Metformin Inhibits high Glucose-induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Proliferation by Promoting Autophagy via AMPK/PPAR-γ
-
摘要:
目的 探讨二甲双胍(Metformin)对高糖培养的小鼠主动脉血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cell,VSMCs)自噬、细胞增殖的影响及其调控机制。 方法 用Western blot检测不同处理组微管相关蛋白轻链-3-Ⅱ(LC3-Ⅱ),Becline-1蛋白水平变化,透射电镜观察各处理组VSMCs自噬小体水平;用Western blot检测不同处理组p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γ蛋白表达水平;用EDU法检测不同处理组VSMCs增殖情况。 结果 二甲双胍、雷帕霉素逆转高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用(P < 0.001);Compound C、GW9662增加高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用(P < 0.05);二甲双胍逆转高糖对AMPK/PPAR-γ通路的负调控(P < 0.01);二甲双胍、雷帕霉素抑制高糖促进的VSMCs增殖(P < 0.001),Compound C、GW9662逆转二甲双胍抑制高糖促VSMCs增殖的作用(P < 0.05)。 结论 高糖促进VSMCs增殖可能是自噬调节相关的,二甲双胍可通过激活AMPK/PPAR-γ通路上调VSMCs自噬水平,抑制高糖促进的VSMCs异常增殖。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and regulatory mechanism of metformin on autophagy and cell proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) cultured in high glucose in mice aortic. Methods Western blot was used to detect the changes in microtubule-associated protein light chain 3-II (LC3-II) and Beclin-1 protein levels in different treatment groups. Transmission electron microscope was used to observe the the level of autophagosomes in VSMCs of each treatment group. Western blot was used to detect the expression levels of p-AMPK/AMPK and PPAR-γ proteins in different treatment groups. The EDU method was used to detect the proliferation of VSMCs in different treatment groups. Results Metformin and rapamycin reversed the inhibitory effect of high glucose on VSMC autophagy (P < 0.001). Compound C and GW9662 enhanced the inhibitory effect of high glucose on VSMC autophagy (P < 0.05). Metformin reversed the negative regulation of high glucose on the AMPK/PPAR-γ pathway (P < 0.01). Metformin and rapamycin inhibited high glucose-induced VSMC proliferation (P < 0.001), and Compound C and GW9662 reversed the inhibitory effect of metformin on high glucose-induced VSMC proliferation (P < 0.05). Conclusion High glucose promotes the proliferation of VSMCs, which may be regulated by autophagy. Metformin can upregulate autophagy levels in VSMCs by activating the AMPK/PPAR-γ pathway, thereby inhibiting the abnormal proliferation of VSMCs induced by high sugar. -
Key words:
- Metformin /
- High glucose /
- Autophagy /
- Vascular smooth muscle cell /
- Proliferation
-
糖尿病显著增加了心血管疾病的发病率和病死率,深入研究糖尿病合并冠心病的分子机制并在此基础上寻找新的治疗靶点,对防治糖尿病合并血管病变具有重要的意义。糖尿病高糖环境下血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cell,VSMCs)的异常增殖、迁移及表型转换等[1- 2],可促进高血压、脑卒中、冠状动脉粥样硬化性心脏病等心脑血管疾病的发生发展。高血糖是最常见的糖尿病合并慢性血管并发症的危险因素之一,其能通过多种机制影响动脉硬化的进展。
自噬即细胞对自身的吞噬作用,指细胞通过形成自噬溶酶体消化自身大分子蛋白及细胞器的降解过程,从而维持细胞稳态[3]。有证据显示自噬可参与多种因素引起的VSMCs增殖[4]、细胞表型转换[5]、细胞内钙离子浓度调节[6],炎性反应、脂质沉积[7]等活动,从而参与动脉硬化的发生发展。目前有关高糖环境下对血管平滑肌细胞自噬的调节以及自噬如何参与调节VSMCs生物功能学的报道甚少。
二甲双胍( Metformin) 是临床上常用降糖药,除了降糖作用以外,其还具有调节血脂、抗炎等多重广泛机制抗动脉粥样硬化的作用[8- 9],其中,二甲双胍通过调节细胞自噬抗动脉粥样硬化的作用也越来越受到重视,如其可通过促进Krueppel样因子2(krueppel-like factor 2,KLF2)介导的自噬抑制泡沫细胞的形成[10],还可通过调节 Runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,Runx2)的自噬降解抑制血管钙化起到抗动脉硬化作用[11]。本文以小鼠血管平滑肌细胞为研究对象,观察自噬是否参与高糖促进VSMCs的增殖,二甲双胍能否通过干预自噬影响高糖促进VSMCs增殖作用,进一步探讨自噬在高糖对VSMCs的作用及可能治疗方向,为临床糖尿病心血管并发症的防治提供新的手段及依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
小鼠主动脉平滑肌细胞(北纳生物,批号:BNCC338213),高糖型DMEM培养基(葡萄糖浓度25 mmol/L)、低糖型DMEM培养基(葡萄糖浓度5.6 mmol/L)( HyClone ,USA),15%胎牛血清( Gibco,USA) ,0.25% EDTA胰蛋白酶(Sigma,USA),PVDF膜(广锐生物,中国),细胞裂解液(碧云天生物,中国),EDU检测试剂盒(碧云天生物,C0078S),单克隆抗体:LC3B单抗(Abcam,ab51520),Becline-1(Proteintech,USA),p-AMPK/AMPK(Proteintech,USA),PPAR-γ(Proteintech,USA),β-actin(Proteintech,USA),二甲双胍( Medchemexpress,USA),雷帕霉素(Sigma,USA),Compound C(Abcam,USA),GW9662(Abcam,USA),二抗IgG-HRP(碧云天生物,中国),BCA法蛋白定量检测试剂盒(碧云天生物,中国), ECL显色试剂盒(碧云天生物,中国)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 VSMCs培养及分组
将小鼠主动脉血管平滑肌细胞重悬于15%胎牛血清、1% 双抗的DMEM/F12 完全培养基中。轻柔操作重悬细胞,转入25 cm2 细胞培养瓶中,置于 37 ℃、5% CO2 培养箱中进行培养,2~3 d更换1次培养液,细胞融合至80%~90%用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化传代,按1∶2~1∶4比例传代,共传 3~5代,选处于对数生长期的的细胞分为不同处理组进行相应处理。
1.2.2 细胞增殖实验
EDU染色法检测小鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖,接种细胞于24孔板培养24 h 并同步化细胞,按不同处理分为8组:对照组、高糖组、二甲双胍组、高糖+二甲双胍组、高糖+雷帕霉素组、高糖+二甲双胍组+Compound C组、高糖+二甲双胍组+GW9662组、高糖+二甲双胍组+雷帕霉素组。二甲双胍浓度为10 mmol/L,作用24 h,雷帕霉素浓度为100 nmol/L,Compound C浓度为10 μmol/L,GW9662浓度为10 μmol/L,作用24 h。按1000∶1的比例稀释EDU溶液,细胞干预结束后加入200 μL 浓度10 μmol/L的EDU培养液孵育2 h时,余按 EdU细胞增殖检测试剂盒说明书继续操作,荧光显微镜下每组随机选5个视野拍照观察。
1.2.3 Western blot检测蛋白表达
Western blot检测LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-I、Becline-1、p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γ蛋白表达,将各组细胞分别处理,每个处理组3个样本,加入100 μL RIPA裂解液,30 min;4℃,12,000 r/min离心5 min;取上清,BCA法定量检测蛋白,取等量蛋白于10% SDS-PAGE 进行电泳分离、转膜。5%的脱脂奶粉室温下摇床封闭,加入一抗以1∶1000稀释,4℃孵育过夜;加入二抗1∶5000稀释,室温孵育2 h,漂洗,配制ECL显影剂于凝胶显影仪上曝光显影,用Bio-Rad Quantity One软件定量分析。
1.2.4 透射电子显微镜观察不同处理组细胞自噬体
收集对照组、高糖组、高糖+二甲双胍组血管平滑肌细胞,使用2.5%戊二醛在4 ℃过夜,然后用ddH2O漂洗,锇酸固定1 h,乙醇及丙酮梯度脱水;再经渗透、树脂包埋、聚合后,制备70 nm厚度的切片;使用醋酸铀-柠檬酸铅染色,MORADA G2电镜下观察3组平滑肌细胞自噬小体的数量并摄片。
1.3 统计学处理
用SPSS 13.0进行统计分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(
$\bar x \pm s $ )表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,组间两两比较采取Tukey法,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。2. 结果
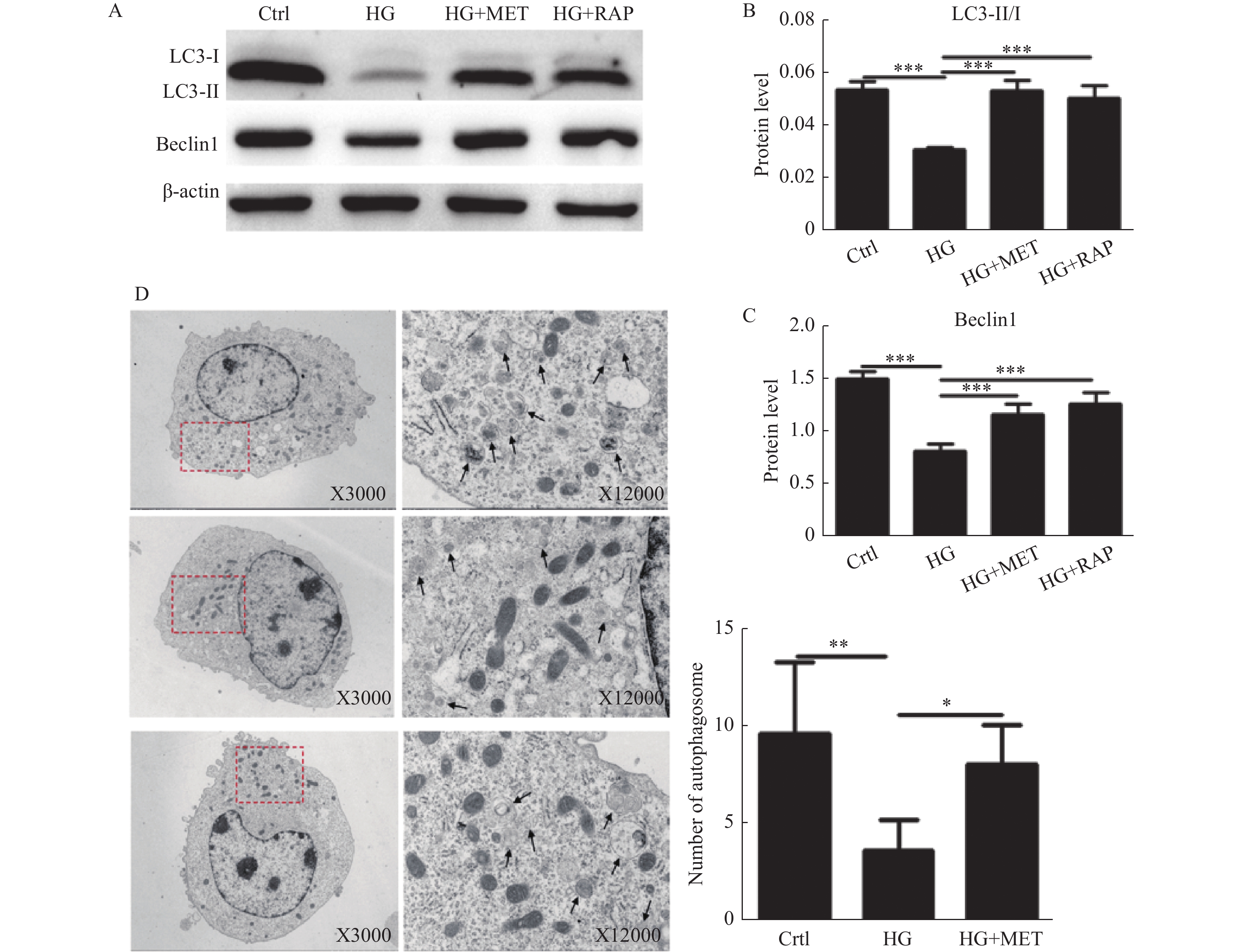
2.1 二甲双胍、雷帕霉素逆转高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用
将小鼠VSMCs分为对照组(5.6 mmol/L葡萄糖)、高糖组(25 mmol/L葡萄糖)、高糖+二甲双胍(10 mmol/L)、高糖+雷帕霉素(100 nmol/L)四组,观察不同组VSMCs自噬蛋白表达情况,结果显示高糖培养下VSMCs LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-I、Becline-1蛋白较对照组表达水平降低(P < 0.001),提示高糖培养抑制VSMCs自噬水平,而二甲双胍及自噬促进剂雷帕霉素可促进高糖培养下的VSMCsLC3-Ⅱ/LC3-I、Becline-1表达水平升高(P < 0.001),提示二甲双胍、雷帕霉素可作为自噬诱导剂,促进VSMCs发生自噬,并逆转高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用。电镜显示高糖培养下VSMCs自噬小体计数较对照组降低,而二甲双胍可显著增加高糖培养下VSMCs自噬小体的数量,证实二甲双胍可逆转高糖培养的VSMCs受抑制的自噬,见图1。
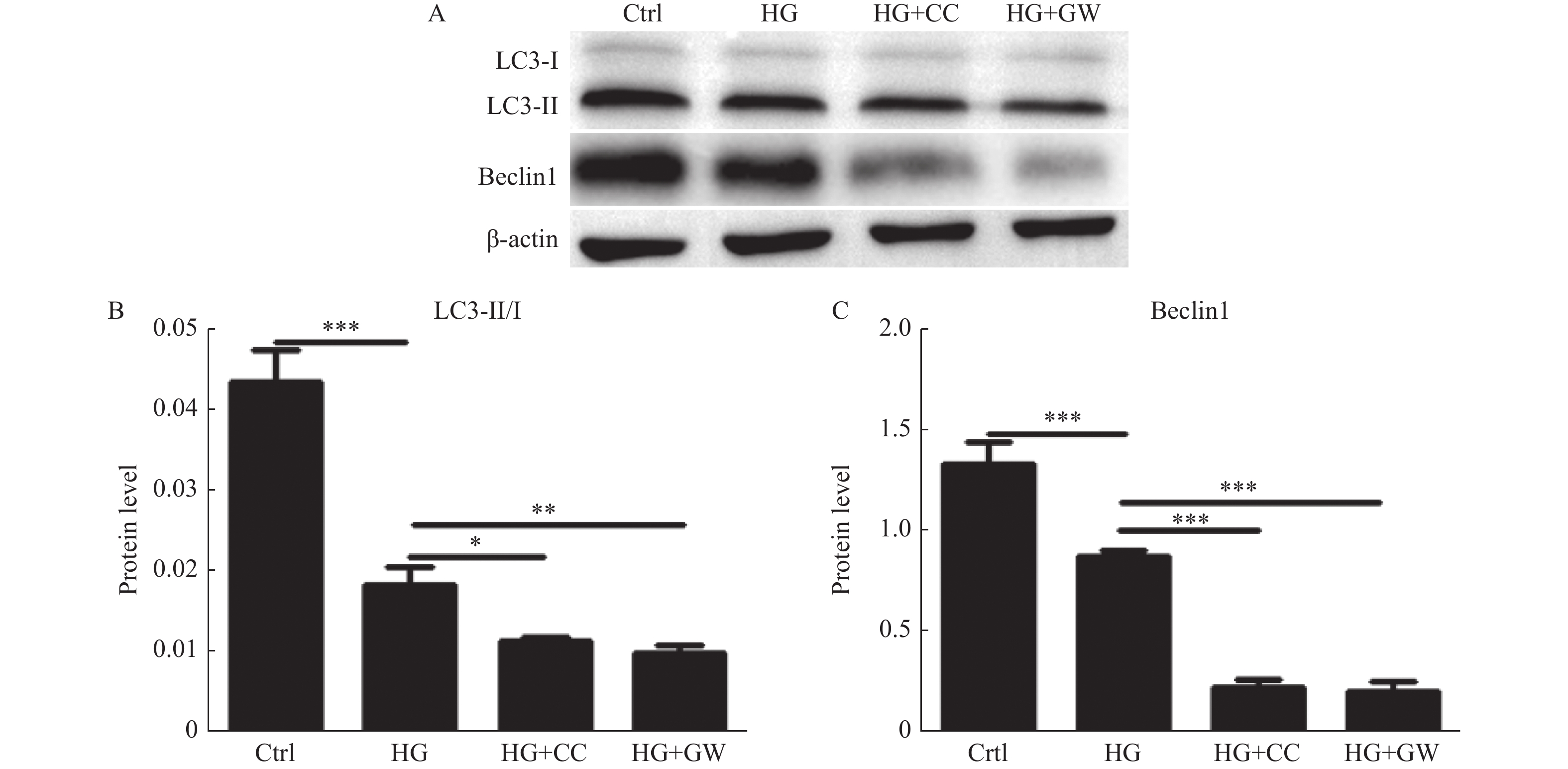
2.2 AMPK、PPAR-γ抑制剂增加高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用
将小鼠VSMCs分为对照组、高糖组、AMPK抑制剂Compound C(10 μmol/L)+高糖组,PPAR-γ抑制剂GW9662(10 μmol/L)+高糖组共4个处理组,用Western blot检测自噬蛋白LC3及Becline-1表达水平,Western Blot结果显高糖抑制VSMCs LC3-Ⅱ/LC3-Ⅰ、Becline-1表达(P < 0.001),而AMPK抑制剂、PPAR-γ抑制剂可进一步抑制高糖培养下VSMCs相关自噬蛋白的表达(P < 0.05),见图2。
2.3 二甲双胍逆转高糖对AMPK/PPAR-γ通路的负调控
将小鼠VSMCs分为对照组、高糖组、MET+高糖组,Compound C+高糖组4个处理组,检测不同组p-AMPK/AMPK表达情况,结果显高糖抑制VSMCs p-AMPK/AMPK表达(P < 0.001),二甲双胍可逆转高糖抑制AMPK通路激活(P < 0.001),而使用AMPK抑制剂后进一步增强高糖抑制AMPK通路激活的作用(P < 0.01)。用高糖、MET+高糖,GW9662+高糖预处理,检测不同组PPAR-γ表达情况,结果显高糖抑制VSMCs PPAR-γ表达(P < 0.001),二甲双胍可逆转其作用(P < 0.01),而使用PPAR-γ抑制剂后进一步增强高糖抑制 PPAR-γ表达的作用(P < 0.05),见图3。
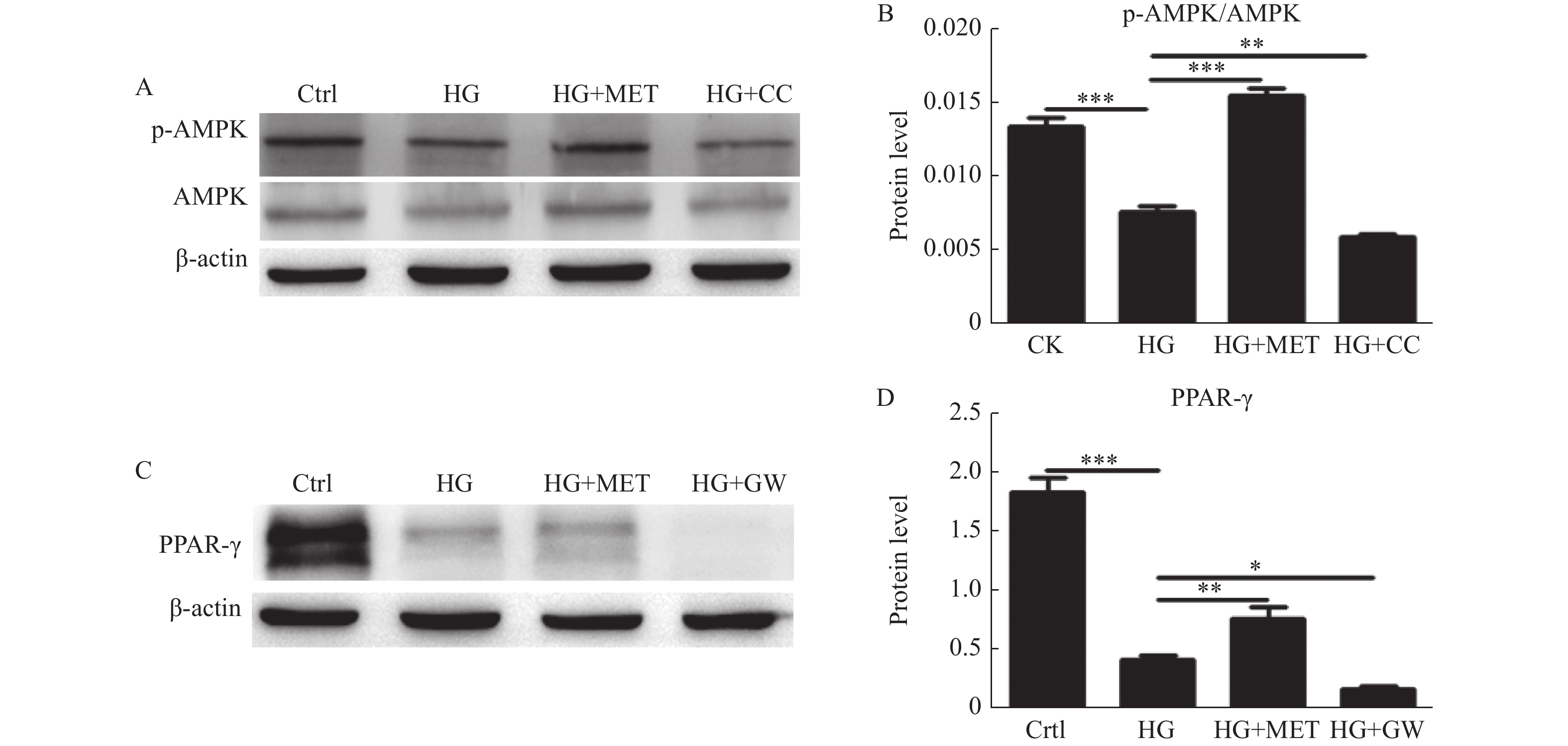 图 3 二甲双胍对高糖培养下VSMCs p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γ表达的影响A:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+CC组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达;B:定量分析不同处理组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达水平;C:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+GW组PPAR-γ的表达;D:定量分析不同处理组PPAR-γ的表达水平。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。Figure 3. Effect of metformin and high glucose on p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γexpression of VSMCs
图 3 二甲双胍对高糖培养下VSMCs p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γ表达的影响A:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+CC组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达;B:定量分析不同处理组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达水平;C:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+GW组PPAR-γ的表达;D:定量分析不同处理组PPAR-γ的表达水平。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。Figure 3. Effect of metformin and high glucose on p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γexpression of VSMCs2.4 二甲双胍抑制高糖促进的VSMCs增殖
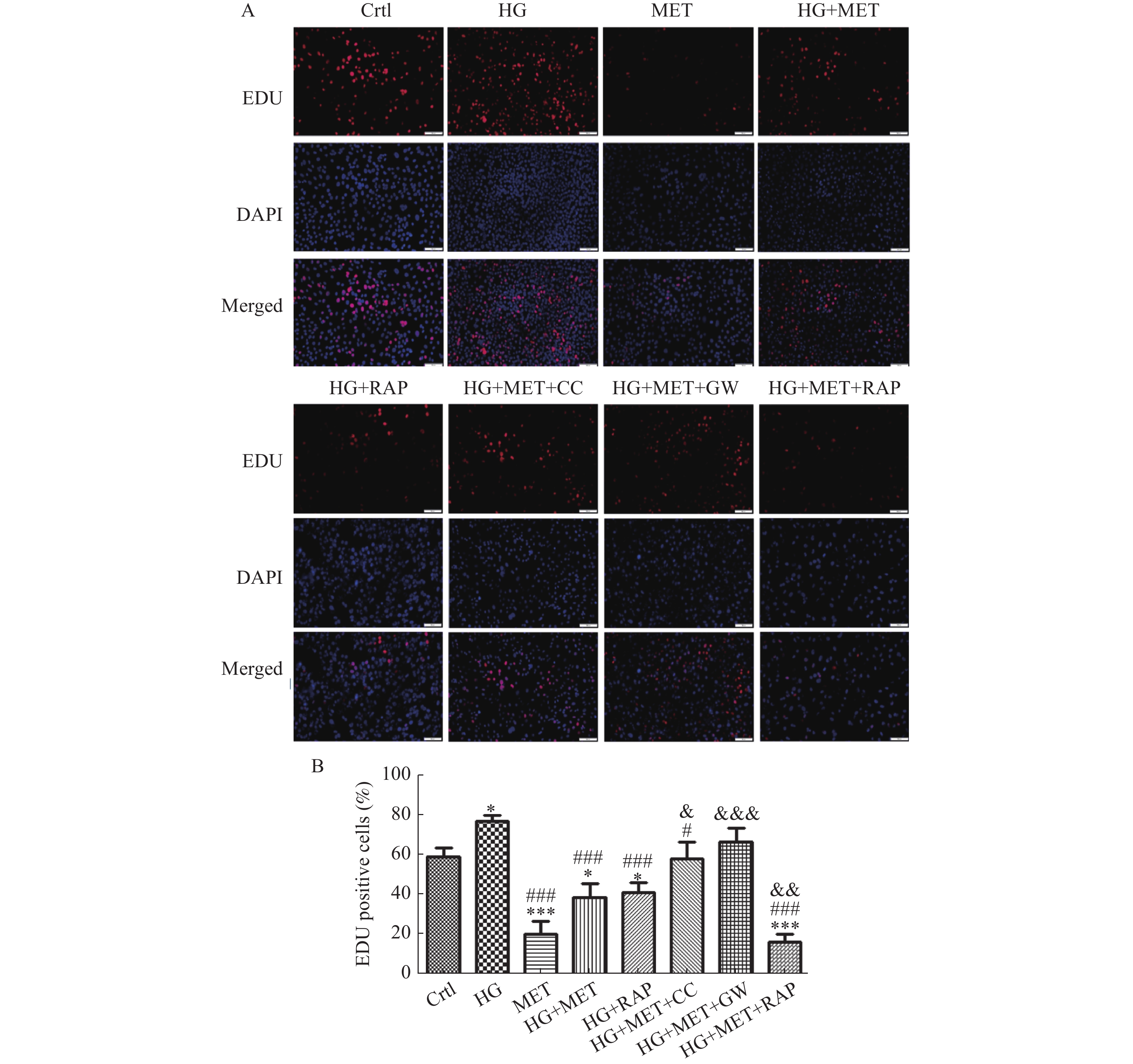
将小鼠VSMCs分为对照组、高糖组、二甲双胍组、高糖+二甲双胍组、高糖+雷帕霉素组、高糖+二甲双胍组+Compound C组、高糖+二甲双胍组+GW9662组、高糖+二甲双胍组+雷帕霉素组8个处理组,EDU染色细胞检测不同组细胞增殖情况,结果显示高糖促进VSMCs增殖(P < 0.05),MET及RAP抑制高糖促进的VSMCs增殖作用,且MET可进一步增强RAP抑制高糖促进的VSMCs增殖作用(P < 0.001)。而使用AMPK抑制剂Compound C及PPAR-γ抑制剂GW9662后可逆转MET抑制HG促进VSMCs增殖的作用(P < 0.05),见图4。
3. 讨论
高血糖是最常见的糖尿病合并慢性血管并发症的危险因素之一,能通过多种机制影响动脉硬化的进展,如可能促进糖基化终末产物的形成,进一步促进炎症反应诱发VSMCs增殖[12-13],脂质代谢紊乱[14],影响各种生长因子的分泌及表达,氧化应激等[15]。多项研究发现高糖还可通过调节自噬参与多种心血管疾病病理生理。如Liu等[16]报道高糖可通过AMPK通路介导血管内皮细胞自噬促进其凋亡,而Xu等[17]报道高糖抑制心肌细胞自噬并促进其凋亡,可能导致糖尿病心肌疾病的发生。研究证实VSMCs的自噬可通过多种形式参与动脉粥样硬化的进程发展,本课题组前期工作也发现自噬参与血管紧张素II诱导的VSMCs细胞表型转换[5],但高糖是否通过自噬参与VSMCs增殖及其相关机制尚不明确。
二甲双胍作为目前临床最常用的降糖用药之一,既往研究显示其还有改善内皮功能[18]、改善胰岛素抵抗[19],减少平滑肌细胞向泡沫细胞转换[20],抗氧化应激等[21]抗动脉粥样硬化作用。近年来有研究显示二甲双胍通过调节自噬抗动脉粥样硬化,如其可通过调节长链非编码RNA牛磺酸上调基因1诱导自噬,抑制血管壁细胞增殖从而起到抗动脉粥样硬化作用[22],还可通过上调Kruppel样因子2介导的自噬抑制APOE基因敲除的小鼠动脉硬化进程及斑块易损性[10]。本研究通过检测LC3、Becline-1等自噬相关蛋白及电镜检测自噬小体等方法发现高糖培养显著抑制VSMCs自噬水平,使用二甲双胍、自噬诱导剂雷帕霉素促进自噬水平并抑制高糖诱导的VSMCs增殖,笔者推测高糖培养可通过抑制自噬调控促进VSMCs增殖。与自噬激动剂雷帕霉素一样,二甲双胍亦可通过促进自噬并抑制高糖培养的VSMCs增殖。本研究还发现雷帕霉素促进自噬并抑制高糖促进VSMCs增殖的作用,二甲双胍联合雷帕霉素可进一步增强其抑制VSMCs增殖的作用,见图4,提示不同机制自噬激活剂的联合可进一步增强抑制高糖促VSMCs增殖的作用。
AMPK/PPAR-γ通路广泛参与细胞代谢和糖代谢过程,也参与调节自噬[23-24],本研究证实高糖环境下可抑制VSMCs AMPK/PPAR-γ通路的激活,二甲双胍则可激活APMK/PPAR-γ通路,并逆转高糖抑制AMPK/PPAR-γ通路的作用。是否AMPK/PPAR-γ通路参与高糖抑制的VSMCs自噬,为进一步证实自噬参与二甲双胍抑制的VSMCs增殖并探究其机制,笔者使用PPAR-γ抑制剂GW9662及AMPK抑制剂Compound C后发现其可进一步增强高糖抑制VSMCs自噬的作用,见图2,并削弱二甲双胍抑制细胞增殖的作用,提示自噬可能参与高糖诱导的VSMCs增殖,高糖可能通过抑制AMPK/PPAR-γ通路抑制VSMCs自噬,从而进一步促进VSMCs增殖,这可能是自噬参与的机制之一。
综上所述,本实验发现高糖环境下促进VSMCs增殖可能是自噬依赖性的,高糖可通过抑制VSMCs自噬促进其增殖,而使用而二甲双胍可通过激活AMPK/PPAR-γ通路上调VSMCs自噬水平,抑制高糖促进的VSMCs异常增殖,这为糖尿病合并血管病变提供了一个新的治疗方向。
-
图 3 二甲双胍对高糖培养下VSMCs p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γ表达的影响
A:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+CC组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达;B:定量分析不同处理组p-AMPK/AMPK的表达水平;C:Western blot检测对照组、HG组、HG+MET组及HG+GW组PPAR-γ的表达;D:定量分析不同处理组PPAR-γ的表达水平。*P < 0.05,**P < 0.01,***P < 0.001。
Figure 3. Effect of metformin and high glucose on p-AMPK/AMPK、PPAR-γexpression of VSMCs
-
[1] Chiong M,Morales P,Torres G,et al. Influence of glucose metabolism on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation[J]. Vasa,2013,42(1):8-16. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000243 [2] Yang M,Fang J,Liu Q,et al. Role of ROS-TRPM7-ERK1/2 axis in high concentration glucose-mediated proliferation and phenotype switching of rat aortic vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2017,494(3-4):526-533. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.10.122 [3] Marino G,Niso-Santano M,Baehrecke E H,et al. Self-consumption: The interplay of autophagy and apoptosis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2014,15(2):81-94. doi: 10.1038/nrm3735 [4] Wu H,Song A,Hu W,et al. The anti-atherosclerotic effect of paeonol against vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by up-regulation of autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology,2018,8:948. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00948 [5] 张紫微,杨丽霞,吕晋琳,等. 血管紧张素Ⅱ诱发自噬对血管平滑肌细胞表型转换的调控作用[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志,2017,25(5):452-456. [6] Phadwal K,Feng D,Zhu D,et al. Autophagy as a novel therapeutic target in vascular calcification[J]. Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2020,206:107430. [7] Peng S,Xu L,Che X,et al. Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory response,attenuates lipid deposition,and improves the stability of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques by modulating autophagy[J]. Frontiers in Ppharmacology,2018,9:438. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00438 [8] Poznyak A V,Litvinova L,Poggio P,et al. From diabetes to atherosclerosis: Potential of metformin for management of cardiovascular disease[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2022,23(17):9738. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179738 [9] Yang Q,Yuan H,Chen M,et al. Metformin ameliorates the progression of atherosclerosis via suppressing macrophage infiltration and inflammatory responses in rabbits[J]. Life Sciences,2018,198:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.017 [10] Wu H,Feng K,Zhang C,et al. Metformin attenuates atherosclerosis and plaque vulnerability by upregulating KLF2-mediated autophagy in apoE−/-mice[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2021,557:334-341. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.04.029 [11] Phadwal K,Koo E,Jones R A,et al. Metformin protects against vascular calcification through the selective degradation of Runx2 by the p62 autophagy receptor[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2022,237(11):4303-4316. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30887 [12] Yang B,Gao X,Sun Y,et al. Dihydroartemisinin alleviates high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and inflammation by depressing the miR-376b-3p/KLF15 pathway[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2020,530(3):574-580. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.095 [13] Yuan T,Yang T,Chen H,et al. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis[J]. Redox Biology,2019,20:247-260. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.09.025 [14] Tiong Y L,Ng K Y,Koh R Y,et al. Melatonin inhibits high glucose-induced ox-LDL/LDL expression and apoptosis in human umbilical endothelial cells[J]. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation,2020,41(4):20200009. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2020-0009 [15] Zhao Y,Lu N,Zhang Y,et al. High glucose induced rat aorta vascular smooth muscle cell oxidative injury: Involvement of protein tyrosine nitration[J]. Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry,2011,67(4):539-549. doi: 10.1007/s13105-011-0099-x [16] Liu J,Wu J,Sun A,et al. Hydrogen sulfide decreases high glucose/palmitate-induced autophagy in endothelial cells by the Nrf2-ROS-AMPK signaling pathway[J]. Cell & Bioscience,2016,6(1):1-17. [17] Xu K,Liu X,Ke Z,et al. Resveratrol modulates apoptosis and autophagy induced by high glucose and palmitate in cardiac cells[J]. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry,2018,46(5):2031-2040. doi: 10.1159/000489442 [18] De Jager J,Kooy A,Schalkwijk C,et al. Long‐term effects of metformin on endothelial function in type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Internal Medicine,2014,275(1):59-70. doi: 10.1111/joim.12128 [19] Van der Aa M P,Elst M,Van De Garde E,et al. Long-term treatment with metformin in obese,insulin-resistant adolescents: Results of a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial[J]. Nutrition & Diabetes,2016,6(8):e228. [20] He X,Chen X,Wang L,et al. Metformin ameliorates Ox-LDL-induced foam cell formation in raw264.7 cells by promoting ABCG-1 mediated cholesterol efflux[J]. Life Sciences,2019,216:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.024 [21] Gopoju R,Panangipalli S,Kotamraju S. Metformin treatment prevents SREBP2-mediated cholesterol uptake and improves lipid homeostasis during oxidative stress-induced atherosclerosis[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,2018,118:85-97. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.02.031 [22] You G,Long X,Song F,et al. Metformin activates the AMPK-mTOR pathway by modulating lncRNA TUG1 to induce autophagy and inhibit atherosclerosis[J]. Drug Design,Development and Therapy,2020,14:457. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S233932 [23] Faghfouri A H,Khajebishak Y,Payahoo L,et al. PPAR-gamma agonists: Potential modulators of autophagy in obesity[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2021,912:174562. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174562 [24] Wang H,Wang A,Wang X,et al. AMPK/PPAR-γ/NF-κB axis participates in ROS-mediated apoptosis and autophagy caused by cadmium in pig liver[J]. Environmental Pollution,2022,294:118659. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.118659 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 许征国,于小伟,仝欣,靳永杰,方美花. miRNA-21对PI3K/Akt信号通路的调控及其对非小细胞肺癌预后的影响. 甘肃医药. 2023(04): 301-303 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 张轩斌,孙潺,崔艳红. microRNA-21与PDCD5表达交互作用及其对老年非小细胞肺癌患者化疗效果的评估. 中国老年学杂志. 2023(21): 5178-5181 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 李静,张宁. 非小细胞肺癌患者小分子靶向药物临床使用分析. 深圳中西医结合杂志. 2022(02): 132-134 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 肖旭阳,杜天宇,周玄,王立坤. 不同剂量射线对非小细胞肺癌患者mTOR信号通路的影响. 锦州医科大学学报. 2021(06): 19-22 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:

