Protective Effect of MiR-193a-5p on Cardiac Function in Rats with Chronic Heart Failure by Regulating IL-33/ST2 Signaling Pathway
-
摘要:
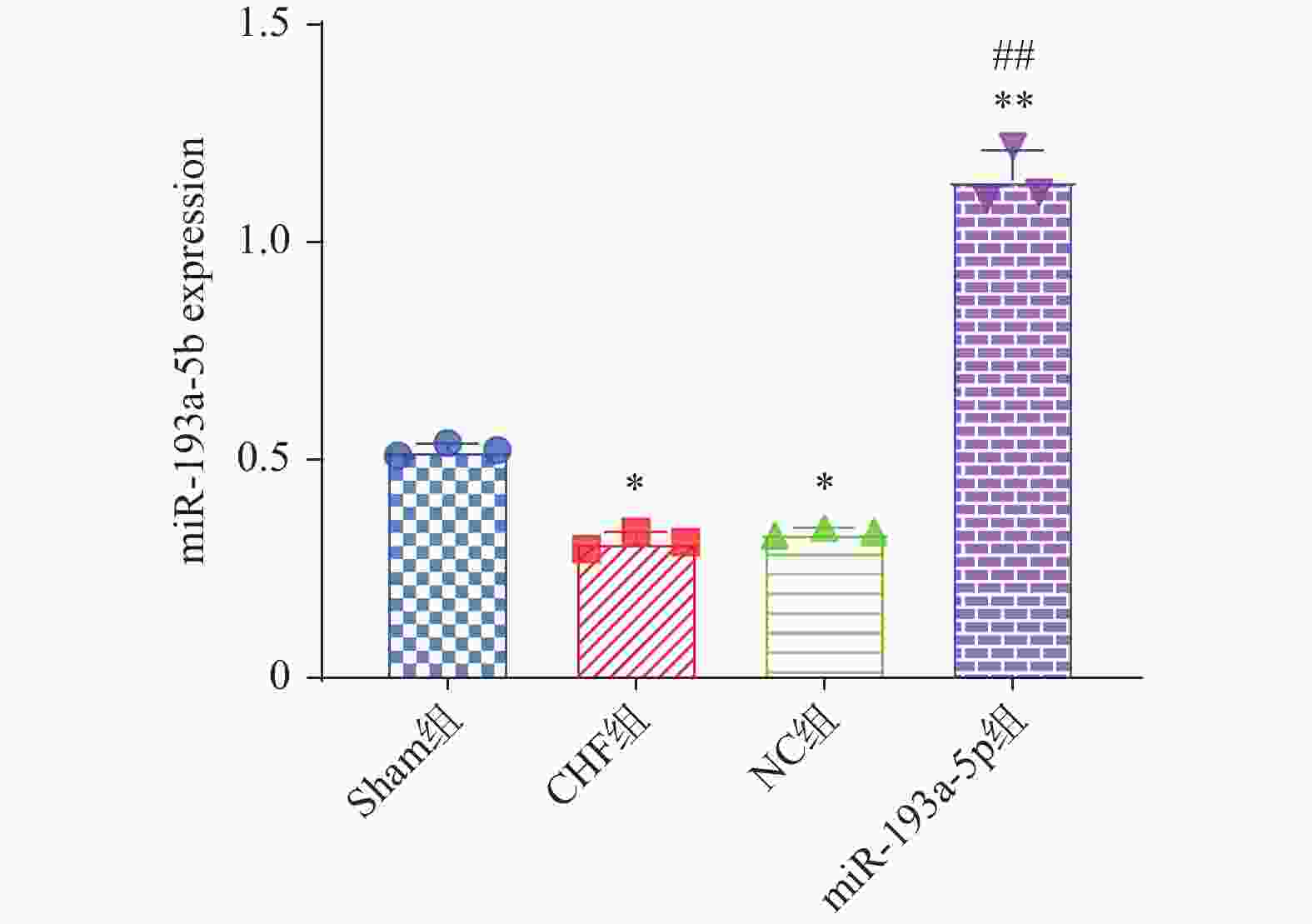
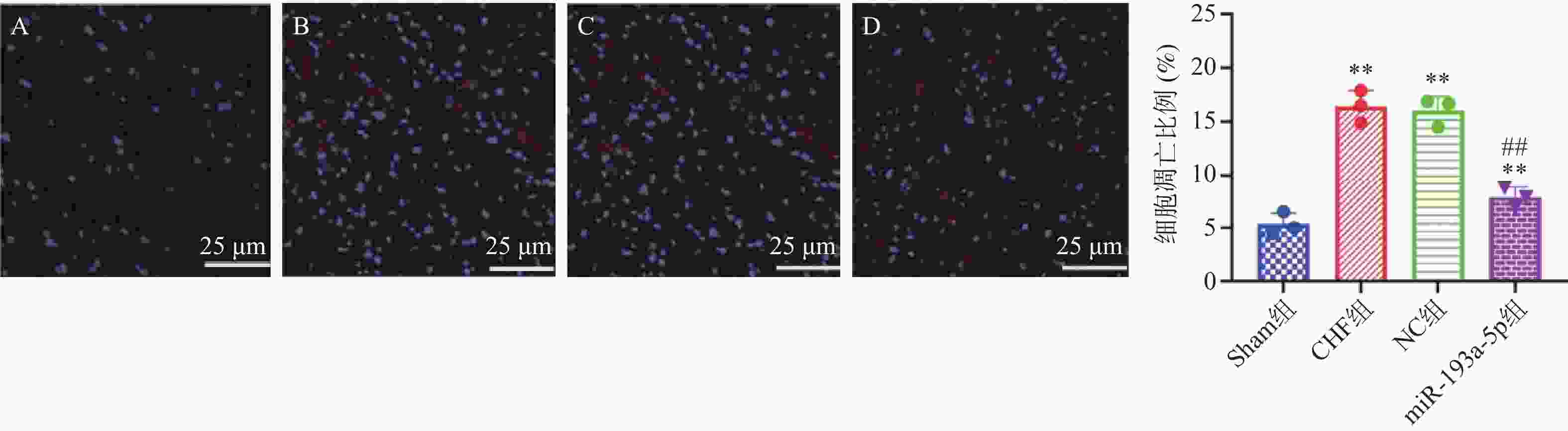
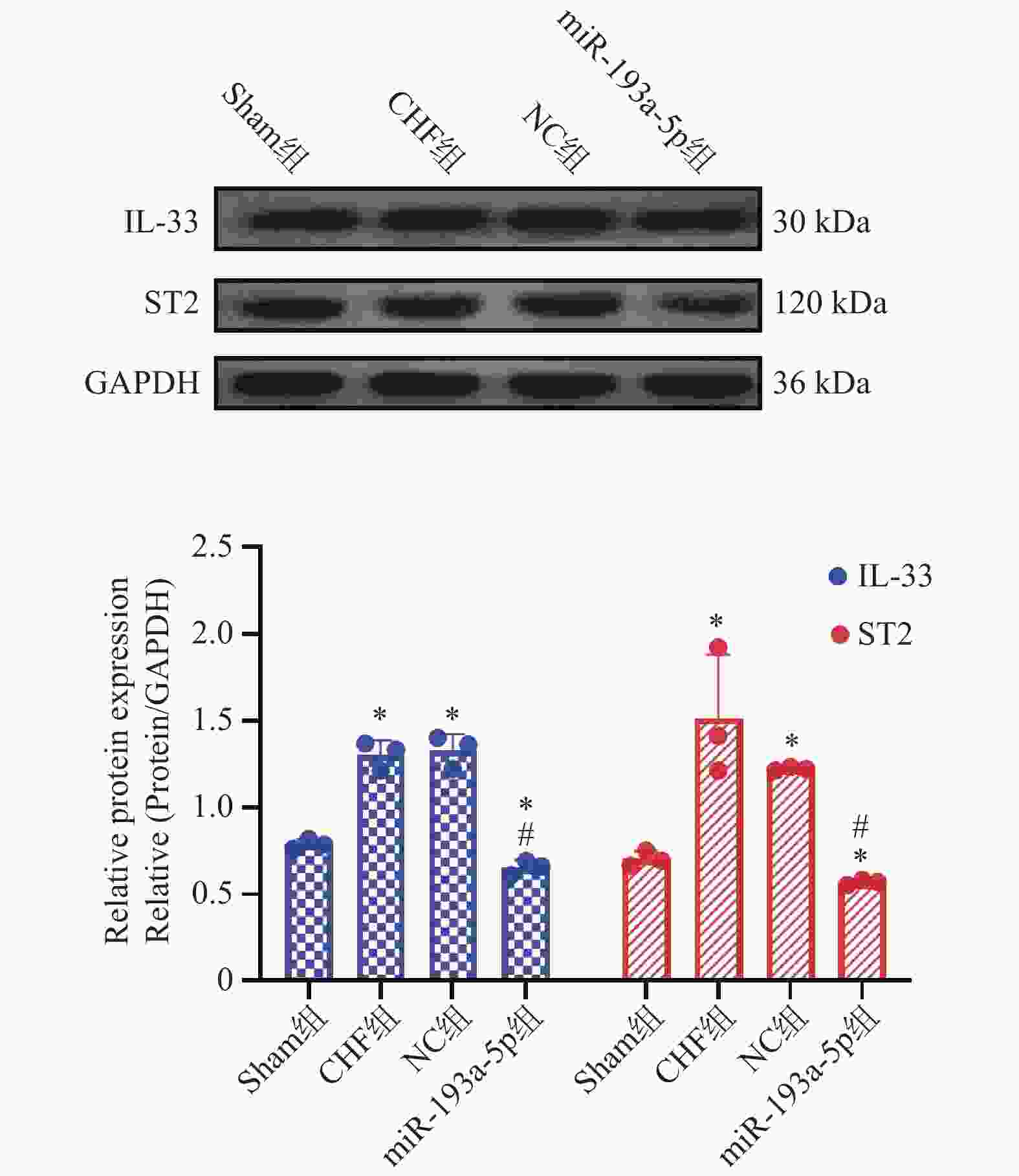
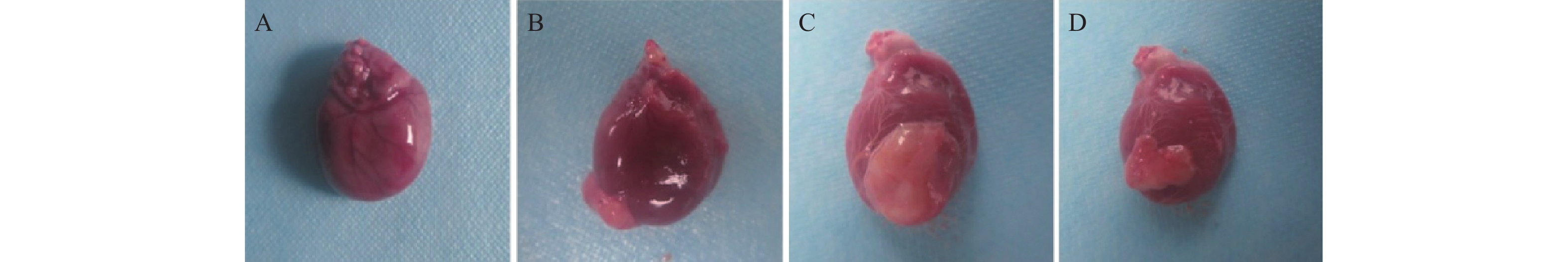
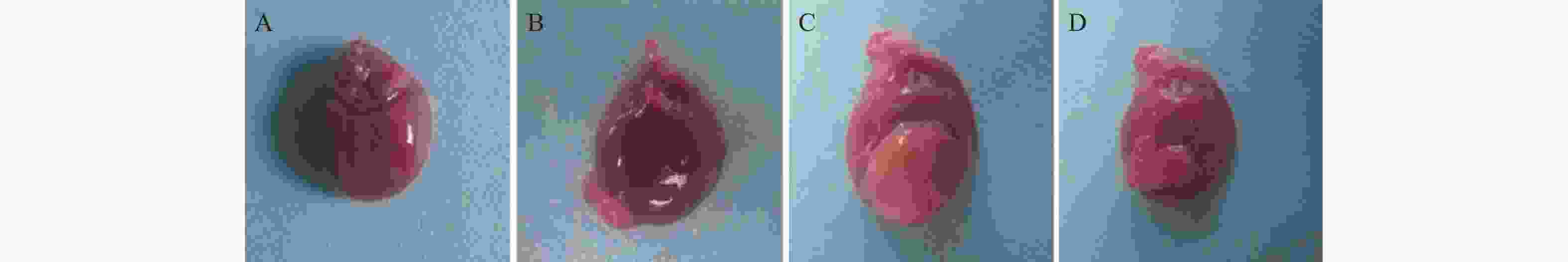
目的 探究过表达miR-193a-5p抑制炎症因子释放对慢性心力衰竭(Chronic heart failure,CHF)模型大鼠心功能的保护作用及对IL-33/ST2信号通路的调控作用。 方法 40只SPF级Wistar大鼠被随机分配为Sham组(n = 10)、CHF组(n = 10)、NC组(n = 10)、miR-193a-5p组(n = 10);除Sham组外其余各组大鼠被用于建立CHF模型。随后,NC组和miR-193a-5p组的大鼠分别通过尾静脉注射5nmol/L的NC-agomiR、miR-193a-5p-agomiR,每3天注射一次,持续4周。而Sham组和CHF组的大鼠则接受等量的生理盐水注射。实验终点多普勒彩色超声仪检测4组大鼠左室后壁厚度(left ventricular posterior wall,LVPWs)、舒张末期左室后壁厚度(left ventricular posterior wall dimensions,LVPWd)、收缩期室间隔厚度(left ventricular systolic interventricular septal,IVSs)、舒张末期室间隔厚度(interventricular septal thickness at diastole,IVSd)和左室射血分数(left ventricular ejection fraction,LVEF),计算4组大鼠心脏表型指数心脏肥大指数(heart weight/body weight,HW/BW)与左心室肥大指数(left heart body weight,LVW/BW)的变化,取4组大鼠心脏组织进行组织形态学分析,采用qPCR技术检测4组大鼠心脏组织中miR-193a-5p的表达水平;利用Tunel染色法检测4组大鼠心肌组织的凋亡; Elisa法测定心肌组织中炎症因子白介素-6(interleukin-6,IL-6)、肿瘤坏死因子α(tumor necrosis factor-alpha,TNF-α)的水平;Western blot检测心肌组织中白介素-33(interleukin-33,IL-33)、血清生长刺激表达基因-2蛋白(growth stimulation expressed gene 2,ST2)蛋白表达水平。 结果 与Sham组相比,CHF组和NC组的心脏体积增大、几何结构改变、心肌变薄以及梗死区域苍白,而miR-193a-5p组则表现出部分缓解。此外,在心脏组织的miR-193a-5p表达水平上,CHF组和NC组呈现降低趋势,而miR-193a-5p组的表达则上升(P < 0.01);CHF组和NC组LVPWs、LVPWd、IVSs、IVSd、HW/BW和LVW/BW上升,LVEF降低(P < 0.01),miR-193a-5p组LVPWs、LVPWd、IVSs、IVSd、HW/BW和LVW/BW降低但高于Sham组,LVEF上升但低于Sham组(P < 0.01);CHF组和NC组IL-6、TNF-α表达上升(P < 0.01),miR-193a-5p组降低但高于Sham组(P < 0.01);CHF组和NC组IL-33及ST2蛋白表达升高,而miR-193a-5p组降低(P < 0.01)。 结论 过表达miR-193a-5p对CHF大鼠心脏功能具有保护作用,其机制可能与降低心肌组织细胞凋亡及抑制IL-33/ST2信号通路相关。 -
关键词:
- miR-193a-5p /
- 慢性心力衰竭 /
- 心功能 /
- 炎症 /
- IL-33/ST2信号通路
Abstract:Objective To investigate the protective effect of miR-193a-5p on cardiac function and the regulation of IL-33 / ST2 signaling pathway in rats with chronic heart failure (CHF). Methods Forty SPF-grade Wistar rats were randomly divided to four groups: Sham group, CHF group, NC group, and miR-193a-5p group, 10 rats in each group. The model of chronic heart failure was duplicated in the CHF group, NC group, and miR-193a-5p group. Subsequently, the rats in the NC group and miR-193a-5p group were received 5 nmol/L of NC-agomiR or miR-193a-5p-agomiR, respectively, via tail vein injection every 3 days for 4 weeks. In contrast, the rats in the Sham and CHF groups were received an equal amount of saline injection. At the endpoint of the experiment, doppler color ultrasonography was used to detect the left ventricular posterior wall thicknesses (LVPWs), left ventricular posterior wall thickness at end-diastole (LVPWd), systolic interventricular septal thicknesses IVSs, end-diastolic interventricular septal thicknesses (IVSd), and left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEFs) in the above rats, and the changes in the cardiac phenotypic indices of HW/BW vs. LVW/BW in the 4 groups, and cardiac tissues of the rats of the 4 groups were selected. Histomorphological analysis was performed, and the expression levels of miR-193a-5p in the cardiac tissues of the four groups of the rats were detected by qPCR; apoptosis was detected by Tunel staining; the levels of the inflammatory factors interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) in the myocardial tissues were measured by Elisa; Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of IL-33 and ST2 protein in myocardial tissues. Results Compared with the Sham group, the hearts in the CHF and NC groups showed increased volume, altered geometry, thinning of the myocardium, and pallor in the infarcted area, whereas the miR-193a-5p group showed partial remission. In addition, the expression levels of miR-193a-5p in cardiac tissues of the CHF and NC groups showed a decreasing trend, whereas showed a significant increase in the miR-193a-5p group (P < 0.01). In CHF group and NC group, LVPWs, LVPWd, IVSS, IVSD HW/BW and LVW/BW increased significantly, and LVEF decreased significantly (P < 0.01). In miR-193a-5p group, LVPWs, LVPWd, IVSs, IVSd, HW/BW and LVW/BW decreased significantly but higher than sham group, and LVEF increased significantly but lower than sham group (P < 0.01). The expression of miR-193a-5p increased significantly in CHF group and NC group, decreased significantly in miR-193a-5p group but still higher than sham group (P < 0.01). The expression of IL-33 and ST2 protein increased significantly in CHF group and NC group, and decreased significantly in miR-193a-5p group (P < 0.01). Conclusion miR-193a-5p has a protective effect on cardiac function in the rats with chronic heart failure. The mechanism might be related to inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors, reducing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and the inhibition of IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- miR-193a-5p /
- Chronic heart failure /
- Cardiac function /
- Inflammation /
- IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. The sequence of primers
引物名称 引物序列 miR-193a-5p-F 5'-TCAGGCCTCAAGCGCT -3' miR-193a-5p-R 5'- CCTAGCATGGCAATG-3' U6-F 5'- GTCATTCGCCGTACACA -3' U6-R 5'-AACGCCGTAGTCTTTGT -3' 表 2 大鼠的LVPWs、LVPWd、IVSs、IVSd及LVEF比较 [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
Table 2. Comparison of LVPWs,LVPWd,IVSs,IVSd and LVEF in the four groups [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
组别 LVPWs(m) LVPWd(m) IVSs(mm) IVSd(mm) LVEF(mm) Sham组 0.27 ± 0.02 0.19 ± 0.03 0.27 ± 0.04 0.17 ± 0.02 91.35 ± 1.84 CHF组 0.44 ± 0.05** 0.32 ± 0.04** 0.43 ± 0.05** 0.31 ± 0.05** 63.15 ± 1.31** NC组 0.42 ± 0.06** 0.34 ± 0.05** 0.42 ± 0.06* 0.32 ± 0.04** 67.19 ± 1.99** miR-193a-5p组 0.34 ± 0.04*# 0.23 ± 0.03*# 0.34 ± 0.04*# 0.24 ± 0.06*# 81.86 ± 1.34*# F 19.40 15.83 24.02 17.66 153.28 P 0.009 0.008 0.007 0.008 0.009 *与Control组相比,**P < 0.01,**P < 0.01;#与CHF组相比,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01。 表 3 大鼠HW/BW和LVW/BW的比较 [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
Table 3. Comparisons of HW/BW and LVW/BW of the rats in the four groups [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
组别 HW/BW LVW/BW Sham组 3.41 ± 0.12 2.33 ± 0.14 CHF组 4.68 ± 0.36** 3.42 ± 0.24** NC组 4.61 ± 0.34** 3.45 ± 0.32** miR-193a-5p组 3.58 ± 0.24# 2.36 ± 0.34# F 36.53 27.44 P 0.009 0.007 *与Control组相比,**P < 0.01,**P < 0.01;#与CHF组相比,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01。 表 4 大鼠血清的IL-6、TNF-α表达水平 [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
Table 4. Level of IL-6,TNF-α [($ \bar x \pm s $),n = 6]
组别 IL-6(pg/mL) TNF-α(ng/L) Sham组 113.41 ± 17.12 121.35 ± 16.84 CHF组 185.98 ± 15.56** 223.15 ± 16.31** NC组 187.10 ± 16.76** 227.19 ± 15.99** miR-193a-5p组 133.88 ± 15.34*# 156.86 ± 16.34*# F 273.16 244.52 P 0.007 0.006 与Control组相比,**P < 0.01,**P < 0.01;与CHF组相比,#P < 0.05,##P < 0.01。 -
[1] Chen J,Wei X,Zhang Q,et al. The traditional Chinese medicines treat chronic heart failure and their main bioactive constituents and mechanisms[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B,2023,13(5):1919-1955. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.005 [2] Xie S,Xu SC,Deng W,et al. Metabolic landscape in cardiac aging: insights into molecular biology and therapeutic implications[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther,2023,8(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01378-8 [3] Mohan I K,Baba K S S S,Iyyapu R,et al. Advances in congestive heart failure biomarkers[J]. Adv Clin Chem,2023,112(8):205-248. [4] Medzikovic L,Aryan L,Ruffenach G,et al. Myocardial fibrosis and calcification are attenuated by microRNA-129-5p targeting Asporin and Sox9 in cardiac fibroblasts[J]. JCI Insight,2023,8(9):e168655. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.168655 [5] Park JH,Mortaja M,Azin M,et al. Nuclear IL-33 in fibroblasts promotes skin fibrosis [J]. J Invest Dermatol,2023,143(7): 1302-1306. [6] Cheon SY,Park JH,Ameri AH,et al. IL-33/Regulatory T-Cell axis suppresses skin fibrosis [J]. J Invest Dermatol,2022,142(10): 2668-2676. [7] Bharati J,Kumar M,Kumar N,et al. MicroRNA193a: an emerging mediator of glomerular diseases[J]. Biomolecules,2023,13(12):1743. doi: 10.3390/biom13121743 [8] 徐泽民,国欣涛,沈娜,等. 微小RNA-193a-5p对心衰模型大鼠心功能的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志.,2020,37(11):2083-2086 [9] Chen L,Yu D,Ling S,et al. Mechanism of tonifying-kidney Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of chronic heart failure[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med,2022,9(11):988360. [10] Tang W,Rao Y,Pi L,et al. A review on the role of MiR-193a-5p in oncogenesis and tumor progression[J]. Front Oncol,2025,15(16):1543215. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1543215 [11] Georgiadis N,Tsarouhas K,Rezaee R,et al. What is considered cardiotoxicity of anthracyclines in animal studies[J]. Oncol Rep,2020,44(3):798-818. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7688 [12] Sun J,Cheng J,Ding X,et al. β3 adrenergic receptor antagonist SR59230A exerts beneficial effects on right ventricular performance in monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension[J]. Exp Ther Med,2020,19(1):489-498. [13] Niazy N,Mrozek L,Barth M,et al. Altered mRNA expression of interleukin-1 receptors in myocardial tissue of patients with left ventricular assist device support[J]. J Clin Med,2021,10(21):4856. doi: 10.3390/jcm10214856 [14] Roger VL. Epidemiology of heart failure: A contemporary perspective[J]. Circ Res,2021,128(10):1421-1434. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318172 [15] Ruxandra-Nicoleta H ,Ovidiu G B,Giorgiana N,et. al. Heart failure and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A review [J]. Acta Cardiol,2020,75(2): 97-104. [16] Mishra S,Kass DA. Cellular and molecular pathobiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol,2021,18(6):400-423. doi: 10.1038/s41569-020-00480-6 [17] Rutkovskiy A,Lyngbakken MN,Dahl MB,et al. Circulating microRNA-210 concentrations in patients with acute heart failure: Data from the akershus cardiac examination 2 study[J]. Clin Chem,2021,67(6):889-898. doi: 10.1093/clinchem/hvab030 [18] Wang W,Li Y,Zhang C,et al. Small extracellular vesicles from young healthy human plasma inhibit cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction via miR-664a-3p targeting SMAD4[J]. Int J Nanomedicine,2025,20(21):557-579. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S488368 [19] 木其尔. miR-193a-5p对结直肠癌相关成纤维细胞生物学行为的影响 [D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古医科大学,2024. [20] Liu YS,Tian XX,Liu D,et al. RelB represses miR-193a-5p expression to promote the phenotypic transformation of vascular smooth muscle cells in aortic aneurysm[J]. Biochimica et biophysica acta,2023,1866(2):194926. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194926 [21] 郭丽宁,常蕊,杨杰,等. MUC4、CUEDC2、miR-193a-5p在子宫内膜癌组织中的表达及其临床价值[J]. 国际检验医学杂志,2022,43(22):2716-2721. [22] Garcia A M,Beatty J T,Nakano S J. Heart failure in single right ventricle congenital heart disease: Physiological and molecular considerations[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,2020,318(4):H947-H965. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00518.2019 [23] Sun Y,Pavey H,Wilkinson I,et al. Role of the IL-33/ST2 axis in cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One,2021,16(11):e0259026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259026 [24] 陆松侠,黄茸茸,胡健力,等. 基于IL-33/ST2信号通路研究补肺汤对慢性支气管炎大鼠[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2023,43(23):5826-5830. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.23.051 -





 下载:
下载: