2024 Vol. 45, No. 5
2024, 45(5): 1-7.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240501
Abstract:
Dopamine D1 receptor (DRD1) is currently known as the dopamine receptor subtype with the most widespread expression in the nervous system. DRD1 plays a role in various signaling pathways to perform many functions such as movement, emotion, cognition, learning and memory, as well as neuroendocrine activities. These functions may be associated with conditions like Parkinson's syndrome, schizophrenia, depression, and immune responses. Changes in the expression of DRD1 often indicate alterations in neurological functions. Therefore, DRD1 has the potential to serve as an indicator of neurological disorders and functional changes, as well as a potential target for the treatment of neurological diseases. This article reviews the distribution and functions of DRD1 in the nervous system, with a particular emphasis on DRD1's involvement in signaling pathways related to the nervous system.
Dopamine D1 receptor (DRD1) is currently known as the dopamine receptor subtype with the most widespread expression in the nervous system. DRD1 plays a role in various signaling pathways to perform many functions such as movement, emotion, cognition, learning and memory, as well as neuroendocrine activities. These functions may be associated with conditions like Parkinson's syndrome, schizophrenia, depression, and immune responses. Changes in the expression of DRD1 often indicate alterations in neurological functions. Therefore, DRD1 has the potential to serve as an indicator of neurological disorders and functional changes, as well as a potential target for the treatment of neurological diseases. This article reviews the distribution and functions of DRD1 in the nervous system, with a particular emphasis on DRD1's involvement in signaling pathways related to the nervous system.
2024, 45(5): 8-15.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240502
Abstract:
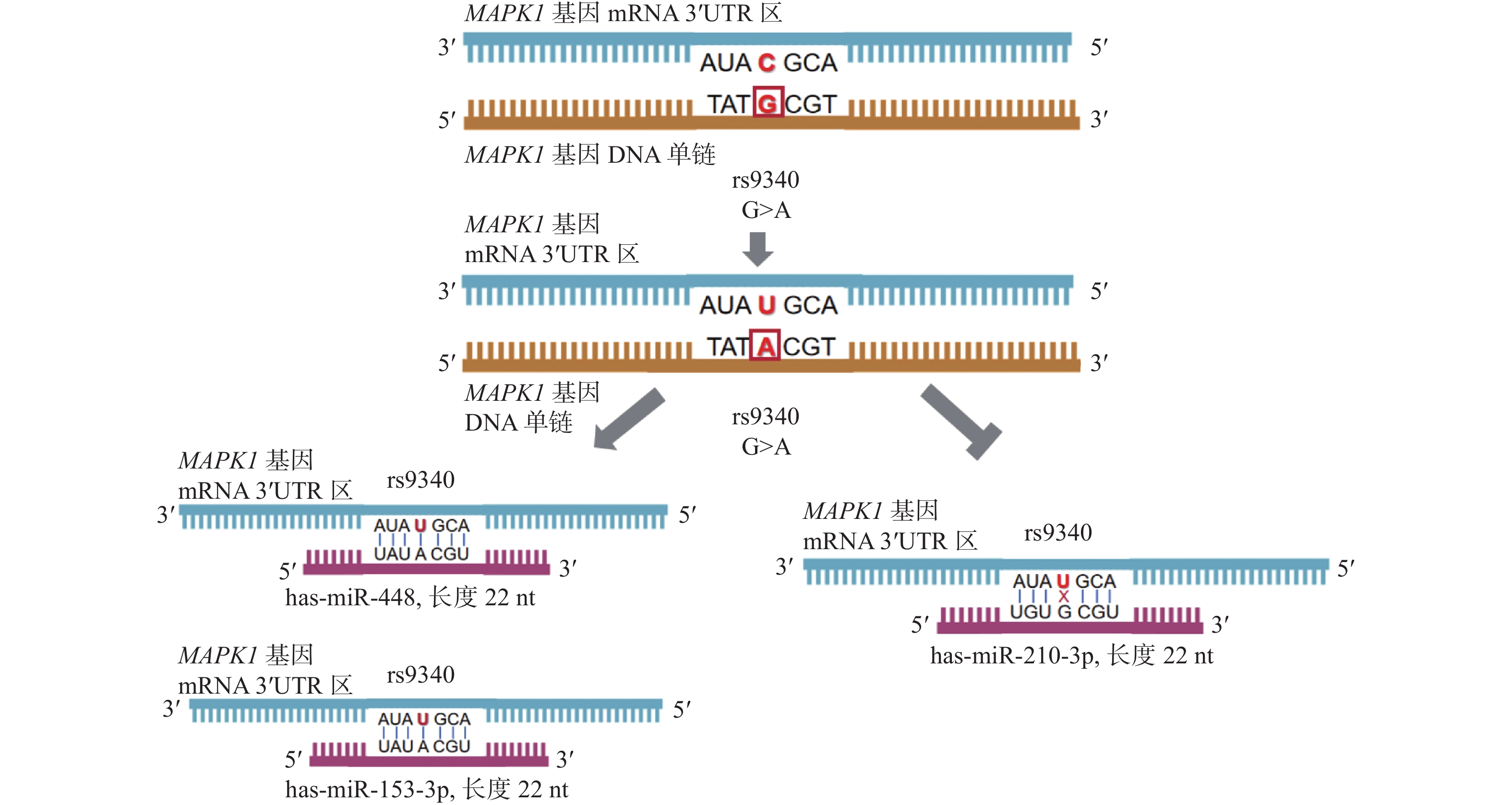
Objective NRAS and MAPK1 genes are important regulators of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway, and their functions and expression levels have been associated with a variety of human tumors. This study Methods 1399 persons of the population were enrolled in the current study, with 416 as the CIN patient group and 983 as the healthy control group. The SNPs loci (rs14804 and rs9340) in the NRAS gene and the MAPK1 gene were genotyped using the TaqMan assays, and the correlation between the two SNPs loci and the risk of CIN was analyzed. Results The difference in the frequency of distribution of SNP locus rs9340 allele (P = 0.008) and genotype (P = 0.002) of MAPK1 gene in the CIN group versus the control group was statistically significant, and allele A may be associated with a higher risk of developing CIN (OR = 1.28, 95%CI 1.07 ~ 1.54), especially for people in the lower age group (≤ 50 years) of CIN risk (OR = 1.35, 95%CI 1.09 ~ 1.67). Conclusion rs9340 in the MAPK1 gene might be correlated with the risk of CIN in the Chinese Han population in Yunnan.
2024, 45(5): 16-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240503
Abstract:
Objective To construct and evaluate the specific CTL cell response induced by HPV16 E6 and E7 multi epitope DNA vaccines and their intervention effects on tumor growth so as to reveal their potential as candidate HPV therapeutic vaccines. Methods The CTL epitopes of human HLA-A*02:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-A*24:02 restriction and C57BL/6 mouse H-2b restriction were predicted by the MHC-I processing and MHC-I binding methods in the IEDB website, and then screened for co-presentation of both based on scoring as well as ELISPOT experiment. The predicted CTL epitopes obtained were constructed into a multi-epitope DNA vaccine (pVAX1-10P), and the immunological interventions were performed in the mice transplanted with TC-1 tumour cells from prophylactic and therapeutic strategies respectively, and the ability of pVAX1-10P to induce specific CTL responses was assessed by flow cytometry. Results Prediction and screening yielded 10 CTL antigenic epitopes co-presented by human and murine MHC molecules. ELISPOT results showed that each peptide in the experimental group induced the specific immune responses in mouse lymphocytes. The constructed multi-epitope DNA vaccine, pVAX1-10P, induced the specific cellular immunity and significantly inhibited the tumour growth in both prophylactic and therapeutic experiments. Conclusion The constructed HPV16 E6 and E7 multi-epitope DNA vaccine, pVAX1-10P can induce specific CTL response and inhibit the tumour growth, which is expected as a promising candidate of HPV therapeutic DNA vaccine.
2024, 45(5): 23-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240504
Abstract:
Objective To explore the histological and ultrastructural changes in lung tissues of piglets with the early onset scoliosis (EOS) with the combination of thoracic insufficiency syndrome (TIS) before and after the treatment with the growth-friendly techniques. Methods Six-week-old piglets were selected and randomly divided into the control group (n=3), the model group (n=5) and the treatment group (n=5). An EOS+TIS piglet model was constructed at 6 weeks of age. At 14 weeks of age, orthodontic treatment was performed at the same time as the tethering was released. The piglets were euthanized at 18 weeks of age, and the lung tissues were taken for HE staining and Masson staining. Pathological observations were conducted on lung parenchyma and pulmonary vascular development in the three groups. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary fibrosis were evaluated quantitatively with the use of following indicators: radial alveolar count (RAC), alveolar wall thickness (AWT), alveolar septal density ratio (ASDR), respiratory film thickness (RFT), average collagen fiber volume (ACFV), pulmonary capillary density (PCD), pulmonary artery wall thickness ratio (WT%), and pulmonary artery wall cross-sectional area ratio (WA%). At the same time, the ultrastructural changes in the lung tissue of piglets model were observed under the transmission electron microscope. Results Compared with the control group, pathological observation of the three piglet groups showed that the model group exhibited the bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary fibrosis, while the treatment group showed the alleviation of these manifestations.The differences in these groups of young pigs RAC, AWT, ASDR, RFT, ACFV and PCD were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The differences between the WT% and WA% groups were not statistically significant(P > 0.05). Under the transmission electron microscopy, the cell structure of the model group was damaged and had the poor integrity, while the cell structure of the treatment group was improved. Conclusion The lung tissue of EOS+TIS piglets shows the characteristics of bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary fibrosis; using growth-friendly technology to treat EOS+TIS piglets, its bronchopulmonary dysplasia and pulmonary fibrosis have been improved to a certain extent.
2024, 45(5): 29-36.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240505
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the impact of TRIM48 overexpression on glioma and explore the underlying mechanism. Methods Twelve nude mice were randomly assigned into two groups: one inoculated with U87 glioma cells stably overexpressing TRIM48 (oeTRIM48 group) and the other with the control cell line (Vector group). Tumor volume was measured every 3 days post-inoculation, and after 4 weeks, the tumors were excised and weighed. Tumor tissues underwent hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and Ki-67 expression was assessed using immunofluorescence. Additionally, the expressions of TRIM48, ERK1/2, and phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) in the tumors of nude mice and human glioma tissue arrays were analyzed through Western blot and immunohistochemistry respectively. Results Compared to the Vector group, the oeTRIM48 group exhibited significantly reduced tumor volume and weight (P < 0.0001). H&E staining indicated a decrease in nuclei and mitotic count in the oeTRIM48 group. Furthermore, Ki-67 expression was significantly lower in the oeTRIM48 group than that in the Vector group (P < 0.0001). The oeTRIM48 group also showed a significantly lower expression of p-ERK1/2 protein compared to the Vector group (P < 0.01). Immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays revealed the high expression of TRIM48 and low expression of p-ERK1/2 in adjacent non-tumoral tissues, with the opposite pattern observed in tumor tissues. Conclusion Overexpression of TRIM48 inhibits the growth and proliferation of glioma, potentially through modulation of the ERK1/2 signaling pathway.
2024, 45(5): 37-43.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240506
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of probiotics interventionon of the expression of Aβ in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion and the protective effect of neurons. Methods Male SD rats were selected as the experimental animals and randomly divided into Sham Group, Model Group, Probiotics Group and Edaravone Group. The common carotid artery was separated only to the Sham Group While a cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model was eatablished to the other groups. The degree of brain injury was evaluated using neurobehavioral scoring; The infarct area of rat brain tissue was observed using TTC staining; HE staining was used to observe the pathological and morphological changes of neurons in the CA1 and cortical regions of the hippocampus in rats; The expression of Aβ proteins was detected using immunohistochemistry experiments. Results Compared with the Sham Group, the Model Group showed an increase in neurobehavioral scores (P < 0.05), an increase in cerebral infarction focus (P < 0.05), neuronal damage in the hippocampal CA1 and cortical regions, and a significant upregulation of Aβ protein expression (P < 0.001, P < 0.05); Compared with the Model Group, the Probiotics Group and Edaravone Group showed a decrease in neurobehavioral scores (P < 0.05) and a reduction in cerebral infarction focus (P < 0.05). The Probiotic Group and the Edaravone Group showed the less neuronal damage in the hippocampal CA1 and cortical regions , and the Aβ protein expression levels were significantly down regulated in both groups (P < 0.001, P < 0.05). The improvement was more significant in Edaravone Group. Conclusion Probiotics intervention can downregulate the expression of Aβ protein, alleviate the brain tissue damage and exert neuroprotective effects in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion.
2024, 45(5): 44-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240507
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of HIF-1α on the migration and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells and its related regulatory mechanism. Methods GBC-SD cells were constructed and transfected with lentivirus, and the experimental group (HIF-1α shRNA), negative control group (empty lentivirus transfection) and blank control group (untreated) were obtained respectively. The expression levels of E-Cadherin, and N-Cadherin proteins were detected by Western blotting assay, Cell scratch assay was ued to detect the migratory ability of GBC-SD cells, and Transwell invasion assay was uesd to detect the invasive ability of GBC-SD cells. Results Compared with the control group, the expression level of E-Cadherin protein in the experimental group was significantly increased (P < 0.001), while the expression level of N-Cadherin protein was significantly decreased (P < 0.001), and there was no remarkable difference in the expression level of E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin proteins between the control groups (P both>0.05). In the experimental group, the cell scratch healing degree was inferior to the control group (P < 0.001) , and the number of penetrating molds was also inferior to the control group (P < 0.001), while there was no obvious otherness in the cell scratch healing degree and the number of penetrating molds between the control groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion Targeted knockdown of HIF-1α can reduce the migration and invasion ability of gallbladder cancer cells, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulation of epithelial mesenchymal transition.
2024, 45(5): 49-59.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240508
Abstract:
Objective To identify key HUB genes involved in lung development through transcriptomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis using tissue samples collected from an established piglet model of early-onset scoliosis with thoracic insufficiency syndrome (EOS+TIS) and its treatment model. Methods EOS+TIS and treatment animal models were established, followed by histological analysis using HE and Masson staining to observe lung tissue morphology and fibrosis severity. Lung tissue samples from three groups (control, model, treatment) were sequenced. Differential analysis was performed using the DESeq2 package in R, and differential gene GO/KEGG enrichment analysis was conducted using the DAVID database. Core genes were identified, relevant pathways were predicted, and validation was done via PCR and Western blot experiments. Results (1) HE staining results: The model group displayed significant bronchopulmonary dysplasia, which was notably improved in the treatment group. (2) Masson staining results: The model group showed severe lung fibrosis, which was alleviated in the treatment group. (3) DESeq2 analysis: The normal vs. model group comparison identified 170 upregulated and 262 downregulated genes, while the model vs. treatment group comparison identified 323 upregulated and 467 downregulated genes. (4) GO functional annotation: Differential genes were mainly enriched in functions like extracellular matrix, plasma membrane composition, immune response, inflammatory response, calcium ion binding, and cytokine activity. KEGG enrichment: Differential genes were primarily enriched in pathways like neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction and cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. (5) Common gene identification: THBS1 was identified as a common gene. (6) PCR and Western Blot validation: THBS1 was downregulated in the model group and upregulated post-treatment (P < 0.05). Western Blot analysis revealed that TGF-β expression was reduced in the model group and increased post-treatment (P < 0.05). Conclusion THBS1 and TGF-β are involved in the process of lung development in the early onset scoliosis with thoracic insufficiency syndrome pig models.
2024, 45(5): 60-65.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240509
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the expression of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan rectetpor 1 (ROR1) in invasive lung adenocarcinoma with different histological grades, and to analyze its relationship with histopathological grade of lung adenocarcinoma so as to explore whether it can be used as a potential indicator for the diagnostic evaluation of invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Methods A total of 290 paraffin-embedded tissue specimens of invasive lung adenocarcinoma were collected, and the relationship between ROR1 expression and invasive lung adenocarcinoma grade was statistically analyzed by HE staining sections. Results ROR1 was significantly highly expressed in the poorly differentiated invasive lung adenocarcinoma (P < 0.001), the Ki-67 index in the low-differentiated group was significantly higher than that in the high-differentiation and medium-differentiated groups(P < 0.001), and the Ki-67 index was higher in the high-expression group than in the low-expression group (P < 0.01). Conclusion There are significant differences in the expression levels of ROR1 in different grades of lung adenocarcinoma, and its expression level is closely related to the degree of differentiation and malignancy of invasive lung adenocarcinoma, which makes it possible to become a new biomarker for the diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma and assist in the evaluation of clinical features and prognosis of lung adenocarcinoma, and provide a scientific basis to formulate personalized treatment strategies for patients.
2024, 45(5): 66-72.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240510
Abstract:
Objective To explore the feasibility of applying the prognosis model based on lysosomal related genes(LRGs) in patients with bladder cancer (BC). Methods Bladder cancer data were downloaded from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) program and dataset of GSE13507 were downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO). Differentially expressed LRGs related to the survival of BC in the TCGA database were screened by differential analysis and single factor proportional hazards model (COX) regression analysis via R software. LASSO regression was used to construct a prognostic risk model. BC patients were divided into the high and low risk groups according to the median risk score. Survival analysis were used to compare the survival differences between the high-risk and low-risk groups of BC patients, and validate in GEO database. Univariate and multivariate cox regression analysis were used to verify whether the risk scores were an independent risk factor affecting the prognosis of BC patients. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used to evaluate the accuracy of prognostic model predictions. GO and KEGG enrichment analysis were used to explore the biological functions and signaling pathways of differentially expressed genes between the high-risk and low-risk groups. Immunoassay was used to explore the differences in immune function between the high-risk and low-risk groups. Results A total of 44 differentially expressed lysosomal related genes were screened, of which 9 genes related to the prognosis were used to construct the prognosis model in this study. Survival analysis showed that the prognosis of the low-risk group was significantly better than that of the high-risk group (P < 0.05), which was verified in GEO database. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the BC prognosis risk scoring model to predict the 1-, 3- and 5-year survival of patients were 0.696, 0.717 and 0.738, respectively. Independent prognostic analysis showed that this prognostic risk model was an independent prognostic factor for BC patients. GO enrichment analysis indicated that the differential genes between the high-risk and low-risk groups were mainly involved in cell structure and function correlation. KEGG enrichment analysis suggested that the differential genes were mainly enriched in PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Immunological analysis showed that there were significant differences in immune cell infiltration and immune function between the two groups. Conclusion Risk model of lysosomal related genes in BC can accurately and effectively predict the prognosis of BC patients.
2024, 45(5): 73-81.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240511
Abstract:
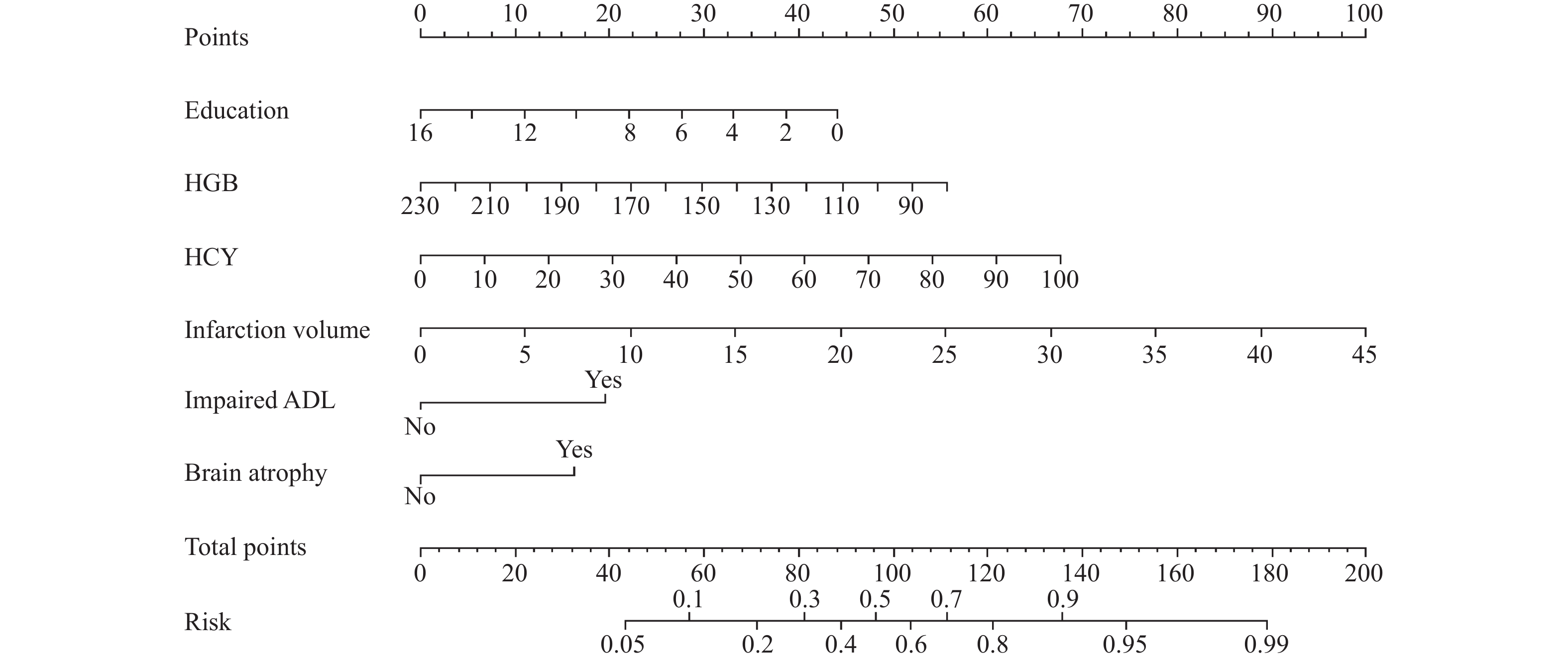
Objective To explore the related factors of cognitive impairment after the acute ischemic stroke and develop a clinical nomogram model. Methods 175 patients with the acute ischemic stroke were selected as the study objects, and the cognitive function was assessed using the simple mental State Scale and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment Scale after the admission. There were 81 cases in post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI) group and 94 cases in post-stroke no cognitive impairment (PSNCI) group. The baseline data, peripheral blood and brain MRI results of the two groups were collected and the univariate and multivariate analysis were used to explore the influencing factors of the cognitive impairment after the acute ischemic stroke, and the prediction model was constructed based on the nomogram and evaluated. Results Multivariate regression analysis showed that several factors, including impaired daily activity, high levels of HCY, larger cerebral infarction volume, and cerebral atrophy, were independent risk factors for early PSCI. On the other hand, education and hemoglobin were identified as the protective factors against PSCI. A nomogram prediction model was created from this data. The ROC curve analysis predicted an area under the curve of 0.830 (95%CI: 0.77-0.89). The calibration curve indicated that the model had the good differentiation and prediction probability, with bias correction tending towards the ideal curve and consistent incidence in actual outcomes. The clinical decision curve showed that the model could provide a better net benefit for clinical use, making it a valuable tool for healthcare professionals. Conclusion The development of PSCI may be overlooked in its early stages. A clinical predictive model that considers multiple factors can aid in the early detection of PSCI and identification of high-risk individuals, which is crucial for the effective prevention and treatment.
2024, 45(5): 82-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240513
Abstract:
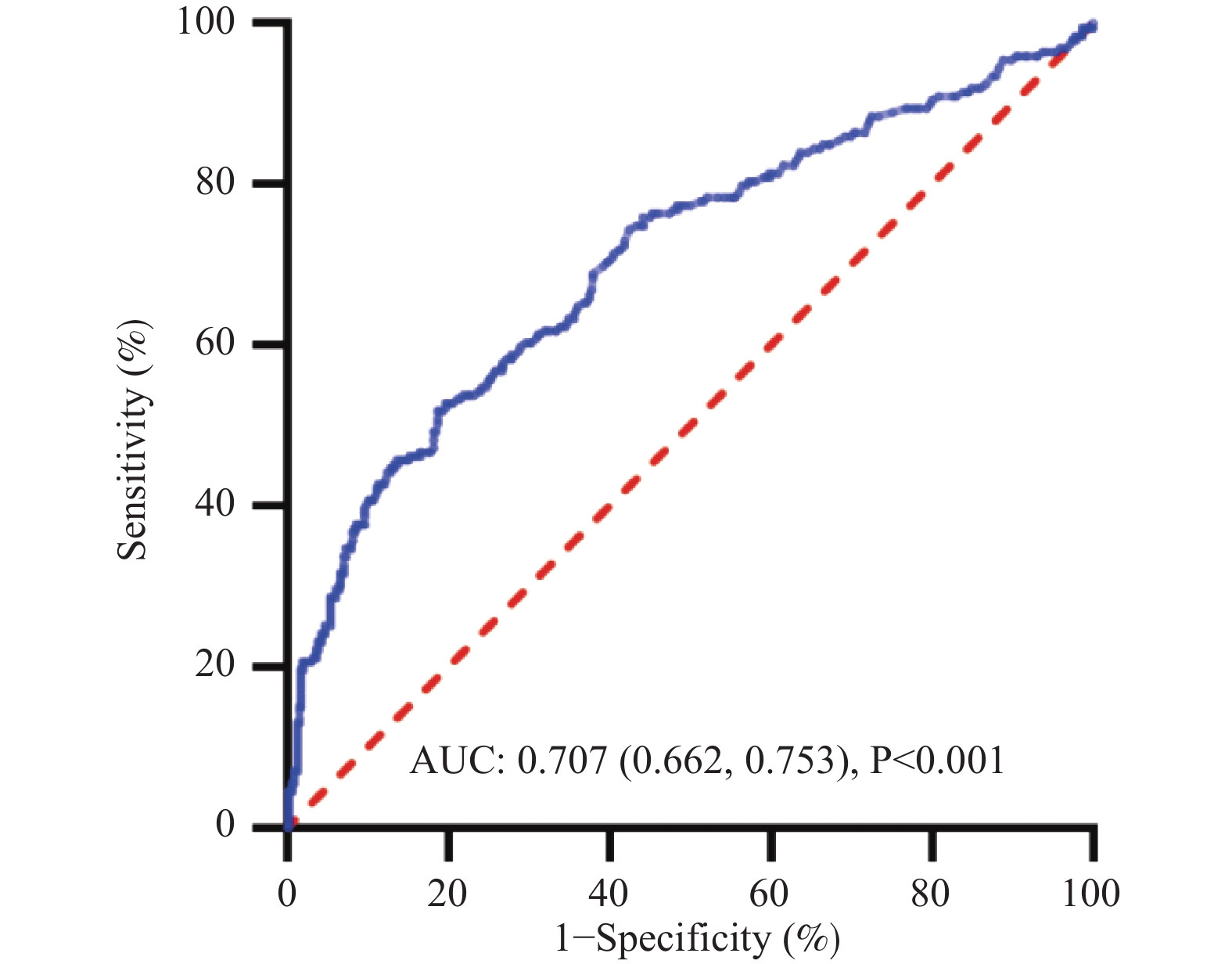
Objective To investigate the predictive value of systemic inflammatory response index (SIRI) for acute ischemic stroke-associated pneumonia of the brain. Methods The baseline data of patients diagnosed with acute ischemic stroke in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2017 to December 2022 were gathered to calculate the SIRI index. Patients were divided into SAP group (665 cases) and Non-SAP (466 cases) group according to whether SAP occurred within 7 days of stroke onset. Logistic regression was used to analyze the relationship between SIRI index and SAP in patients with acute ischemic stroke-associated pneumonia of the brain, and ROC was used to analyze the predictive value of SIRI for SAP. Results The analysis included 665 patients with acute ischemic stroke whose median age was 67.00 (56.00~76.00) years old, and the incidence of SAP was 29.92%. The age, the incidence of atrial fibrillation, the use rate of acid suppressive drugs, the use rate of indwelling gastric tube, fasting blood glucose, the proportion of moderate and severe patients in the NHISS score, the number of white blood cells, neutrophils, monocytes, and SIRI index in the SAP group were higher than those in the non SAP group (P < 0.05). However, the hemoglobin value and lymphocyte number in SAP group were lower than those in non SAP group (P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that age, indwelling gastric tube, higher NHISS score group and SIRI index were the risk factors of SAP in patients with acute ischemic stroke. ROC analysis showed that the prediction accuracy of SIRI for patients with acute ischemic stroke-associated pneumonia of the brain was 0.707 (95%CI: 0.662~0.753, P < 0.001). Conclusion SIRI index is correlated with the occurrence of acute ischemic stroke- associated pneumonia and has the predictive value for it.
2024, 45(5): 88-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240514
Abstract:
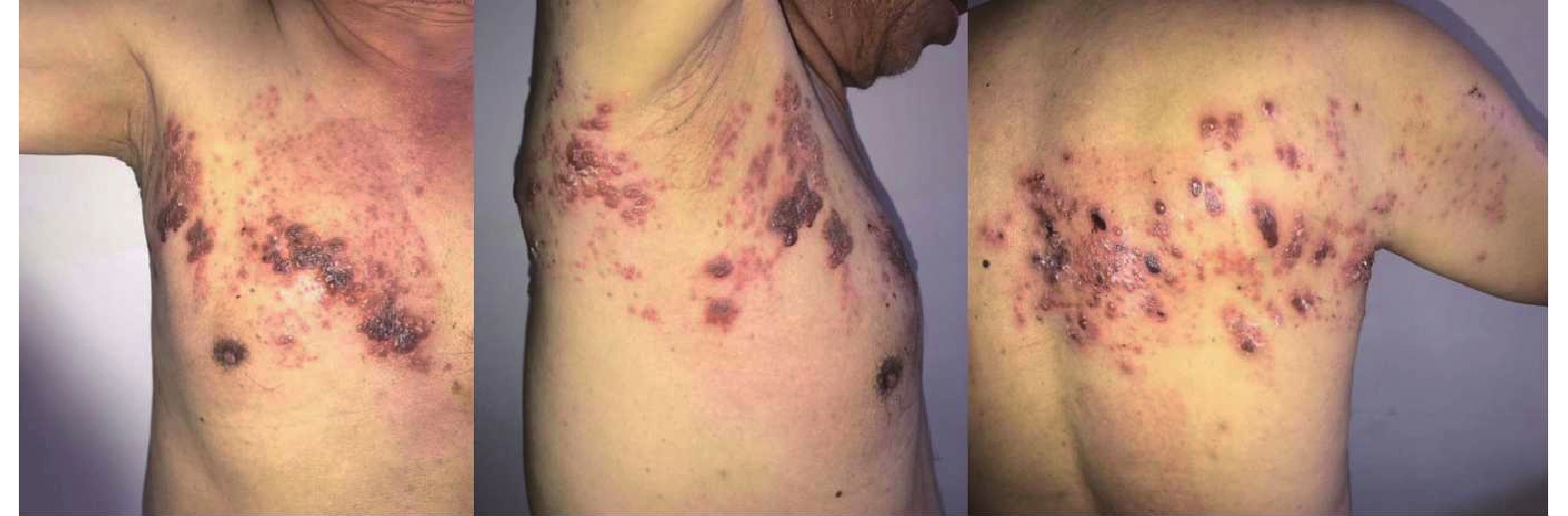
Objective To evaluate the clinical effect of ultrasound-guided intercostal nerve pulsed radiofrequency on the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in the upper thoracic segment after herpes zoster infection. Methods A total of 67 patients with postherpetic neuralgia in the intercostal nerve of the thoracic region (segments 1, 2, and 3) and back region were included in this study. The patients were randomly assigned into an experimental group and a control group based on the type of treatment method. The experimental group consisted of 34 participants, including 15 males and 19 females, with an average age of (50.6±11.5) years. Pulsed radiofrequency procedure was performed on the intercostal nerves of segments 1, 2, and 3 under the ultrasound guidance for the subjects in the experimental group. The control group comprised 33 subjects, including 16 males and 17 females, with an average age of (51.5±12.7) years. Intercostal nerve block procedure was performed on segments 1, 2, and 3 under the ultrasound guidance for the patients in the control group. The visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores and Pain DETECT scale scores were compared before the treatment and 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after the treatment for the two groups. The recurrence rate of symptoms within 1 year after the treatment was determined and compared between the two groups. Results Complete follow-up was achieved in the 67 patients after the treatment, and the study subjects did not present with adverse reactions. The VAS pain scores and Pain DETECT scale scores at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after the treatment were significantly better in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). The VAS pain scores and Pain DETECT scale scores at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after the treatment were significantly improved compared with the pre-treatment scores for the two groups (P < 0.05). The recurrence rate of symptoms within 1 year after the treatment was significantly lower in the experimental group than in the control group (P < 0.05). These results showed that pulsed radiofrequency method was more effective for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in the upper thoracic segment after herpes zoster infection and had less adverse effects compared with the intercostal nerve block approach. Conclusion Ultrasound-guided intercostal nerve pulsed radiofrequency treatment is effective and safe for the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia in the upper thoracic segment after herpes zoster.
2024, 45(5): 94-102.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240515
Abstract:
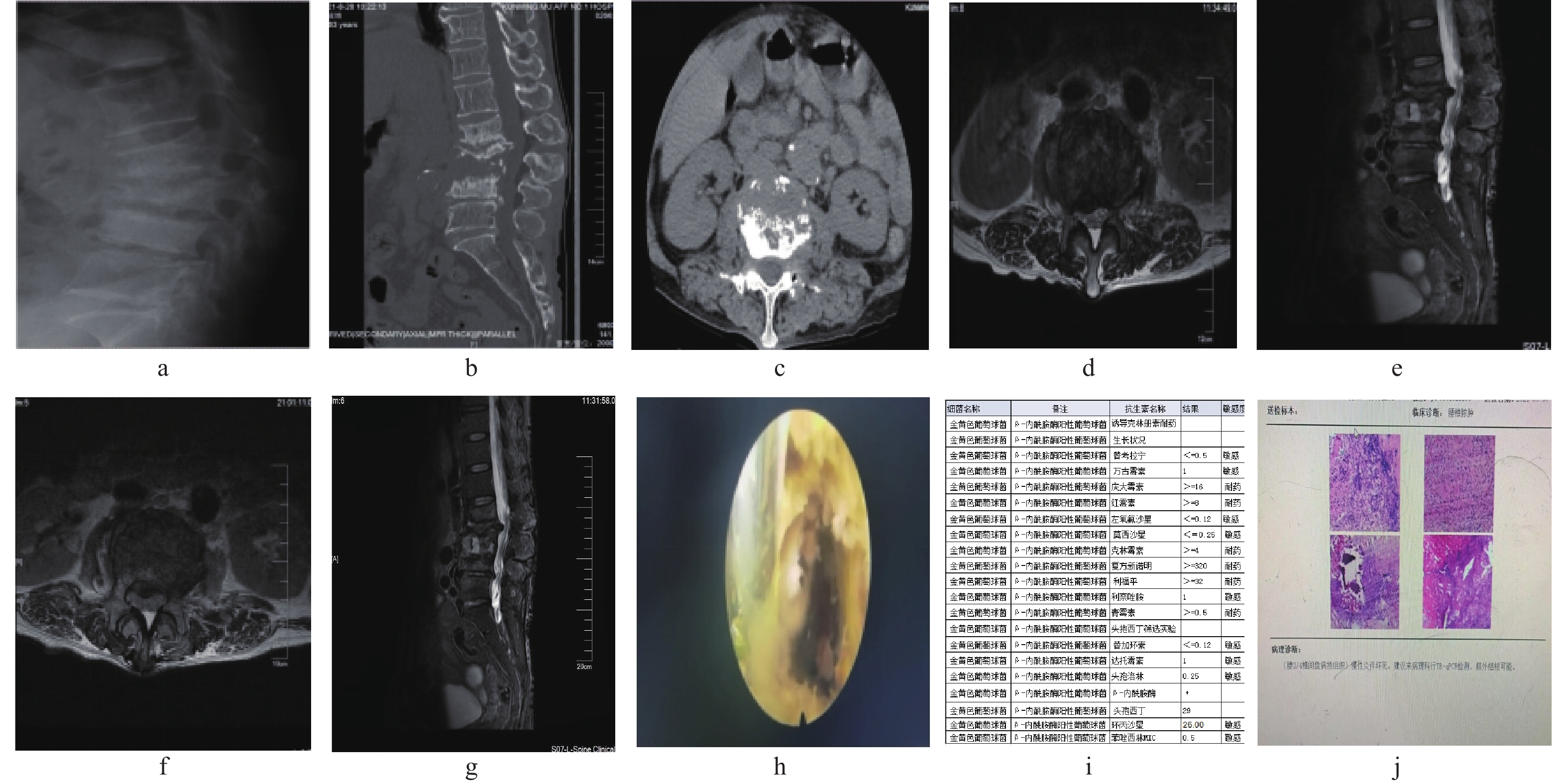
Objective To evaluate the efficiency of posterolateral approach in the treatment of single-segment nonspecific lumbar spondylodiscitis by observation of the clinical results of posterior lateral percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic debridement (PTED) approach and posterior single segmental lumbar debridement, bone graft and internal fixation in the treatment of single segment nonspecific lumbar spondylodiscitis. Methods In this study, 42 patients ( males 24 and females 18 with an average age of 54 years) with nonspecific lumbar spondylodiscitis treated in the Department of Orthopaedics of the 1st Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from June 2016 to June 2023 were analyzed retrospectively. They were divided into group A (n = 21) and group B (n = 21). All the patients in group A were treated with posterolateral percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic debridement combined with soft tissue immersion to improve the detection rate of etiology. All the patients in group B were treated with posterior single-segment lumbar focus debridement, bone graft and internal fixation. The visual analogue scale score of low back pain (VAS), Japanese Orthopaedic Association Lumbar vertebra score (JOA) and lumbar vertebra ODI scale were compared before and after the operation to evaluate the remission of clinical symptoms, infection indexes such as white blood cells, hypersensitive C-reactive protein, ESR, the therapeutic effect of pathogenic drug-resistant bacteria, bacterial culture rate and postoperative complications. Results The positive rate of pathogen culture obtained through posterior lateral percutaneous foramen debridement combined with soft tissue soaking method was 90%. The score of ODI in group A was lower than that in group B on the 7th day after operation. Among the infection indexes, CRP and ESR in group A were much lower than those in group B at 3 and 7 days after the operation, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic debridement (PTED)in the treatment of lumbar spondylodiscitis combined with soft tissue immersion has a high bacterial culture rate, which can effectively reduce the pain of patients, improve the quality of life, and significantly reduce the index of infection. it is safe and effective for high-risk patients with multiple underlying diseases, strong bacterial virulence, high fever, high inflammation index, high risk of infection with internal fixation and inability to tolerate general anesthesia surgery.
2024, 45(5): 103-108.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240516
Abstract:
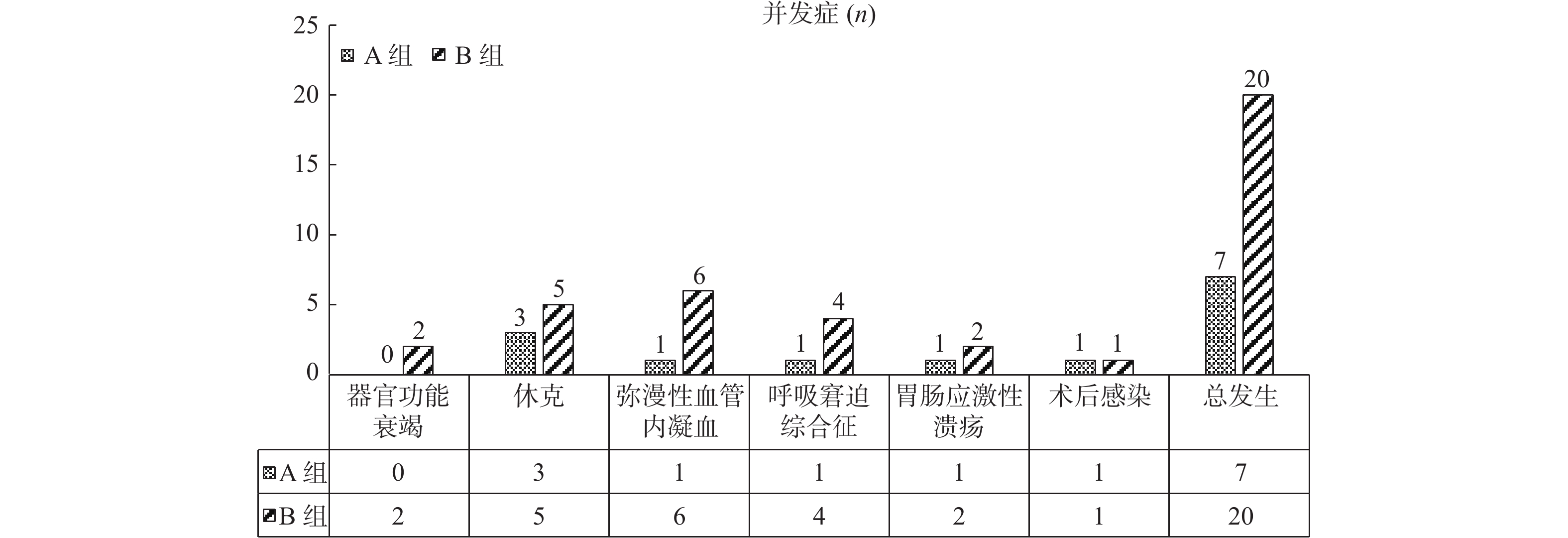
Objective To analyze the clinical effects of rapid rehabilitation technology combined with injury control in the rehabilitation of patients with multiple injuries and the occurrence of complications, and to explore the factors affecting the occurrence of complications. Methods The clinical data of 108 patients with multiple injuries from October 2020 to November 2022 in Honghe Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University were collected and divided into group A (55 cases) and group B (53 cases). Group A was treated with rapid rehabilitation measures + injury control, group B was treated with conventional rehabilitation measures + injury control. The clinical efficacy, complications and related influencing factors were compared between the two groups. Results The blood coagulation function, lactic acid, temperature recovery time and intraoperative blood loss in group A were significantly better than those in group B (P < 0.05), but the operative time was longer (P < 0.05). Postoperative ISS score, Mb, CK and HMGB1 levels in group A were lower than those in group B (P < 0.05). The incidence of complications in group A (7 cases) was lower than that in group B (20 cases)(P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that treatment and rehabilitation measures were the main factors affecting the postoperative complications. Conclusion Rapid rehabilitation technology combined with injury control in the treatment of patients with multiple injuries has a good clinical effect and can significantly reduce the incidence of postoperative complications, among which a good rehabilitation treatment is the key to reduce complications.
2024, 45(5): 109-115.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240517
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the value of Adler grading with color Doppler ultrasound in the diagnosis of cervical cancer, and to analyze its correlation with pathological indexes. Methods 136 patients with cervical cancer in the hospital from January 2020 to January 2023 were retrospectively included as the cervical cancer group, and 80 patients with benign cervical lesions in the hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. All patients received the color Doppler ultrasound examination, and the color Doppler image characteristics and Adler grade were compared between the two groups. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was plotted to analyze the diagnostic value of color ultrasound in cervical cancer. Cervical cancer group was divided into grade 0 to 1 group and grade 2 to 3 group according to Adler grade. Pathological indexes of grade 0 to 1 group and grade 2 to 3 group were compared to analyze the relationship between the pathological indexes and Adler grade. Results Cervical hyperecho, cervical isoecho, cervical enlargement, Adler grade, PSV, EDV in cervical cancer group were higher than those in the control group, and cervical hypoecho, cervical normal size, RI were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The ROC curve showed that cervical echo, cervical size, PSV, EDV and RI had the certain diagnostic value for cervical cancer, and Adler grade had the high diagnostic value for cervical cancer (AUC = 0.758, 0.590, 0.902). The clinical stage, microvascular density, PSV and EDV in grade 2-3 group were higher than those in grade 0-1 group, the maximum lesion diameter was longer than that in grade 0-1 group, and RI was lower than that in grade 0-1 group (P < 0.05). The Phi coefficient correlation analysis showed that Adler grade was positively correlated with the clinical stage (Phi = 0.203, P = 0.018). The results showed that Adler grade was positively correlated with the microvascular density, maximum lesion diameter, PSV and EDV (r = 0.664, 0.363, P = 0.000), and negatively correlated with RI (r = -0.597, P = 0.000). Conclusion Color ultrasound Adler grading technique has the high diagnostic value in patients with cervical cancer, which is closely related to the clinical stage, microvascular density, maximum lesion diameter and other pathological indicators.
2024, 45(5): 116-122.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240518
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the relationship between the level of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets and the pathological characteristics of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), as well as its prognostic value for chemotherapy. Methods A total of 80 patients with AML in Beijing Aerospace General Hospital from April 2017 to April 2022 were selected as the study group, and 80 healthy volunteers matched for gender and age were selected as the control group. The general data and peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets levels (CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+) of the two groups were compared, and the peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets levels of patients with different pathological characteristics in the study group before the chemotherapy were compared.The clinical data and peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets of patients with the different prognosis were compared in the study group, and the influencing factors of poor prognosis of AML were analyzed, and the value of peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets in predicting poor prognosis of AML was analyzed. Results Compared with the control group, the levels of peripheral blood CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+ in the study group before the chemotherapy were significantly decreased (P < 0.05); the levels of CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+ in peripheral blood of patients with positive NPM1 mutation, positive FLT3-ITD mutation, and low-risk stratification were higher than those of patients with negative NPM1 mutation, negative FLT3-ITD mutation, and high-risk stratification, respectively (P < 0.05); The age and high-risk stratification of the poor prognosis patients in the research group were higher than those of the good prognosis patients, and the levels of CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+ in peripheral blood before chemotherapy were lower than those of the good prognosis patients (P < 0.05); Age, risk stratification, CD4+/CD8+, the CD3+ and CD4+ levels in peripheral blood before the chemotherapy were all factors influencing poor prognosis in AML patients (P < 0.05); The areas under the curve (AUC) of CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+ in peripheral blood before the chemotherapy for predicting poor prognosis in AML were 0.702, 0.738, and 0.759, respectively. Conclusion The decrease in CD4+/CD8+, CD3+ and CD4+ levels in peripheral blood of AML patients is associated with NPM1 mutation, FLT3-ITD mutation and risk stratification, and has certain predictive value in predicting poor prognosis of AML.
2024, 45(5): 123-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240519
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) in children with burns, so as to provide a reference for the early diagnosis and prevention of SIRS. Methods A retrospective analysis of the clinical data of 329 children with burns who were admitted to the Burn Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2020 to December 2022 and met the inclusion criteria was conducted using a case-control method. The age, gender, cause of injury, season of injury, total burn area, area of third-degree burns, pre-hospital first aid methods, and first serum examination upon admission of the children were statistically analyzed. The serum markers encompassed C-reactive protein (CRP), Interleukin-6 (IL-6), procalcitonin (PCT), prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), fibrinogen (FIB), D-dimer (DD), and blood glucose level. According to the modified SIRS scoring criteria, the children were divided into a SIRS group (150 cases) and a non-SIRS group (179 cases). An epidemiological survey was conducted and the risk factors for the occurrence of SIRS in children with burns were analyzed. Results (1) The incidence of burns in children aged ≥2 and <6 years was the highest in this study. The gender composition ratio of children in each age group was analyzed, and the difference was not statistically significant (χ2 = 3.480, P = 0.326). (2)Moderate burns were the most common, accounting for 217 cases (65.9%). The difference in the degree of burns among age groups was statistically significant (χ2=10.841, P < 0.05). (3) There were 277 cases of hot liquid burns (84.2%). The composition ratio of the cause of injury in children of different age groups was analyzed, and the difference was statistically significant (H=49.144, P < 0.05). (4) The incidence of burns in children in winter was 30.39% (100/329), which was higher than in other seasons. The distribution of the season of injury in children with burns in different years was analyzed, and the difference was statistically significant (χ2 = 25.390, P < 0.05). (5) Nearly half of the children with burns in this survey did not receive treatment after the burn, accounting for 46.8%. The second most common was improper treatment, accounting for 38%. There were only 50 cases of correct treatment, accounting for 15.2%. In this survey, the number of cases in the group with a time of admission ≤8h after injury accounted for more than half, accounting for 66.3%, followed by >12 h and ≤24 h, accounting for 15.2%. The proportion of >24 h and ≤72 h was the lowest, accounting for only 8.8%. (6) The burn index, blood glucose levels, c-reactionProtein, Interleukin-6, procalcitonin, and prothrombin time were identified as independent risk factors for SIRS in children with burns (all P < 0.05), with serological indicators and the burn index showing a positive correlation with the occurrence of SIRS. Conclusion The hospitalized children with burns treated at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University are mainly boys with moderate hot liquid burns aged over 2 and under 6 years. The combination of serum examination and burn index with the modified SIRS score can improve the specificity of assessing the occurrence of SIRS after burns, and provide a high clinical reference value for the diagnosis and early prevention of SIRS in clinical practice.
2024, 45(5): 130-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240520
Abstract:
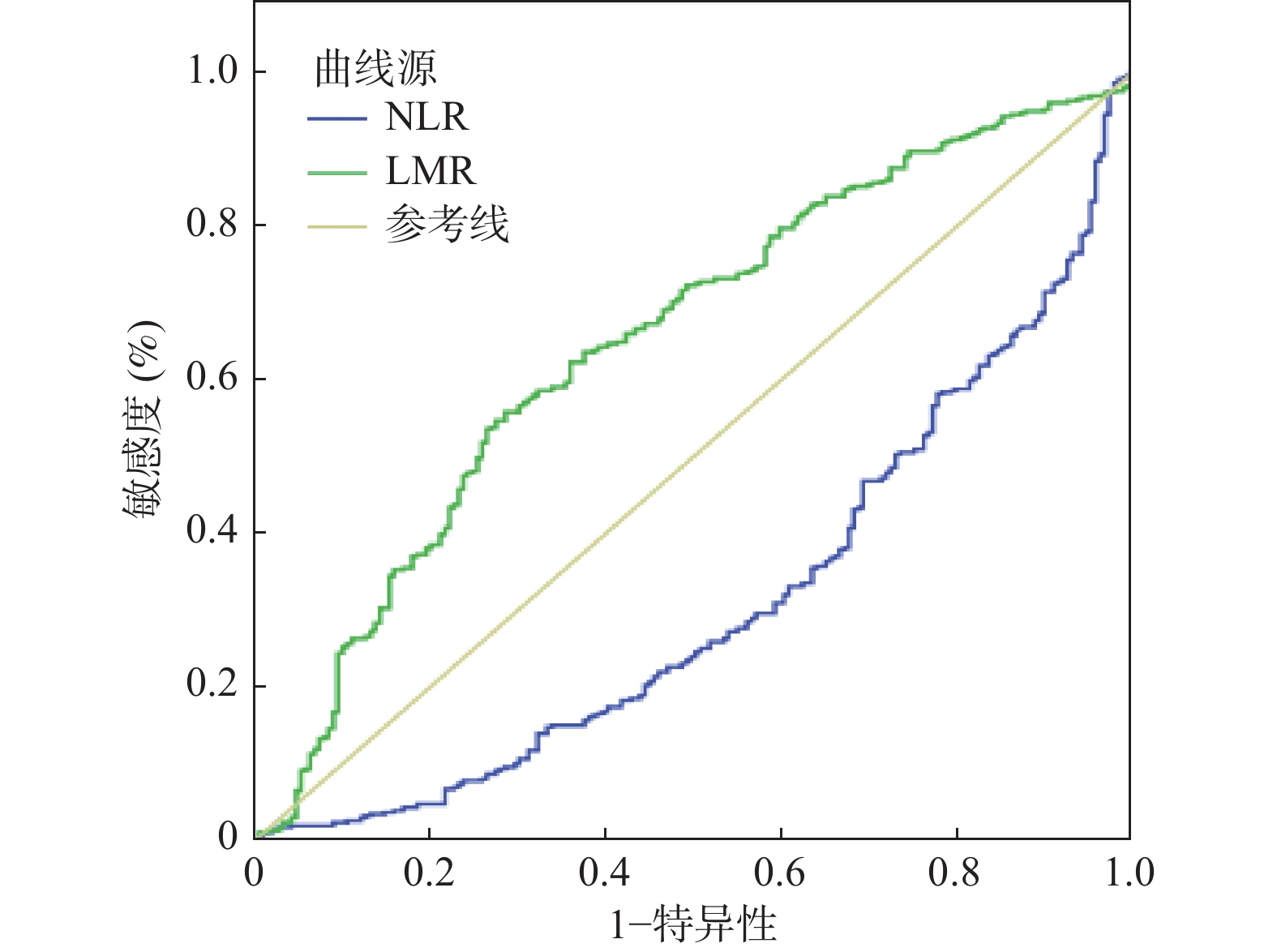
Objective To analyze the morbidity rate and severity of retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) so as to provide a basis for the clinical prevention and treatment and reduce the severity of ROP. Methods 648 premature infants, including 371 males and 277 females, who underwent the fundus examination at Kunming Children’ s Hospital from September 2018 to September 2023 were selected and divided into a non ROP group and a ROP group (including pre threshold ROP, threshold ROP, and rapidly advancing posterior pole ROP (A-ROP). The parameters of gestational age, birth weight, and blood routine were collected, and chi square test was used to detect gender group differences. Univariate analysis of variance was used to analyze the inter group differences in gestational age and birth weight. Rank sum test was used to detect the inter group differences in blood routine data, and the logistic regression analysis were conducted to establish the relevant independent risk factors, and evaluate the early predictive value of LMR and NLR for ROP by drawing receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Results The rank-sum test showed that the differences in gestational age, daytime age, and birth weight were statistically significant (P < 0.05) in the four groups compared with the no-ROP, pre-threshold, threshold, and A-ROP groups. The white blood cell count, neutrophil count, monocyte count, hemoglobin, and NLR ratio were significantly lower and the LMR ratio was significantly higher in the three ROP groups compared to the children in the no-ROP group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Multi-factor logistic regression analysis suggested that birth weight, gestational age, hemoglobin, NLR, and LMR were independent risk factors for the development of ROP (P < 0.05). The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve for LMR was 0.651 (95%CI: 0.605-0.698), with a best predictive value was 7.36, corresponding to a sensitivity of 55.8% and a specificity of 71.4%. Conclusion Birth weight, gestational age, hemoglobin, and NLR are independent risk factors for ROP, with birth weight, gestational age, and hemoglobin as the protective factors. LMR has some early predictive value for ROP.
2024, 45(5): 136-143.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240521
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics of 53 cases of congenital hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome) caused by UGT1A1 gene mutation in Yunnan Province and the characteristics of UGT1A1 gene mutation. Methods 53 cases were selected from the Department of Gastroenterology of Kunming Children’ s Hospital from January 2017 to December 2022 and divided into Gilbert syndrome (GS) group and Crigler-Najjar-2 (GN-2)group. The clinical data and genetic test results of children with type I1 syndrome (CN-2 group)and the clinical manifestations, laboratory test results and gene polymorphisms of the children were retrospectively analyzed. Results Children from the ethnic minority had the higher incidence in both groups. The proportion of females in CN-2 group was higher than that in GS group. In terms of liver system, the levels of TBil and IDB in CN-2 group were higher than those in GS group, with statistical significance (all P values < 0.05). The liver structure in GS group was normal, while 3 patients in CN-2 group had the abnormal liver and biliary structure. In the extra-hepatic system, there were no abnormalities in blood system and glucose metabolism, abnormal blood lipids and thyroid function metabolism, vitamin D deficiency in GS group, vitamin A and D deficiency and vitamin E decreased in CN-2group. There were cardiac structural abnormalities in both groups, but the incidence of CN-2 group was higher than that of GS group. Among all the patients, the mutation frequency of c.1456T>G in exon 5 was the highest (32 cases, 60.37%), followed by c.1091C>T (14 cases, 60.37%). Exon 1, C.211g>A (6 cases, 11.32%), and C.1198a >C (4 cases, 7.55%). The frequency of c.1456T>G mutation in GS group and CN-2 group was 69.23% and 57.5%(9 and 23 cases), respectively, and there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05). Among the two groups, the second most frequent mutation was c.1091C>T (4 cases and 10 cases), and there was no statistical significance between the two groups (P > 0.05).The frequencies of UGT1A1 haplotypes 1、3 and 4 were statistically significant between GS group and CN-2 group (P < 0.05). There is no significant difference in gender and ethnic groups among the four major mutation forms of UGT1A1 (P > 0.05). Conclusion The clinical manifestations of the liver system and extrahepatic system are different between GS group and CN-2 group. The highest mutation frequency of UGT 1A1 gene is c.1456T>G in exon 5.
2024, 45(5): 144-150.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240522
Abstract:
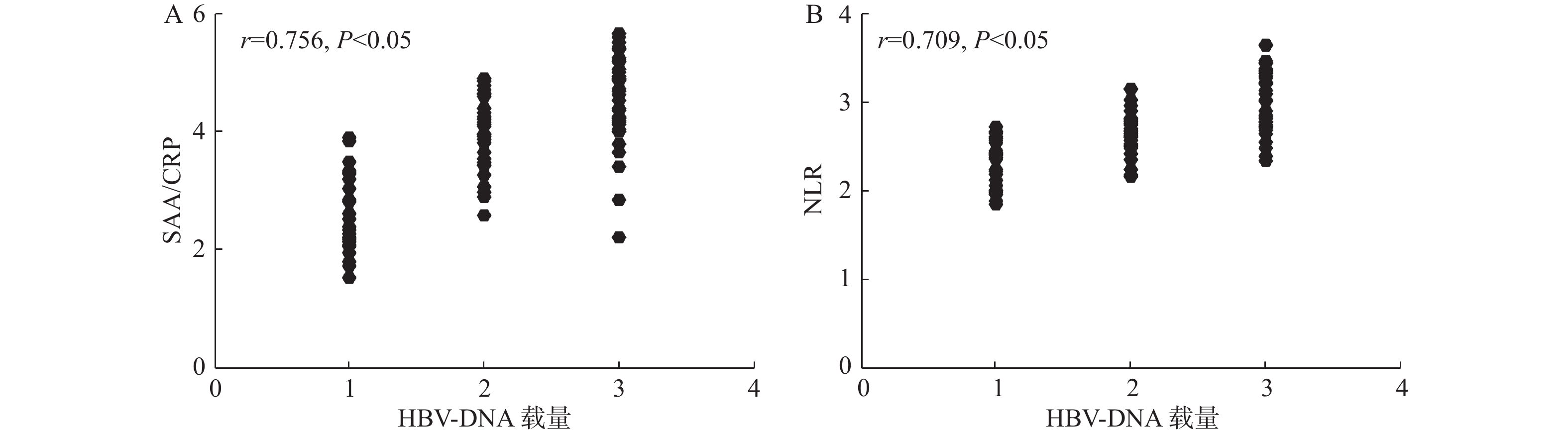
Objective To investigate the correlation and clinical significance of peripheral blood serum amyloid A (SAA) to C-reactive protein (CRP) ratio (SAA/CRP), neutrophils lymphocytes ratio (NLR) and HBV-DNA levels and disease severity in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB), so as to find out the correlation between SAA and CRP (SAA/CRP), neutrophils lymphocytes ratio (NLR) and hepatitis B virus-deoxyribonucleic acid (HBV-DNA). Methods From June 2020 to June 2022, 100 patients with CHB in our hospital were selected as the study subject and were divided into the mild group (simple CHB, 36 cases), the moderate group (cirrhosis in the compensated stage of hepatitis B, 33 cases) and the severe group (cirrhosis in the decompensated stage of hepatitis B, 31 cases) according to the degree of disease. And at the same time, another 50 healthy volunteers with the same age were selected as the control group. Different disease degrees, general information, serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in the control group, and serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in patients with different HBV-DNA loads in the study group were compared respectivly and the correlation between the serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in patients with CHB and HBV-DNA loads and disease degrees were analyzed. The correlation between the serum SAA/CRP, NLR levels and HBV-DNA load and the degree of disease in CHB patients was analyzed. All patients were treated with the antiviral therapy for 24 weeks, and serum SAA/CRP, NLR levels and the change values of patients with different antiviral efficacies were compared before the treatment and 12 weeks and 24 weeks after the treatment and the value of the change values of serum SAA/CRP, NLR levels before and after the treatment was analyzed so as to predict the efficacy of the therapy. Results Serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in severe patients > moderate patients > mild patients > control group (P < 0.05); serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in high carrier patients > moderate carrier patients > mild carrier patients (P < 0.05); serum SAA/CRP and NLR levels in CHB patients were positively correlated with HBV-DNA load (r = 0.756, 0.709) , and disease extent (r = 0.776, 0.745) were positively correlated (P < 0.05);The levels of peripheral blood SAA/CRP and NLR at 12 and 24 weeks after the treatment were higher in non-responders than in responders, and the change values were lower than in responders (P < 0.05); the AUCs predicted by SAA/CRP∆1 and NLR∆1 alone were 0.752, 0.773 for SAA/CRP△1 and NLR△1 alone, and 0.861 for combined prediction of △1; the AUCs for SAA/CRP△2 and NLR△2 alone were 0.796 and 0.819, respectively, and 0.967 for combined prediction of △2, which were greater than those for combined prediction of △1 (P < 0.05). Conclusion SAA/CRP and NLR are significantly correlated with HBV-DNA load and disease extent in CHB, and the changes in their levels can be used clinically to assess the disease and predict the prognosis, so as to target the follow-up treatment and improve the prognosis.
2024, 45(5): 151-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240523
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the effect of bronchoalveolar lavage combined with low molecular weight heparin on the prognosis with prone ventilation due severe pneumonia. Methods 102 patients with the severe pneumonia from hospitals from January 2021 to January 2023 were selected as the study subjects and randomly divided into a control group (51 cases, conventional treatment+low molecular weight heparin) and a study group (51 cases, conventional treatment+low molecular weight heparin+bronchoalveolar lavage) using a random number table method. Blood gas indexes [blood oxygen saturation (SaO2), partial arterial oxygen pressure (PaO2), partial arterial carbon dioxide pressure (PaCO2)], respiratory dynamics indexes [respiratory work done (WOB), airway resistance (Raw), dynamic compliance (Cdyn)], pulmonary function indexes [forced vital capacity (FVC), 1 second maximum expiratory volume (FEV1), maximum expiratory flow rate (PEF)], inflammatory factors [tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8)], and D-dimer levels before and the first week of treatment were compared between the two groups. And the incidence of adverse prognosis (death, ICU admission, intubation and invasive ventilator) was calculated in the two groups. Results After one week of the treatment, the levels of SaO2 and PaO2 in the study group were higher than those in the control group, while PaCO2 was lower than those in the control group (t = 4.649, 3.774, 4.792, P < 0.05); After one week of the treatment, the WOB and Raw levels in the study group were lower than those in the control group, while the Cdyn levels were higher than those in the control group (t = 7.207, 5.401, 3.150, P < 0.05); After one week of the treatment, the FVC, FEV1, and PEF in the study group were higher than those in the control group (t = 3.834, 3.960, 3.908, P < 0.05); After one week of the treatment, the study group had TNF- α、 The levels of IL-6, IL-8, and D-dimer in the control group were lower than those in the control group (t = 5.642、5.002、6.712、4.127, P < 0.05); The incidence of poor prognosis in the study group was lower than that in the control group (χ2=4.547, P < 0.05). Conclusion Bronchoalveolar lavage, combined with low molecular weight heparin, can shorten the duration of clinical symptom disappearance and hospital stay, improve the blood gas indexes, respiratory dynamics, enhance lung function and reduce the level of inflammatory factors in patients with severe pneumonia.
2024, 45(5): 157-163.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240524
Abstract:
Objective To explore the efficacy of combination therapy of Ginkgo biloba injection and donepezil in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD) based on cerebral hemodynamics and inflammatory factors. Methods A total of 90 patients with AD in Zhangjiakou Shalingzi Hospital from March 2020 to January 2022 were randomly divided into a control group (45 cases) and a study group (45 cases). Both groups received the conventional symptomatic treatment. On this basis, the control group was given donepezil treatment, and the study group was given ginkgo leaf injection combined with donepezil treatment. The therapeutic effects, cerebral hemodynamic parameters [mean flow velocity (MFV) and pulsatility index (PI) of bilateral middle cerebral arteries (bilateral MCA) and basilar arteries (BA)], inflammatory factors [interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-1β], s100β protein, Aβ-amyloid 1-42 (Aβ1-42), bradykinin (BK), cognitive function, activities of daily living, and adverse reactions were compared between the two groups. Results Compared with the control group (77.78%), the total effective rate of the study group (93.33%) was significantly improved (P < 0.05); 1, 3, and 6 months after the treatment, the MFV of BA and bilateral MCA in the study group was higher than that in the control group, while the PI of BA and bilateral MCA was lower than that in the control group (P < 0.05); The levels of serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β in the study group were lower than those in the control group 1, 3, and 6 months after the treatment (P < 0.05); 1, 3, and 6 months after the treatment, the levels of serum s100β protein, Aβ1-42, and BK in the study group were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05); 1, 3, and 6 months after the treatment, the score of the mini-mental state examination scale (MMSE) in the study group was higher than that in the control group, while the scores of the AD assessment subscale cognitive scale (ADAS-cog) and activities of daily living scale (ADL) were lower than those in the control group (P < 0.05); The incidence of adverse reactions in the study group (13.33%) was not significantly different from that in the control group (8.89%) (P > 0.05). Conclusion The efficacy of ginkgo biloba injection combined with donepezil in the treatment of AD is significant, which may be achieved by improving cerebral hemodynamics, downregulating inflammatory factors, and regulating the levels of serum s100β protein, Aβ1-42, and BK.
2024, 45(5): 164-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240525
Abstract:
Objective To explore the clinical efficacy of intrathoracic injection of thrombin combined with drainage tube suspension in the treatment of refractory pneumothorax, and to observe the effect of this treatment scheme on the closure time of leakage and the incidence of fever. Methods From June 2020 to June 2022, 106 patients with refractory pneumothorax were prospectively selected and divided into a control group (53 cases) and a study group (53 cases) according to random number table. The control group was treated with intrathoracic injection of thrombin+conventional closed thoracic drainage, while the study group was treated with intrathoracic injection of thrombin+drainage tube suspension. The clinical efficacy, retention time, leakage closure time, hospitalization time, complications (fever, pleural adhesion, mediastinal emphysema) of the 6MWT groups were observed, and the lung function indexes [vital capacity (VC), residual volume (RV), pulmonary carbon monoxide diffusion (DLCO), total lung volume (TLC)] and blood gas analysis indexes [arterial oxygen partial pressure (PCO2) before and after the treatment were compared. Results After the treatment, the total effective rate of the study group was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). The retention time, leakage closure time and hospitalization time of the study group were shorter than those of the control group (P < 0.05). The complications in the study group were less than those in the control group (P < 0.05). After the treatment, the levels of VC, RV, DLCO and TLC in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, and higher in the study group than in the control group (P < 0.05). After the treatment, PaO2, PaO2/FiO2, and SaO2 in the two groups were higher than those before the treatment, PaCO2 and Borg dyspnea index were lower than those before the treatment, and 6MWT was longer than that before the treatment, and compared with the control group, the change range in the study group was greater (P < 0.05). Conclusion Thoracic injection of thrombin combined with drainage tube suspension is effective in the treatment of refractory pneumothorax, which can improve the pulmonary function index and blood gas index, relieve dyspnea symptoms, improve exercise tolerance, shorten the recovery time, and will not increase complications.
2024, 45(5): 170-177.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240526
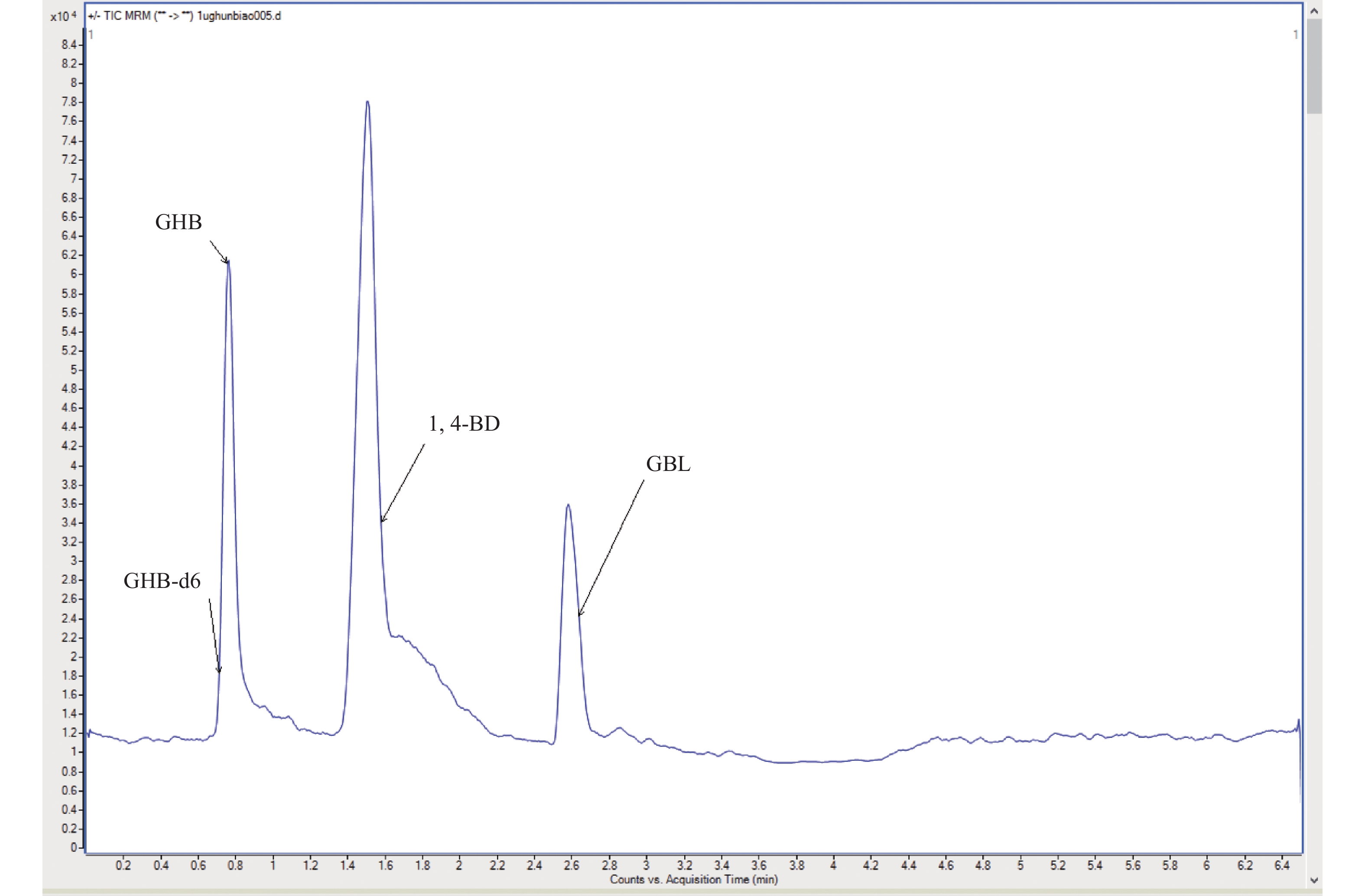
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of alcohol on endogenous GHB content in human blood. Methods LC-MS/MS inspection method was established in the blood for γ- Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), γ- butyrolactone (GBL) and 1,4-butanediol (1,4-BD). 22 healthy subjects were selected as the research subjects to simulate the real cases of drinking alcohol. The levels of GHB in their blood were detected before and after drinking to compare the endogenous GHB levels in the blood before and after drinking. Results GHB in the concentration range of 0.1~50 μg/mL had a good linear relationship and there was a good linear relationship between GBL and 1,4-BD in the concentration range of 0.15~50 μg/mL (R2 > 0.999).The limits of detection of GHB, GBL and 1,4-BD were 0.015 μg/mL, 0.025 μg/mL and 0.01 μg/mL, respectively, and the limits of GHB, GBL and 1,4-BD quantification were 0.1 μg/mL, 0.15 μg/mL and 0.15 μg/mL. The matrix effects of the three compounds ranged from 18.2% to 20.1%, the recoveries were 81.6% to 92.3%, the intra-day and inter-day precision of RSD were less than 10%, and the accuracy was -5.8%-7.0%. The content of GHB in the blood after 7 hours of drinking were higher than that before drinking alcohol (P < 0.05), and the concentration range was 0.71-3.81 μg/mL. Conclusion The content of endogenous GHB in human blood has increased after 7 hours of drinking alcohol, but the concentration was lower than 4 μg/mL, which can provide the data support for the assessment of endogenous and exogenous GHB involved in real cases, enriching the forensic toxicology data of GHB .
2024, 45(5): 178-183.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240527
Abstract:
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is widely used in neurology and epilepsy is one of them. Combined with the electroencephalogram (EEG), fNIRS could record the whole state of seizure, which is beneficial to the understanding of the pathophysiological mechanism of epilepsy. In addition, fNIRS contributes to the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy with the assistance of the epileptic focus localization and the evaluation of lateralization of language function. This paper aims to review the application and research progress of fNIRS in epilepsy so as to provide the reference for researchers.
Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is widely used in neurology and epilepsy is one of them. Combined with the electroencephalogram (EEG), fNIRS could record the whole state of seizure, which is beneficial to the understanding of the pathophysiological mechanism of epilepsy. In addition, fNIRS contributes to the diagnosis and treatment of epilepsy with the assistance of the epileptic focus localization and the evaluation of lateralization of language function. This paper aims to review the application and research progress of fNIRS in epilepsy so as to provide the reference for researchers.
2024, 45(5): 184-189.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240528
Abstract:
Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), as a kind of multi-dimensional health utility index, has been widely used in the health economics evaluation and disease burden evaluation. At present, there are no detailed reports on the calculation methods of QALYs under different research types. This paper mainly discusses the basic principle and process of QALYs calculation, and further summarizes how to select the suitable QALYs estimation method according to the research design in the specific research, so as to provide a reference for researchers, and promote its application in the field of health research in China.
Quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), as a kind of multi-dimensional health utility index, has been widely used in the health economics evaluation and disease burden evaluation. At present, there are no detailed reports on the calculation methods of QALYs under different research types. This paper mainly discusses the basic principle and process of QALYs calculation, and further summarizes how to select the suitable QALYs estimation method according to the research design in the specific research, so as to provide a reference for researchers, and promote its application in the field of health research in China.
2024, 45(5): 190-194.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240529
Abstract:
Objective To investigate and evaluate the humanistic care ability of the nursing interns before and after the intervention of narrative education, and comprehensively understand the practical status and application value of the narrative teaching method in nursing education through the comparison. Methods A total of 180 nursing interns of 2022 from the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected by random sampling method, and narrative education was carried out on them, which combined the online viewing of life-and-death movies and TV works with the offline communication and discussion of life stories around them. The Caring Ability Evaluation Scale (CAI) was used to conduct the self-evaluation before and after the narrative education intervention. Results The scores of the self-evaluation of nursing interns' caring ability before and after the intervention were (177.70±16.77) points and (187.78±17.24) points respectively, and there was a statistically difference (P < 0.05). Conclusion Narrative education has a positive significance in improving the humanistic care ability of nursing interns, and the impact of narrative education on nursing interns is obvious in cognition. The intern’ s gender, education background and family relationship also have a great impact on the humanistic care ability.
2024, 45(5): 195-200.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240530
Abstract:
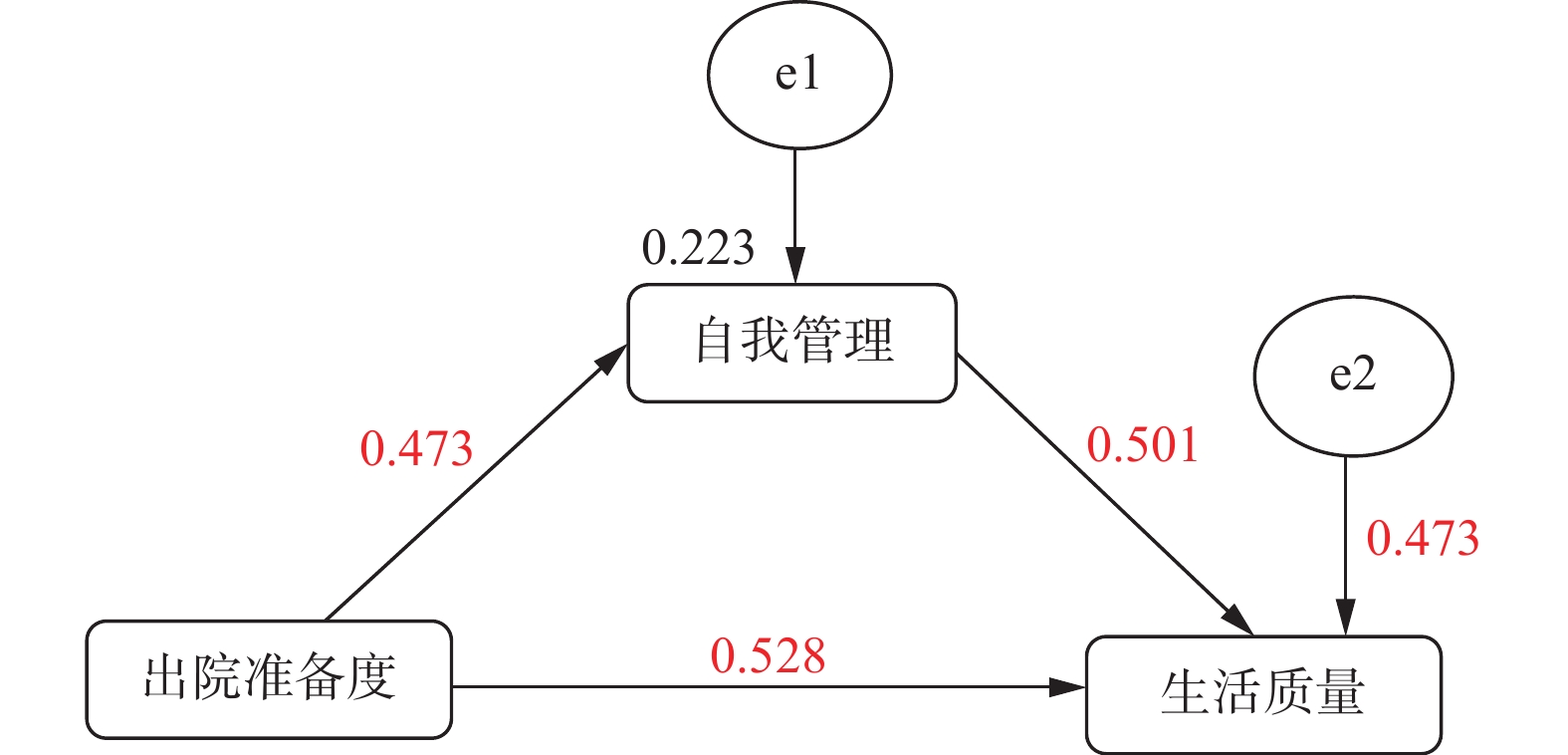
Objective To explore the relationship between the self-management, hospital discharge readiness and the quality of life in patients with type B aortic dissection. Methods A total of 143 patients with type B aortic dissection in a tertiary hospital in Kunming were selected by convenient sampling method. General data questionnaire, aortic dissection self-management scale, discharge readiness scale and quality of life scale were used to investigate the patients. Results The scores of discharge readiness, self-management and quality of life of patients with type B aortic dissection were (78.55±6.6), (117.68±7.39) and (64.53±3.02) respectively. There were correlations among the discharge readiness, self-management and quality of life in patients with type B aortic dissection (P < 0.05). The direct effect of discharge readiness on the quality of life was 0.528, the indirect effect was 0.237, the total effect was 0.765, and the mediating effect accounted for 30.98% of the total effect. Self-management played a partial mediating role between the discharge readiness and the quality of life. Conclusion There is still room for the improvement in discharge readiness, self-management ability and quality of life in patients with type B aortic dissection. The self-management ability of patients with type B aortic dissection plays a partial mediating role between the discharge readiness and the quality of life. In order to improve the quality of life of patients, the two aspects of discharge readiness and self-management can be improved.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS