Effect of miR-34a on Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Stem Cells
-
摘要:
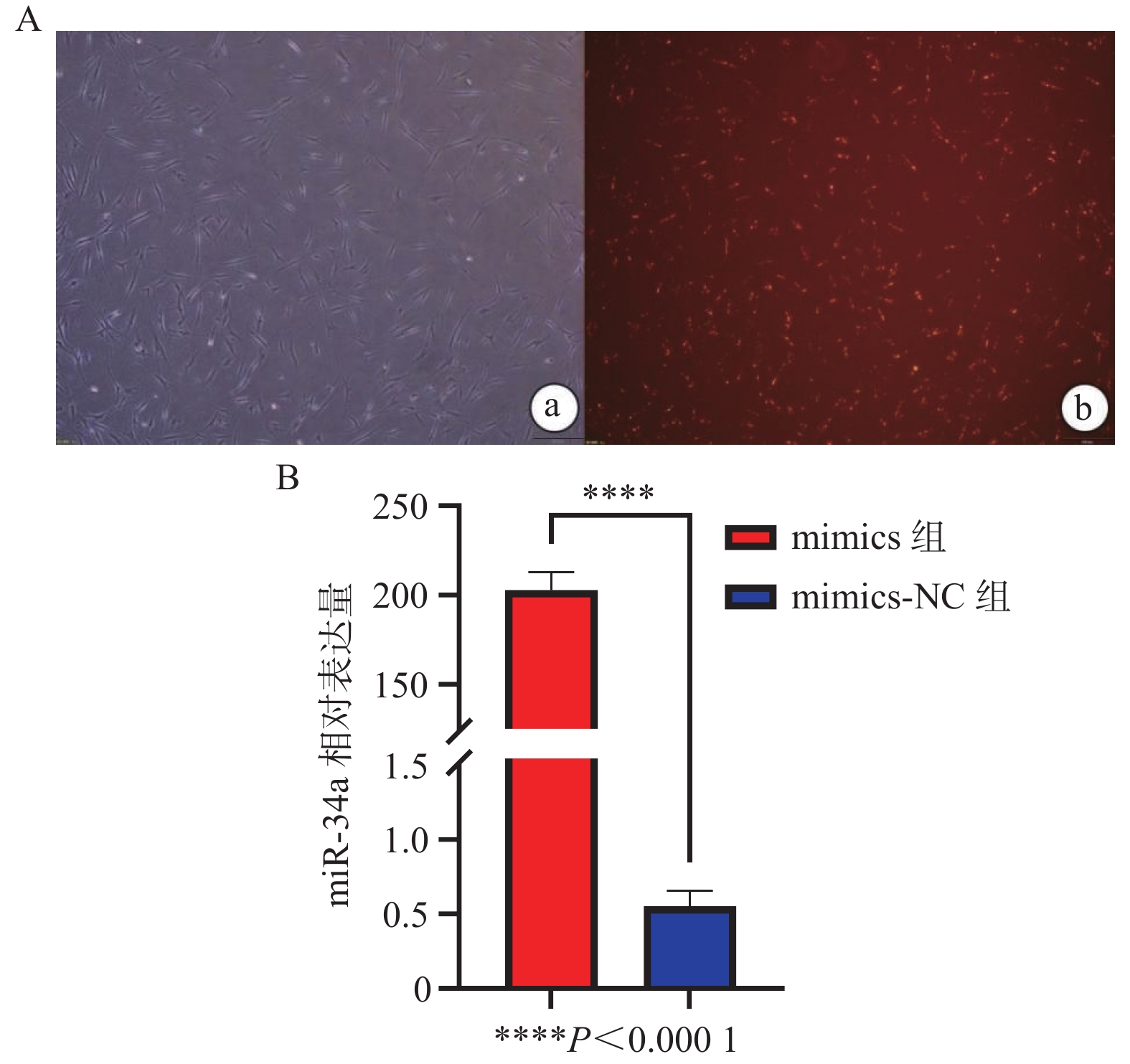
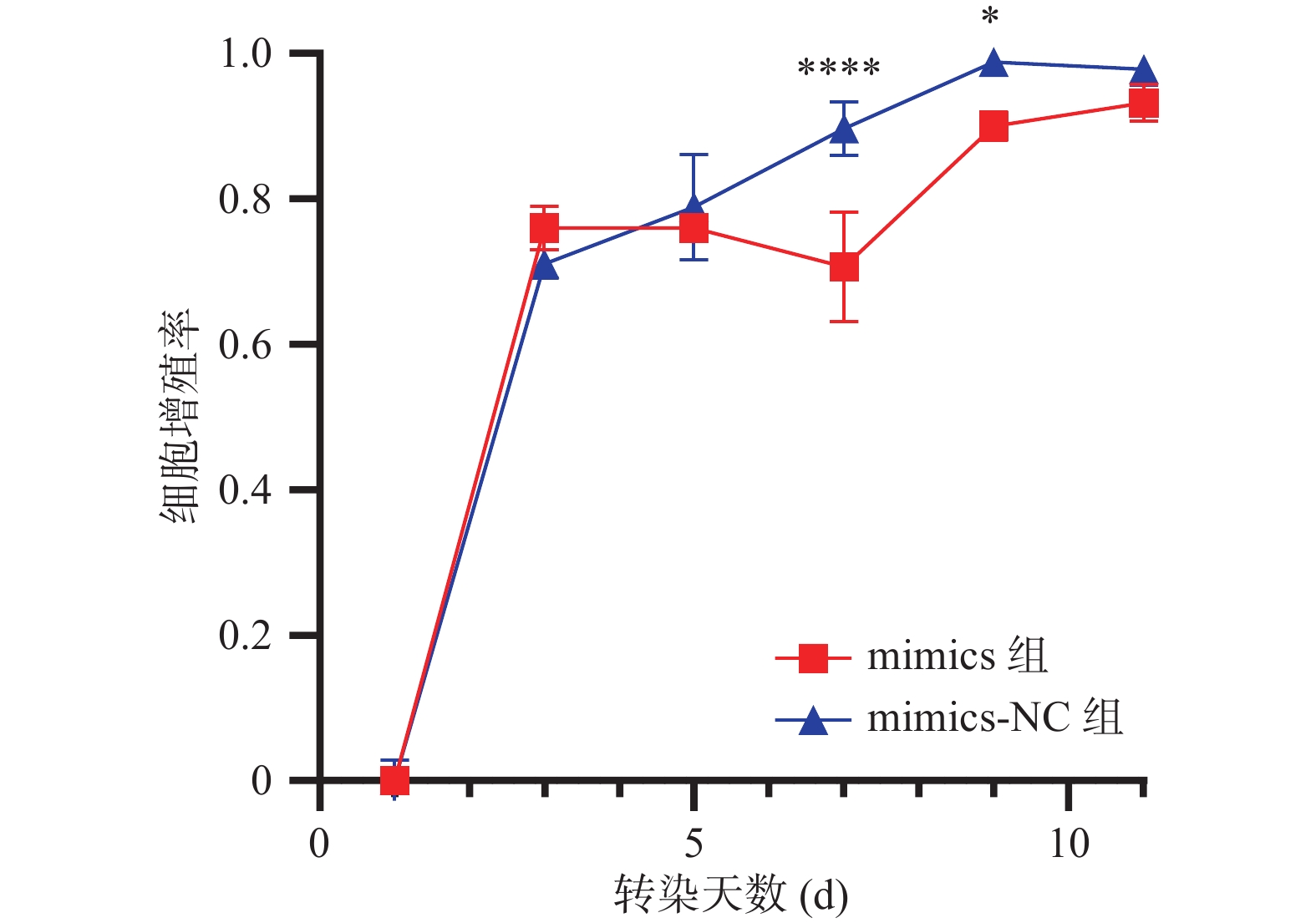
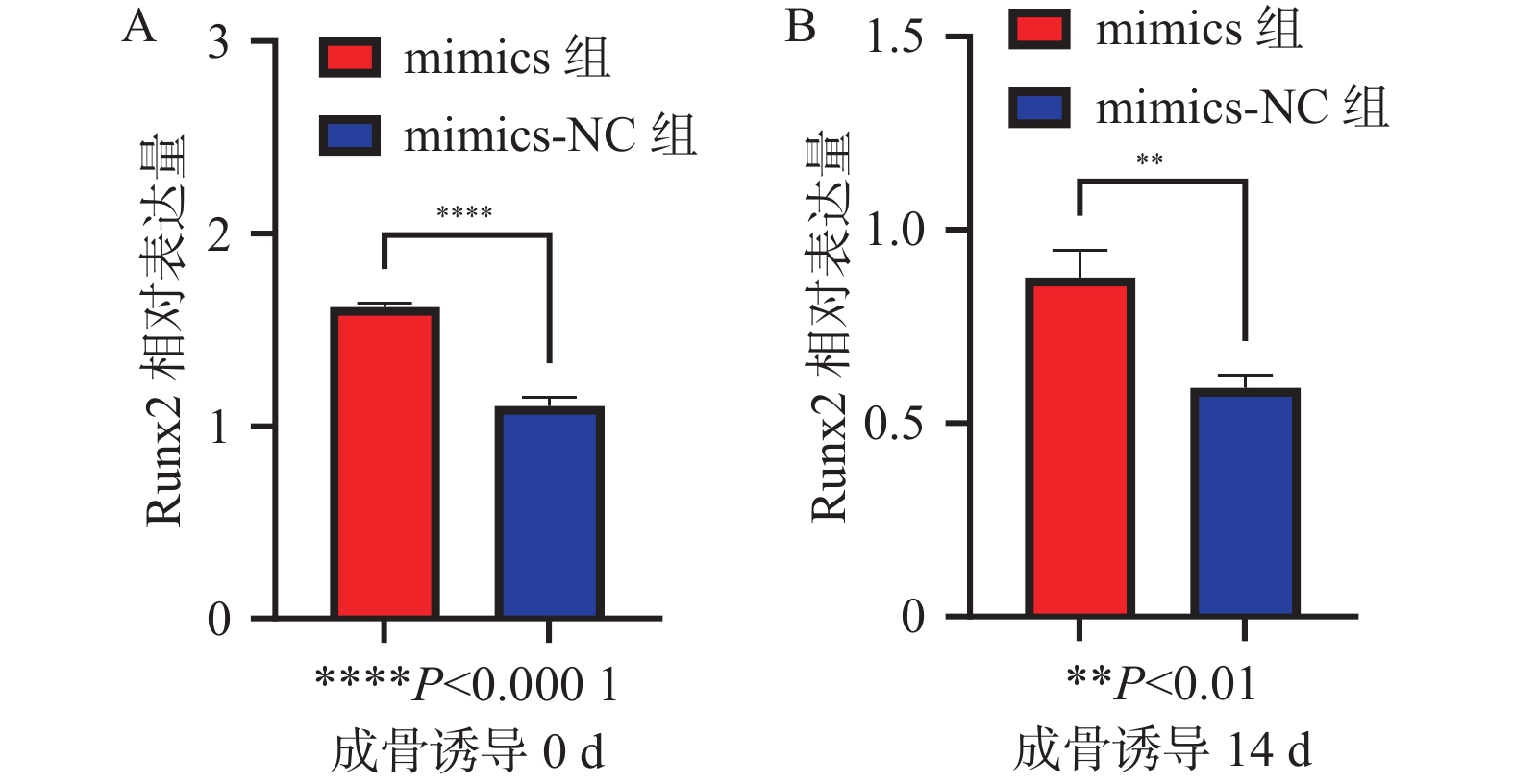
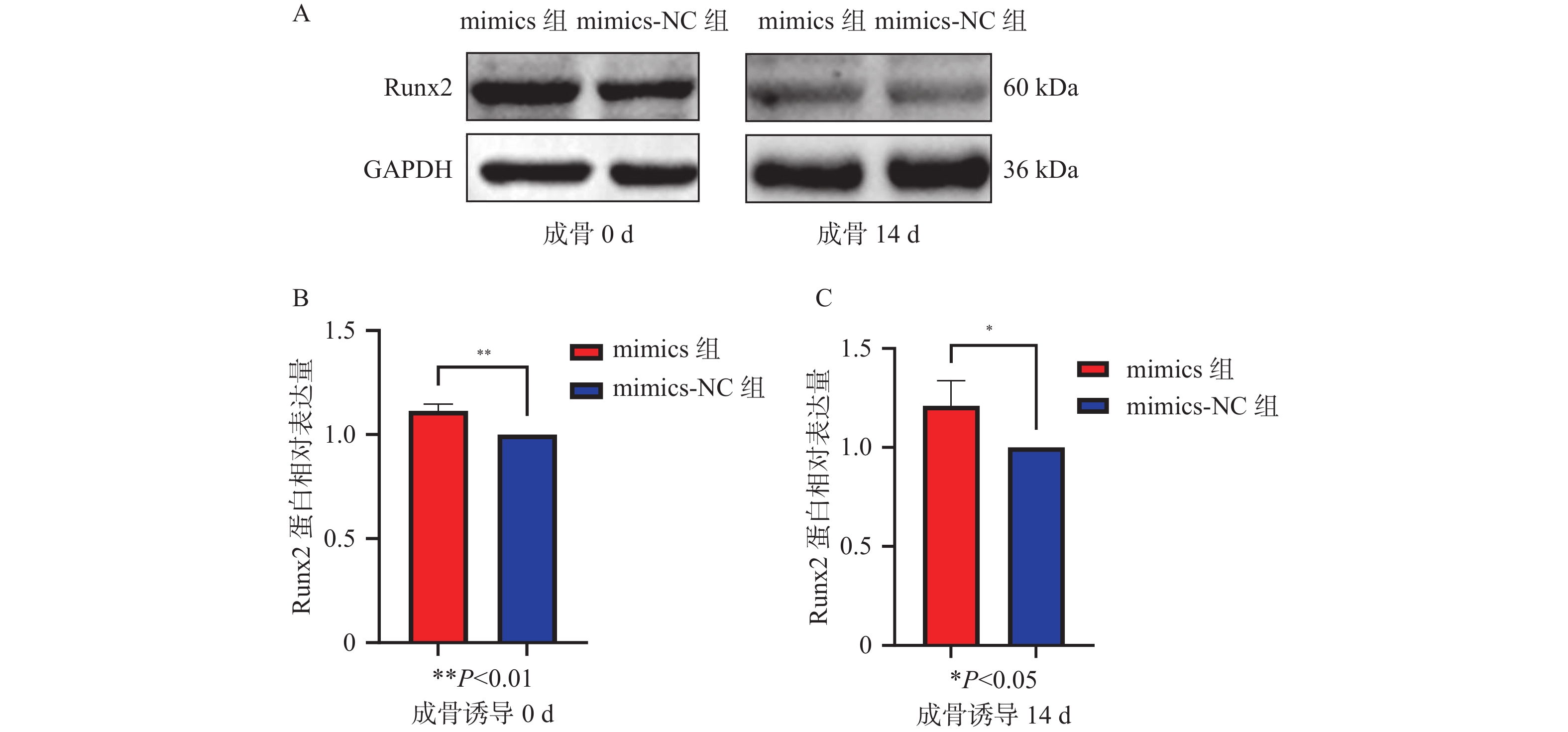
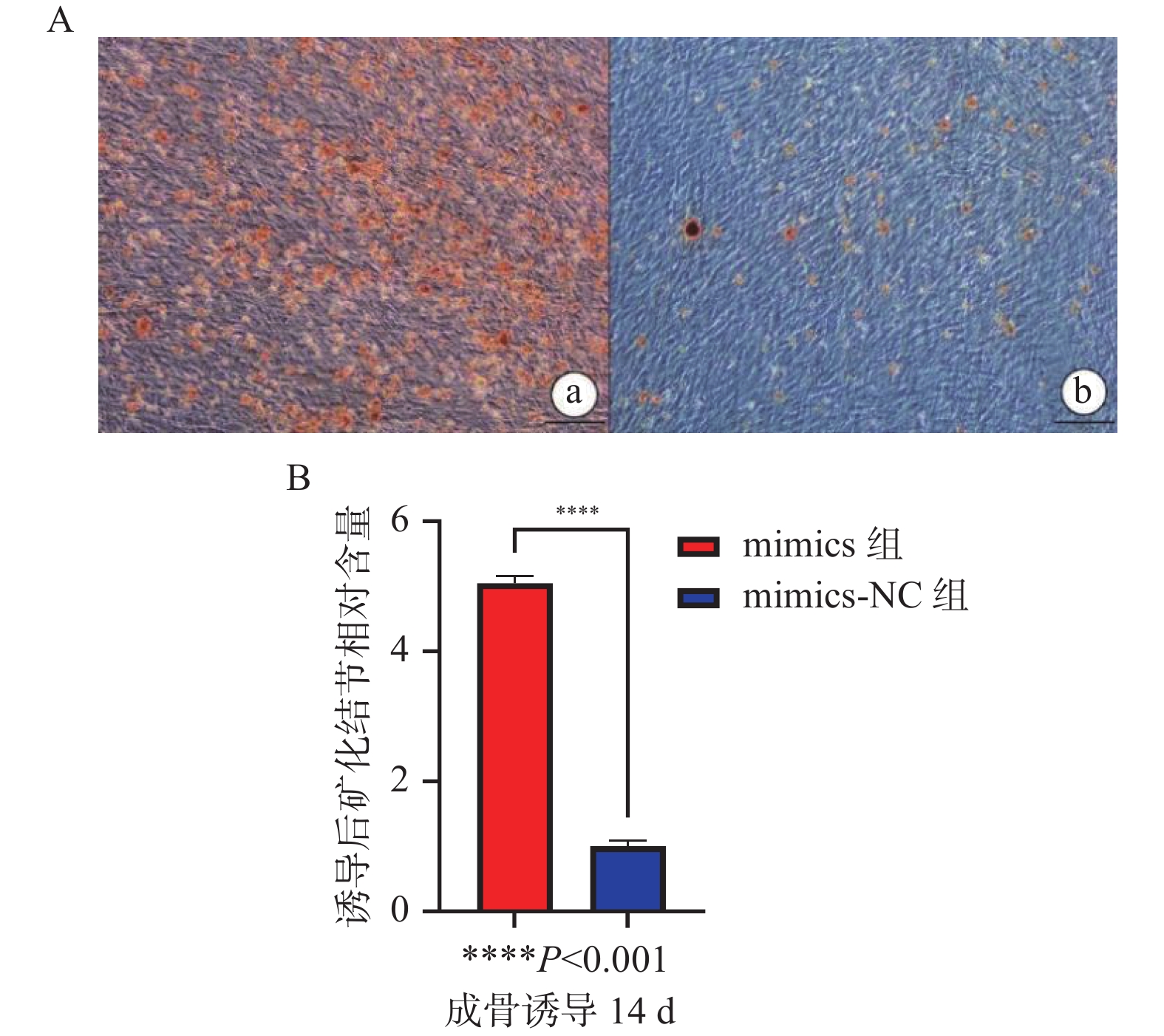
目的 探讨miR-34a对人牙周膜干细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响。 方法 体外分离培养人牙周膜干细胞(hPDLSCs),构建miR-34a的模拟物转染至hPDLSCs中,实验分组为mimics组(miR-34a过表达组)、mimics-NC组(空载组)。实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)法检验转染效率、CCK-8检测hPDLSCs在转染后的增殖能力。诱导转染miR-34a的hPDLSCs成骨分化,收集成骨分化后第0天、14 d hPDLSCs,qRT-PCR法检测成骨标志Runt相关转录因子2(Runx2)的表达水平、Western blot法检测Runx2相关蛋白的表达水平、茜素红染色显示矿化结节形成情况。 结果 mimics组的miR-34a表达水平显著高于mimics-NC组(P < 0.05)。第1~5天,mimics组、mimics-NC组的增殖率差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);第5~11天,mimics组增殖率明显低于mimics-NC组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。转染miR-34a的hPDLSCs经过成骨诱导后,在第0天和第14天mimics组Runx2的mRNA表达水平均高于mimics-NC组(P < 0.05),mimics组Runx2蛋白表达水平也高于mimics-NC组(P < 0.05),成骨诱导14 d后 mimics组矿化结节多于mimics-NC组。 结论 在体外条件下,miR-34a抑制hPDLSCs的增殖活性,促进人牙周膜干细胞的成骨分化。 Abstract:Objective To investigate the effects of miR-34a on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal stem cells. Methods Human periodontal stem cells (hPDLSCs) were isolated and cultured in vitro, and miR-34a mimetics were constructed and transfected into hPDLSCs. The experimental groups were subsequently categorized into the mimics group (miR-34a overexpression group) and the mimics-NC group (control group without load). The transfection efficiency was assessed using real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR), while CCK-8 assays were used to evaluate the proliferation capacity of hPDLSCs post-transfection. Osteogenic differentiation of miR-34a-transfected hPDLSCs was induced, with samples being collected at day 0 and day 14 after the osteogenic induction. The expression level of Runx2-associated transcription factor 2 (Runx2) was quantified via qRT-PCR, protein levels of Runx2-associated proteins were analyzed through Western blot, and mineralized nodule formation was examined using alizarin red staining. Results The expression level of miR-34a in the mimics group was significantly higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the value-added rate between the mimics group and the mimics-NC group on days 1~5 (P > 0.05), and the value-added rate between the mimics group and the mimics-NC group was significantly lower than that between the mimics-NC group and the mimics-NC group on days 5~11, and the difference was statistically significant. After the osteogenic induction, the mRNA expression level of Runx2 in the mimics group was higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05), and the expression level of Runx2 protein in the mimics group was also higher than that in the mimics-NC group (P < 0.05), and there were more mineralized nodules in the mimics group than in the mimics-NC group after 14 days of osteogenic induction. Conclusion Under in vitro conditions, miR-34a inhibits the proliferative activity of hPDLSCs and promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells. -
Key words:
- MicroRNA-34a /
- Human periodontal ligament stem cells /
- Proliferation /
- Osteogenesis
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1. Primers sequences
基因 引物序列 miR-34a Forward 5' -ACTGGTACTCAGACAACGAGAT-3' Reverse 5' -ACGTCAATGTCCCTGATGTTATG-3' U6 Forward 5' -AAAGCAAATCATCGGACGACC-3' Reverse 5' -GTACAACACATTGTTTCCTCGGA-3' Runx2 Forward 5' -CCGCCTCAGTGATTTAGGGC-3' Reverse 5' -GGGTCTGTAATCTGACTCTGTCC-3' β-actin Forward 5' -TTGTCGCCCTTTTCTACTTTGCC-3' Reverse 5' -CAATGTCCAGCCCATGATGGTTC-3' -
[1] Heo H,Bae J H,Amano A,et al. Supplemental or dietary intake of omega-3 fatty acids for the treatment of periodontitis: A meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Periodontol,2022,49(4):362-377. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.13603 [2] Zeng W Y,Ning Y,Huang X. Advanced technologies in periodontal tissue regeneration based on stem cells: Current status and future perspectives[J]. J Dent Sci,2021,16(1):501-507. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2020.07.008 [3] Haas A N,Furlaneto F,Gaio E J,et al. New tendencies in non-surgical periodontal therapy[J]. Braz Oral Res,2021,35(Supp 2): e095. [4] Xue W,Yu J,Chen W. Plants and their bioactive constituents in mesenchymal stem cell-based periodontal regeneration: A novel prospective[J]. Biomed Res Int,2018,2018:7571363. [5] Liu L,Guo S,Shi W,et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote periodontal regeneration[J]. Tissue Eng Part A,2021,27(13-14):962-976. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2020.0141 [6] Zhao Z,Liu J,Weir M D,et al. Human periodontal ligament stem cells on calcium phosphate scaffold delivering platelet lysate to enhance bone regeneration[J]. RSC Adv,2019,9(70):41161-41172. doi: 10.1039/C9RA08336G [7] 赵军,刘丽娜. 微小RNA调控牙周膜干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J]. 口腔医学研究,2022,38(3):220-222. [8] 陈雪,李子坚,李力力,等. 抑癌基因p53调控的微RNA——miR-34基因家族[J]. 生命的化学,2008,28(5):544-548. [9] 王苟思义,袁贤瑞,蒋星军. 新型microRNA—miR-34在肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2009,21(3):418-424. [10] Hong M,Zhang X B,Xiang F,et al. MiR-34a suppresses osteoblast differentiation through glycolysis inhibition by targeting lactate dehydrogenase-A (LDHA)[J]. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim,2020,56(6):480-487. doi: 10.1007/s11626-020-00467-0 [11] Meng X,Wang W,Wang X. MicroRNA-34a and microRNA-146a target CELF3 and suppress the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells under cyclic mechanical stretch[J]. J Dent Sci,2022,17(3):1281-1291. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.11.011 [12] Arya P N,Saranya I,Selvamurugan N. RUNX2 regulation in osteoblast differentiation: A possible therapeutic function of the lncRNA and miRNA-mediated network[J]. Differentiation,2024,140:100803. [13] 朱凌兰,许生敏. 牙周膜干细胞分化、增殖特性与牙周组织再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(45):7369-7373. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.45.027 [14] Deng W,Meng Y,Wang B,et al. In vitro experimental study on the formation of microRNA-34a loaded exosomes and their inhibitory effect in oral squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cell Cycle,2022,21(16):1775-1783. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2070832 [15] Yan S,Dong W,Li Z,et al. Metformin regulates chondrocyte senescence and proliferation through microRNA-34a/SIRT1 pathway in osteoarthritis[J]. J Orthop Surg Res,2023,18(1):198. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-03571-5 [16] 李泽豪,任小元,王世兵,等. 介导siRNA传递的非病毒载体及其研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2014,26(4):392-399. [17] 吴雪,段少宇,梁萍,等. miR-34a靶向STAT1基因调控牙周膜细胞增殖及凋亡的分子机制[J]. 中国美容医学,2021,30(4):115-118. [18] Yin M,Zhang Z,Wang Y. Anti-tumor effects of miR-34a by regulating immune cells in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Med,2023,12(10):11602-11610. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5826 [19] Yang Z,Liu T,Ren X,et al. Mir-34a: A regulatory hub with versatile functions that controls osteosarcoma networks[J]. Cell Cycle,2022,21(20):2121-2131. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2087755 [20] Yi J,Liu D,Xiao J. LncRNA MALAT1 sponges miR-30 to promote osteoblast differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by promotion of Runx2 expression[J]. Cell Tissue Res,2019,376(1):113-121. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2963-2 [21] Krzeszinski J Y,Wei W,Huynh H,et al. miR-34a blocks osteoporosis and bone metastasis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and Tgif2[J]. Nature,2014,512(7515):431-435. doi: 10.1038/nature13375 [22] 程孟文,周毅. MiR-34a在牙周膜细胞成骨向分化中的作用[J]. 口腔医学研究,2017,33(9):928-932. [23] 褚晓杰,吕文涛,包忠蕾,等. MicroRNA-34a间接促进成骨细胞分化并抑制炎症因子缓解绝经后骨质疏松[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志,2023,16(2):133-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-2591.2023.02.006 [24] Jia C,Shuhua Y,Peng L,et al. MicroRNA regulates the toxicological mechanism of four mycotoxins in vivo and in vitro[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology,2022,13(4):923-934. [25] Chen L,Holmstrom K,Qiu W,et al. MicroRNA-34a inhibits osteoblast differentiation and in vivo bone formation of human stromal stem cells[J]. Stem Cells,2014,32(4):902-912. doi: 10.1002/stem.1615 [26] 陈伟健,晋大祥,谢炜星,等. Runx2基因参与骨代谢相关通路的研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(4):557-560. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7108.2018.04.028 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 胡建粤. 无创呼吸机联合氧驱动雾化吸入治疗慢性阻塞性肺病急性加重患者的疗效分析. 实用中西医结合临床. 2024(21): 46-49 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: