CircRNA EZH2 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Prostate Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-30c-5p
-
摘要:
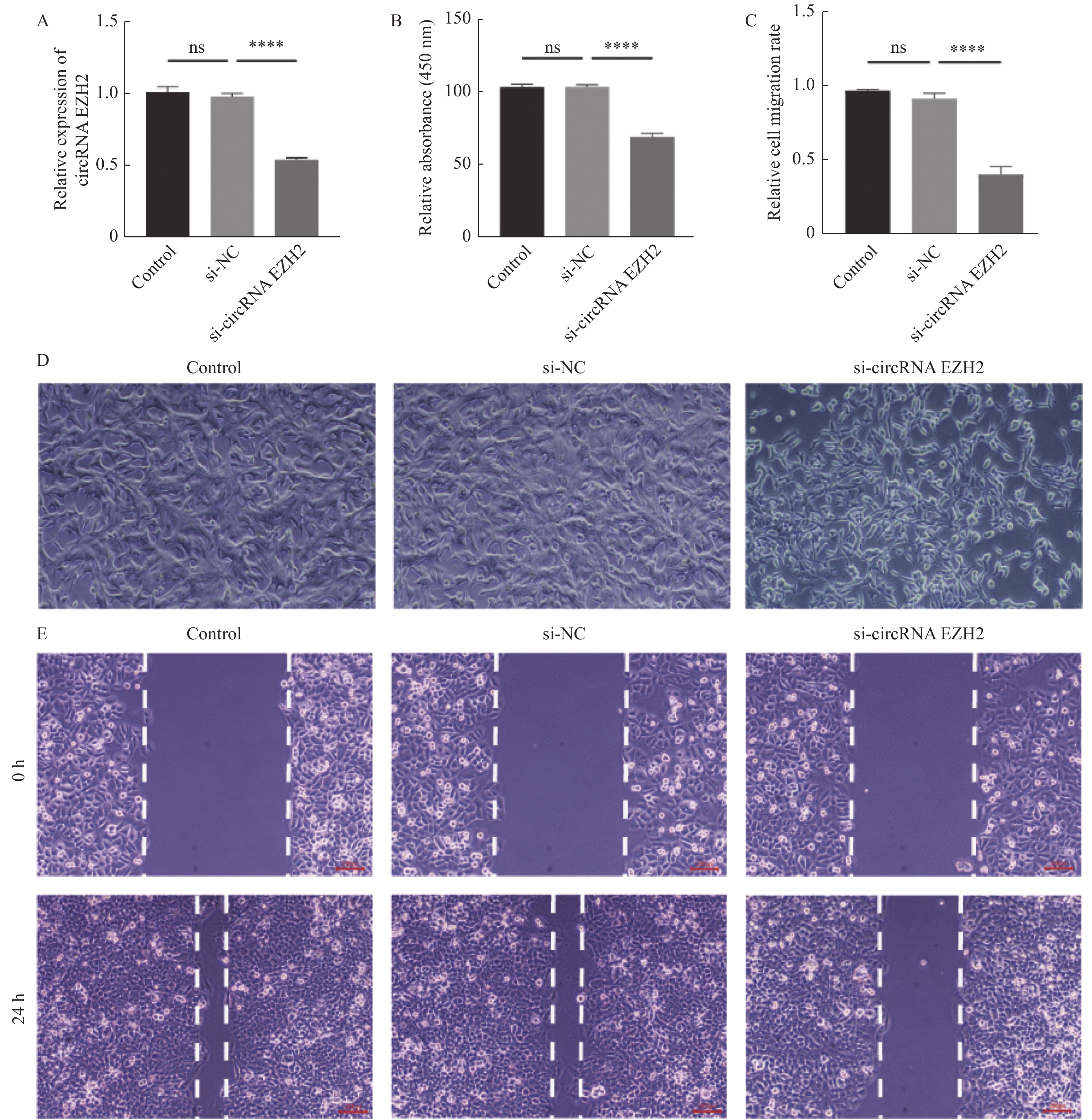
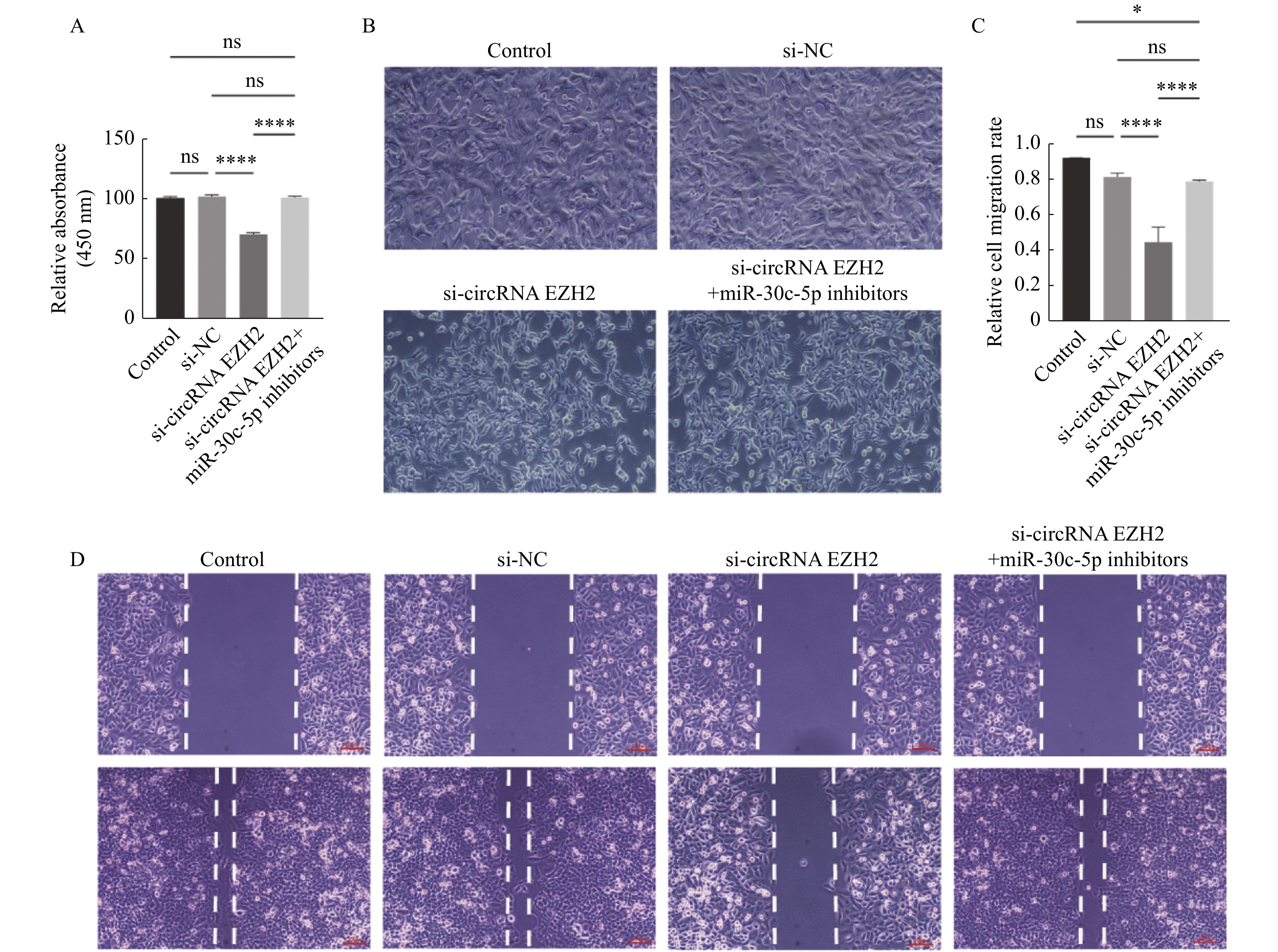
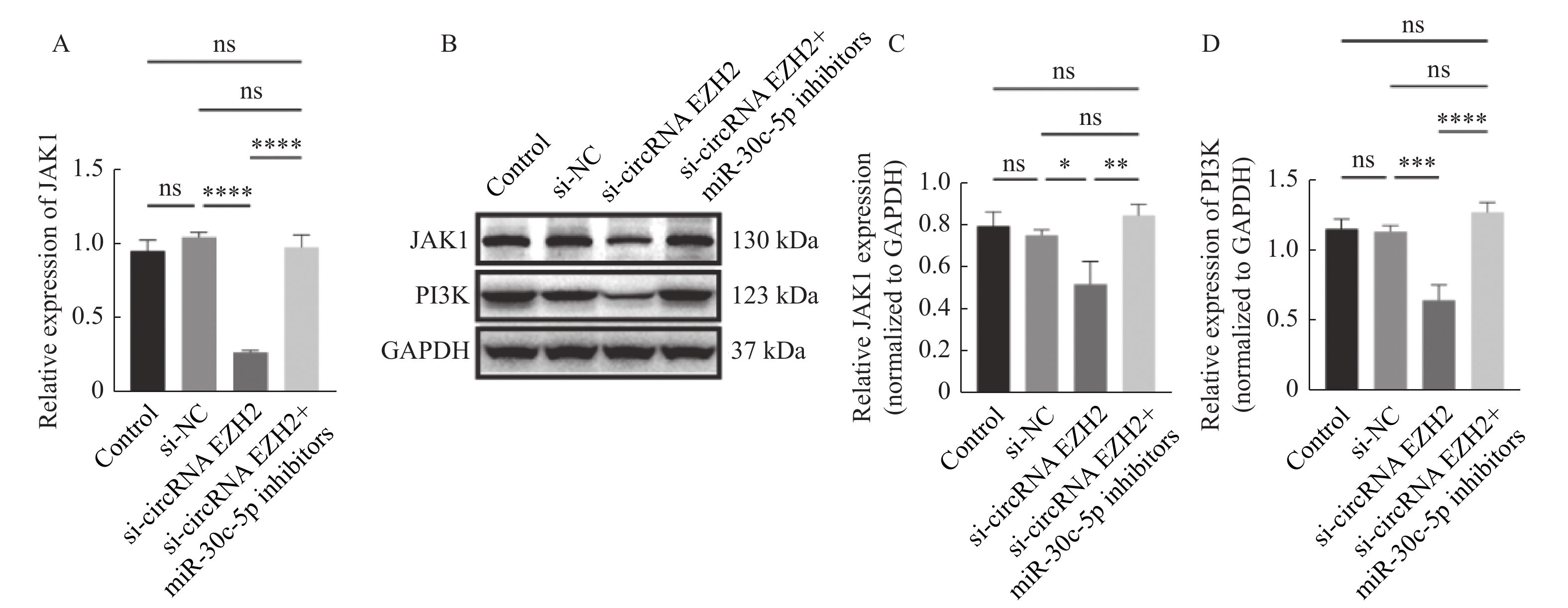
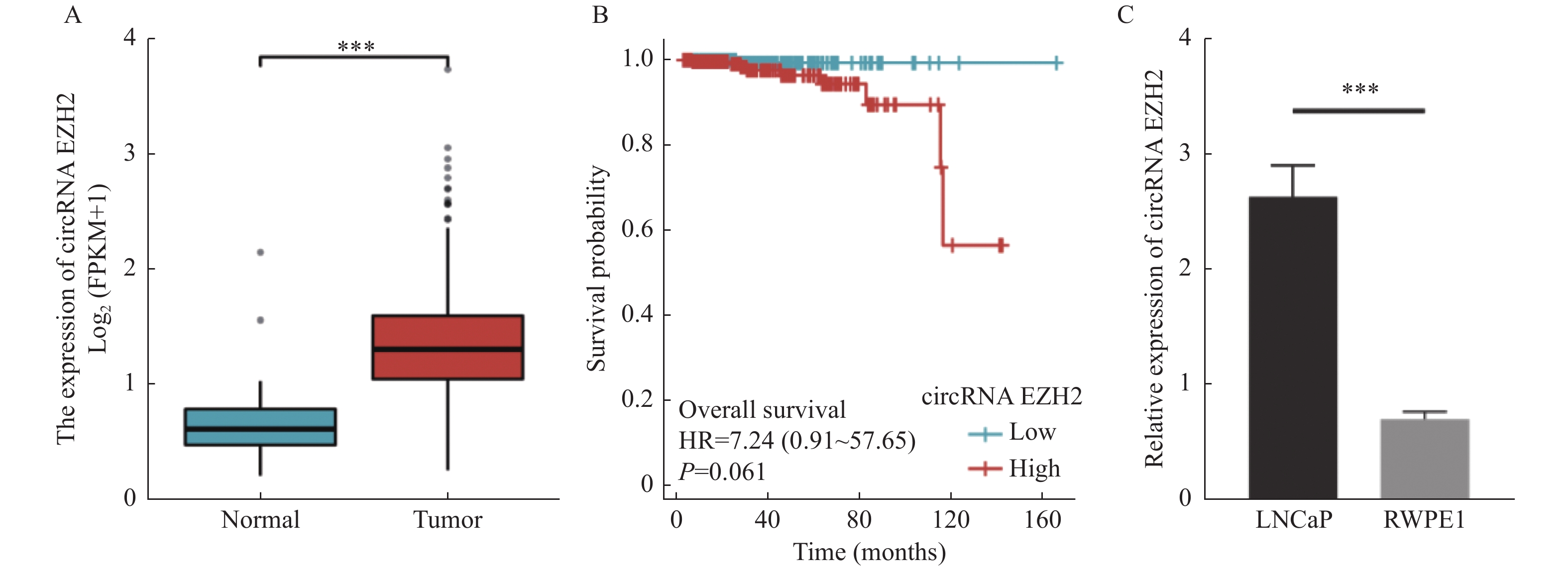
目的 探究circRNA EZH2通过调控miR-30c-5p对前列腺癌细胞的增殖和迁移的影响及其相关作用机制。 方法 通过TCGA数据库分析circRNA EZH2在前列腺癌组织中的表达差异及生存曲线;转染siRNA敲降前列腺癌LNCaP细胞中的circRNA EZH2表达后,CCK-8实验和划痕实验观察LNCaP细胞增殖和迁移,RT-qPCR和Western blot法测定miR-30c-5p、JAK1和PI3K蛋白的表达。 结果 在前列腺癌组织中circRNA EZH2的表达显著上调(P < 0.0001),且高表达circRNA EZH2的患者生存率降低;沉默circRNA EZH2的LNCaP细胞较正常LNCaP细胞的增殖和迁移能力下降(P < 0.0001),miR-30c-5p表达增高(P < 0.0001),JAK1表达降低(P < 0.0001),PI3K信号受抑制。 结论 EZH2在前列腺癌中高表达,通过调控miR-30c-5p激活PI3K信号通路促进前列腺癌LNCaP细胞的增殖和迁移。 -
关键词:
- 前列腺癌 /
- 环状RNA-EZH2 /
- miR-30c-5p /
- 增殖 /
- 迁移
Abstract:Objective To investigate the effect and related mechanism of circRNA EZH2 on proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells through miR-30c-5p. Methods The expression difference and survival probability of EZH2 in prostate cancer were analyzed according to TCGA database. SiRNA were transfected to silence EZH2 in prostate cancer LNCaP cells, and proliferation and migration of LNCaP cells were detected by CCK-8 assay and wound healing assay, and the expression of miR-30c-5p, JAK1 and PI3K proteins were determined by RT-qPCR and western blot. Results The expression of EZH2 was up-regulated in prostate cancer tissues, and the survival rate of patients with high expression of EZH2 decreased. Compare with normal LNCaP cells, the proliferation and migration of EZH2-silenced LNCaP cells were decreased, miR-30c-5p expression was increased, JAK1 expression was decreased, and PI3K signal was inhibited. Conclusion EZH2 is highly expressed in prostate cancer and can promote the proliferation and migration of LNCaP cells by regulating miR-30c-5p/JAK1 axis and acting on PI3K signaling pathway. -
Key words:
- Prostate cancer /
- CircRNA EZH2 /
- miR-30c-5p /
- Proliferation /
- Migration
-
1953年,Kowalski首次[1]发现肝硬化患者存在明显心脏结构异常,最初认为该疾病只存在于酒精性肝硬化中,随着研究的深入,人们发现其存在于各种病因所导致的肝硬化患者。肝硬化患者长期的肝纤维化、肝窦细胞外基质累积、细胞表型变化等会使得肝脏微结构改变,同时伴随肝窦内皮细胞、肝星状细胞及巨噬细胞等的功能失调,共同使得肝内阻力增加,引发门静脉高压症,此类患者往往出现内脏及全身动脉血管舒张,引发高动力循环。当疾病进展到晚期时,侧支循环生成,血管活性物质紊乱,最终将导致心血管结构与功能障碍,表现出一系列异常的心脏和血管状态。本文将围绕肝硬化所导致的心脏和血管疾病及其机制进行综述。
1. 门静脉高压症(portal hypertension,PHT)
肝硬化PHT是指肝硬化患者门静脉血流受阻,血流量增加,使得门静脉及其属支压力升高,引起的一系列临床综合征,表现为腹水、脾脏肿大与脾功能亢进、食管和胃静脉曲张等[2]。接近90%的PHT可归因于肝硬化[3]。
肝硬化PHT的发病机制可用“后向血流学说”“前向血流学说”“液递物质学说”来解释[4]:“后向血流学说[5]”认为,肝纤维化和假小叶的形成使得肝脏结构破坏和血管功能改变,门静脉血流受阻,导致门静脉高压,该学说被认为是PHT发生最根本的原因;“前向血流学说[6]”将门静脉血流阻力升高、门体侧支循环形成、高动力循环及内脏主动充血的出现、门静脉血流量增加等作为门静脉高压持续存在的重要原因;此外,“液递物质学说[7]”表示,随着肝病的进展,肝脏对外周血管中活性物质的灭活作用下降,血管活性物质通过侧枝循环躲避肝脏灭活,导致调节机体血管阻力及血流量的物质失衡,最终使得门静脉压力功能性升高。
戚晓亮等[8]将PHT的病理生理机制分为细胞病变与血管病变2方面。肝窦内皮细胞功能障碍和失调对肝内血管阻力变化发挥着主要作用,激活的肝星状细胞在肝纤维化进展上发挥着核心作用。不仅如此,激活的肝星状细胞还可压迫肝血窦,增加阻力,进一步加重PHT,属于细胞病变机制。血管病变机制认为,血栓形成是导致PHT的关键病理因素,肝外来自内脏循环血流量的增加、门体侧支循环的形成等也会进一步加重PHT的发展。
2. 高动力循环
在高动力循环状态中,血管扩张会引起血管反应性下降、顺应性上升,其变化情况与高动力循环程度及动脉血压成正比,主要表现为心输出量增加、心率加快、外周血管阻力降低和血压下降等[9],与肝病的严重程度明显相关[10]。
高动力循环的形成是以血管舒张为基础,与血管活性因子密切相关,具体如下:(1)一氧化氮(nitric oxide,NO):在肝硬化患者中,肝内微循环中NO浓度较低,而在其他内脏循环中NO浓度较高,导致了导致肝内血管舒张不足、阻力增加,而其他内脏血管恰恰相反,进而引发和加重高动力循环[11];(2)一氧化碳(carbon monoxide,CO):肝硬化患者肝静脉中CO水平显著高于外周静脉,加重高动力循环[12];(3)前列环素:肝硬化患者中可观察到前列环素的表达显著升高,其可通过与血管平滑肌上腺酷环化酶结合生成环腺昔一磷酸,引起血管舒张[13];(4)过氧化氢(H2O2):肝硬化PHT患者过度生成的H2O2会通过降低肠系膜动脉对去甲肾上腺素的反应性来参与高动力循环的形成[14]。此外,内皮衍生的超极化因子、肿瘤坏死因子-α、肾上腺髓质素、硫化氢等物质也可直接或间接的导致内脏血管舒张,从而加重高动力循环[15]。
3. 门静脉性肺动脉高压(portal pulmonary hypertension,POPH)
POPH是肝硬化门静脉高压患者较严重的血管并发症,在肝硬化或门静脉高压患者中患病率为1%~6%[16],通常出现在门静脉高压症后的4~7 a[17],其与门静脉高压及肝硬化的严重程度之间未表现出明显相关性,但和预后相关[17]。
POPH的发病机制目前主要归结于以下几个方面:(1)高动力循环:随着肝病的进展,患者内脏血管舒张,外周阻力降低,心脏通过增加心排出量进行代偿,患者会呈现出高动力循环和全身阻力降低的一种血管状态,在此循环状态中,长期的肺动脉血流增加导致血管所受的压力也增加,进而会使得肺血管内皮细胞损伤,最终导致了原位血栓的形成及血管内皮细胞的增殖,形成了肺动脉高压[18];(2)血管活性物质紊乱:门静脉压力升高及侧支血管的形成使得原本在肝脏中代谢的血管活性物质直接从体循环进入肺循环,导致血管活性物质紊乱。主要表现为循环中血管内皮素-1,IL-6等收缩因子增加,而NO、前列环素等舒张因子降低[19]。此外,一些缩血管物质也会参与血管增殖过程,使肺部血管发生重构、收缩,最终导致肺动脉压力进行性升高;(3)遗传因素:POPH的基因分析发现,基因ENG在该人群中突变频率最大[20],随后Nikolie等[21]的研究发现POPH患者相较于其他原因的肺动脉高压患者血浆骨形态发生蛋白-9(bone morphogenetic protein-9,BMP-9)水平明显降低。此外,POPH还与雌激素信号转导及细胞生长调节因子的遗传变异有关。这些表明遗传因素在POPH发展中可能发挥着重要的作用;(4)其他因素:POPH风险增加与自身免疫性肝炎和女性相关,而丙型肝炎感染与晚期肝病患者风险降低相关[22]。潜在的POPH患者氧化应激的程度增高,抗氧化功能下降,且常伴有NO产生减少[23]。
4. 舒张功能障碍(diastolic dysfunction,DD)
肝硬化中DD的情况很常见,目前其患病率大小的说法不一,范围大约在25.7%~81.4%之间。DD主要表现为E/A降低,可通过多普勒超声心动图,组织多普勒超声心动仪和心脏核磁共振等手段进行评估。DD会随着肝硬化疾病的进展而恶化且在腹水患者中更常见[24],患有DD的患者预后更差[25]。
舒张功能障碍可以预测TIPS术后死亡[26],是由于使用TIPS降低门静脉高压可能会使左心房直径与肺血管压力进一步增加,而肝硬化患者无法控制增加的前负荷,但在TIPS术后几个月后舒张容积会恢复正常,同时还会伴随轻度的左心室肥大[27]。DD可能导致围手术期心血管不良事件发生和肝移植后死亡率增加,临床医生应注意DD的失代偿性肝硬化患者[28]。
在肝硬化舒张功能障碍患者的尸检分析中,心脏主要表现为左心肥大、斑片状纤维化和内膜下水肿,这些异常导致左心室硬度增加,舒张功能障碍因舒张受损而形成[29],长期的高动力循环、高心输出量、高心率可能会通过此机制发挥作用[30]。钠摄入量的增加可能会促进心脏肥大的发展[31],表明钠储留可能会引发DD。脑利钠肽前体(Pro-BNP)可反映出心脏肥大[32],也意味着可间接通过Pro-BNP去观察患者的舒张功能。此外,长期的RASS激活对心血管系统表现出有害的影响,RASS阻断可改善左心室舒张功能[33]。随后Tamara等[34]在动物实验中发现,Titin调节、PKA水平、胶原蛋白水平也可能是肝硬化DD的发生机制。
5. 收缩功能障碍
正常情况下,收缩功能障碍主要指的是左心室的排空问题,通常是心肌收缩功能受损的结果,表现为射血分数(ejection fraction,EF)降低。但在肝硬化患者中发生的收缩功能障碍会被高动力循环状态所掩盖,患者在静息状态下所测得的EF多在正常范围,不会表现出收缩功能障碍,只有在刺激(运动、药物等)下,心脏才会表现出其潜在的收缩功能不全[35]。
肝硬化收缩功能异常与β-肾上腺素能受体、内源性大麻素、脂多糖、心肌细胞肌丝、肿瘤坏死因子等物质密切相关:(1)β-肾上腺素能受体:β-肾上腺素能受体主要扮演着对心脏收缩的刺激作用,肝硬化患者长期的血管舒张会使得交感神经被激活,最终会使得β-肾上腺素受体脱敏及功能障碍[36];(2)内源性大麻素:内源性大麻素系统主要有大麻素-1(cannabinoid-1,CB1)和大麻素-2(cannabinoid-2,CB2)2种类型。CB1受体抑制剂可以减轻细胞死亡、改善炎症、代谢参数[37]。CB2受体可通过激活自噬依赖性途径抑制肝脏炎症[38];(3)脂多糖(lipopolysaccharides,LPS):在肝硬化患者血浆中LPS含量显著增加,其可显著降低心脏收缩力、肌浆网中的钙储存和钙瞬时振幅[39];(4)心脏细胞肌丝:肌球蛋白重链(myosin heavy chain,MHC)有a、b 2种类型,被称作为“分子马达”。a-MHC属于快速亚型,而b-MHC属于慢速亚型,心脏收缩与a-MHC的含量呈正相关,b-MHC含量增加会对心脏收缩起抑制作用[36]。在肝硬化心脏中,a-MHC的主导地位被b-MHC所取代,这也就导致了肝硬化患者的收缩功能障碍[40];(5)肿瘤环死因子-α(Tumor necrosis factor,TNF-α):是关键的促炎细胞因子,对心肌收缩发挥抑制作用。Juni等[41]将TNF-α直接作用于离体的大鼠心脏时,大鼠心率、肌力和松弛速度都会显著下降,且TNF-α降低了心肌细胞的肌小节缩短和返回速度。除此之外,心脏细胞中钙处理异常、线粒体损伤及能量危机也极可能是导致收缩功能障碍的重要机制之一[40]。
6. 心电生理异常
目前已报道的与肝硬化相关的心电生理异常主要包括QT间期延长、机电不同步及变时性功能不全3种类型。其中,QT间期延长受到更多的关注,似乎也暗示了它的重要性。
6.1 QT间期延长
QT间期指心电图中从QRS波起始到T波终末的时间。QT间期延长在肝硬化伴上消化道出血患者中普遍存在,其发生率与肝病的严重程度密切相关[42],但其可能无法有效预测住院死亡[43]。QT间期取决于心率,因此须对其进行调整并表示为心率校正变量(QTc)[36],目前大多数研究采用的校正方法为Bazett法,其次为Fridericia法[44]。Papadopoulos VP等[44]的研究认为,肝硬化患者QTc间期延长与性别、年龄和病因无关,β-受体阻滞剂会缩短QTc间期,急性消化道出血期间QTc间期会延长。Anoop N等[45]以校正QTc≥440 ms为判定QTc间期延长的标准,对接受肝移植检查的439患者进行研究分析发现,QTc间期延长与CCM特征的心脏结构或功能异常无关,并提出肝硬化的CCM和QTc间期延长可能是2个不同的实体,具有不同的病理生理学起源的假设。
6.2 机电不同步及变时性功能不全
机电不同步是指电信号的发作(心电图的QRS复级)和机械收缩(心室收缩)之间通常非常紧密耦合的时间间隔发生广泛变化。变时性功能不全(chronotropic incompetence,CI)是肝硬化自主神经病变的一个常见特征,其被定义为无法有效增加心率或心肌收缩力以响应运动或药物刺激,目前CI还没有明确的诊断标准及发生机制。
目前此类电生理异常的临床相关性仍不清晰,未来还需进行更多的研究。
7. 肝硬化心肌病(cirrhotic cardiomyopathy,CCM)
CCM是肝硬化的常见并发症,其被定义为肝硬化患者在无已知心脏疾病的情况下,在应激或负荷时出现心室收缩反应受损和(或)心脏舒张功能改变,并伴有电生理异常的心脏功能异常[45]。约60%的肝硬化患者存在肝硬化心肌病[46]。
CCM最早是在2005年的蒙特尔世界胃肠病学大会上进行了定义,十多年后,随着超声心动图技术的快速发展,CCM联盟在2019年更新了定义[46],见表1。Razpotnik M等[46]根据2019年的诊断标准观察收缩功能障碍患病率更高。但可能存在入选群体及检测方法等方面的误差,未来需有更多的研究进一步验证。
表 1 CCM的定义[46]Table 1. Definition of CCM2005年 2019年 收缩功能障碍
(任意一种情况)收缩功能障碍
(任意一种情况)对压力测试的钝性收缩反应 左心室射血分数≤50% 左心室射血分数<55% 绝对GLS<18%或>22% 舒张功能障碍
(任意一种情况)舒张功能障碍
(任意一种情况)减速时间>200 ms 间隔e’<7 cm/s 等容松弛时间>80 ms E/e'比值≥15 E/A<1 LAVI>34 mL/m2 支持标准 TR>2.8 m/s 机电异常 进一步验证 对压力的反应时性反应异常 变时性或正性肌力反应异常 机电解耦 心电图改变 QTc间期延长 机电解耦 左心房扩大 心肌质量变化 左心质量增加 血清生物标志物 BNP前体和BNP增加 腔室扩大 肌钙蛋白1增加 CMRI的ECV CCM是晚期肝病的一种表现形式。随着肝病的进展,患者心脏结构与功能障碍达到一定程度时,可诊断为CCM。但在达到诊断标准前,肝硬化也会引起心脏结构与功能发生变化,因此在该综述中将CCM部分进行了分开介绍。
CCM的发生机制与上述收缩、舒张功能障碍、心电生理异常等段落部分重叠,不再重复叙述。
8. 肝硬化合并其他心血管疾病
肝硬化患者发生其他心血管疾病的风险会更高。与正常人相比,肝硬化患者的非梗阻性动脉粥样硬化的发生率更高,且急性冠状动脉综合征在肝硬化腹水患者中患病率更高[47]。患有肝硬化的患者进行皮冠状动脉介入治疗比不患肝硬化的患者术后死亡与不良预后的风险更高[48]。这些研究表明,肝硬化对患者心血管系统的影响可能会增加患其他心血管疾病的风险,加快疾病的进展,此段落不属于本文讨论的重点,仅做简要阐述。
9. 小结
随着肝病的进展,肝硬化患者会表现出一系列心脏和血管疾病。目前的研究发现其发病机制尚不十分清晰,且无完善的治疗体系,未来还需不断对其发生机制进行研究,增加治疗方案,改善患者的预后。
-
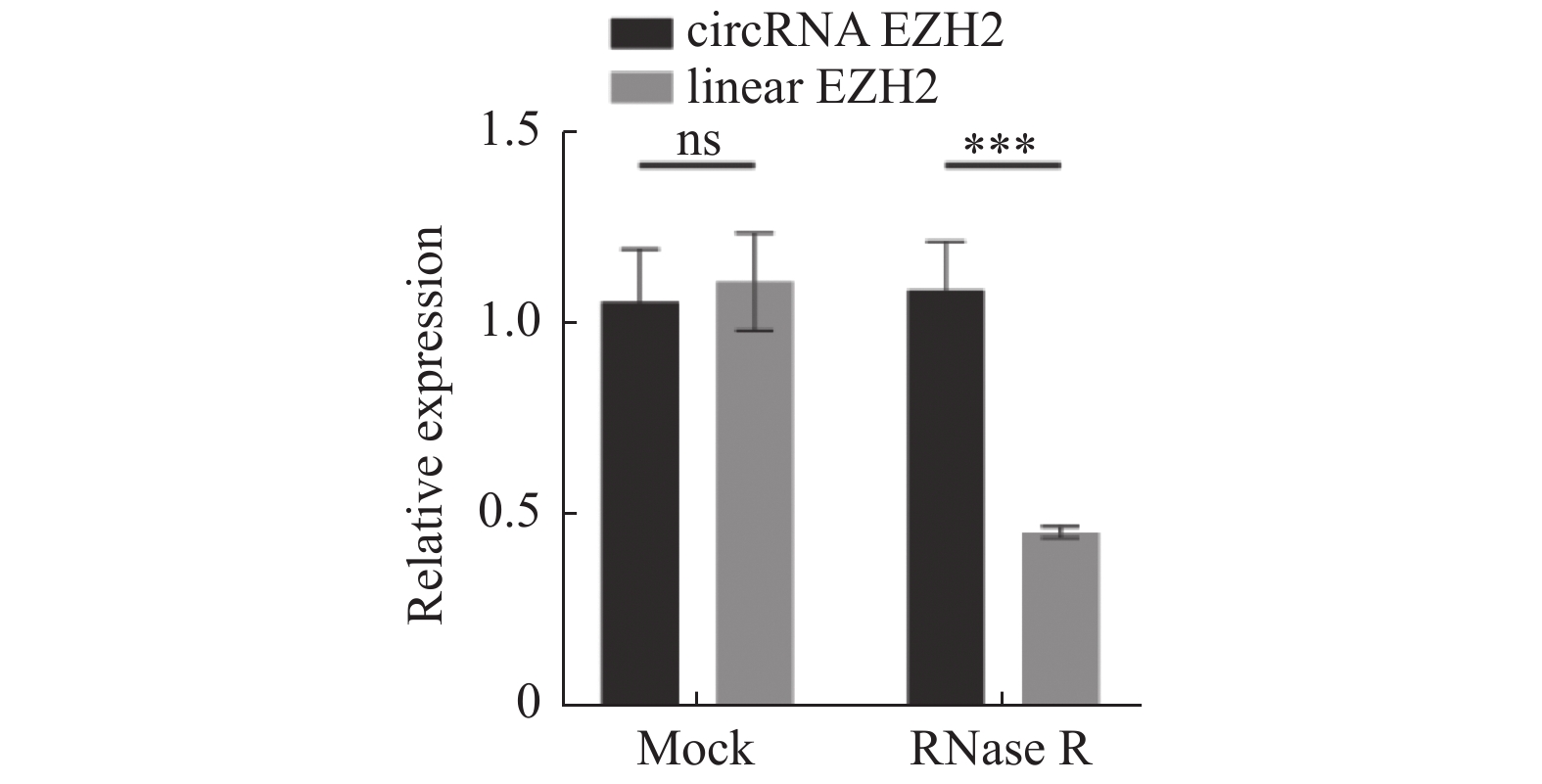
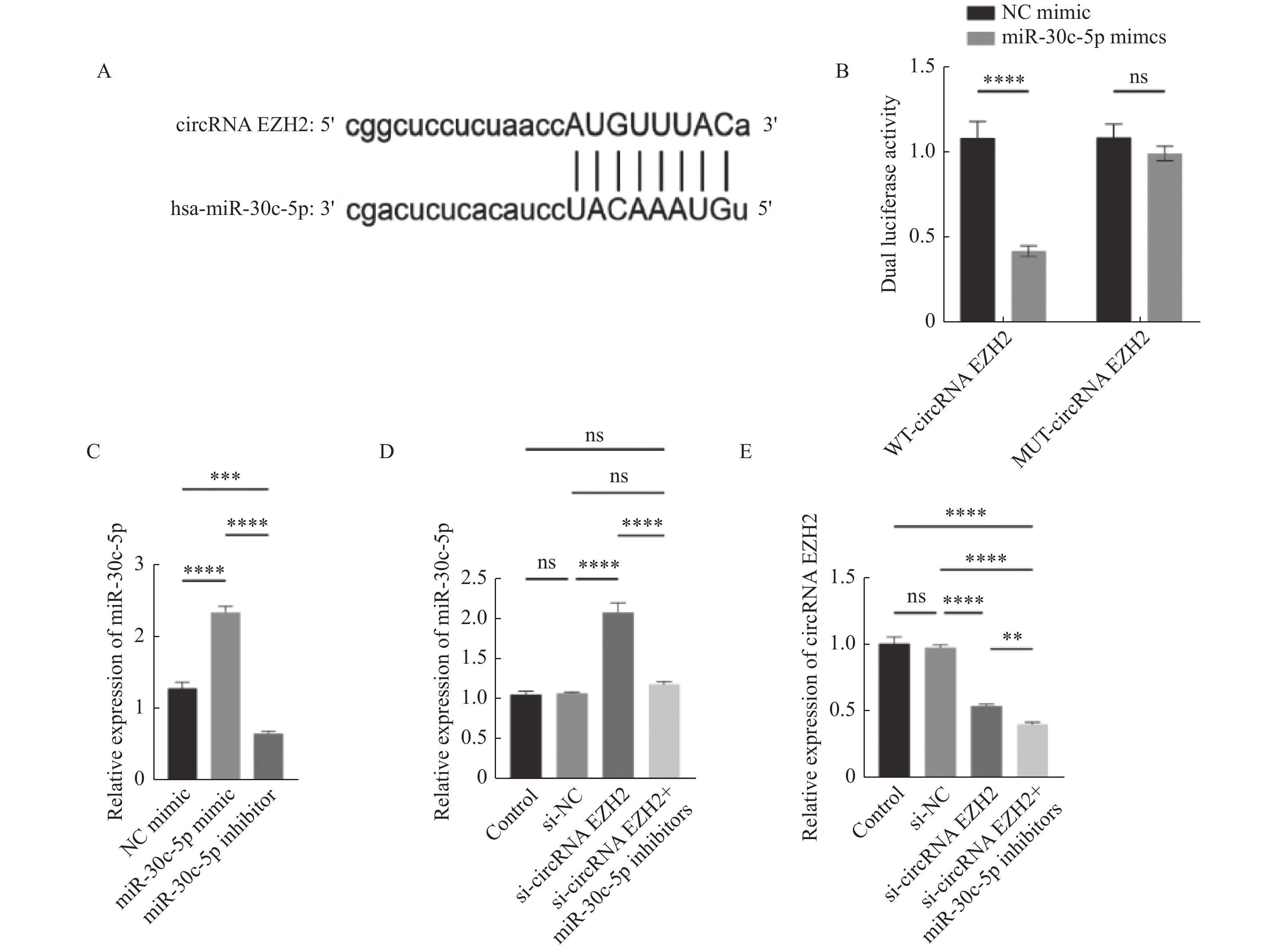
图 4 CircRNA EZH2靶向miR-30c-5p
A:circRNA EZH2和miR-30c-5p的配对序列;B:双荧光素酶报告基因检测WT/MUT-circRNA EZH2插入的报告基因和miR-30c-5p mimic及其阴性对照共转染LNCaP细胞后的荧光素酶活性;C:RT-qPCR实验检测miR-30c-5p抑制剂的干扰效果;D:miR-30c-5p的RT-qPCR结果分析;E:circRNA EZH2的RT-qPCR结果分析。**P < 0.01;***P < 0.001;****P < 0.0001。
Figure 4. CircRNA EZH2 targeted miR-30c-5p
表 1 RT-qPCR所需引物序列
Table 1. Primer sequences
基因 引物序列(5′-3′) circRNA EZH2 Forward Primer:GGACCACAGTGTTACCAGCAT Reversed Primer:GTGGGGTCTTTATCCGCTCAG miR-30c-5p Forward Primer:GCAGTGTAAACATCCTACACTCT Reversed Primer:TCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGCTGA JAK1 Forward Primer:ATGTCCTTGTTGAGAGTGA Reversed Primer:CATCCTTGACGGTGTAATAC GAPDH Forward Primer:TGTGGGCATCAATGGATTTGG Reversed Primer:ACACCATGTATTCCGGGTCAAT U6 Forward Primer:GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT Reversed Primer:CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT -
[1] Rebello R J,Oing C,Knudsen K E,et al. Prostate cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers,2021,7(1):9. [2] Swami U,McFarland T R,Nussenzveig R,et al. Advanced prostate cancer:Treatment advances and future directions[J]. Trends Cancer,2020,6(8):702-715. [3] Rebbeck,T R. Prostate cancer genetics:Variation by race,ethnicity,and geography[J]. Semin Radiat Oncol,2017,27(1):3-10. [4] Wang C,Tan S,Li J,et al. CircRNAs in lung cancer - Biogenesis,function and clinical implication[J]. Cancer Lett,2020,492:106-115. [5] Liu Y,Chen S,Zong Z H,et al. CircRNA WHSC1 targets the miR-646/NPM1 pathway to promote the development of endometrial cancer[J]. J Cell Mol Med,2020,24(12):6898-6907. [6] Huang,G,Liang M,Liu H,et al. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis,2020,11(12):1065. [7] Wen J,Li X,Ding Y,et al. Lidocaine inhibits glioma cell proliferation,migration and invasion by modulating the circEZH2/miR-181b-5p pathway[J]. Neuroreport,2021,32(1):52-60. [8] Zhou Y,Shi H,Du Y,et al. lncRNA DLEU2 modulates cell proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating miR-30c-5p/SOX9 axis[J]. Aging (Albany NY),2019,11(18):7386-7401. [9] Herichova I,Reis R,Hasakova K,et al. Downregulation of miR-30c-5p expression in colorectal cancer tissue is sex-dependent[J]. Physiol Res,2020,69(Suppl 3):S479-S487. [10] Tanaka T,Okada R,Hozaka Y,et al. Molecular pathogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma:impact of miR-30c-5p and miR-30c-2-3p regulation on oncogenic genes[J]. Cancers (Basel),2020,12(10):2731. [11] Liu J,Lichtenberg T,Hoadley K A,et al. An integrated TCGA Pan-Cancer clinical data resource to drive high-quality survival outcome analytics[J]. Cell,2018,173(2):400-416. [12] Chen B,Lai J,Dai D,et al. JAK1 as a prognostic marker and its correlation with immune infiltrates in breast cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY),2019,11(23):11124-11135. [13] Ma X,Zhao X,Zhang Z,et al. Differentially expressed non-coding RNAs induced by transmissible gastroenteritis virus potentially regulate inflammation and NF-κB pathway in porcine intestinal epithelial cell line[J]. BMC Genomics,2018,19(1):747. [14] Gao F,Du Y,Zhang Y,et al. Circ-EZH2 knockdown reverses DDAH1 and CBX3-mediated cell growth and invasion in glioma through miR-1265 sponge activity[J]. Gene,2020,726:144196. [15] Yang J,Nie J,Ma X,et al. Targeting PI3K in cancer:mechanisms and advances in clinical trials[J]. Mol Cancer,2019,18(1):26. [16] Taylor B S,Schultz N,Hieronymus H,et al. Integrative genomic profiling of human prostate cancer[J]. Cancer Cell,2010,18(1):11-22. [17] Tang Y,Pan J,Huang S,et al. Downregulation of miR-133a-3p promotes prostate cancer bone metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2018,37(1):160. [18] Liu J M,Yu C P,Chuang H C,et al. Androgen deprivation therapy for prostate cancer and the risk of autoimmune diseases[J]. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis,2019,22(3):475-482. [19] Edlind M P,Hsieh A C. PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling in prostate cancer progression and androgen deprivation therapy resistance[J]. Asian J Androl,2014,16(3):378-386. -






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载: