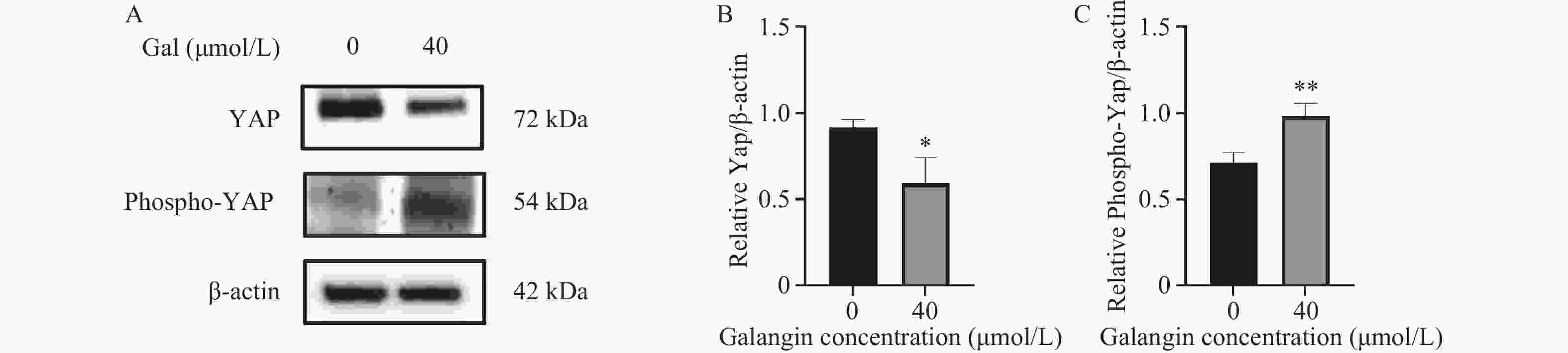
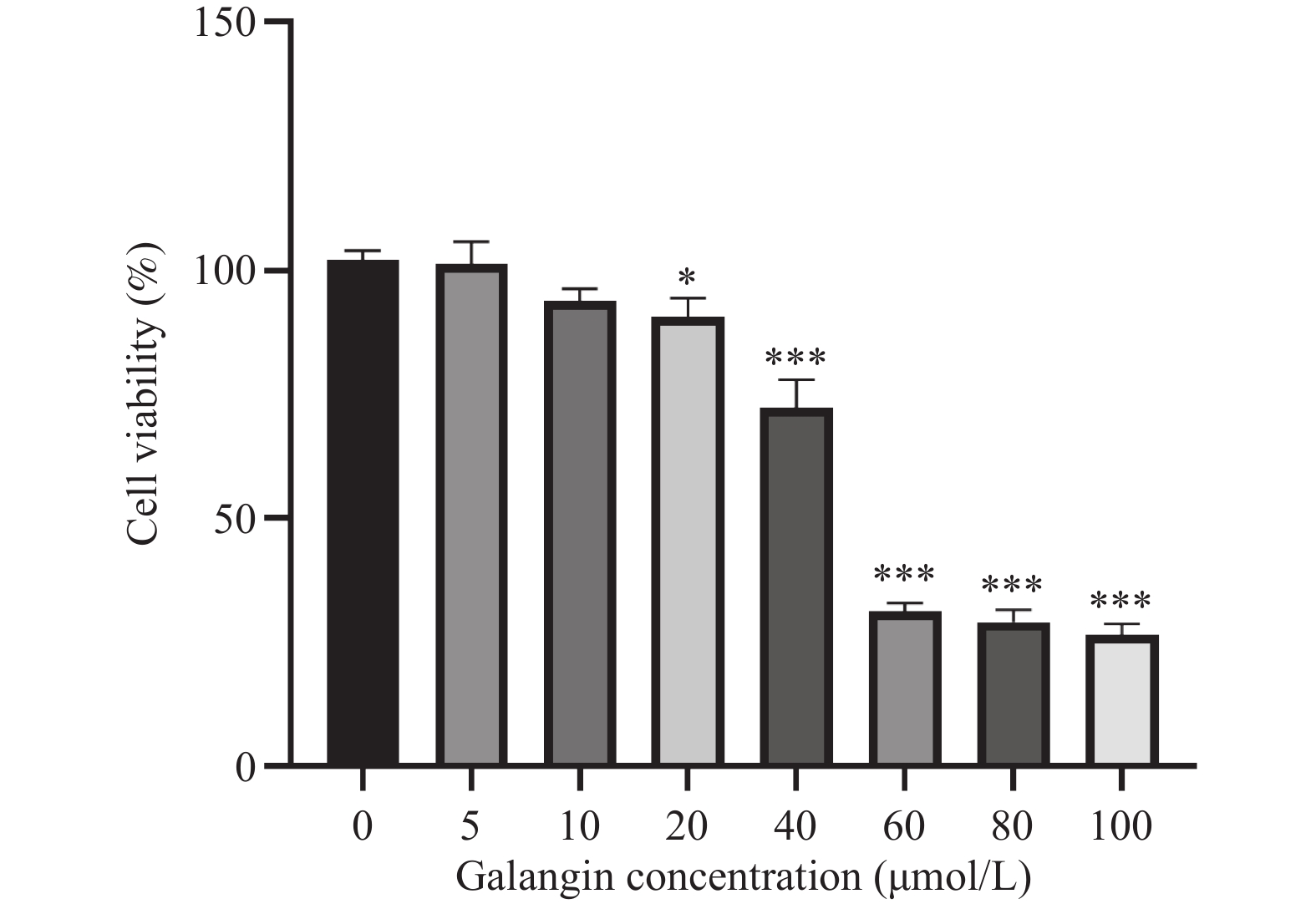
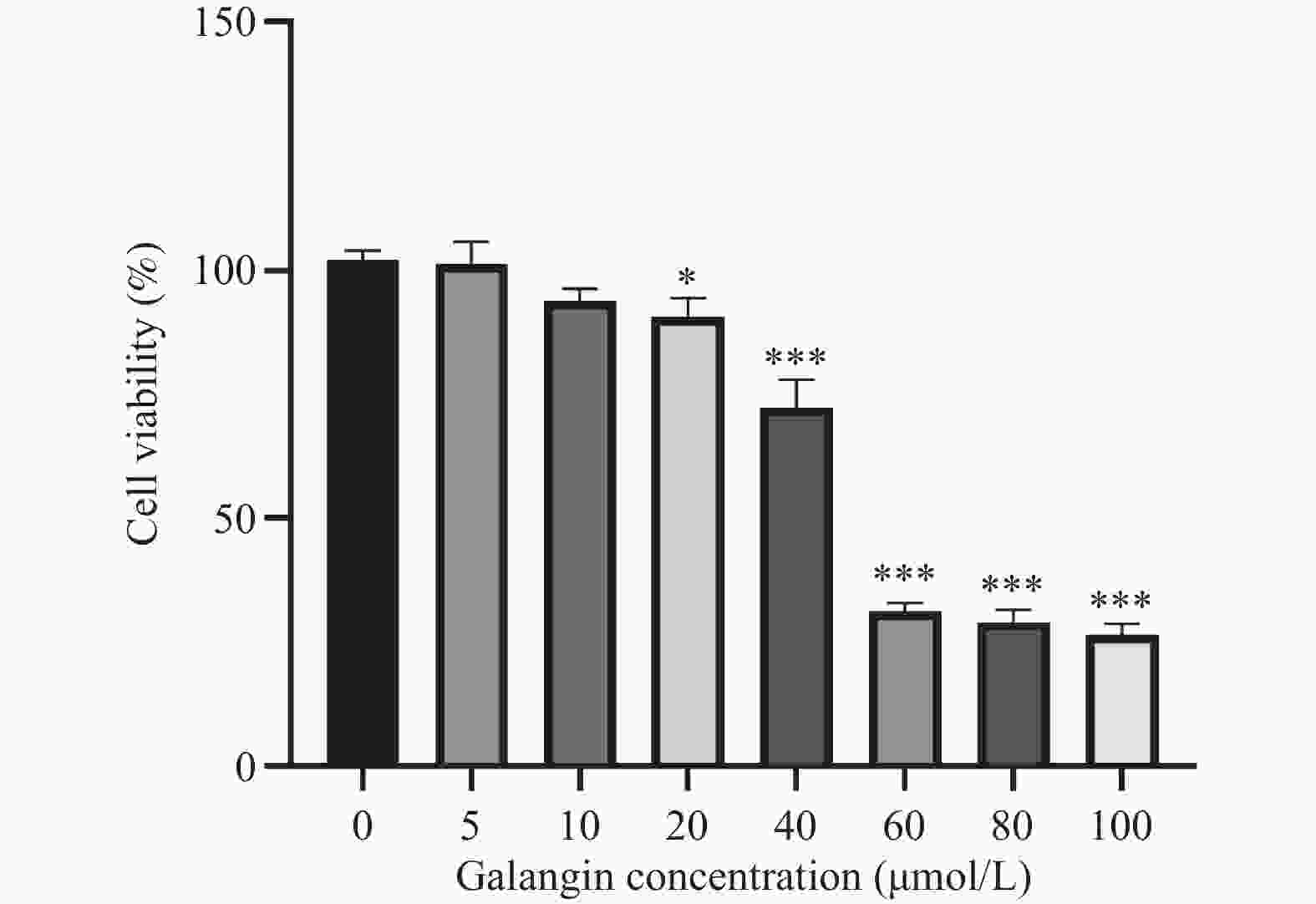
目的 探讨高良姜素对宫颈癌Hela细胞迁移、侵袭能力的影响及其潜在机制。 方法 用不同浓度的高良姜素(0、5、10、20、40、60、80、100 µmol/L)干预宫颈癌细胞48 h,采用 CCK-8 实验检测高良姜素对细胞活力的影响及筛选高良姜素的半数致死量;将Hela细胞分为对照组(0 μmol/L)、高良姜素组(40 μmol/L处理)。划痕愈合实验和Transwell小室法分别检测各组细胞的迁移和侵袭能力,Western blot法检测各组细胞中E-cadherin、 N-cadherin蛋白的表达;DIA定量蛋白质组学技术检测并筛选两组之间的差异表达蛋白质;利用KEGG Pathway、基因集富集分析(GSEA)方法对差异基因进行生物学功能富集分析;Western blot法验证富集的Hippo/YAP信号通路相关蛋白YAP和p-YAP表达水平。 结果 与对照组(0 μmol/L)比较,高良姜素以浓度依赖性方式抑制宫颈癌Hela细胞活性(P < 0.05;P < 0.001);与对照组(0 μmol/L)比较,高良姜素(40 μmol/L)干预后宫颈癌Hela细胞的划痕愈合能力和侵袭能力明显降低(P < 0.001);与对照组(0 μmol/L)比较,高良姜素组(40 μmol/L)E-cadherin蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05)、 N-cadherin 蛋白表达降低(P < 0.001);KEGG和GSEA富集结果发现,高良姜素抑制宫颈癌恶性进展与Hippo/YAP信号通路显著相关,Western blot验证发现Hippo信号通路中标志性蛋白p-YAP蛋白表达水平升高(P < 0.01),YAP蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05)。 结论 高良姜素作用于Hela 细胞后,抑制细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭能力,并表现出剂量依赖;其机制可能与Hippo/YAP信号通路激活相关。 -
关键词:
- 高良姜素 /
- 宫颈癌 /
- 迁移 /
- 侵袭 /
- Hippo/YAP信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of galangin on the migration and invasion abilities of cervical cancer Hela cells and its potential mechanisms. Methods Hela cells were treated with different concentrations of galangin (0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 µmol/L) for 48 hours, and CCK-8 assay was used to assess the impact of galangin on cell viability and to determine the half-maximal lethal concentration (LC50) of galangin. Hela cells were divided into a control group (0 μmol/L) and a galangin group (40 μmol/L treatment). Scratch wound healing assays and Transwell chamber assays were conducted to evaluate the migration and invasion abilities of the cells in each group. Western Blot was used to detect the protein expression of E-cadherin and N-cadherin. DIA quantitative proteomics technology was used to detect and screen the differentially expressed proteins between the two groups. Biological function enrichment analysis of the differential genes was performed using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) Pathway and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) methods. Western Blot was used to verify the expression levels of Hippo/YAP signaling pathway-related proteins YAP and p-YAP. Results Compared to the control group (0 μmol/L), galangin (40 μmol/L) significantly inhibited the viability of Hela cells in a concentration-dependent manner (P < 0.05; P < 0.001). Compared with the control group (0 μmol/L), the scratch healing ability and invasion ability of cervical cancer Hela cells treated with galangin(40 μmol/L) were significantly reduced (P < 0.001). The expression of E-cadherin protein was increased (P < 0.05) and the expression of N-cadherin protein was decreased (P < 0.001) in the galangin group (40 μmol/L) compared to the control group (0 μmol/L). KEGG and GSEA enrichment results indicated that the inhibition of malignant progression in cervical cancer by galangin was significantly associated with the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. Western Blot confirmed that the expression level of the hallmark protein p-YAP in the Hippo signaling pathway was increased (P < 0.01), while the expression level of YAP protein was decreased (P < 0.05). Conclusion Galangin inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion abilities of Hela cells in a dose-dependent manner. The underlying mechanism might be associated with the activation of the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- Galangin /
- Cervical cancer /
- Migration /
- Invasion /
- Hippo/YAP signaling pathway
-
-
[1] Bray F,Laversanne M,Sung H, et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians,2024,74(3): 229-263. [2] Wang K,Chen Q,Shao Y, et al. Anticancer activities of tcm and their active components against tumor metastasis[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie,2021,133: 111044. [3] Liang X,Wang P,Yang C, et al. Galangin inhibits gastric cancer growth through enhancing STAT3 mediated ROS production[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2021,12: 646628. [4] 陈郑,哈文波. 高良姜素抗肿瘤作用机制的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2017,23(9):1752-1756. [5] 贺文煜,张海明,余涛, 等. 高良姜素对缺氧诱导因子-1α诱导胃癌细胞上皮间质转化的作用机制[J]. 中国药理学通报,2023,39(5): 839-843. [6] 加鹏飞,余小超,刘小波, 等. 高良姜素通过激活cgas/sting信号通路抑制骨肉瘤mg63细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2024,31(7): 675-680. [7] 古扎力努尔买提沙,木塔力甫·艾买提,艾尔肯·肉孜比拉力, 等. 高良姜素对宫颈癌siha细胞凋亡及基因表达的影响[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2016,39(12): 1595-1600. [8] Ito D,Cao P,Kakihana T, et al. Chronic running exercise alleviates early progression of nephropathy with upregulation of nitric oxide synthases and suppression of glycation in zucker diabetic rats[J]. PloS One,2015,10(9): e0138037. [9] 郑军,马勇智. 中药的作用机理浅谈[J]. 昆明医学院学报,2009,30(S2):397-398. [10] Fang D,Xiong Z,Xu J, et al. Chemopreventive mechanisms of galangin against hepatocellular carcinoma: A review[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & Pharmacotherapie,2019,109: 2054-2061. [11] 冯真英,李泽森,陈丹, 等. 高良姜中高良姜素的提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 广东医科大学学报,2023,41(4): 373-377+382. [12] Wang D,Chen J,Pu L,Yu L,Xiong F,Sun L,Yu Q,Cao X,Chen Y,Peng F,Peng C. Galangin: A food-derived flavonoid with therapeutic potential against a wide spectrum of diseases. Phytother Res. 2023 Dec;37(12): 5700-5723. [13] Wang H X,Tang C. Galangin suppresses human laryngeal carcinoma via modulation of caspase-3 and akt signaling pathways[J]. Oncology Reports,2017,38(2):703-714. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5767 [14] Pastushenko I,Blanpain C. Emt transition states during tumor progression and metastasis[J]. Trends in Cell Biology,2019,29(3):212-226. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2018.12.001 [15] Huang L,Sun J,Ma Y, et al. Msi2 regulates nlk-mediated emt and pi3k/akt/mtor pathway to promote pancreatic cancer progression[J]. Cancer Cell International,2024,24(1): 273-273. [16] Chen K,Xue R,Geng Y, et al. Galangin inhibited ferroptosis through activation of the pi3k/akt pathway in vitro and in vivo[J]. FASEB Journal : Official Publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology,2022,36(11): e22569. [17] Ma S,Meng Z,Chen R, et al. The hippo pathway: Biology and pathophysiology[J]. Annual Review of Biochemistry,2019,88: 577-604. [18] Jiang L,Ji W K,Gong Y Q,et al. MiR-520f-3p inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colorectal cancer cells by targeting Yes-associated protein 1[J]. Biocell,2023,47(8):1803-1810. doi: 10.32604/biocell.2023.029516 [19] Piccolo S,Dupont S,Cordenonsi M. The biology of yap/taz: Hippo signaling and beyond[J]. Physiological Reviews,2014,94(4):1287-1312. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00005.2014 -





 下载:
下载: