Study on Differential Expression Profile of lncRNA between Concurrent Chemoradioresistant Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cell Lines and Parental Cell Lines
-
摘要:
目的 分析鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗细胞株与亲本细胞株间差异表达的长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNA,lncRNA),探索lncRNA在鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗中可能发挥的作用。 方法 体外构建鼻咽癌CEN1和CNE2细胞同期放化疗抵抗模型,诱导鼻咽癌细胞同期放化疗抵抗细胞株CEN1CRR和CNE2CRR,应用高通量测序筛选2组细胞株间差异表达的lncRNAs,对差异表达的lncRNAs的靶基因进行GO和KEGG分析。 结果 以Log2FC > 1或 < -1,FDR < 0.05为差异表达标准,和CNE1相比,CNE1CRR差异表达的lncRNAs2746个(358个上调,2063 个下调);和CNE2相比,CNE2CRR差异表达的lncRNAs3475个(265个上调,520个下调);此外,387个lncRNAs在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR中表达同时下调,49个lncRNAs在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR中同时上调。在GO分析中发现,2组细胞中差异表达lncRNAs的靶基因在生物过程(biological process,BP)、分子功能(molecular function,MF)、细胞成分(cellular component,CC)等方面均有参与。在KEGG分析结果中发现,CNE1组细胞中,差异lncRNAs的靶基因主要富集的信号通路有细胞凋亡、病毒致癌、代谢途径等。CNE2组细胞中,差异lncRNAs的靶基因主要富集的信号通路有代谢途径(硫辛酸、磷酸戊糖、花生四烯酸、醚脂质)、T细胞受体信号通路、核苷酸切除修复等(P < 0.05)。 结论 同期放化疗抵抗细胞株与亲本细胞株的lncRNA表达谱存在明显差异,这些差异表达的lncRNA可能参与了鼻咽癌的同期放化疗抵抗,并为其机制研究奠定基础。 -
关键词:
- 长链非编码RNA(lncRNA) /
- 表达谱 /
- 鼻咽癌细胞 /
- 同期放化疗抵抗 /
- 高通量测序
Abstract:Objective To analyze the long non coding RNA (lncRNA) differentially expressed between nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines resistant to concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy and their parent cell lines, and explore the possible role of lncRNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma resistance to concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Methods The concurrent chemoradiotherapy resistance model of nasopharyngeal carcinoma CEN1 and CNE2 cells was constructed in vitro, and the concurrent chemoradiotherapy resistance cell lines CEN1CRR and CNE2CRR of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells were induced. The differentially expressed lncRNAs between the two groups of cell lines were screened by high-throughput sequencing, and the target genes of the differentially expressed lncRNAs were analyzed by GO and KEGG. Results With Log2FC > 1 or < - 1 and FDR < 0.05 as the differential expression criteria, 2746 lncRNAs (358 up-regulated and 2063 down-regulated) were differentially expressed in CNE1 CRR compared with CNE1. Compared with CNE2, CNE2CRR differentially expressed 3475 lncRNAs (265 up-regulated, 520 down-regulated). In addition, 387 lncRNAs were downregulated in CNE1CRR and CNE2CRR, and 49 lncRNAs were upregulated in CNE1CRR and CNE2CRR. GO analysis showed that the target genes differentially expressing lncRNAs in the two groups of cells were involved in biological process (BP), molecular function (MF), and cell component (CC). In the KEGG analysis results, it was found that in CNE1 group cells, the main signal pathways for the enrichment of target genes of differential lncRNAs were apoptosis, viral carcinogenesis, metabolic pathways, etc. In CNE2 group, the target genes of differential lncRNAs were mainly enriched through metabolic pathways (lipoic acid, pentose phosphate, arachidonic acid, ether lipid), T cell receptor signaling pathways, nucleotide excision repair, etc. (P < 0.05). Conclusions There are significant differences in lncRNA expression profiles between concurrent chemoradiotherapy-resistant cell lines and parental cell lines. These differentially expressed lncRNAs may participate in concurrent chemoradiotherapy resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and lay a foundation for its mechanism research. -
鼻咽癌(nasopharyngeal carcinoma, NPC)起源于鼻咽粘膜上皮,是头颈部最常见的恶性肿瘤之一。鼻咽癌发病具有明显的地域聚集性,75%以上的病例集中在东亚及东南亚,尤其是我国的华南地区[1]。我国鼻咽癌的标准化年龄发病率约3/100 000,约占全球鼻咽癌发病总人数的39%,明显高于世界平均水平[2-3]。同期放化疗是Ⅱ~ⅣA期鼻咽癌最重要的根治性治疗手段,由于肿瘤细胞本身及治疗过程中获得的抗性,部分患者出现治疗失败,最终导致死亡[4]。lncRNA作为一种潜在的肿瘤标志物,有研究发现lncRNA通过介导细胞凋亡[5]、肿瘤干细胞样特性[6-8]、DNA损伤修复[9]等方面调控鼻咽癌细胞的增殖、侵袭及迁移能力,改变鼻咽癌细胞对治疗的敏感性。然而,lncRNA在鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗中的表达谱及作用机制仍不清楚。本研究通过诱导鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗细胞模型,利用高通量测序筛选同期放化疗抵抗细胞株与亲本细胞株间lncRNA的差异表达谱,并进行生物信息学分析,初步了解其在鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗中的作用及机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 研究材料
高分化细胞CNE1和低分化细胞CNE2,及经同步放化疗处理后得到的抵抗细胞株CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR,RPMI-1640培养基,顺铂(购自Sigma公司),Hisq Xten高通量测序仪(Illumina美国),CBOT簇生成仪(Illumina 美国),Qubit(Invitrogen 美国),核糖体试剂盒Ribo-ZeroTM rRNA Removal Kit(illumina美国),反转录试剂盒(Thermo),PCR引物及琼脂糖(生工)。
1.2 研究方法
1.2.1 构建同期放化疗抵抗模型
鼻咽癌CNE1和CNE2细胞均暴露于浓度为0.05 µg/mL的顺铂完全培养基中,并予6 Gy的6 Mv X-ray照射,细胞接触顺铂至24 h后予更换新鲜培养基,待残余细胞恢复生长后重复上述处理,共10次,得到鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗细胞株CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR。利用克隆形成法验证细胞对同期放化疗的抗性,以单击多靶模y = 1 - [1 - exp(-k*x)]^N拟合细胞生存曲线[10],计算D0、Dq值。
1.2.2 构建lncRNA和mRNA差异表达谱
本研究lncRNA和mRNA差异表达谱的构建,由上海英拜生物有限公司完成。采用Trizol法提取总RNA,使用试剂盒Ribo-ZeroTMrRNA Removal Kit去除rRNA;加入RNA片段化反应缓冲液经高温加热使RNA片段化;以片段RNA为模板反转录合成一链cDNA,然后加入二链反应体系(dUTP代替dTTP),以一链cDNA为模板链合成二链cDNA,3′端加上polyA ,两端连接测序接头;AmpureBeads对文库进行纯化和筛选,PCR对一链cDNA进行扩增构建文库;浓度(Quibit)及片段大小(琼脂糖凝胶电泳)质检合格后,应用Illumina Xten进行高通量测序;原始数据转化后,与参考基因库(人GRCh38基因组)进行比对,FPKM法对基因量化及归一化处理,以 Log2FC > 1或 < -1,FDR < 0.05为标准,筛选差异表达谱。
1.2.3 差异lncRNA靶基因预测
根据lncRNA功能与邻近的编码蛋白基因具有相关性的原理预测顺式作用靶基因(cis-gene),筛选位于lncRNA上下游10 K-100 K以内的蛋白编码基因作为该lncRNA顺式作用的靶基因。
1.2.4 差异lncRNA靶基因功能分析
对差异表达的lncRNA进行Cluster分析并展示,行基因本体论(GO)、KEGG通路富集分析。以P-value < 0.05为显著性差异标准。
1.2.5 qRT-PCR验证lncRNAs差异表达谱
随机选取4个同时差异表达的lncRNAs进行定量反转录聚合酶链反应(quantitative reversse transcription polymerase chain reaction,qRT-PCR)验证。按照说明书操作,先将每种RNA反转录成cDNA,再进行qRT-PCR扩增,以GAPDH为内参。用2-ΔΔCt法计算lncRNA的相对表达量。
1.3 统计学处理
采用SPSS25.0进行结果分析,组间资料用t检验,计量资料用(
$\bar x \pm s $ )表示,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
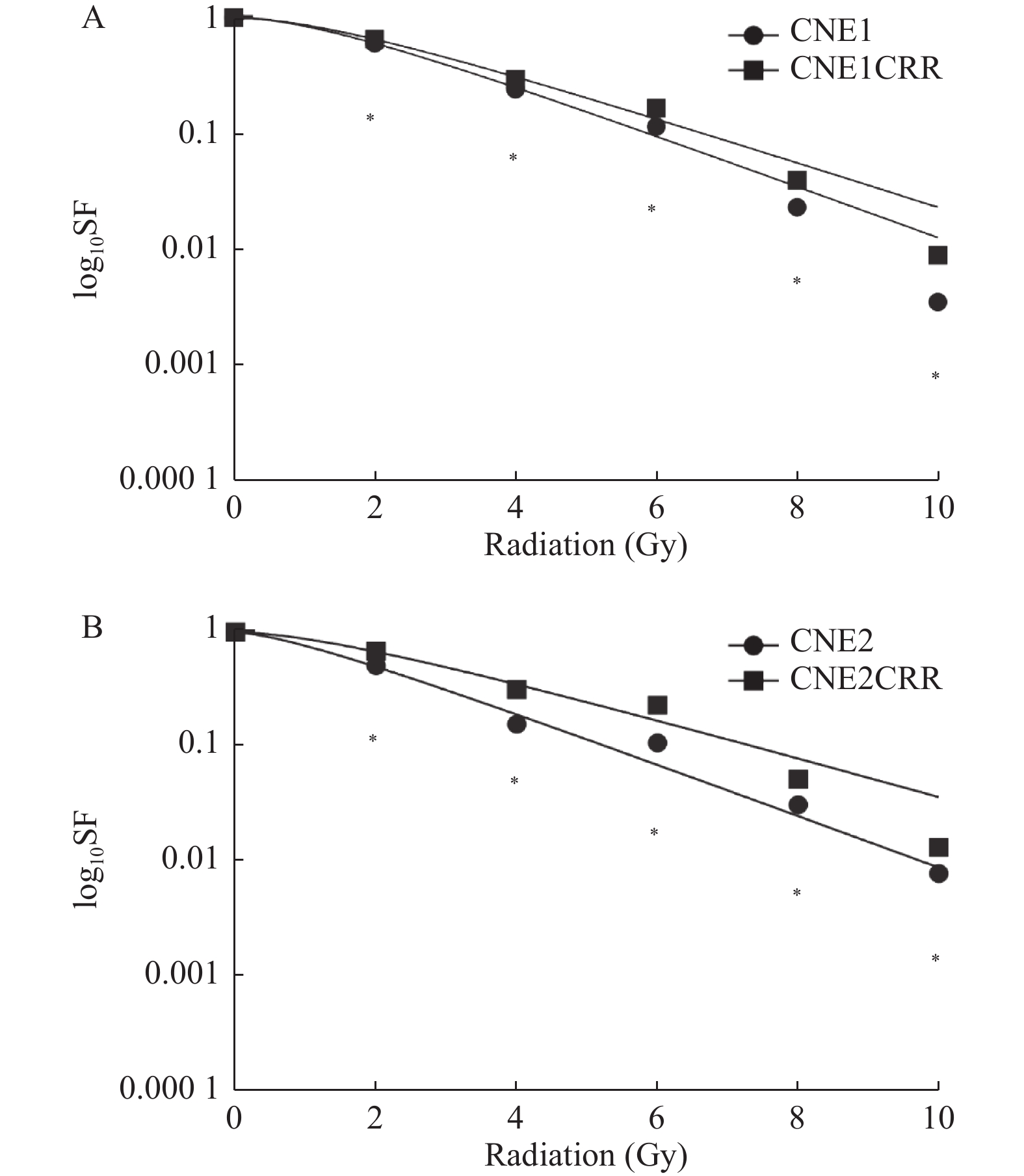
2.1 同期放化疗细胞的抗性验证
同一放射剂量下,CNE1和CNE2克隆团数量明显少于相对应的放化疗抵抗细胞株CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR的克隆团数量(P < 0.05),单击多靶模型拟合生存曲线见图1;CNE1CRR、CNE2CRR的放射生物学参数SF2、Dq、D0高于相对应的CNE1、CNE2,见表1。
表 1 CNE1和CNE2放化疗抵抗细胞鉴别的放射生物学参数Table 1. Radiobiological parameters to identify the chemoradioresistance of CNE1 andCNE2分组 SF2 D0(Gy) Dq(Gy) CNE1 0.60 1.96 1.41 CNE1 CRR 0.65 2.30 1.53 CNE2 0.50 1.93 0.89 CNE2 CRR 0.68 2.55 1.57 2.2 lncRNA与mRNA差异表达分析
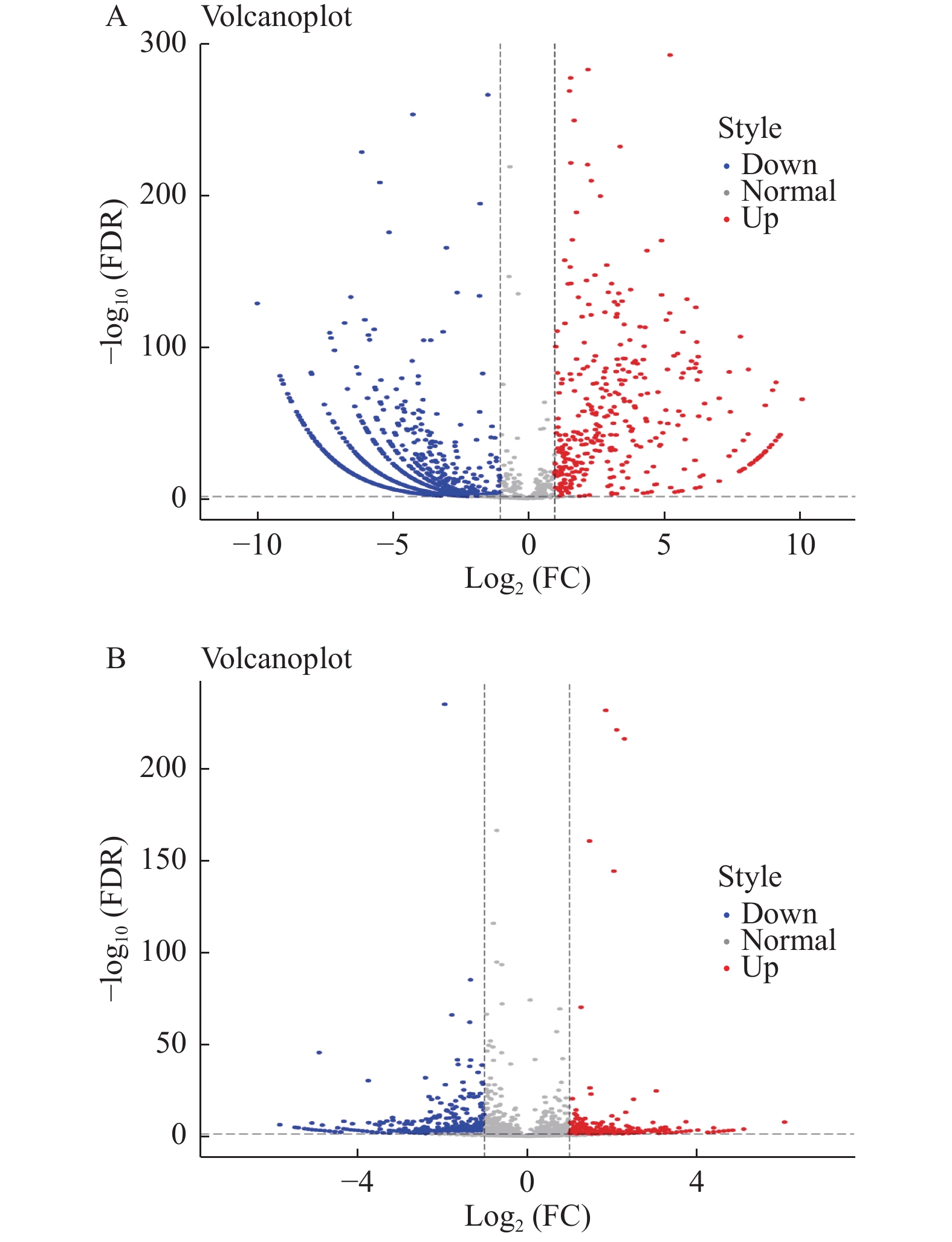
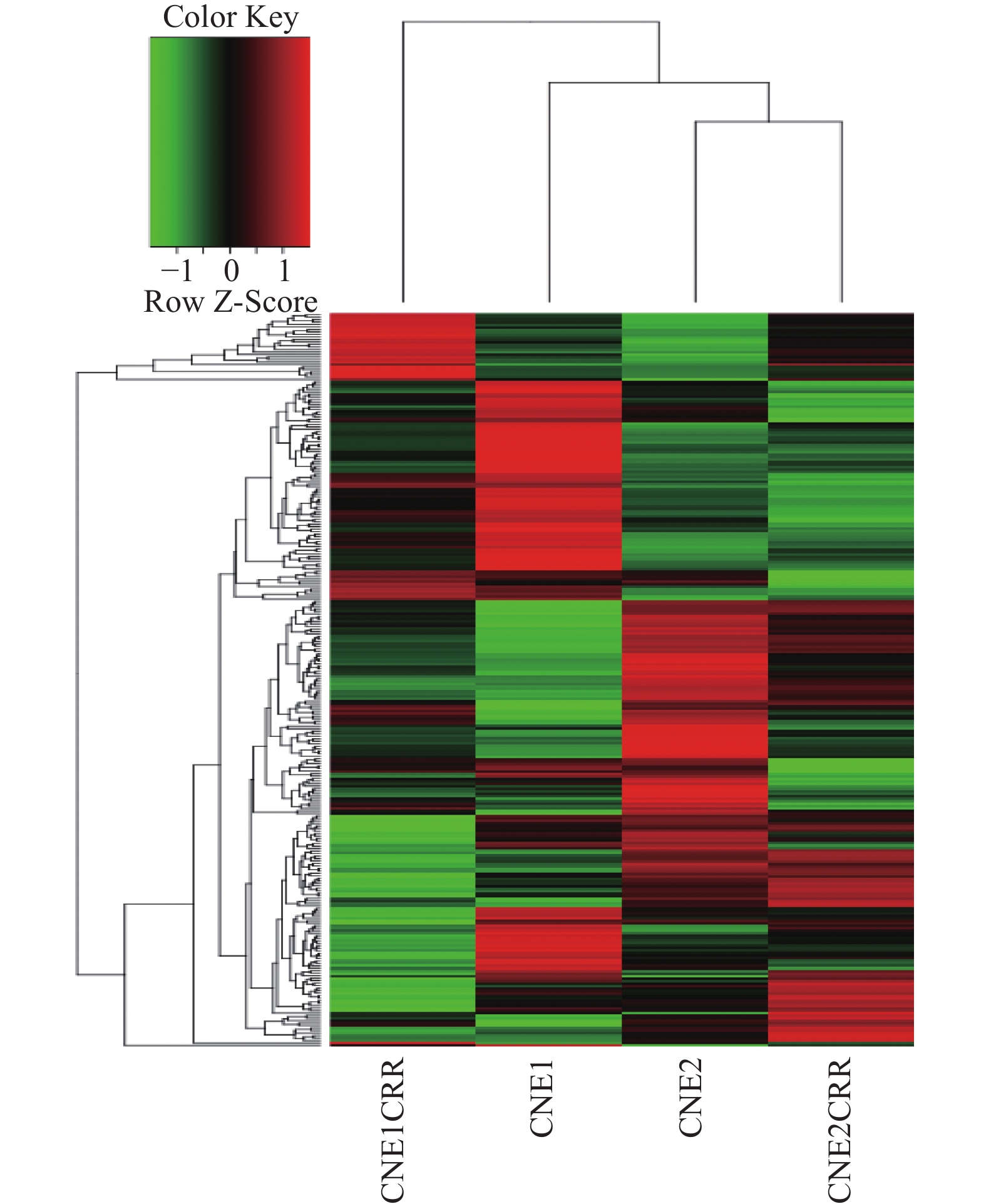
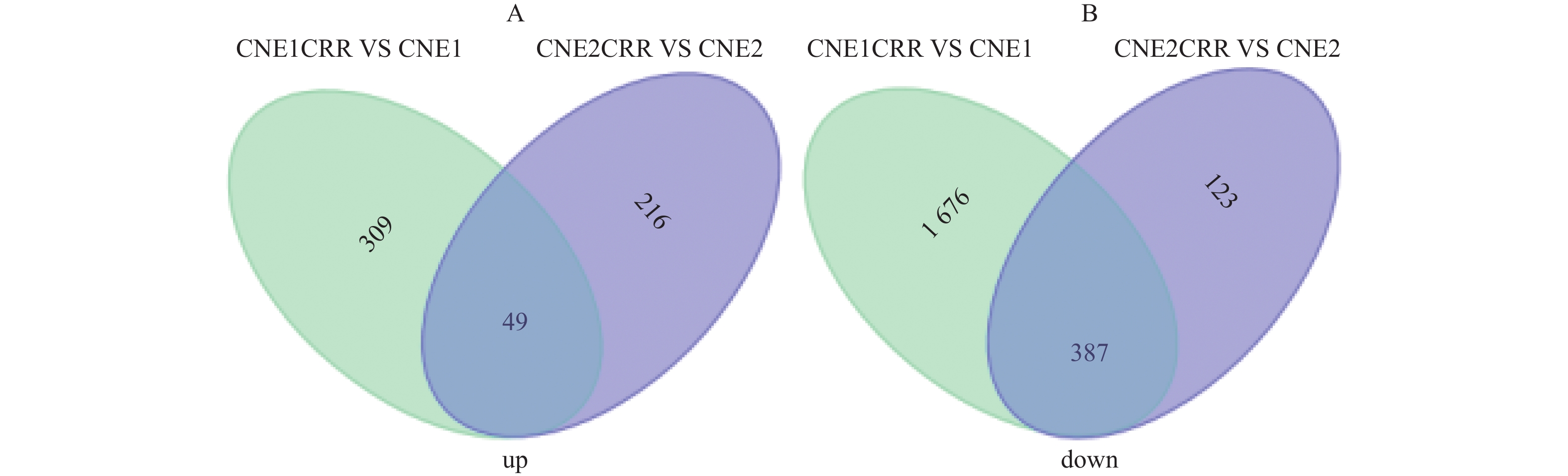
CNE1CRR与CNE1比较,差异表达lncRNAs共有2746个(其中358个显著上调,2063 个显著下调),同时检测出差异表达mRNA7749个(其中显著上调2332个,显著下调5417个);CNE2CRR与CNE2比较,差异表达lncRNAs共有3475个,(其中显著上调265个,显著下调520个),同时检测出差异表达mRNA1878个(其中显著上调661个,显著下调1217个);49个lncRNAs在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR中共同上调,387个lncRNAs在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR共同下调。对2组细胞中差异表达的lncRNAs绘制火山图,见图2;聚类热图见图3;韦恩图见图4。并列举抵抗细胞株中上调或下调前10位lncRNAs,见表2。
表 2 CNE1CRR 及CNE2CRR中上调或下调前10位的lncRNAsTable 2. Top 10 lncRNAs up-regulated and down-regulated in CNE1CRR and CNE2CRR上调lncRNA Log2FC 下调lncRNA Log2FC CNE1CRR USP27X-AS1 10.13 LOC100505817 −9.96 LOC100131315 10.12 LOC102723739 −8.77 LINC00514 9.32 LINC01004 −8.71 LINC00466 9.16 LOC102724281 −8.51 XIST 8.77 CPS1-IT1 −8.44 COLCA1 8.62 CDKN2B-AS1 −8.41 LOC102724360 7.96 GABPB1-AS1 −8.23 LOC101929042 7.44 LOC100505771 −8.22 LOC101926931 7.06 SNHG10 −8.03 LOC101929173 6.47 AC091729.9 −7.96 CNE2CRR LOC100507103 4.84 LOC101928152 −5.82 DBH-AS1 4.63 LINC00239 −5.46 LOC101927037 4.52 LINC00992 −5.39 LOC102724255 4.26 LOC101929173 −5.39 LINC00470 4.02 LINC00638 −5.24 LOC113230 3.84 SEC24B-AS1 −5.07 LOC101928430 3.58 IL21-AS1 −4.89 LOC100996442 3.52 TMEM254-AS1 −4.87 LOC642366 3.39 LINC00968 −4.87 LRP4-AS1 3.39 LOC101928117 −4.77 2.2.1 lncRNA靶基因预测
本研究仅进行了顺式靶基因预测。在CNE1这组细胞中,295个lncRNA有416个顺式靶基因,在CNE2这组细胞中,961个lncRNA有1335个顺式靶基因。
2.2.2 靶基因GO及KEGG分析
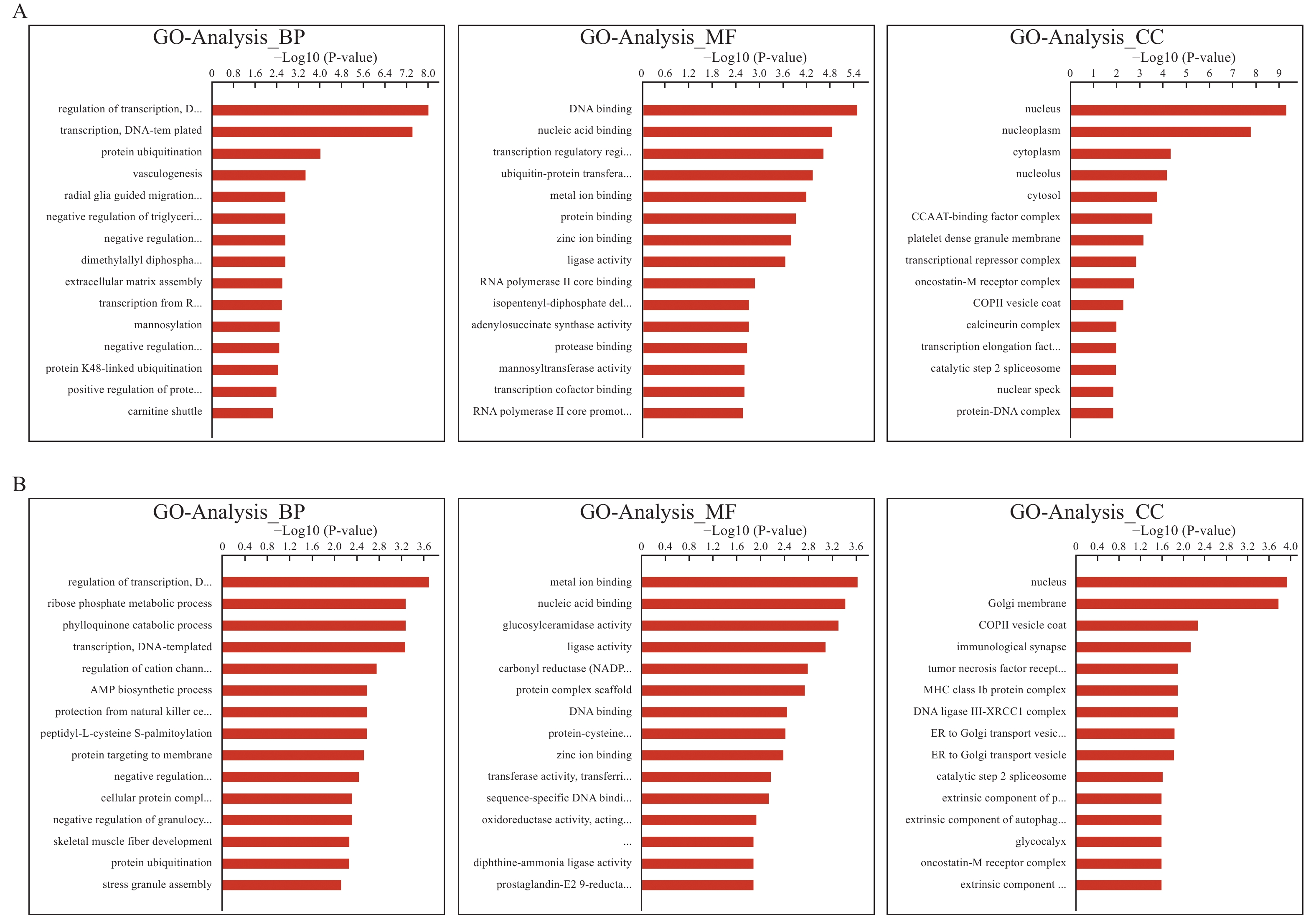
对靶基因进GO和KEGG功能富集分析,CNE1组中差异表达lncRNA的靶基因主要富集的生物过程(biological process,BP)有DNA为模板转录调控、蛋白质泛素化、血管生成等;分子功能(molecular function,MF)有DNA结合、核酸结合、金属离子结合等;细胞成分(cellular component,CC)有核质、核仁、细胞质等生命活动,见图5A。CNE2组中差异表达lncRNA的靶基因主要富集的生物过程(Venn diagram of differentially expressed lncRNAs between CNE1CRR and CNE1,CNE2CRR and CNE2BP)有DNA为模板转录调控、核糖磷酸代谢过程、叶醌分解代谢过程等;分子功能(MF)有金属离子结合、核酸结合、葡萄糖基神经酰胺酶活性等;细胞成分(CC)有核、高尔基膜、免疫性突触、肿瘤坏死因子受体等生命活动,见图5B。
分别选取2组细胞中差异表达lncRNA靶基因富集前10位的通路制作表格,不足10位的展示全部,见表3。结果显示,在CNE1组中,靶基因主要富集的信号通路包括细胞凋亡、病毒致癌、代谢途径、肿瘤坏死因子TNF信号通路、EB病毒感染等。CNE2组中,靶基因主要富集的信号通路包括代谢途径(硫辛酸、磷酸戊糖、花生四烯酸、醚脂质)、T细胞受体信号通路、核苷酸切除修复等。
表 3 CNE1和CNE2组差异lncRNAs靶基因通路富集Table 3. Pathway enrichment of differentially expressed lncRNAs target genes in CNE1 and CNE2 groups通路编号 通路名称 富集指数 数量 FisherP CNE1组 04141 Proteinprocessingin endoplasmic reticulum 2.21 14 < 0.0001* 05162 Measles 2.17 11 0.01* 04210 Apoptosis 2.35 8 0.02* 05203 Viral carcinogenesis 1.79 14 0.02* 01212 Fatty acid metabolism 2.76 5 0.03* 05169 Epstein-Barr virus infection 1.71 13 0.04* 05166 HTLV-I infection 1.61 16 0.04* 00310 Lysine degradation 2.6 5 0.04* 01100 Metabolic pathways 1.25 55 0.04* 00900 Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis 3.78 14 0.04* CNE2组 00590 Arachidonic acid metabolism 4.81 4 0.01* 04660 T cell receptor signaling pathway 3.75 5 0.01* 00565 Ether lipid metabolism 5.84 3 0.01* 04141 Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum 2.92 6 0.02* 03420 Nucleotide excision repair 5.22 3 0.02* 05014 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 4.54 3 0.03* 00785 Lipoic acid metabolism 27.24 1 0.04* 00030 Pentose phosphate pathway 5.84 2 0.05 *P < 0.05。 2.3 qRT-PCR验证结果
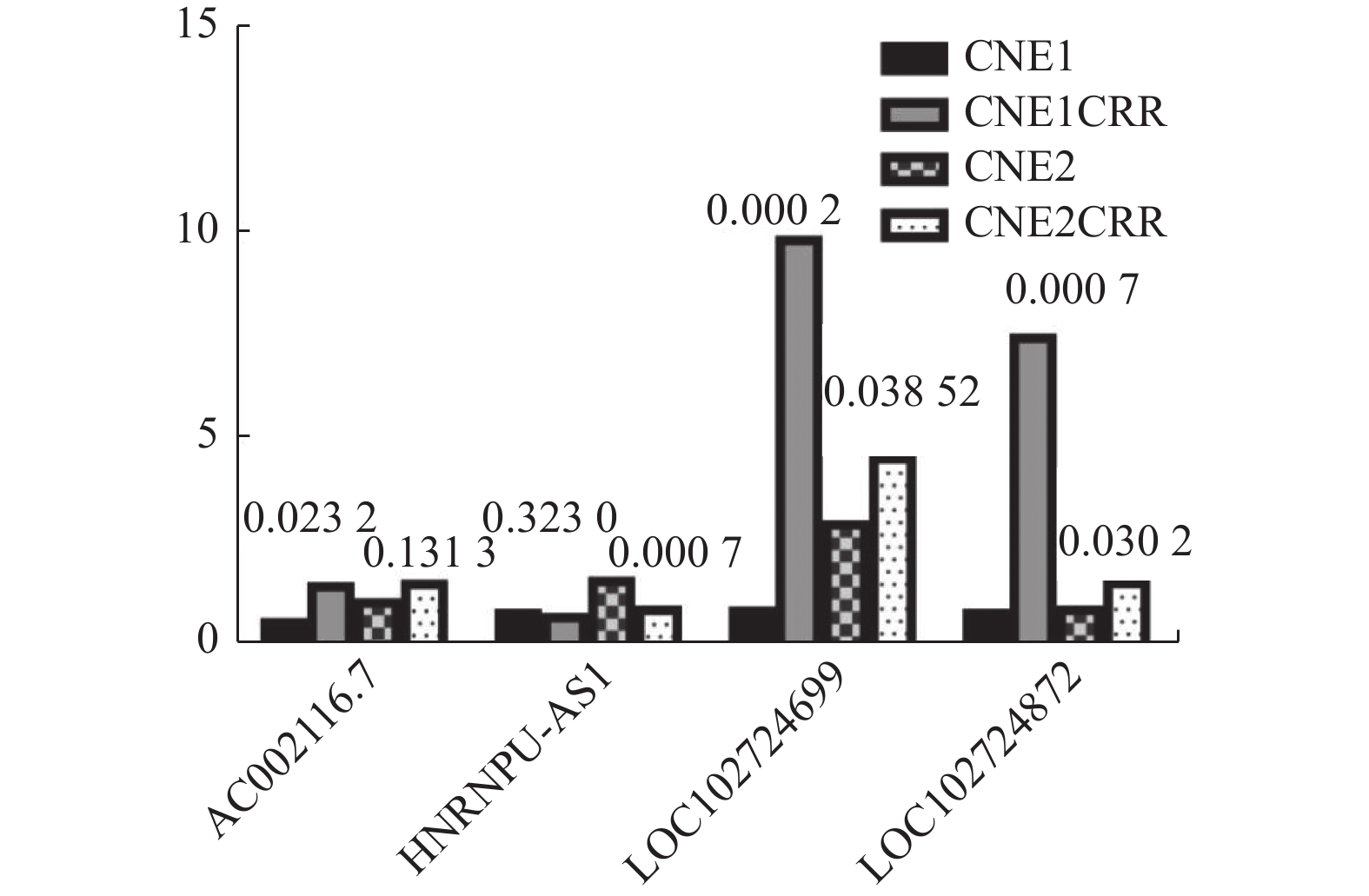
将检测lncRNAs的Ct值进行2-ΔΔCT转换后进行统计学分析,结果显示四个lncRNAs的qRT-PCR与测序得到的表达趋势一致,其中AC002116.7、LOC102724699、LOC102724872三个lncRNAs在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR中表达同时上调,lncRNA HNRNPU-AS1在CNE1CRR和CNE2CRR中同时表达下调,但CNE1和CNE1CRR中差异表达的HNRNPU-AS1,CNE2和CNE2CRR中的差异表达的AC002116.7,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),见图6。
3. 讨论
lncRNA是一种长度大于200个核苷酸,且不编码蛋白质的非编码RNA[11]。在过去的很长一段时间里,lncRNA被认为是转录组的“垃圾”,随着高通量测序技术和生物信息学的发展,大量lncRNA被发现,它们的神秘面纱也被逐渐被揭晓。越来越多的研究表明,lncRNA在肿瘤组织中表达差异,并且表达水平与肿瘤分期及预后息息相关[12-13]。这表明lncRNA参与了肿瘤的发生发展,不仅如此,lncRNA还参与了肿瘤的放疗抵抗或化疗耐药[14-15]。因此,lncRNA成为了肿瘤领域的研究热点,治疗敏感性是肿瘤领域中的重要板块,故lncRNA在治疗抵抗中的重要性不言而喻。目前lncRNA在治疗抵抗中作用的具体机制尚不清楚,探讨其在治疗抵抗中的作用具有现实意义。
鼻咽癌恶性程度高,容易发生区域淋巴结转移及颅底骨质破坏,同期放化疗是鼻咽癌最主要的治疗方式,和单纯放疗相比,同期放化疗能让患者获得更高的局控率,并从总体生存期(overall survial,OS)中获益[16]。同时,同期放化疗抵抗的问题也日趋明显,但目前绝大多数研究仅从化疗耐药或放疗抵抗单方面来探究肿瘤细胞的抵抗机制。当放疗和化疗联合应用时,化疗有放疗增敏的作用,因此,肿瘤细胞产生放化疗抵抗的原因必然有别于单独放/化疗,因此,本研究将放疗和化疗相结合来探讨肿瘤治疗抵抗的机制。Guo等[17]通过逐渐增加放射剂量建立CNE2放疗抵抗细胞株,然后应用高通量测序方法建立放化疗抵抗细胞株和母细胞株lncRNAs的差异表达谱,发现781个已知的lncRNAs与辐射抗性相关,其中表达上调310个,表达下调471个。在本研究中,发现差异表达lncRNAs共有3475个,其中显著上调265个,显著下调520个。2个研究中的差异表达谱区别明显,这可能是诱导方法不同所致,且本研究的诱导方法更贴近临床治疗模式。为了解lncRNA在鼻咽癌同期放化疗中的作用,笔者还对差异表达lncRNA顺式作用的靶基因进行预测,并进行GO及KEGG通路分析。结果显示lncRNA通过多方面来调控细胞对放化疗的抗性。此外,笔者随机选取了4个在2组细胞中同时差异表达的lncRNAs,应用qRT-PCR实验对本次测序结果进行验证,结果表明lncRNAs的变化趋势与测序结果基本一致。Niu等[18]研究发现HNRNPU-AS1在宫颈癌患者及细胞中表达缺失,且预示不良预后;它通过miR-205-5p/AXIN2 轴调控Wnt/β-catenin通路,抑制细胞增殖、促进细胞凋亡。Zhang等[19]发现HNRNPU-AS1在肝细胞癌中表达降低,具有抑制增殖、转移,促进自噬作用。在放化疗抵抗的鼻咽癌细胞中HNRNPU-AS1表达降低,但其具体作用机制有待于进一步研究。除此之外,笔者通过二代基因测序构建了治疗抵抗和原始肿瘤细胞的lncRNA差异谱,这些差异表达的lncRNA可能参与了治疗抵抗的关键作用。
本研究从细胞层面上探讨了鼻咽癌同期放化疗抵抗时lncRNA表达谱的变化情况,为进一步研究lncRNA在放化疗抵抗中的作用机制提供科学依据,为今后寻找合理的干预措施减少鼻咽癌放化疗抵抗,进一步提高鼻咽癌放化疗疗效打下了基础。
-
表 1 CNE1和CNE2放化疗抵抗细胞鉴别的放射生物学参数
Table 1. Radiobiological parameters to identify the chemoradioresistance of CNE1 andCNE2
分组 SF2 D0(Gy) Dq(Gy) CNE1 0.60 1.96 1.41 CNE1 CRR 0.65 2.30 1.53 CNE2 0.50 1.93 0.89 CNE2 CRR 0.68 2.55 1.57 表 2 CNE1CRR 及CNE2CRR中上调或下调前10位的lncRNAs
Table 2. Top 10 lncRNAs up-regulated and down-regulated in CNE1CRR and CNE2CRR
上调lncRNA Log2FC 下调lncRNA Log2FC CNE1CRR USP27X-AS1 10.13 LOC100505817 −9.96 LOC100131315 10.12 LOC102723739 −8.77 LINC00514 9.32 LINC01004 −8.71 LINC00466 9.16 LOC102724281 −8.51 XIST 8.77 CPS1-IT1 −8.44 COLCA1 8.62 CDKN2B-AS1 −8.41 LOC102724360 7.96 GABPB1-AS1 −8.23 LOC101929042 7.44 LOC100505771 −8.22 LOC101926931 7.06 SNHG10 −8.03 LOC101929173 6.47 AC091729.9 −7.96 CNE2CRR LOC100507103 4.84 LOC101928152 −5.82 DBH-AS1 4.63 LINC00239 −5.46 LOC101927037 4.52 LINC00992 −5.39 LOC102724255 4.26 LOC101929173 −5.39 LINC00470 4.02 LINC00638 −5.24 LOC113230 3.84 SEC24B-AS1 −5.07 LOC101928430 3.58 IL21-AS1 −4.89 LOC100996442 3.52 TMEM254-AS1 −4.87 LOC642366 3.39 LINC00968 −4.87 LRP4-AS1 3.39 LOC101928117 −4.77 表 3 CNE1和CNE2组差异lncRNAs靶基因通路富集
Table 3. Pathway enrichment of differentially expressed lncRNAs target genes in CNE1 and CNE2 groups
通路编号 通路名称 富集指数 数量 FisherP CNE1组 04141 Proteinprocessingin endoplasmic reticulum 2.21 14 < 0.0001* 05162 Measles 2.17 11 0.01* 04210 Apoptosis 2.35 8 0.02* 05203 Viral carcinogenesis 1.79 14 0.02* 01212 Fatty acid metabolism 2.76 5 0.03* 05169 Epstein-Barr virus infection 1.71 13 0.04* 05166 HTLV-I infection 1.61 16 0.04* 00310 Lysine degradation 2.6 5 0.04* 01100 Metabolic pathways 1.25 55 0.04* 00900 Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis 3.78 14 0.04* CNE2组 00590 Arachidonic acid metabolism 4.81 4 0.01* 04660 T cell receptor signaling pathway 3.75 5 0.01* 00565 Ether lipid metabolism 5.84 3 0.01* 04141 Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum 2.92 6 0.02* 03420 Nucleotide excision repair 5.22 3 0.02* 05014 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) 4.54 3 0.03* 00785 Lipoic acid metabolism 27.24 1 0.04* 00030 Pentose phosphate pathway 5.84 2 0.05 *P < 0.05。 -
[1] Gong L,Kwong D L,Dai W,et al. The stromal and immune landscape of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its implications for precision medicine targeting the tumor microenvironment[J]. Frontiers in Oncology,2021,11:744889. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.744889 [2] Chen Y P,Chan A,Le QT,et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Lancet,2019,394(10192):64-80. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30956-0 [3] 梁锌,杨剑,高婷,等. 中国鼻咽癌流行概况[J]. 中国肿瘤,2016,25(11):835-840. doi: 10.11735/j.issn.1004-0242.2016.11.A001 [4] Chen Y P,Ismaila N,Chua M,et al. Chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy for definitive-intent treatment of stage II-IVA nasopharyngeal carcinoma:CSCO and ASCO guideline[J]. J Clin Oncol,2021,39(7):840-859. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.03237 [5] Huang B,Li Y,Deng Z,et al. Regulatory mechanism of lncRNA CTBP1-AS2 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and apoptosis via the miR-140-5p/BMP2 axis[J]. Protein Pept Lett,2022,29(7):621-630. [6] Cui M,Chang Y,Fang Q G,et al. Non-coding RNA Pvt1 promotes cancer stem cell-Like traits in nasopharyngeal cancer via inhibiting miR-1207[J]. Pathol Oncol Res,2019,25(4):1411-1422. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0453-1 [7] Estrada-Meza C,Torres-Copado A,Loreti G L,et al. Recent insights into the microRNA and long non-coding RNA-mediated regulation of stem cell populations[J]. 3 Biotech,2022,12(10):270. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03343-8 [8] Tang Y,He X. Long non-coding RNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:biological functions and clinical applications[J]. Mol Cell Biochem,2021,476(9):3537-3550. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04176-4 [9] Wang Y H,Guo Z,An L,et al. LINC-PINT impedes DNA repair and enhances radiotherapeutic response by targeting DNA-PKcs in nasopharyngeal cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis,2021,12(5):454. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03728-2 [10] 刘珊. 结直肠癌细胞同期放化疗抵抗关键调控基因的筛选[D]. 昆明: 昆明医科大学, 2015. [11] Bridges M C,Daulagala A C,Kourtidis A. LNCcation:lncRNA localization and function[J]. J Cell Biol,2021,220(2):e202009045. [12] Zheng J,Zhao Z,Ren H,et al. LncRNA HCG11 facilitates nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through regulating miRNA-490-3p/MAP3K9 Axis[J]. Front Oncol,2022,12:872033. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.872033 [13] Guo C,Ma X,He H,et al. Expression of ANCR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients and its clinical significance[J]. Medicine (Baltimore),2021,100(33):e26834. [14] Guo Z,Wang Y H,Xu H,et al. LncRNA linc00312 suppresses radiotherapy resistance by targeting DNA-PKcs and impairing DNA damage repair in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Dis,2021,12(1):69. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03302-2 [15] Xiao J,He X. Involvement of non-coding RNAs in chemo- and radioresistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Cancer Manag Res,2021,13:8781-8794. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S336265 [16] Lee A,Tung S Y,Ng W T,et al. A multicenter,phase 3,randomized trial of concurrent chemoradiotherapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy versus radiotherapy alone in patients with regionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma:10-year outcomes for efficacy and toxicity[J]. Cancer,2017,123(21):4147-4157. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30850 [17] Li G,Liu Y,Liu C,et al. Genome-wide analyses of long noncoding RNA expression profiles correlated with radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via next-generation deep sequencing[J]. BMC Cancer,2016,16:719. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2755-6 [18] Niu Z,Wang F,Lv S,et al. HNRNPU-AS1 regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis via the microRNA 205-5p/AXIN2 axis and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway in cervical cancer[J]. Mol Cell Biol,2021,41(10):e11521. [19] Zhang L,Zhao Y,Guan H,et al. HnRNPU-AS1 inhibits the proliferation,migration and invasion of HCC cells and induces autophagy through miR-556-3p/ miR-580-3p/SOCS6 axis[J]. Cancer Biomark,2022,34(3):443-457. doi: 10.3233/CBM-210261 -







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:

