2023 Vol. 44, No. 11
2023, 44(11): 1-8.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231101
Abstract:
Objective To explore the mechanism of Dendrobium officinale against inflammatory aging based on network pharmacology and molecular docking and experimental verification. Methods We used related databases to obtain the action targets of the main components of Dendrobium officinale and the genes of aging rats, then intersected them to obtain the final target. STRING database was used to build a protein-protein interaction(PPI) network. DAVID database was used to conduct enrichment analysis of Gene Ontology(GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genomes(KEGG). AutoDock software was to perform molecular docking verification on the main active components and key targets. Then, the aging rats were gavaged with dendrobium polysaccharide solution for ten week, the expression levels of IL-6 and IL-10 proteins were detected to verify the predicted targets. Results Through database retrieval, 28 active components and 492 target genes were screened out. There were 64 intersections. Enrichment analysis yielded 283 GO functional enrichment entries and 71 KEGG pathway enrichment entries. The main pathway is the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Calcium signaling pathway, EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance, HIF-1 signaling pathway, Apelin signaling pathway, VEGF signaling pathway, etc. The results of molecular docking showed that each target(AKT1, STAT3, NOS3, GSK3B) and active ingredient(Dentatin, Rutaecarpine, Nodakenetin, Evodaiamine) spontaneously combined and formed stable hydrogen bonds. Animal experiments showed that the content of IL-6 in the medium dose group significantly decreased compared to the blank group, low dose group, and Bailing capsule group, and the content of IL-10 in the low dose group increased compared to the blank group. Conclusions Dendrobium officinale has a delaying effect on the decline of the immune system in elderly rats. It is mainly related to the decrease of IL-6 content and the increase of IL-10 content in the serum. Its mechanism may be related to the expression of key genes AKT1, STAT3, NOS3, GSK3B regulated by components in Dendrobium officinale, such as Dentatin, Rutaecarpine, Nodakenetin, and Evodaiamine.
2023, 44(11): 9-15.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231102
Abstract:
Objective To investigate Artemisinin-affected cell proliferation and aerobic glycolysis on clear cell renal carcinomas(ccRCC) through regulating ENO2 and clarify the mechanism. Methods ccRCC cell lines OSRC2 and ACHN were exposed to 0, 10, 20, 30, and 40 μmol/L Artemisinin, OSRC2 and ACHN cells treated with 25 μmol/L Artemisinin or transfected with si-ENO2 at the same time. CCK-8 assay detected cell proliferation, glucose consumption, and lactate production were detected by glucose test kit and lactate test kit. The expressions of HK2, LDHA, and ENO2 were detected by Western blot, and ENO2 mRNA expression was detected by RT-qPCR. Results The survival rate of OSRC2 and ACHN cells were decreased with the increase of Artemisinin concentration and treatment time, the IC50 of OSRC2 cells was 25.47 μmol/L, and the IC50 of ACHN was 26.31 μmol/L. ENO2 was upregulated in OSRC2 and ACHN cells(P < 0.01), and Artemisinin diminished ENO2 expression in cancer cells(all P < 0.05). Exposure to Artemisinin(25 μmol/L) or knocking down ENO2 significantly inhibited the survival of OSRC2 and ACHN cells(all P < 0.001), glucose consumption(P < 0.05), lactate production(all P < 0.05) and protein expression of HK2 and LDHA(all P < 0.05). Compared with si-ENO2 group, the survival rate(P < 0.001), glucose consumption(P < 0.05), lactate production(all P < 0.05) and the expression of HK2 and LDHA(all P < 0.05) of OSRC2 and ACHN cells in knocking down ENO2 and treated with 25 μmol/L Artemisinin group were decreased. Conclusion Artemisinin can inhibit the survival rate and aerobic glycolysis of ccRCC cells, and plays a role by downregulating the expression of ENO2 in ccRCC.
2023, 44(11): 16-21.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231103
Abstract:
Objective To explore the role of miR-148a-3p in osteogenic differentiation and enamel development during in vitro tooth organogenesis and uncover its underlying molecular mechanism. Methods Human dental pulp stem cells and oral epithelial cells were obtained. Human dental pulp stem cells were transfected with miR-148a-3p mimics, miR-148a-3p inhibitors, or a negative control. A three-dimensional co-culture system was established by seeding human dental pulp stem cells onto the Matrigel matrix and overlaying them with oral epithelial cells. The impact of miR-148a-3p on cell proliferation and protein expression was assessed using MTT assay. The expression levels of osteogenic marker RUNX2 and enamel development marker E-cadherin were determined through Western blotting. The interaction between SMURF2(SMAD-specific E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase 2) and miR-148a-3p was validated via a luciferase reporter assay. Results Downregulation of miR-148a-3p using its inhibitor in human dental pulp stem cells led to reduced cell viability in the 3D co-culture system(P < 0.05). Conversely, upregulation of miR-148a-3p using its mimic increased the expression of osteogenic marker RUNX2 and enamel development marker E-cadherin in the co-culture setting(P < 0.05). TargetScan software predicted a binding site for miR-148a-3p within the 3’ -UTR of SMURF2. Luciferase report Experiments showed that miR-148a-3p mimics significantly inhibited the luciferase activity of wild-type(P < 0.05), while Western blot results showed that miR-148a-3p mimics significantly down-regulated the expression of SMURF2(P < 0.05). Conclusion The research findings suggest that miR-148a-3p potentially regulates the expression of RUNX2 and E-cadherin by targeting SMURF2, thereby participating in osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells and enamel development in oral epithelial cells during in vitro tooth organogenesis. This study provides promising therapeutic targets for dental repair and treatment.
2023, 44(11): 22-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231104
Abstract:
Objective To obtain the optimal extraction process of narciclasine from Hymenocallis littoralis by response surface center design. Methods Based on the single factor experiment, temperature, time and liquid-to-solid ratio were selected to establish a mathematical model combined with the Box-Behnken test. The influence degree of the three factors on the extraction rate of narciclasine was analyzed and investigated to determine the optimal extraction conditions. Results The optimum extraction conditions were as follows: extraction temperature 90.97 ℃, extraction time 4.13 h, liquid-solid ratio 5.09 mL∶1 g. The predicted and verified values of narciclasine extraction were 3.42×10-4% and 3.38×10-4%, respectively. Conclusion The optimized extraction process based on the response surface method is stable, feasible, and predictable, which could be used for the extraction of active components from Hymenocallis littoralis, and has laid the groundwork for the development and utilization of Hymenocallis littoralis.
2023, 44(11): 29-37.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231105
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the intervention effect and mechanism of Saikosaponin A on noise-induced tinnitus in a mouse model. Methods Fifty mice were randomly divided into control group(Control group), noise-induced tinnitus mouse model group(BBN group), and SSA-L group, SSA-M group and SSA-H group based on BBN group with 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg and 40 mg/kg of Caihu saponin A by gavage, respectively, 10 mice in each group. The tinnitus behavior of mice was detected; the depression-like behavior of mice was assessed by the open field experiment, elevated cross-maze experiment and forced swimming experiment; the hearing of mice was measured by ABR threshold; and IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression in the auditory cortex of mice were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blotting. Results Compared with the Control group, mice in the BBN group had significantly lower GPIAS% values at 3 d, 14 d and 28 d after 2 h of noise exposure(P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups had significantly higher GPIAS% values at 3 d, 14 d and 28 d after 2 h of noise exposure in a dose-dependent manner( P < 0.05). Compared with the Control group, mice in the BBN group had significantly reduced time and distance to the central zone, number and time to the open arm, and significantly higher immobility time and ABR thresholds under Click and 8, 16 and 32 kHz acoustic stimulation( P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups had significantly higher time and distance to the central zone, and The number and time of entering the open arm were significantly increased, and the immobility time and Click and ABR thresholds under 8, 16 and 32 kHz acoustic stimulation were significantly decreased( P < 0.05). Compared with the Control group, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression were significantly increased in the auditory cortex of mice in the BBN group( P < 0.05); compared with the BBN group, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β mRNA and protein expression were significantly decreased in the auditory cortex of mice in the SSA-L, SSA-M and SSA-H groups( P < 0.05). Conclusion Saikosaponin A can improve depressive behavior and hearing in noise-induced tinnitus mice, which may be closely related to the inhibition of inflammatory factors in the auditory cortex of tinnitus mice.
2023, 44(11): 38-46.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231106
Abstract:
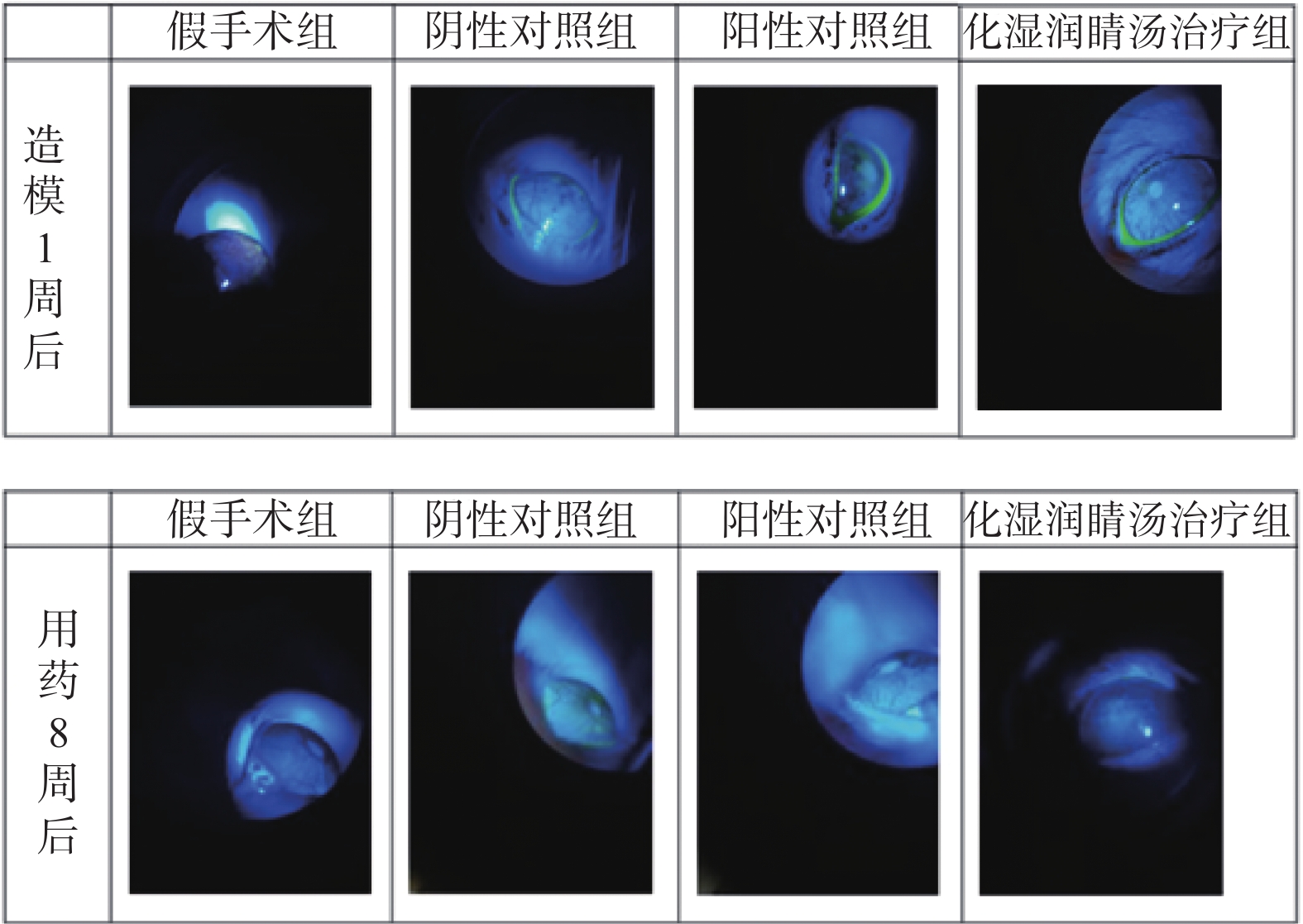
Objective To observe whether Huashi Runjing Decoction can inhibit the inflammatory response in rats with desmoplastic male dry eye disease, and to explore its potential mechanism of action. Methods 60 healthy male SD rats were randomly divided into 4 groups: sham surgery group of 15, negative control group of 15, positive control group of 15, Huashi Running Decoction group of 15). The sham operated group rats only underwent abdominal incision without removing both testicles and epididymis; Rats in the negative control group, positive control group and Huashi Runjing Decoction group were removed both testicles and epididymis. After 1 week of modeling, the model was validated by fluorescein staining(FL), break-up time(BUT), and tear secretion test(SIT). After the wound healed, the rats were given the appropriate drug interventions. The degree of corneal breakage, tear film rupture time and tear secretion of rats in each group were detected by FL method, BUT method and SIT method respectively after 8 weeks of drug administration. The levels of COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 in the serum of each group of rats were observed by ELISA; HE staining was used to observe the pathomorphological changes in the lacrimal gland tissue of rats in each group. The expression of key inflammatory factors COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 in the lacrimal gland tissues of rats in each group was observed by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Results Compared with the sham-operated group, the negative control group, positive control group and Huashi Runjing Decoction group showed an increase in the area of sodium fluorescein positive staining in the cornea, a significant increase in FL score, a shortening of tear film rupture time and a decrease in tear secretion, an increase in serum COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 levels, atrophy of the lacrimal gland tissue vesicles, an irregular shape, a disorganized structure, a decrease in intracytoplasmic zymogen particles, and a large number of inflammatory cell infiltrations. The expression levels of inflammatory factors COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 increased in the tissues(P < 0.05); Compared with the negative control group, the Huashi Runjing Decoction group showed a significant decrease in the area of sodium fluorescein positive staining, a significant decrease in FL score, a significant increase in tear film rupture time and tear secretion, a decrease in serum COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 levels, a decrease in atrophy of the lacrimal gland tissue vesicles, a more regular shape, a clearer structure, an increase in the number of intracytoplasmic zymogen particles, an increase in inflammatory cell infiltration and a decrease in the area of lacrimal gland tissue. The expression levels of COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 in lacrimal gland tissues were reduced(P < 0.05). Conclusion Huashi Runjing Decoction could reduce the protein expression of COX-2, TNF-α and IL-6 in the lacrimal gland tissue of castrated male dry eye disease rats, and inhibit the inflammatory response.
2023, 44(11): 47-55.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231107
Abstract:
Objective Bioinformatics was used to analyze the correlation between CAV1 expression and its prognostic value and immune infiltration in various tumors and to clarify its value in evaluating tumor prognosis. Methods The mRNA expression level of CAV1 gene was analyzed based on TCGA and GTEx databases, the protein expression level of CAV1 gene was analyzed by CPTAC database, the correlation between CAV1 expression and survival and prognosis of tumor patients was analyzed by univariate COX regression, and the tumor immunohistochemistry level of CAV1 expression was analyzed by HPA database. Spearman correlation analysis of tumor and immune infiltrating cells. Results The mRNA expression of the CAV1 gene was different in 26 tumor tissues(P < 0.05), and the high expression of CAV1 had adverse effects on the overall survival of bladder urothelial carcinoma, low-grade glial carcinoma of the brain and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. It is closely related to various tumor immune infiltrating cells in BLCA, LGG, and HNSC. Univariate COX regression analysis showed that CAV1(HR = 1.489, P = 0.0078) and age(HR = 1.424, P = 0.0022) were risk factors for overall survival in BLCA patients, while CAV1(HR = 2.432, P = 0.0006) and WHO grade(HR = 3.023, P = 0.0004) were risk factors for overall survival in LGG patients.CAV1(HR = 1.432, P = 0.0085) and clinicopathological classification(HR = 1.806, P = 0.0006) were risk factors for overall survival in HNSC patients. Conclusion The expression and regulation of CAV1 gene are correlated with the occurrence and development of BLCA, LGG and HNSC, patient prognosis and tumor immunity. They may be a prognostic factor of BLCA, LGG and HNSC patients.
2023, 44(11): 56-62.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231108
Abstract:
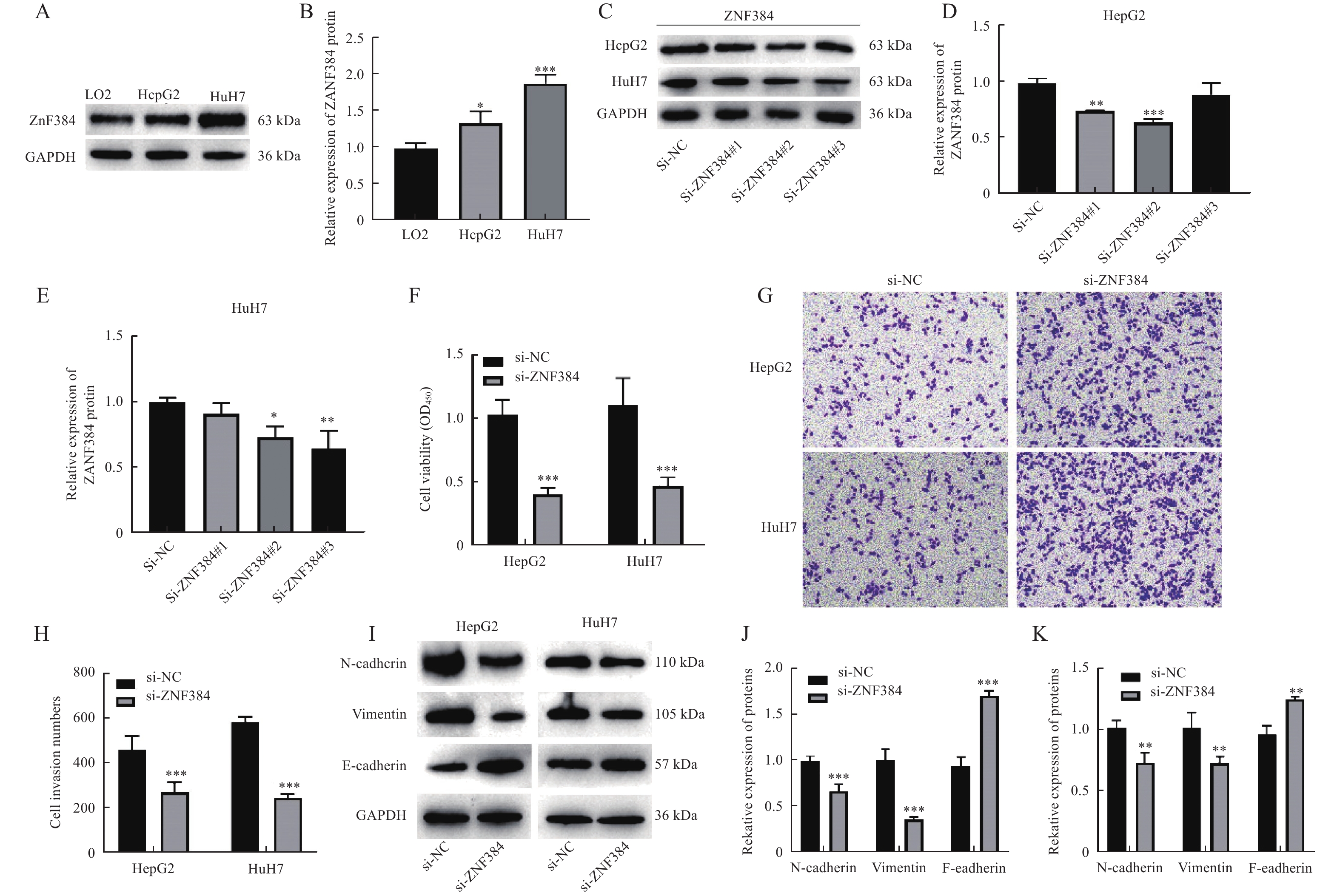
Objective To investigate the effect of ZNF384 on the proliferation and metastasis of HCC by regulating GCLM and demonstrate the specific mechanism. Methods si-ZNF384 and pcDNA-GCLM were transfected into HepG2 and HuH7 cell lines of HCC, respectively. Western blot was carried out to detect the expressions of ZNF384 and GCLM proteins as well as the expressions of EMT-markers N-cadherin, Vimentin and E-cadherin. CCK-8 assessed cell proliferative activity. Transwell assay was conducted to measure cell migration. Dual-luciferase experiment verified the binding relationship between ZNF384 and GCLM. The localization of ZNF384 and GCLM in HepG2 cells was detected by FISH assay. Results The expressions of ZNF384 and GCLM in HepG2 and HuH7 cells were increased(P < 0.05). Knockdown of ZNF384 inhibited the proliferation(P < 0.001) and migration(P < 0.001) of HepG2 and HuH7 cells, suppressed the expression of interstitial markers N-cadherin(P < 0.01) and Vimentin(P < 0.01), and promoted the expression of epithelial marker E-cadherin(P < 0.01). Database and dual-luciferase experiments confirmed that ZNF384 is bound to the promoter of GCLM. Overexpression of GCLM reversed the inhibitory effect of knocking down ZNF384 on the proliferation, migration and EMT of HepG2 and HuH7 cells(P < 0.05). Conclusion Knocking down ZNF384 can repress the proliferation and metastasis of HCC cells by inhibiting GCLM.
2023, 44(11): 63-69.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231109
Abstract:
Objectives To investigate the effects of sacubitril/valsartan (S/V) on cardiac function and ventricular arrhythmias in patients with chronic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction(HFrEF)who underwent primary prevention of sudden cardiac death (SCD) after implantation of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD). Methods HFrEF patients who were hospitalized in the Cardiovascular Department of the First People’ s Hospital of Yunnan Province from September 2017 to December 2022 and received S/V treatment and ICD implantation for primary prevention of SCD were included. ① We calculated the S/V dose of patients at 12 months of follow-up, as well as cardiac ultrasound indicators (LVEF, LVEDD, LAD) at 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment; ② ICD was used to record ventricular arrhythmia events and treatment status, dynamic electro-cardiogram indicators: average number of ventricular premature beats per hour, standard deviation (SDNN) of all sinus rhythm RR intervals, and corrected average QT interval (QTc). Results A total of 56 patients were included. (1) At one-year follow-up, the average medication dose for S/V in all patients was 94.6 mg bid. (2) Following up for 3 months, LVEF, LVEDD, and LAD improved compared to before treatment (P < 0.05); LVEF, LVEDD, and LAD improved after 6 months of follow-up compared to 3 months of treatment (P < 0.05); LVEF, LVEDD, and LAD improved after 12 months of follow-up compared to 6 months of treatment (P < 0.05). (3) Compared with 1-6 months of follow-up, the incidence of VT/VF, NSVT and monitored ventricular brachytherapy decreased during 7-12 months of follow-up (P < 0.05).(4) Compared with before treatment, SDNN increased from (94.38±26.42)ms to (102.23±20.36)ms and average QTc decreased from (441.92±10.64)ms to (411.46±6.00)ms during 1-year follow-up(P < 0.05). Conclusions (1) For HFrEF patients implanted with ICD for primary prevention of SCD, their cardiac structure and function was continued to improve within one year of receiving S/V treatment; (2) S/V reduced the occurrence of ventricular arrhythmias during the follow-up period of this study.
2023, 44(11): 70-75.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231110
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of intrauterine hyperglycemia on peripheral inflammatory reaction of cord blood of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus(GDM). Methods The objects of this study were the offspring of women who delivered in the first affiliated hospital of Kunming Medical University from November 2019 to May 2023.The GDM group included 108 infants(67 male cases and 41 female cases) of mothers with GDM.The control group included 150 infants(82 male cases and 68 female cases) of women with normal glucose tolerance.The concentrations of umbilical vein blood serum IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, L-8, IL-10, IL-17, TNF-α, IFN-α, IFN-γ and IL-12P70 were measured by flow cytometry CBA technology. Results The levels of vein cord blood serum pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α were higher than the control group, the differences was statistical (6.65±0.51 vs 4.02±0.40, P = 0.007; 13.96±1.10 vs 7.36±0.50, P = 0.040; 1.27±0.10 vs 0.56±0.01, P = 0.020). The level of IFN-γ was lower than the control group(5.67±0.50 vs 10.54±0.90, P = 0.038), the differences were statistical. There was no differences in the levels of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12P70, IL-17, IFN-α. Conclusion Even in GDM offspring with good blood sugar control during pregnancy, the innate immune system is overactivated, and pro-inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α are released excessively, laying a clinical foundation for further understanding whether the activation of the peripheral innate immune system in the GDM intrauterine hyperglycemic environment can induce the occurrence of neuroinflammation in the brain and its contribution in neuroinflammation.
2023, 44(11): 76-81.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231111
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the effects of various dosages of vitamin D(VitD) supplementation on bone metabolism and growth and development indicators of preterm infants. Methods Preterm infants with gestational age < 34 weeks or birth weight < 1500 g were divided into high-dose group(Total vitamin D intake ≥900 IU) and low-dose group(Total vitamin D intake < 900 IU) based on the VitD intake. Multiple linear regression approach for the analysis of the relationships between VitD intake and growth and development indicators(including the growth rate of weight, length, and head circumference) and bone metabolism indicators(including serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Alkaline phosphatase, calcium, and phosphorus levels) of preterm infants at 28 days after birth or discharge. Results A total of 229 preterm infants met inclusion criteria, including 135 cases in the high-dose group and 94 cases in the low-dose group. There were no significant differences in serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and calcium levels among the groups(P > 0.05). Preterm infants in high-dose group had a lower incidence of hypophosphatemia(χ2 = 6.215, P = 0.045) and a higher level of serum alkaline phosphatase(Z = 3.174, P = 0.002) compared to the low-dose group. There were no significant differences in the growth rate of weight and length among the groups(P > 0.05). Preterm infants with high-dose group had a higher percentage of the growth rate of head circumference ≥5 mm per week(χ2 = 4.036, P < 0.001) and a higher growth rate of head circumference(β = 1.510, 95%CI: 0.751~2.269, P < 0.001) compared to the low-dose group. Conclusion High-dose vitamin D intake can stabilize bone metabolism and promote the growth rate of head circumference in preterm infants.
2023, 44(11): 82-86.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231112
Abstract:
Objective To establish a method for sterility test of non-aqueous clonazepam injection, and explore the effect of organic solvent on sterility test. Methods With reference to the 2020 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia, the effects of organic solvents in Clonazepam injection on the filtration membranes and cups of different materials of the collector were investigated by membrane filtration test and membrane permeability test, as well as the effects of pH value of the sample solution and the variety and quantity of the rinsed solution on the microorganisms in the sample. Results Benzyl alcohol, acetic acid and anhydrous ethanol caused the dissolution of composite cellulose membrane, nylon membrane and PVDF membrane in different degrees, and the dissolution of composite cellulose membrane was more serious, and the benzyl alcohol remaining in the cup and filter membrane was insoluble in the medium and caused turbidity. The reaction of propylene glycol with AS cup made the medium cloudy. The pH range of the culture-medium was 5.99 ~ 7.16 after washing with different rinsing solutions. Conclusions We have developed a rational sterile testing method, which provides a good reference value for the sterile inspection of injections using organic phases as solvents.
2023, 44(11): 87-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231113
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the variables that affect social anxiety in leukemia-affected kids. Methods In order to better understand the 92 leukemia patients at the hematology unit of Kunming Children's Hospital, basic demographic data and measures of social anxiety were gathered through questionnaire surveys of the patients and their families. The external relationship between social anxiety and a child's own status and family circumstances was investigated using difference analysis, the internal factors affecting anxiety level were discovered using correlation analysis, and the pre-factors of social anxiety level in children with leukemia were investigated using QCA configuration analysis. Results Children with leukemia had higher levels of social anxiety at the maintenance phase of treatment, in homes with only one parent, when grandparents were the primary caregivers, and when the monthly family income ranged from 4001 to 8000 yuan(P < 0.05). Children's emotions and behaviors were strongly influenced by how much they perceived other people's assessments and opinion(P < 0.05). Evaluation-driven and self-coordinated antecedent configurations both have an impact on how much social anxiety leukemia patients experience. Conclusions Since children with leukemia are more likely to have social anxiety, it is important to monitor their emotional and psychological well-being during the course of their treatment and during the maintenance phase. Children who exhibit social anxiety symptoms should receive psychological counseling as soon as possible. In order to lessen social anxiety in children with leukemia, try using nursing or medical social workers to intervene in specific group activities, build the bond between kids and their families, and boost their psychological resilience.
2023, 44(11): 94-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231114
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy of continuous renal replacement therapy(CRRT) in patients with severe burn sepsis. Methods Forty patients with sepsis caused by severe burns who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to the Department of Burns of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2020 to January 2023 were retrospectively analyzed. According to the treatment, patients were divided into control group and treatment group, with 20 patients in each group. The control group was given conventional symptomatic and supportive treatment, and the treatment group was given continuous renal replacement therapy on the basis of conventional treatment. The venous blood of the control group and the treatment group was taken before treatment and 24, 48, 72 hours after treatment. White blood cells(WBC), calcitonin(PCT), serum creatinine(Scr), blood urea nitrogen(BUN) level. In addition, the length of hospital stay and the total cost of hospitalization were compared between the two groups. Results Before treatment, the levels of C-reactive protein(CRP), interleukin-6(IL-6), white blood cell(WBC), procalcitonin(PCT), serum creatinine(Scr) and blood urea nitrogen(BUN) in the two groups were compared, the P value was above 0.05, and the difference was not significant in the statistical data. 72 hours after treatment group C reactive protein(CRP) and interleukin 6(IL - 6), white blood cell(WBC), calcitonin(PCT), serum creatinine(Scr), blood urea nitrogen(BUN) level, the results show that numerical value was lower than the control group, experimental group and the difference between the P value is less than 0.05, has significant statistical significance. In addition, the length of hospital stay and total hospital costs were also statistically lower in the CRRT group than in the usual care group. Conclusion In severe burn patients with sepsis, continuous renal replacement therapy has a significant effect, which can effectively remove inflammatory mediators, prevent and treat uncontrolled inflammatory response, and effectively relieve the symptoms caused by systemic infections such as burn wound sepsis. It has a good application prospect in the prevention and treatment of stress injury and organ injury caused by sepsis in clinical practice. At the same time, it can also bring certain economic and social benefits.
2023, 44(11): 100-107.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231115
Abstract:
Objective To systematically describe and evaluate self-help intervention in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, to provide guidance for future self-help intervention research through evidence mapping method. Methods Related studies on self-help intervention for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were searched in CNKI, Wanfang Data, VIP, CBM, PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, and EMBASE from inception to November 2022. The quality of the studies was assessed using the risk of bias(RoB) tool and A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Review-2(AMSTAR-2). Based on the Nursing Outcome Classification, the outcome indexes were classified. An evidence mapping framework was established, using Microsoft Excel tools for data extraction and coding, and using bubble charts to comprehensively present the research content. Results A total of 41 randomized controlled trials and 2 systematic reviews/Meta-analyses were included, which involved three intervention types with 10 self-help intervention methods. Including self-administered(3, 7%), pure self-help(20, 47%), and guided self-help(20, 47%). The main intervention methods included a self-service manual, internet platform, dedicated management software, etc. The main outcome indicators included blood glucose level(34, 79%), self-management ability(14, 33%), and quality of life(9, 21%).18(42%) of the research conclusions were classified as "beneficial", 24(56%) of the research conclusions were classified " probably beneficial". In addition, the intervention duration was mainly within 6 months, and the study sites were concentrated in hospitals and communities. Conclusion Self-help intervention may be effective for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. At the same time, it is easy to implement and promote. However, its effectiveness are different for different types、methods and approaches of interventions. In the further study, we can use data-driven and robotics to build self-help interventions, and we also need to focus on the durability of the intervention's effects.
2023, 44(11): 108-112.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231116
Abstract:
Objective To explore and analyze the clinical application efficacy and prospect of neuronavigation positioning assisted endoscopic transnasal sphenoid approach for resection of pituitary adenomas under general anesthesia. Methods A total of 68 patients who underwent pituitary adenoma surgery at the Neurosurgery Department of Yangjiang People's Hospital from September 2018 to April 2023 were collected and divided into two groups: an experimental group of 34 patients(neuronavigation-assisted endoscopic transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenoma resection) and a control group of 34 patients(microscopic transsphenoidal approach for pituitary adenoma resection). The surgery-related indicators, complication indicators, and preoperative and postoperative endocrine hormone indicators were analyzed and evaluated in both groups. Results The probability of total tumor resection in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group in postoperative imaging comparison, with statistical significance(P<0.05). The comparison of surgical time, bleeding volume, hospitalization time, surgical bleeding volume, and postoperative patient hormone indicators showed that the experimental group was significantly lower than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusions Neuronavigation positioning assisted endoscopic transnasal sphenoid approach for resection of pituitary adenoma has the advantages of small trauma, safety, high efficiency, short hospital stay, and high total resection rate. This represents a novel and effective strategy for wide clinical application.
2023, 44(11): 113-119.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231117
Abstract:
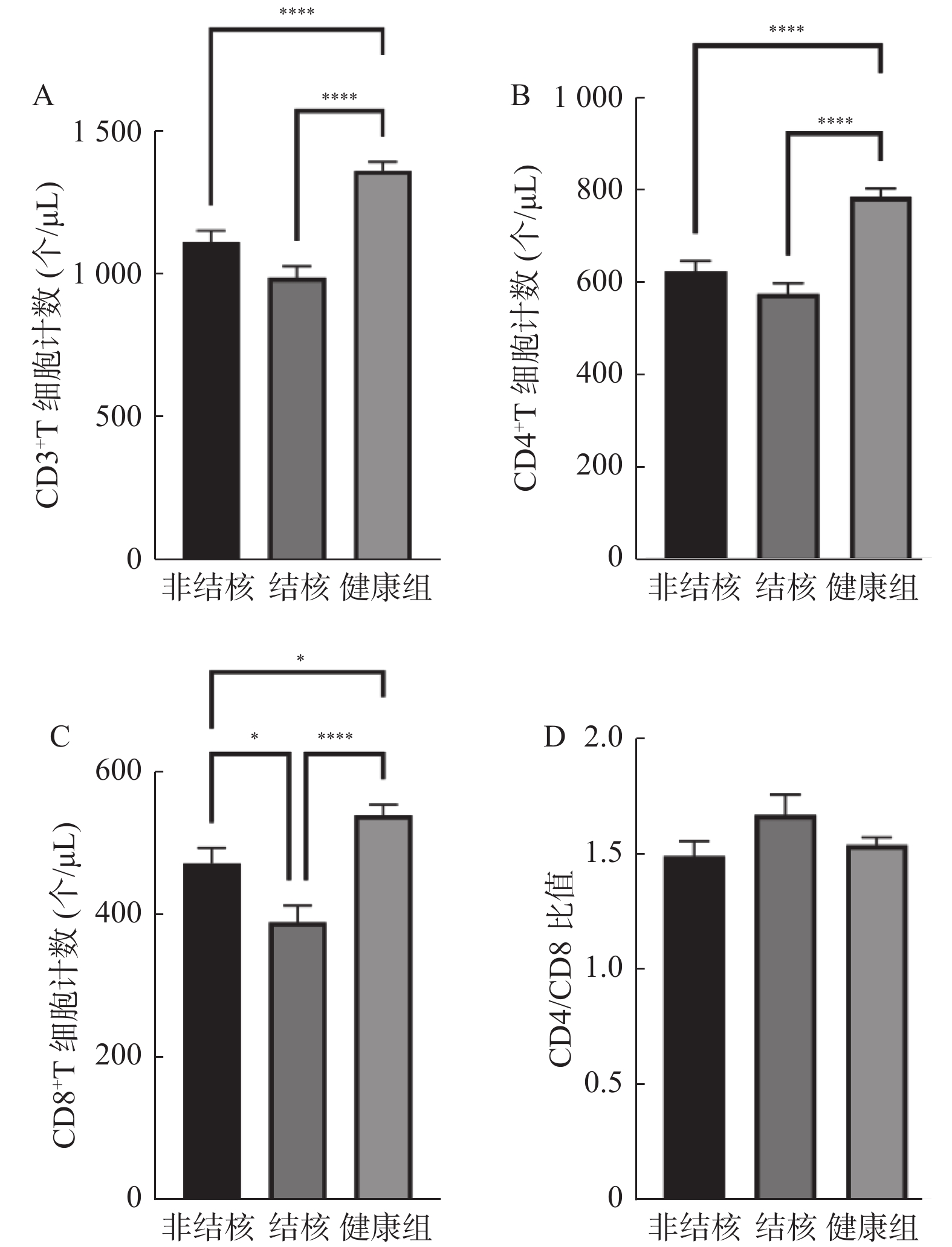
Objective To analyze the differences in liver and kidney function, immune function, and drug resistance between nontuberculous mycobacteria-infected people and healthy people. Methods We collected 122 cases of Nontuberculous Mycobacterium infected people and 130 cases of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected people in The Third People’ s Hospital of Kunming from May 2021 to March 2022, which were divided into non-Mycobacterium tuberculosis group and tuberculosis group respectively. And 150 cases of healthy people in the same period were selected as a healthy control group. We analyzed the difference in sex, age, liver and kidney function, peripheral blood T lymphocyte subsets and drug sensitivity tests between three groups. Results There was no significant difference between the non-tuberculosis group, tuberculosis group, and healthy group in different ages and sexes(P > 0.05). The TBIL, ALT, AST, GGT, CR and UA of the non-tuberculosis group were significantly higher than those in the tuberculosis group and healthy group( P < 0.05). TBIL, ALT, AST and GGT in the non-tuberculosis group were significantly higher than those in the tuberculosis group( P < 0.05). The CD3 +T, CD4+T and CD8+T lymphocyte count in the non-tuberculosis group and tuberculosis group were significantly lower than those in the healthy group(P < 0.05). The CD8 +T lymphocyte count in the non-tuberculosis group was significantly higher than that in the tuberculosis group(P < 0.05). The top three drug-resistance medicines in the non-tuberculosis group were imine/doxycycline, doxycycline and minocycline, and the drug resistance rates were 99.18%, 78.69% and 72.95% respectively. The top three drug resistance medicine in the tuberculosis group were isoniazid, rifampicin, and rifapentine, and the drug resistance rates were 22.32%, 17.69% and 16.15% respectively. Conclusion Compared with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a non-Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected person has more serious liver function damage, and the immune function is prone to disorder and damage. Non-tuberculous mycobacteria are more resistant to antibiotics, and the drug resistance is stronger. We should strengthen the identification of non-tuberculous mycobacteria and mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in a clinic and use the drug regimen reasonably.
2023, 44(11): 120-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231118
Abstract:
Objective To explore the care burden and influencing factors of the primary caregivers of severe mental illness patients in Xundian County, Kunming City. Methods The primary caregivers of registered severe mental illness patients in Xundian County were investigated by questionnaire. The contents of the questionnaire included Self-Rating Anxiety Scale(SAS), Self-Rating Depression Scale(SDS) , Perceived Social Support Scale(PSSS), Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale(CD-RISC)and Caregiver Burden Inventory(CBI). Results Family income, continuous care duration, PSSS total score and CDRISC total score had negative effects on CBI score(all P < 0.05). The patients had an accident and were diagnosed as epileptic affective disorder, paranoid mental disorder, bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder and schizophrenia, took care of the patient every week, and the total score of SAS and SDS had a positive impact on the CBI score(all P < 0.05). Conclusions The higher the family income, the longer the duration of continuous care, the better the understanding of social support and psychological resilience of the intensive caregivers, the more they can reduce the care burden of major caregivers of patients with severe mental illness. The caretakers with accident-causing behaviors and epileptic affective disorder, paranoid mental disorder, bipolar disorder, schizoaffective disorder, and schizophrenia, and the longer the caretakers cared for the patients per week, the higher the anxiety and depression score and the higher the caregiving burden.
2023, 44(11): 126-134.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231119
Abstract:
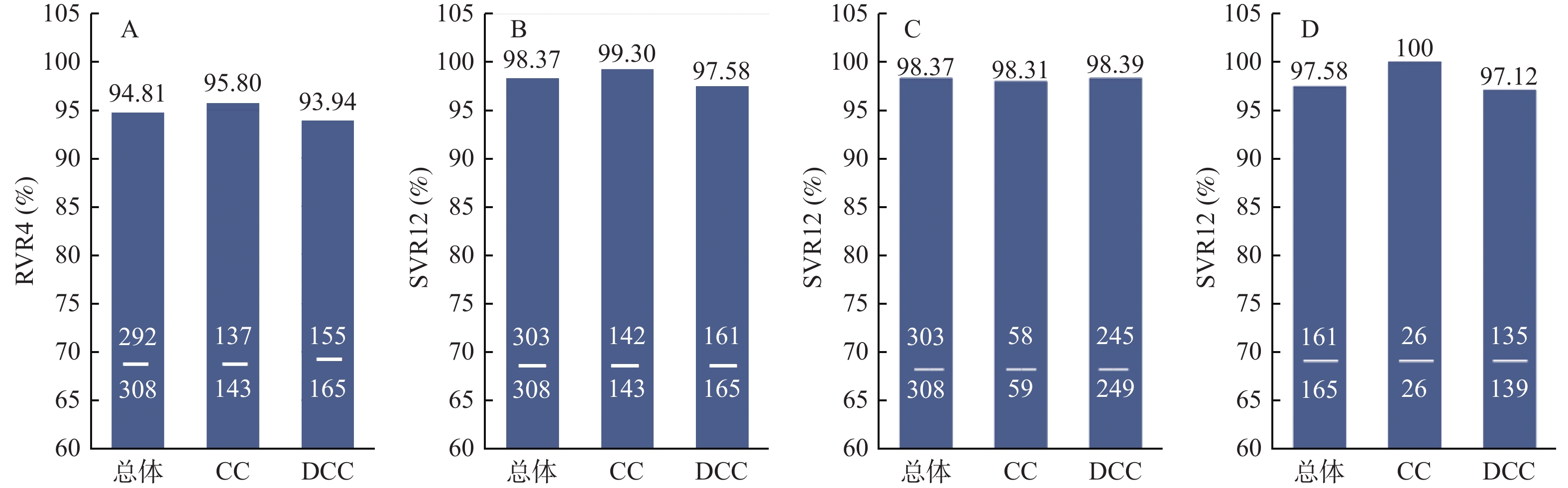
Objective To investigate the efficacy and safety of Sofosbuvir/Velpatasvir ± ribavirin(SOF/VEL±RBV) in the treatment of genotype 3 chronic hepatitis C cirrhotic patients. Methods Patients diagnosed with genotype 3(GT3) HCV infection and treated at the Third People's Hospital of Kunming City from June 2018 to February 2023 were retrospectively included. All patients had liver cirrhosis and were treated with SOF/VEL+RBV for 12 weeks, SOF/VEL therapy for 12 or 24 weeks if favorable ribavirin contrainminated or ribavirin intolerant. The virologic indexes, liver and kidney function indexes and adverse reactions of the patients were analyzed before treatment, 4 weeks, 12 weeks and 12 weeks after drug withdrawal. Results A total of 319 patients were included, including 308 cases in SOF/VEL+RBV group and 11 cases in SOF/VEL group. After 12 weeks off-treatment, the sustained virological response(SVR12) rate in SOF/VEL+ RBV group was 98.37%(303/308), and the levels of APRI score and FIB-4 index were decreased compared with baseline(P < 0.05). The levels of total bilirubin, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase were all decreased, and the differences were statistically significant(all P < 0.05). The SVR12 rate of SOF/VEL group was 72.73%(8/11). The adverse reactions were mild hemolytic anemia(15.26%), fatigue(8.12%) and rash(8.77%) in SOF/VEL+RBV group, and fatigue(9.09%) in 1 case in SOF/VEL group. Conclusion SOF/VEL+RBV could achieve higher SVR12 and well tolerated for GT3 HCV-infected patients either with compensated cirrhosis or decompensated cirrhosis patients. Liver function, renal function and liver fibrosis could also be improved after treatment.
2023, 44(11): 135-139.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231120
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the correlation between PEAR1 gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke, so as to provide a scientific basis for further research on the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke, and provide new ideas for disease prevention and treatment Methods A total of 150 patients with acute ischemic stroke in the Department of Neurology, Yan’ an hospital affiliated to the Kunming Medical University were selected as the experimental group and 150 healthy persons as the control group, a polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism(PCR-RFLP) was used to analyze the Single-nucleotide polymorphism at rs12041331 in PEAR1 gene. The genotypes were verified by sequencing. Results Chi-square test results showed that between the ischemic stroke group and control group, the distribution of GG, GAandAA genotypes and allele frequency of G, A on PEAR1 gene rs12041331G > A polymorphism site had significant differences(p < 0.05). The proportion of diabetes mellitus and hypertension and the level of homocysteine homocysteine(HCY) in the ischemic stroke group were significantly higher than those in the control group(p < 0.05).Logistic regression analysis showed that mutations at the PEAR1 gene rs12041331G > A site might be a risk factor for ischemic stroke. Conclusion The polymorphism of PEAR1 gene rs12041331G > A site is associated with ischemic stroke Genetic predisposition. The PEAR1 gene rs12041331G > A site may be a candidate gene for ischemic stroke risk prediction.
2023, 44(11): 140-144.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231121
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the relationship between leptin(LEP) 、serum uric acid(SUA) and obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM). Methods According to body mass index(BMI), 111 newly diagnosed T2DM patients were divided into normal weight group(69 cases) and T2DM combined with obesity group(42 cases), The differences in LEP, sex, smoking status, age, drinking status, blood pressure, blood lipid, fasting blood glucose, OGTT-2h, glycated hemoglobin(HBA1c), fasting insulin(FINS), insulin 2 hours after meals, HOMR-IR and UA were compared between the two groups. Logistic regression analysis was used to screen the independent risk factors of type 2 diabetes combined with obesity. Results There were statistically significant differences in alcohol consumption, OGTT-2h, HBA1c, and UA between the two groups(P < 0.05), but no statistically significant differences in LEP between the two groups(P > 0.05). Regression analysis showed that UA could enter the equation, while LEP could not. Conclusions Patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, regardless of whether they are combined with obesity, have obvious insulin resistance and leptin levels. Uric acid is an independent risk factor for type 2 diabetes with obesity.
2023, 44(11): 145-151.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231122
Abstract:
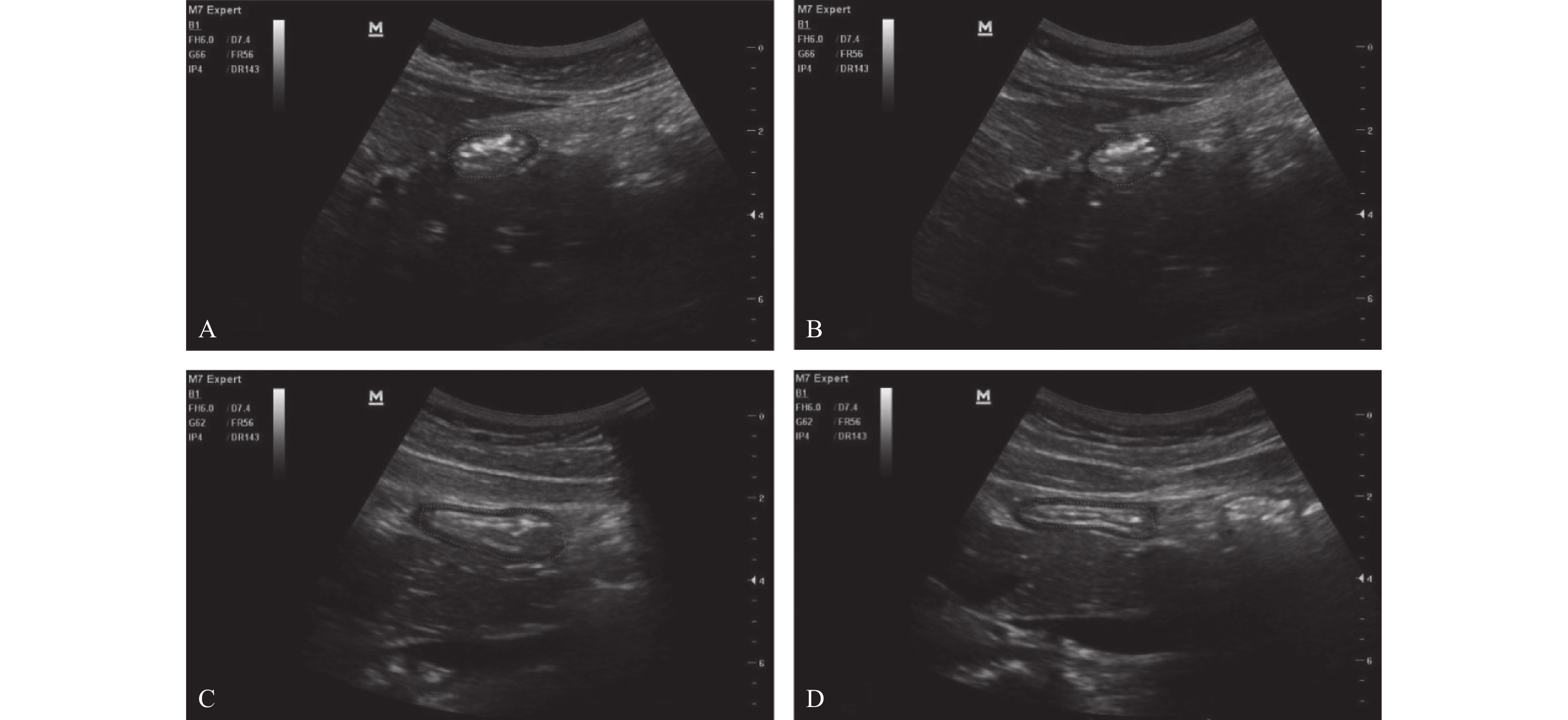
Objective To investigate the application of point-of-care gastric antrum ultrasonography in the risk assessment of aspiration in children undergoing emergency surgery. Methods A total of 120 cases of pediatric emergency surgery in Jingzhou Central Hospital of Hubei Province from December 2020 to December 2021, aged 1-12 years, American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I-III, scheduled for surgical treatment, were selected. First, according to whether it met the fasting guidelines issued by the American Society of Anesthesiologists in 2017, the clinical gastric emptying of the children were evaluated. The children were divided into clinical fasting group(CE group) and clinical full group(CF group), and then Mindray M7 ultrasound was used to qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate the gastric contents in the gastric antrum. The children were divided into ultrasound empty group(UE group) and ultrasound full group(UF group), and the consistency of clinical and ultrasound evaluation methods was recorded. The cross-sectional area(CSA) of the gastric antrum was measured before and after gastric tube suction in children in the right lateral position. The changes of CSA before and after gastric tube suction, the type and amount of food eaten before surgery, and the time interval between eating and ultrasound examination were recorded. Results A total of 108 children were finally included for statistical analysis. The consistency between clinical and ultrasound examination was poor, 92 cases(85.2%) were judged as fasting by both ultrasound and clinical. 4 cases(3.7%) were judged as fasting by ultrasound but full stomach by clinical examination. 9 cases(8.3%) were judged as full stomach by ultrasound but fasting by clinical examination. 3 cases(2.8%) were judged as full stomach by both ultrasound and clinical, (kappa=0.255, P=0.006). There was a well correlation between food intake and CSA in gastric antrum before gastric tube aspiration(r =0.840, P<0.05). Before aspiration, the gastric antrum CSA in the UF group was significantly larger than the UE group(P<0.05); After suction, there was no significant difference in gastric antrum CSA between the two groups(P=0.324). The UF group consumed more formula milk and high-fat food, the amount of food suctioned by the gastric tube and the food intake were more than UE group(P<0.05), The ultrasound interval time in the UF group was shorter than the UE group(P<0.05). The incidence of vomiting in the two groups was 8.3% and 5.2% respectively, and there was no significant difference between the two groups(P=0.674). Conclusion Preoperative gastric antral ultrasonography combined with the type and amount of food intake in children undergoing emergency surgery can effectively help anesthesiologists to make an appropriate judgment of whether the stomach is full under emergency circumstances, so as to adjust the anesthesia strategy in time and choose the appropriate airway management.
2023, 44(11): 152-157.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231123
Abstract:
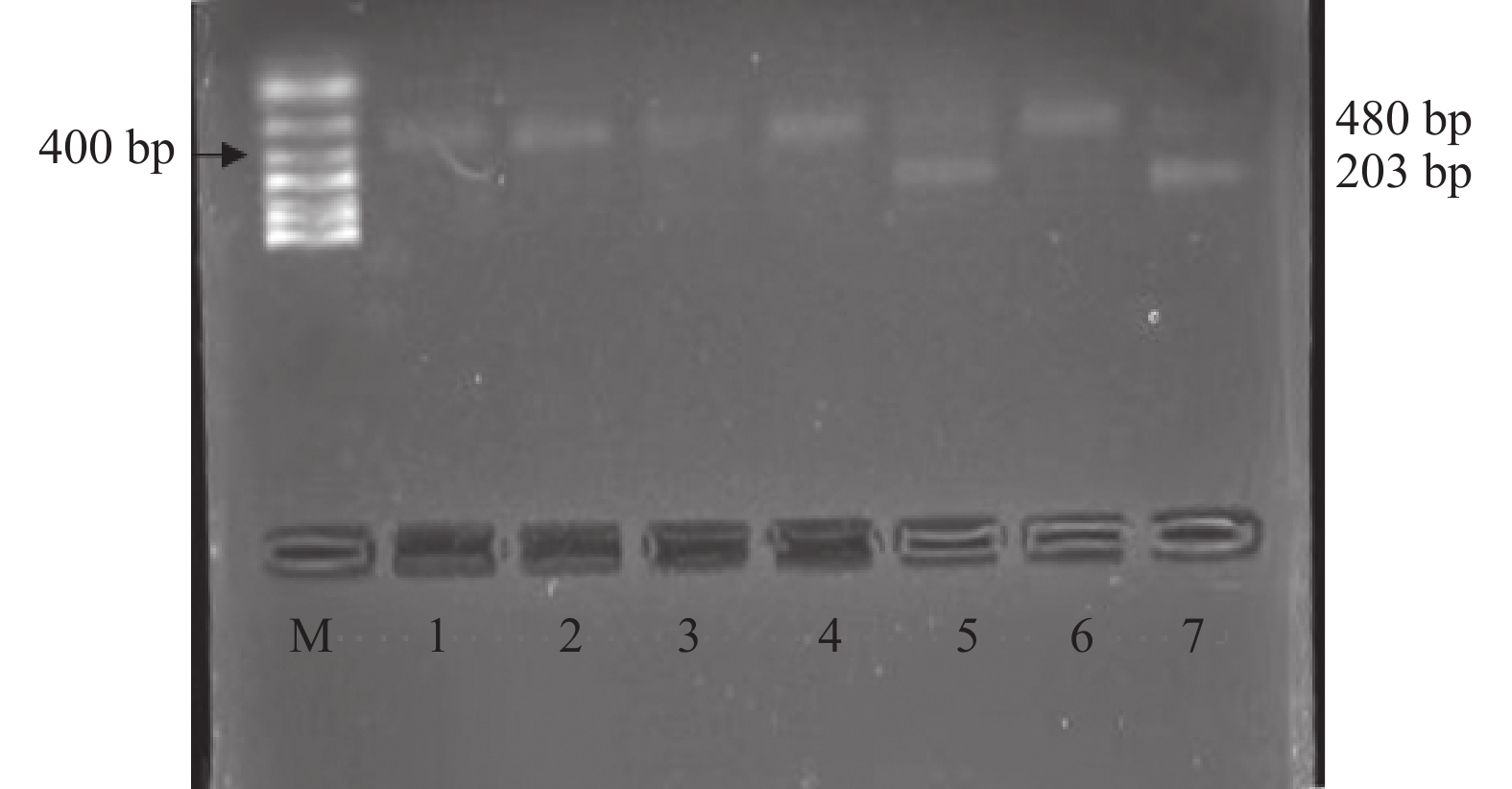
Objective To investigate the prevalence of HIV-1 drug resistance and genotypes in HIV/AIDS patients before antiretroviral therapy in Dali Bai Autonomous Prefecture(Dali) , so as to provide a theoretical basis for more effective antiviral drug application in the clinic. Methods A total of 122 adults with HIV/AIDS on initial antiretroviral therapy were recruited in Dali from January to August 2018 before antiretroviral therapy.Amplification of HIV-1 pol genes for drug resistance analysis. Results A total of 114 samples were successfully sequenced and 7 HIV-1 genotypes were identified according to the phylogenetic analysis, including three predominant genotypes such as CRF08_BC(59.6%, 68/114)、CRF07_BC(25.4%, 29/114)and CRF01_AE(7.0%, 8/114). The HIV-1 genotypes showed statistical differences among the main transmission route(χ2 = 25.637, P < 0.001). CRF08_BC were mainly in heterosexual and drug users, and CRF01_AE were mainly in homosexual.Surveillance drug resistance mutations(SDRMs) were 21.9%(25/114).A higher proportion of mutations E138A(9.6%, 11/114)and V179D/E(9.6%, 11/114)were accessory drug-resistant mutations. HIV-1 drug-resistant rate was 1.8%(2/114), and NRTIs and NNRTIs were 0.9%(1/114)respectively. Conclusion In HIV-1/AIDS patients before antiretroviral therapy in Dali, HIV-1 genotypes are multiple, with a low prevalence rate of HIV-1 drug resistance. To maintain effective public health antiretroviral therapy strategies, it is essential to strengthen the monitoring of HIV-1 drug resistance and master the data, and timely select and adjust the first-line antiretroviral therapy plan.
2023, 44(11): 158-163.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231124
Abstract:
This paper reviews the diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, hazards, mechanisms, risk factors, risk assessment and targeted care of urinary tract infection (UTI) in patients with ureteral dermatostomy. The paper proposes the necessity of constructing and promoting a scientific and feasible early risk warning score for urinary tract infection in patients with ureteral dermatostomy for these potential risk factors. The aim is to provide a reference for the study of risk factors of urinary tract infection in ureteral cutaneous stomy patients, the development of an early warning model, and the formulation and implementation of clinical decision-making.
This paper reviews the diagnostic criteria, epidemiology, hazards, mechanisms, risk factors, risk assessment and targeted care of urinary tract infection (UTI) in patients with ureteral dermatostomy. The paper proposes the necessity of constructing and promoting a scientific and feasible early risk warning score for urinary tract infection in patients with ureteral dermatostomy for these potential risk factors. The aim is to provide a reference for the study of risk factors of urinary tract infection in ureteral cutaneous stomy patients, the development of an early warning model, and the formulation and implementation of clinical decision-making.
2023, 44(11): 164-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231125
Abstract:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is emerging as one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases in children worldwide, and bile acids, which play an important role in the enterohepatic circulation are becoming increasingly prominent in its pathogenesis. In recent years, it has been found that bile acids are[1 ] signaling molecules for farnesol X receptor and G protein-coupled receptor 5, both of which act as bile acid receptors to regulate systemic metabolism. The imbalance of bile acid metabolism is closely related to the severity of NAFLD. This article reviews the role of bile acids and their receptors in the progression of NAFLD with the aim of providing new targets for the noninvasive diagnosis and treatment of NAFLD.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is emerging as one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases in children worldwide, and bile acids, which play an important role in the enterohepatic circulation are becoming increasingly prominent in its pathogenesis. In recent years, it has been found that bile acids are[
2023, 44(11): 170-174.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231126
Abstract:
Objective To establish a systematic psychological intervention based on S-ABC framework, and to explore its effects on perioperative psychological distress and immune function in patients with primary liver cancer. Methods A medical management team was established to construct systematic psychological intervention measures based on S-ABC framework. A total of 76 patients with primary liver cancer admitted from January 2021 to May 2022 were selected and divided into control group and experimental group by random number method according to different perioperative treatment methods(26 cases of hepatic arterial chemoembolization, 30 cases of laparoscopic hepatectomy, 20 cases of open hepatectomy), with 38 cases in each group. On the basis of finishing nursing, the control group was given routine psychological guidance, and the experimental group was given systematic psychological intervention measures based on the S-ABC framework. The degree of psychological distress and immune function were compared between the two groups at admission, 1, 3, and 6 months after intervention. Results The psychological pain scores of two groups of patients at admission and 1, 3, and 6 months after intervention were [experimental group: (6.53 ± 1.54) points, (3.66 ± 1.12) points, (2.13 ± 0.94) points, and (0.87 ± 0.70) points; control group: (6.16 ± 1.46) points, (4.45 ± 1.11) points, (3.95 ± 1.09) points, and (2.26 ± 0.86) points], and showed no statistically significant difference in admission time (P > 0.05); After intervention, the psychological pain score of the experimental group decreased significantly, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The immune function indicators of CD3+, CD4+, CD8+, CD4+/CD8+ at admission and 1, 3, and 6 months after intervention had no statistically significant differences (P > 0.05) between the two groups of patients. After implementing intervention measures, the experimental group of patients had significantly better indicators than the control group, with a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). Conclusion The systematic psychological intervention measures based on S-ABC framework can effectively reduce the psychological pain of patients, improve body immunity, and promote the rehabilitation of patients, which is worthy of clinical promotion and reference.
2023, 44(11): 175-182.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231127
Abstract:
Objective To explore the influence of wearable device-based pulmonary rehabilitation(PR) mode on the rehabilitation effect of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease(COPD). Methods The patients with COPD who were hospitalized in our hospital from October 2019 to August 2021 were selected as the research objects. Thirty-four patients who entered the group first received routine PR training programs as the control group. Thirty-four patients who were enrolled later were given wearable device-based PR training for the experimental group. Compare the effects of different PR training modes on the effect of patients’ PR at eight weeks after discharge. Results There were significant differences after the intervention. The 6MWT walking distance test group(443.47 ± 97.04) meters vs control group(389.65 ± 115.64) meters, The ADL score experimental group(94.41 ± 7.76) points vs control group(87.65 ± 12.63) points, The respiratory rate experimental group(19.65 ± 3.87) beats/minute vs control group(22.56 ± 3.64) beats/minute, and the heart rate experimental group(81.5 ± 99.12) beats/minute vs control group(91.35 ± 12.72) beats/minute, P < 0.05; Compared with the intervention before and after the intervention, the walking distance of 6MWT in the experimental group increased by (64 ± 57.51) meters, ADL score increased(5.44 ± 6.08) points, the respiratory rate decreased(3.18 ± 3.70) beats/minute, heart rate decreased(4.71 ± 8.47) beats/minute, oxygen saturation increased(1 ± 2.17)%, and mMRC score decreased dyspnea. P < 0.05. Conclusion Research on PR based on wearable devices can effectively improve the symptoms of dyspnea in patients with COPD and improve exercise tolerance and activities of daily living.
2023, 44(11): 183-187.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231128
Abstract:
Objective To verify the validity of difficult venous access score in pediatric peripheral venipuncture and explore its applicability in pediatric venous access indwelling strategy. Methods The convenience sampling method was used to select inpatients in the pediatric department of a tertiary hospital in Kunming, Yunnan Province as the research subjects. Riker’ s three-variable pediatric Difficult Intravenous Access(DIVA) Assessment Tool was used to evaluate 374 children undergoing venipuncture catheterization. The predictive value of the tool was evaluated using indicators such as the area under the ROC curve, sensitivity, specificity, and Youden index. Results Comparing this DIVA score with Riker’ s study, the difference was not statistically significant(P > 0.05). In contrast, the difference in DIVA scores between the failed puncture group and the successful puncture group was statistically significant(P < 0.001). As the DIVA score increased from 0 to 6, the first venipuncture success rate of the corresponding children gradually decreased from 92.9% to 54.5%. The area under the ROC curve of the DIVA score was 0.648. When the total score was 3 points, the scale had the greatest predictive value. Conclusion The three-variable DIVA score has a certain ability to identify difficult venous access in children. It has a good prediction accuracy, and can be used for evaluation before pediatric peripheral venipuncture.
2023, 44(11): 188-194.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20231129
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the supportive care needs of patients after radical surgery for breast cancer based on the Kano model and define their attributes. Methods Convenience sampling was used to select 210 patients who underwent radical surgery for breast cancer and were hospitalized in a tertiary cancer specialty hospital in Yunnan Province from June 2021 to December 2021. The Kano model, Supportive Care Needs Survey-Short Form 34(SCNS-SF34), and Better-Worse two-dimensional matrix were used to classify patients' supportive care needs. Furthermore, factor selection lines and sensitivity screening were applied to identify the needs that require significant improvement and rank them. Results A total of 210 questionnaires were distributed, and 200 valid questionnaires were collected, with an effective response rate of 95.2%. There were 2 mandatory attribute needs(5.9%), 4 desired attribute needs(11.8%), 23 attractive attribute needs(67.6%), and 5 indifferent attribute needs(14.7%). Fifteen needs were identified as priorities for improvement, with the highest sensitivity being 0.228 and the lowest being 0.012. Conclusion Healthcare professionals should continuously improve and optimize supportive care measures based on patients’ different needs to enhance their healthcare experience.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS