2024 Vol. 45, No. 2
2024, 45(2): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240201
Abstract:
In the past 20 years, the development of artificial intelligence has made rapid progress, and it is increasingly applied in the medical field, including medical image-assisted diagnosis and treatment, health management, disease risk prediction and so on. In this paper, the application status of artificial intelligence-assisted detection and diagnosis system based on deep learning in anorectal diseases is summarized, and the new methods related to the diagnosis and treatment of anorectal diseases at home and abroad are summarized. It mainly reviews the research progress of artificial intelligence technology in the diagnosis and treatment of anal fistula, perianal abscess, hemorrhoids and other anorectal diseases.
In the past 20 years, the development of artificial intelligence has made rapid progress, and it is increasingly applied in the medical field, including medical image-assisted diagnosis and treatment, health management, disease risk prediction and so on. In this paper, the application status of artificial intelligence-assisted detection and diagnosis system based on deep learning in anorectal diseases is summarized, and the new methods related to the diagnosis and treatment of anorectal diseases at home and abroad are summarized. It mainly reviews the research progress of artificial intelligence technology in the diagnosis and treatment of anal fistula, perianal abscess, hemorrhoids and other anorectal diseases.
2024, 45(2): 7-13.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240202
Abstract:
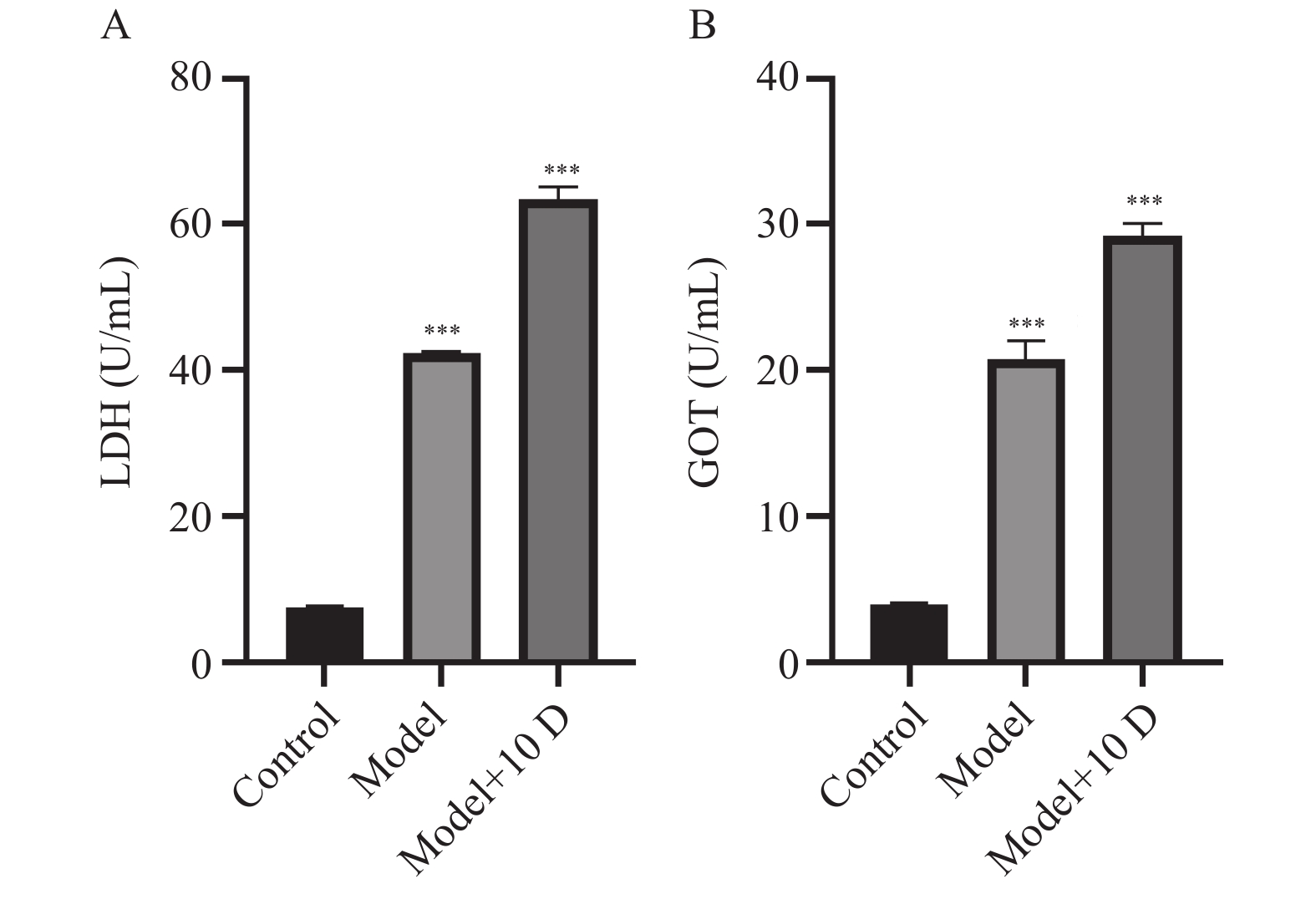
Objective To investigate the role of HK2 and VDAC1 in diacetylmorphine-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Methods A dose-escalation method was used to establish a rat model of diacetylmorphine addiction. Forty SD rats were randomly divided into three groups, the normal group (n=10) was injected with an equal amount of saline subcutaneously, the model group (n=15) was injected with 5 mg/kg of diacetylmorphine for the first time, and then the dose was increased by 2.5 mg/ (kg·d) day by day for 20 days, and the group of model + 10 D (n=15) continued to increase the dose based on the model group up to the 10th day. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) were detected by ELISA; HE staining was used to observe the pathological changes of myocardial tissues in each group; TUNEL staining was used to detect apoptosis in myocardial tissues in each group; and immunohistochemistry, RT-q-analysis, and immunochemistry were used to detect apoptosis in myocardial tissues in each group. Immunohistochemistry, RT-qPCR and Western blot were used to detect the mRNA and protein expression of HK2, VDAC1 and apoptosis-related factors. Results HE staining revealed that myocardial tissues exhibited different degrees of damage with the prolongation of diacetylmorphine intervention. Compared with the normal group, serum LDH, GOT content and myocardial apoptosis rate increased in the model group, mRNA and protein levels of HK2 and anti-apoptotic factor Bcl-2 decreased, mRNA and protein levels of VDAC1 and pro-apoptotic factors Bax and Caspase-3 increased, and the protein level of Clevead Caspase-3 increased; in the model + 10 D group the above indexes, there was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). Conclusion Diacetylmorphine can cause cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and VDAC1 may be involved in the process of cardiomyocyte apoptosis caused by diacetylmorphine.
2024, 45(2): 14-22.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240203
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between rs712 and rs7973450 located at the 3′ UTR region of the KRAS gene and the risk of cervical cancer (CC) and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in Chinese Han population in Yunnan province. Methods A total of 2405 individuals (461 subjects with CIN, 961 subjects with CC and 983 healthy controls) were enrolled. The SNPs were genotyped used TaqMan assay and the correlation of these SNPs with CIN and CC was analyzed. Results The A allele of rs7973450 might be a protective factor for the occurrence of CIN (P = 0.004, OR= 0.651, 95%CI 0.487 ~ 0.871) and CC (P = 7.00 × 10-4, OR= 0.667, 95%CI 0.529 ~ 0.844). There was no significant difference in allelic and genotypic distribution of rs712 among CIN, CC and Control groups (P > 0.017). The haplotype assay showed thatrs712A-rs7973450G was associated with increased risk of CIN (P = 4.00 × 10-4; OR= 1.714, 95%CI 1.269 ~ 2.314) and CC (P = 3.84 × 10-5, OR= 1.667, 95%CI 1.305 ~ 2.131). While haplotype rs712A-rs7973450A was associated with a lower risk of CC (P = 0.012, OR= 0.790, 95%CI 0.658 ~ 0.950). Conclusion The A allele of rs7973450 in 3′ UTR of KRAS gene might be the protective factor for the occurrence of CIN and CC in a Chinese Han population in Yunnan province.
2024, 45(2): 23-31.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240204
Abstract:
Objective To explore the possible effects and the underlying molecular mechanisms of xueshuantong [The main active component is panax notoginseng (PNS)] on the cognitive function and neural excitability of mice with Alzheimer’ s disease (AD). Methods The APP/PS1 mice were used as an animal model for AD research, at the stage when amyloid protein was not detected in mice (2 months of age). Mice in the xueshuantong group (APP/PS1+PNS) were administered by gavage once a day at a dose of 60 mg/kg for six months (for 8 months of age). The mice of the control group were given 0.9% sodium chloride (APP/PS1+Vehicle) intragastric treatment of the same volume, while the wild-type mice of the same age were given 0.9% sodium chloride intragastric treatment as the normal control group (WT+Vehicle) (15 mice in each group, n=15). After six months, the cognitive function of the mice was evaluated by the Novel Object Recognition (NOR) task and Morris Water Maze (MWM) test. The activity of BACE1, the distribution and expression of Nav1.1α, as well as the expression and enzymatic hydrolysis of Navβ2 (Navβ2 full-length and Navβ2-CTF fragments) in cortex and hippocampus were detected by EEG, Western blot and cell surface biotinylation assay, respectively. Results The NOR task showed that compared with the mice in the APP/PS1+Vehicle group, the Discrimination index (DI) of mice in the APP/PS1 group was significantly increased after xueshuantong administration (P < 0.05). The MWM test found that, the escape latency of the mice in the xueshuantong group was shortened followed six months in gastric administration (P < 0.05), while the stay time in the target quadrant and the number of platforms significantly increased (P < 0.05) after the removal of the platform. The results of EEG recording showed that xueshuantong reduced the frequency of spike-wave discharges in APP/PS1 mice (P < 0.05). Furthermore, xueshuantong significantly reduced the expression of BACE1 (P < 0.05). In the APP+PNS group, the expression of Navβ2 full-length was increased (P < 0.05), as well as corrected the abnormal distribution of Nav1.1α inside and outside of neurons (P<0.05). Conclusion Treatment with xueshuantong can significantly improve the learning and memory ability and correct the abnormal excitability of the brain in AD model mice. The mechanism may be related to the inhibition of BACE1 activity, the reduction of APP/PS1-induced excessive enzyme digestion of Navβ2, the correction of the abnormal expression and distribution of Nav1.1α in cortical and hippocampal neurons, as well as the subsequent regulation of neuronal excitability.
2024, 45(2): 32-38.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240205
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the changes of OAT expression in bone cells in chronic renal failure (CRF)and involved mechanism, and to explore the effect of OAT expression on bone metabolism. Methods Randomly divide the rats into a control group (n=6)and a model group (n=6).The model group established a rat chronic renal failure model using "single nephrectomy+adenine gavage" method, and the red blood cell (RBC) and hemoglobin (HGB)of the rat body were measured using a blood routine analyzer; Measure indicators such as creatinine (Cr), urea nitrogen (BUN), uric acid (UA), blood calcium (Ca2+), and blood phosphorus (P3+) using a fully automated biochemical analyzer; Pathological examination of rat kidneys; X-ray examination of rat tibia; Immunohistochemical examination of bone tissue OAT1 level. Results The bone density of the model group rats is lower than that of the control group;The calcium and phosphorus metabolism of rats in the model group was in metabolic disorder, and the OAT1 value of bone tissue binding was much lower than that of the control group(P=0.0018), which was statistically significant. (P=0.0018) Conclusion Chronic renal failure affected the binding ability of OAT1 in bone tissue, leading to the metabolic disorder for calcium absorption and phosphorus metabolism, thus aggravating renal osteodystrophy (P<0.05).
2024, 45(2): 39-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240206
Abstract:
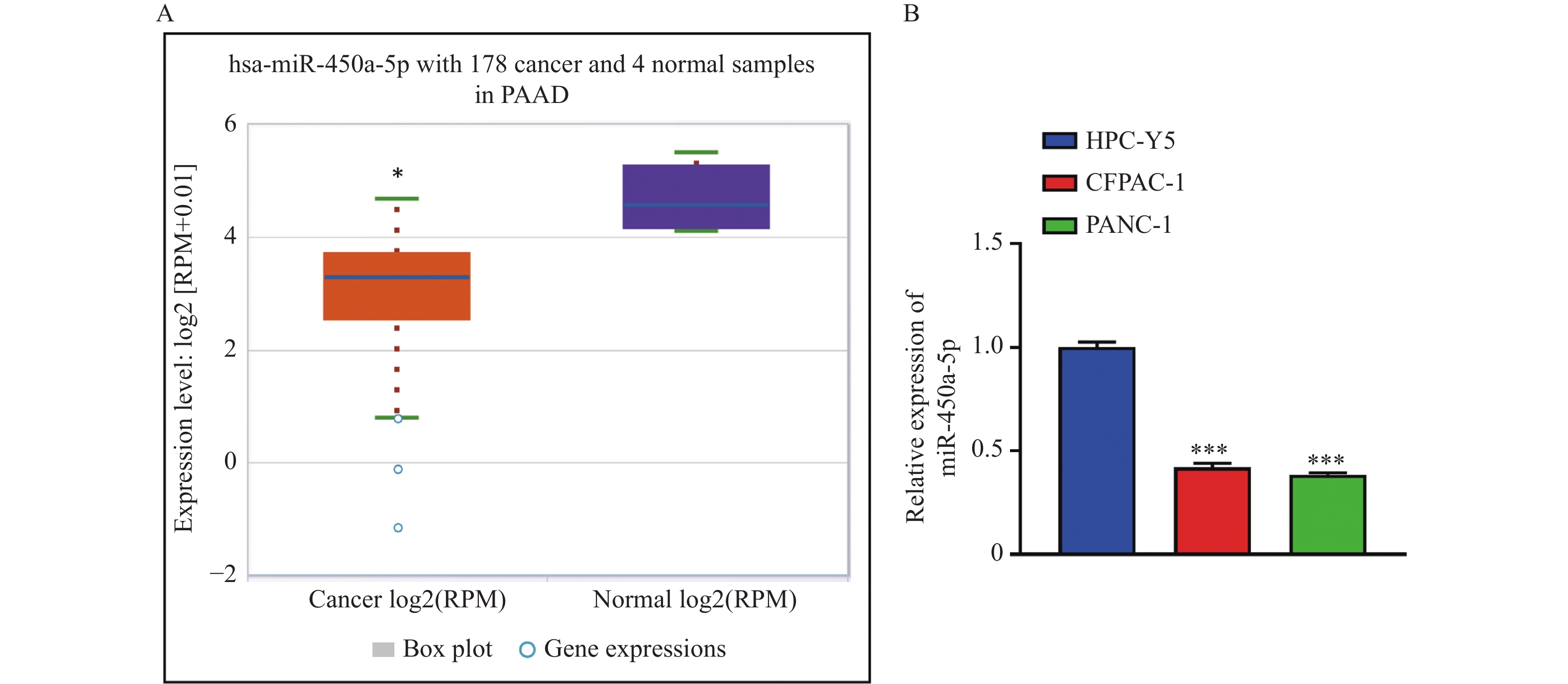
Objective To observe the effect of a new cell delivery tool (MSC exo) on the proliferation of pancreatic cancer by transferring targeted genes. Methods Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis(NTA) were used to identify human mesenchymal stem cell exosomes(MSC-exo) and transport miR-450a-5p into CFPAC-1, to explore the effect of miR-450a-5p targeting BZW2 on inhibiting the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Results The expression of miR-450a-5p was low in pancreatic cancer tissue (P<0.05), and the expression of CD63 and TSG101 of MSC-exo-miR-450a-5p in CFPAC-1 cells was higher than that of MSC-exo by Western blot(P<0.05). CCK-8 and EdU results showed that MSC-exo-miR-450a-5p significantly inhibited the proliferation of CFPAC-1 cells (P<0.05). Cell scratch and Transwell experiments showed that MSC-exo-miR-450a-5p can inhibit the migration and invasion of CFPAC-1 cells (P<0.05). Through dual luciferase assay, it was confirmed that miR-450a-5p targets BZW2, and RT-qPCR and Western blotting showed a negative correlation (P<0.05) between miR-450a-5p and BZW2 expression. Overexpression of BZW2, CCK-8, EdU, cell scratch, and Transwell experiments confirmed that pc-BZW2 reversed the anti-cancer function of MSC-exo-miR-450a-5p on CFPAC-1. Western blot detected PCNA,Ki-67,MMP2,MMP9, and the results were consistent with the above experiments (P<0.05). Conclusion hMSC exo is a new delivery system, targeting BZW2 to transport miR-450a-5p to inhibit the biological malignancy of pancreatic cancer cells, which provides an important clue for the research of targeted treatment of pancreatic cancer.
2024, 45(2): 49-56.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240207
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the expression of KIF20A in ESCC and its effect on Eca109 cell biological behavior and ferroptosis. Methods The expression of KIF20A in ESCC was predicted by bioinformatics analysis. KIF20A knockdown /overexpression Eca109 cell line was constructed, Experimental groups: control group, KIF20A knockdown group, KIF20A overexpression group, and the effects of KIF20A on the proliferation, invasion, and migration of Eca109 cells were detected by CCK-8, Transwell invasion assay and cell scratch assay. On this basis, the ferroptosis model induced by RSL3 was established, and GSH and MDA contents were detected. Results Compared with the control group, the cell proliferation activity of the KIF20A knockdown group was significantly decreased (P < 0.05), and that of the KIF20A overexpression group was significantly increased (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the invasion and migration ability of the KIF20A knockdown group was decreased (P < 0.05), and the invasion and migration ability of the KIF20A overexpression group was increased (P < 0.05). After RSL3 induction, the GSH content in the cell lysate of the KIF20A knockdown group was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05), and the MDA content was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion KIF20A is highly expressed in ESCC and plays a role in promoting proliferation, invasion, migration and inhibiting ferroptosis in Eca109 cells.
2024, 45(2): 57-64.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240208
Abstract:
Objective Meta-analysis was conducted to assess the risk of secondary infection caused by tocilizumab (TCZ) in the treatment of Corona Virus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), in order to provide an evidence-based basis for the safety of tocilizumab in patients with COVID-19. Methods Cochrane Library, PubMed, Web of Science, CNKI, SinoMed and Wanfang databases were searched in computer to collect randomized controlled trial and cohort study of treating COVID-19 with tocilizumab from December 19, 2019 to December 30, 2022. A meta-analysis of the results of each study was performed using RevMan 5.4.1 software. Results A total of 1691 references were screened and eighteen studies involving 3933 patients were included. The incidence of secondary infection in the tocilizumab with the standard treatment group and standard treatment group was 19.14% (331/ 1729 ) and 12.11% (267/ 2204 ), respectively. Meta-analysis showed that the tocilizumab + standard treatment group had a higher incidence of secondary infection than the standard treatment group [RR = 1.35, 95%CI (1.05, 1.74), P = 0.02]. The results of the subgroup analysis showed that the risk of secondary infection with different doses of tocilizumab was different. The incidence of secondary infection was significantly higher in the subgroup with doses of 400~800 mg/d tocilizumab than in the standard care group [RR = 1.48, 95%CI (1.19, 1.84), P = 0.0004 ]. The incidence of secondary infection in subgroups with doses of ≤400 mg/d tocilizumab was also significantly higher than that in the standard treatment group [RR = 1.87, 95%CI (1.28, 2.72), P = 0.001]. However, there was no statistical significance between the subgroup 6~8 mg/kg tocilizumab and the standard treatment group. Conclusions Tocilizumab may increase the risk of secondary infection in patients with COVID-19 compared with standard treatment, and the benefits and risks of tocilizumab should be carefully evaluated before clinical administration. Moreover, large and high-quality studies are needed for further evaluation.
2024, 45(2): 65-76.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240209
Abstract:
Objective Systematically evaluate the efficacy of probiotics in treating osteoporosis. Methods Computer search of Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PubMed, Embase, VIP, CNT and Wanfang data knowledge service platform, the search time limit of August 15, 2023, included as a randomized controlled experiment of probiotics for the treatment of osteoporosis. Two researchers independently screened the literature, extracted the data, and evaluated the risk of bias in the included literature. The effects of probiotic treatment on BMD, blood calcium, vitamin D, parathyroid hormone, osteocalcin, bone alkaline phosphatase and adverse reactions were analyzed by using Stata A. 14 and Revman. 5.4 software. Results Eight articles were finally included, Including 744 study subjects, The results of the Meta-analysis showed that, Add probiotics to traditional drug therapy, Can increase hip bone mineral density in patients[WMD 0.05(0.01, 0.10)] g/cm3, Increase the calcium ion concentration in the patient's blood [WMD 0.26(0.02, 0.50)]mmol/L mmol/L, Increase the concentration of blood osteocalcin [WMD 1.84(0.60, 3.07)] ng/mL, Lower the bone-specific alkaline phosphatase concentration [SMD-1.06(-2.06, -0.07)], And reduce the incidence of nausea and diarrhea, However, there was no significant change in vitamin D and parathyroid hormone. Conclusion The addition of probiotics on the basis of routine treatment may improve the level of bone mineral density and reduce the adverse reactions of gastrointestinal tract, which is beneficial to the prognosis of patients.
2024, 45(2): 77-84.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240210
Abstract:
Objective To explore the role of TMAO from gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), we detected the serum level of TMAO and its precursor metabolites in NAFLD, as well as the expression level of Eubacterium rectum, Bacteroidetes multiforme, Lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in the intestinal flora. Methods We collected 118 subjects and divided into NAFLD group (86 cases) and healthy control group (32 cases) randomly. We also detected the serum level of TMAO and its precursor metabolites in subjects by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry detection (LC-MS), and the expression of target bacterial DNA was detected by qRT-PCR. Results Serum TMAO, TMA and choline levels were significantly increased in NAFLD (P<0.05), and liver fat content was positively correlated with TMAO (P<0.05). The expression level of Lactobacillus and Eubacterium rectum in NAFLD group were increased (P<0.05); the expression level of Bifidobacterium and Bacteroides multiform were decreased (P<0.05).The serum TMAO level was positively correlated with Eubacterium rectum (r=0.280, P<0.05), and negatively correlated with Bifidobacterium (r=-0.332, P<0.05). Conclusion The level of TMAO in serum shows a positive correlation with NAFLD. The structure of intestinal flora in individuals with NAFLD is altered and linked to TMAO. This suggests that the intestinal flora may have a significant impact on the development of NAFLD through TMAO.
2024, 45(2): 85-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240211
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the need for and utilization of health services among six Zhiguo ethnic minority groups in Yunnan Province, aiming to provide further evidence for the improvement of healthcare. Methods Using stratified random sampling, 1921 individuals from six Zhiguo ethnic minority groups, aged 15 and above, were investigated with a structured questionnaire between August and December 2022. A structured questionnaire was used to collect participants’ information on health service needs and utilization. Results Among the surveyed participants, the two-week prevalence rate was found to be 22.54%, while the prevalence rate of chronic diseases was 38.52%. Among the residents, the risk of two-week prevalence was higher for females (OR=1.564), individuals aged ≥60 years (OR=1.727), and those who reported poorer health utility value (OR=5.277), while it was lower for residents of Keno (OR=0.470) and Lahu (OR=0.659) ethnicity, as well as those who reported higher EQ-VAS scores (OR=0.446/0.174). Meanwhile, residents aged ≥45 years (OR=3.392/7.072) were at higher risk for chronic disease prevalence, while it was lower for Keno ethnicity (OR=0.409), unmarried individuals (OR=0.479), and those with higher education levels (OR=0.629/0.603), higher EQ-VAS scores (OR=0.208)P < 0.05. Additionally, among the participants, the treatment rate for two-week illness was 14.32%, while the non-treatment rate stood at 36.49%. Furthermore, the one-year hospitalization rate was reported as 19.89%, with a corresponding rate of individuals who needed hospitalization but did not receive it being recorded at 15.86%. Among the residents, the likelihood of treatment for two-week illness was higher for females (OR=1.461) and residents aged ≥45 years (OR=1.510/1.560), whereas it was lower for individuals with higher EQ-VAS scores (OR=0.445). The likelihood of hospitalization within one year was also higher for residents aged ≥60 years (OR=2.029) and individuals of Nu (OR=1.599), Lisu (OR=1.688), and Keno (OR=1.968) ethnicity, whereas those with high EQ-VAS scores (OR=0.325) had a lower risk (P < 0.05). Conclusion In Yunnan Province, the need for healthcare services among six Zhiguo ethnic minority groups in this study is relatively low; however, the high prevalence of chronic diseases raises concerns. The utilization of healthcare services appears to be relatively sufficient, but the utilization of outpatient services still needs to be improved.
2024, 45(2): 94-98.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240212
Abstract:
Objective To explore the characteristics and diagnostic significance of ultrasound signs in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Methods This study focused on 81 children with acute appendicitis and divided them into two groups based on pathological examination results: 34 children with severe progressive appendicitis (41.98%) and 47 children with simple appendicitis (58.02%). By analyzing the indirect and direct signs of ultrasound detection, as well as pathological examination data, and using ROC curve analysis to analyze the area under the curve (area under curve, AUC) of ultrasound signs combined, a comprehensive analysis is conducted to score the ultrasound examination results of children. Results The detection rates of wall continuity interruption/low-level clarity, intraluminal fluid accumulation, periappendiceal or abdominal fluid accumulation, periappendiceal hyperechogenicity, cecal and ileal wall thickening in the advanced group were higher than those in the simple group (P < 0.05); The scores of indirect, direct, and combined ultrasound signs in the progressive group were higher than those in the simple group (P < 0.05); Under the ROC curve, the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of combined signs were 98.77%, 97.53%, 98.77%, and 96.30%, respectively, higher than those of indirect signs and direct signs. The AUC was 0.835, higher than those of indirect signs and direct signs (P < 0.05). Conclusion The combined diagnosis of ultrasound examination signs can provide objective evidence for the early diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children, and can also achieve dynamic monitoring of the disease, which is conducive to the formulation of clinical treatment plans.
2024, 45(2): 99-104.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240213
Abstract:
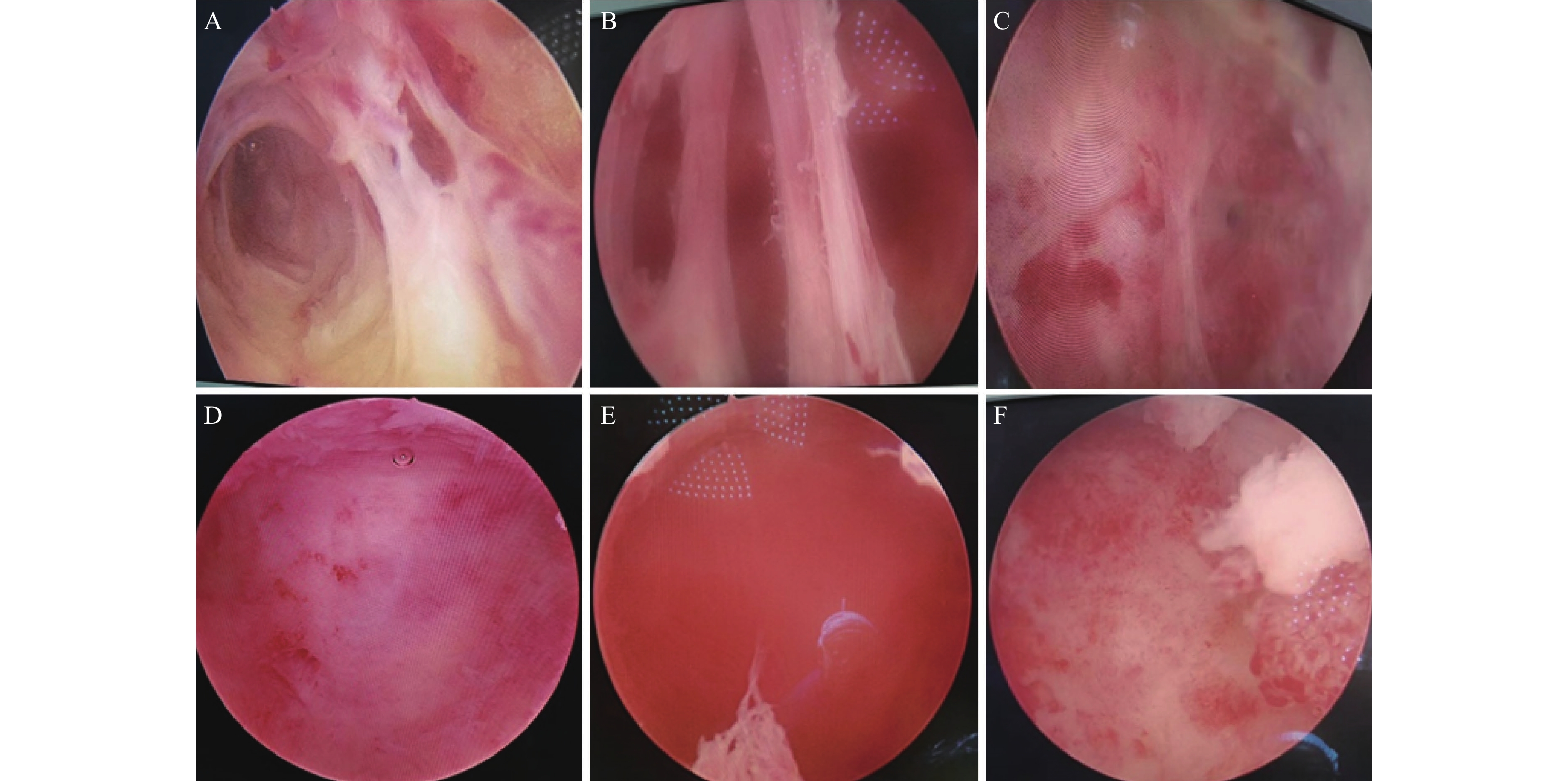
Objective To compare the clinical efficacy of abdominal ultrasound-guided endoscopic retrograde appendicitis therapy (ERAT) with laparoscopic appendectomy (LA) for acute uncomplicated appendicitis using propensity score matching. Methods The clinical data of 441 patients with acute uncomplicated appendicitis admitted to the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from March 2020 to April 2023 were collected. The cases were classified based on the differences in surgical method and divided into the ERAT group (n = 30) and LA group (n = 411). The clinical efficacy of patients was compared between the two groups after reducing confounding bias by propensity score matching (PSM). Results After PSM, a total of 30 pairs of patients in the two groups were successfully matched, and the baseline data of the two groups met the requirements for comparability. At 24 hours after the operation, the ERAT group exhibited lower white blood cells, neutrophil counts, and C-reactive protein levels compared to the LA group, and these differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the operation time and total effective rate between the ERAT group and the LA group (P > 0.05). However, the ERAT group had lower intraoperative blood loss and shorter pain relief time compared to the LA group, and these differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Abdominal ultrasound-guided endoscopic retrograde appendicitis treatment is an effective, safe, and feasible technique with good prospects for the treatment of acute uncomplicated appendicitis.
2024, 45(2): 105-111.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240214
Abstract:
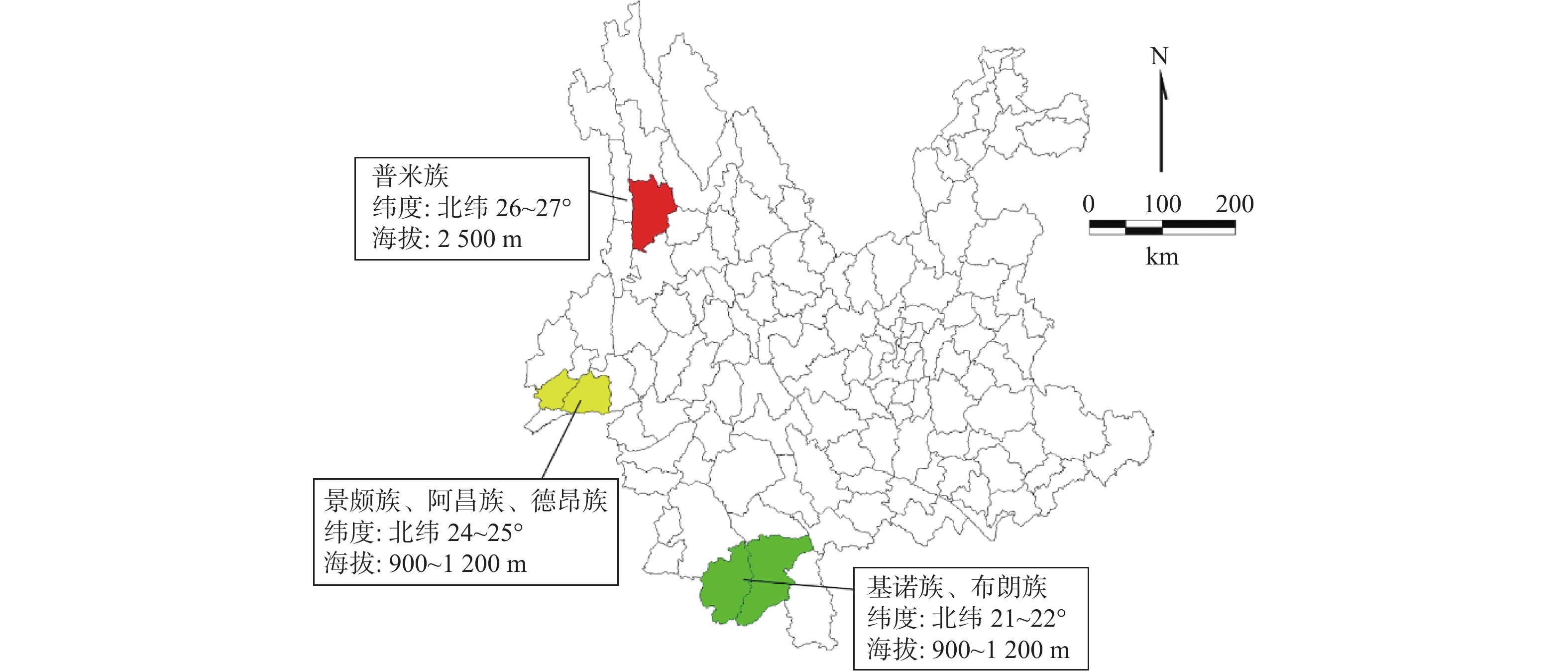
Objective To assess the nutritional status of vitamin D and associated factors among adults of six ethnic minority groups native to Yunnan Province, and provide evidence for policy making. Methods Between May 2019 and August 2020, a total of 690 adults were selected from Jinuo, Bulang, Jingpo, Deang, Achang and Pumi ethnic groups according to the sex and age composition in the 6th national census. A questionnaire survey and an anthropometric examination were conducted by trained health workers, and serum 25(OH)D levels were determined with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Results The median of serum 25(OH)D was 28.7(P25~P75∶24.3~33.8) ng/mL, and the prevalence of vitamin D sufficiency, insufficiency and deficiency were 44.2%、47.5% and 8.3%, respectively. There were significant differences in serum 25(OH)D levels among the six ethnic groups(χ2=139.29, P < 0.01). Multivariate logistic regression showed that ethnic groups living in higher latitude areas(Pumi, Jingpo, Deang, and Achang), women, and those whose BMI≥24.0 were more likely to be vitamin D insufficient or deficient. Conclusion More than half of the ethnic adults suffer from vitamin D malnutrition which also varies across ethnicities. Further surveillance and interventions among key areas and populations are needed.
2024, 45(2): 112-116.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240215
Abstract:
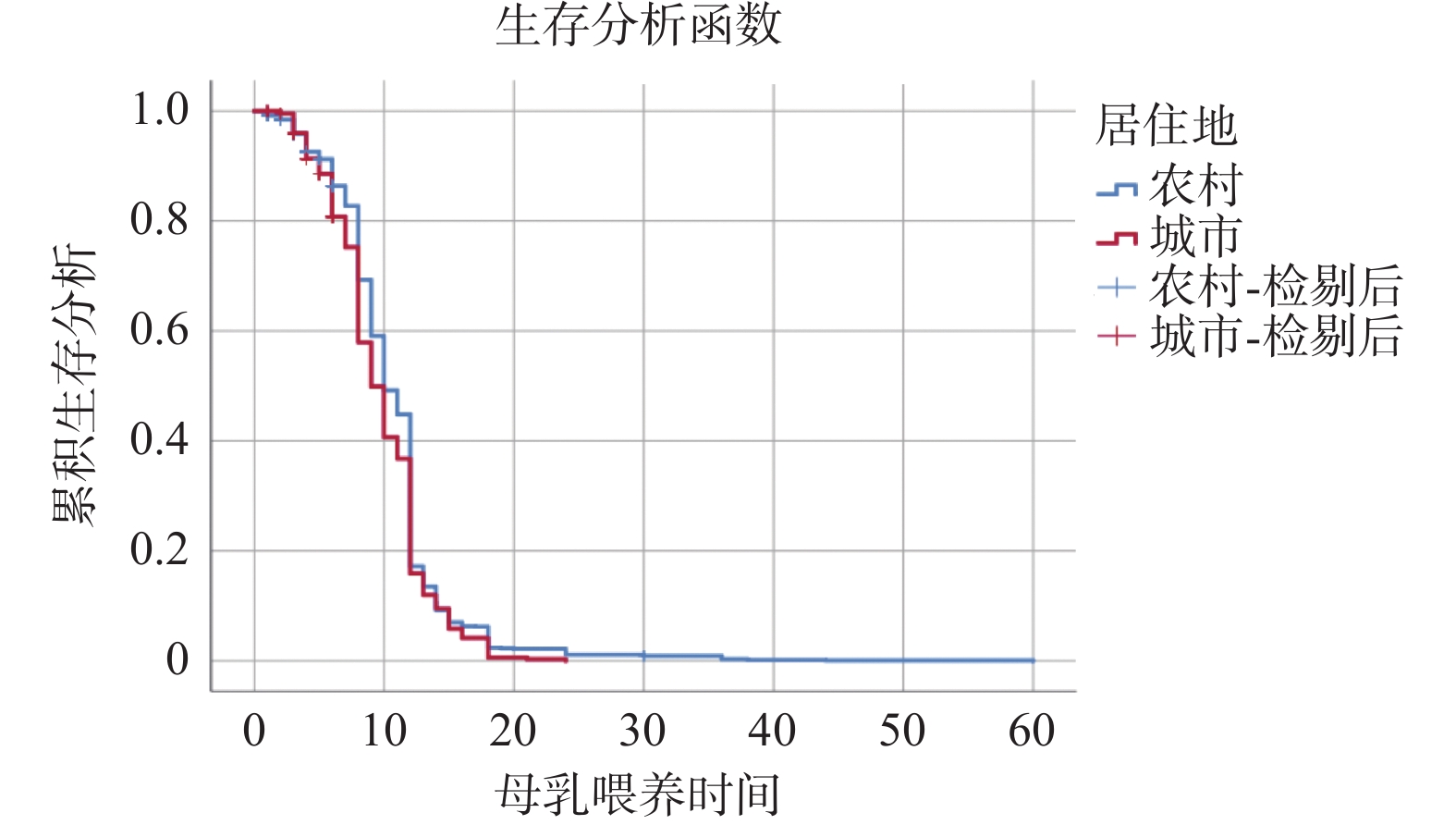
Objective To understand the current situation of breastfeeding duration in children aged 0-5 years in Yunnan Province, and to explore the influencing factors of breastfeeding duration. Methods Using the data of the 6th National Health Service Survey in Yunnan Province, 1582 children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province were selected as the research subjects, and the Kaplan-Meier method and Cox regression were used to analyze the influencing factors of breastfeeding duration. Results The mean duration of breastfeeding for children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province was 9.29 months, and region, time of complementary food addition, time of suckling and family income were the main factors influencing the duration of breastfeeding. Conclusion The duration of breastfeeding for children aged 0~5 years in Yunnan Province deviates significantly from the recommendations provided by both the World Health Organization(WHO) and China's child breastfeeding guidelines. Given the current situation, the relevant departments must enhance their focus on this issue.
2024, 45(2): 117-122.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240216
Abstract:
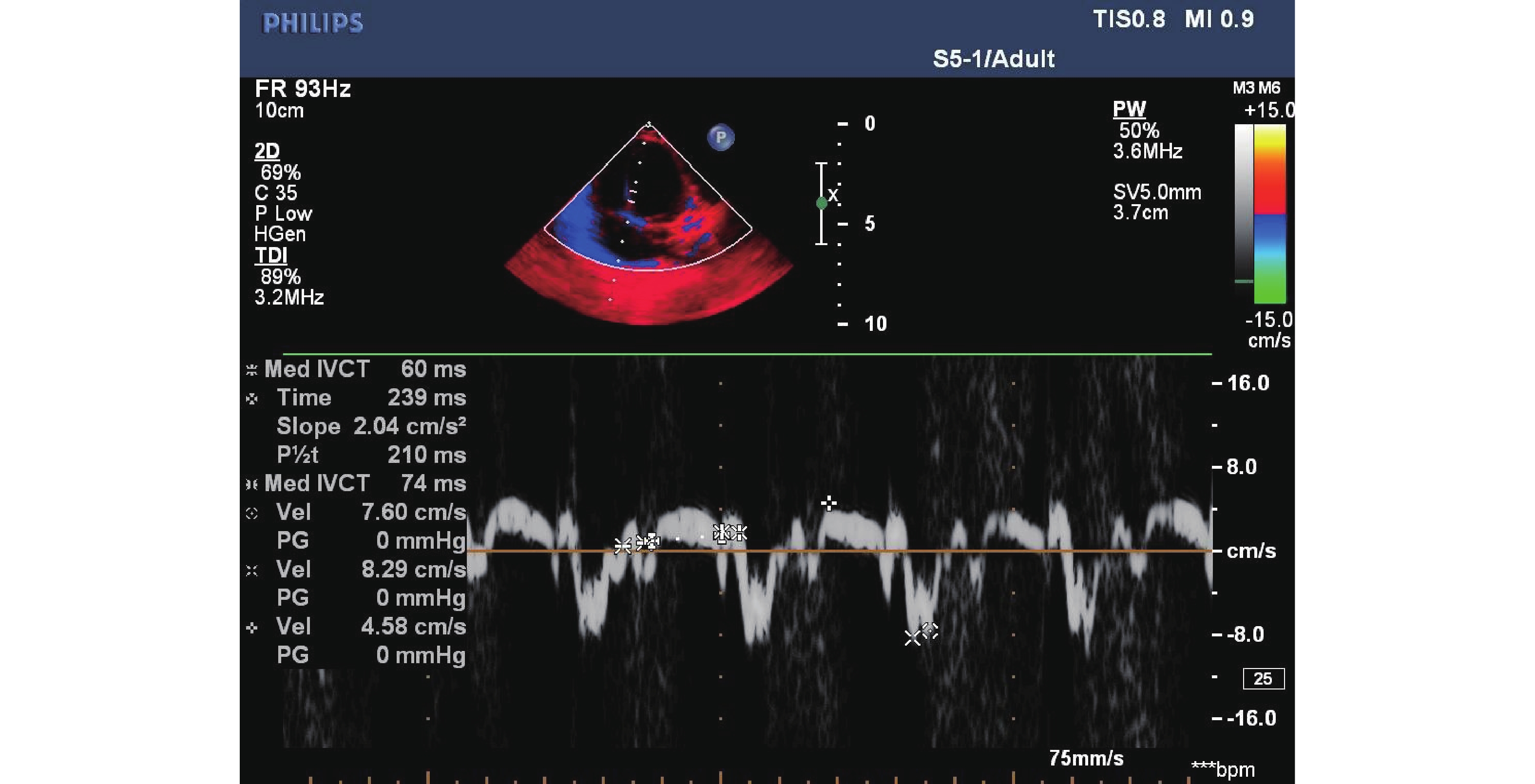
Objective To apply ultrasound to monitor cardiac function changes after anthracycline exposure in children with acute leukemia, in order to obtain the indicators of early changes in their cardiac function. Methods Children with acute leukemia from 2018 March to December 2020 in the Children’ s Hospital of Kunming Medical University were enrolled according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, their routine cardiac ultrasound and tissue Doppler condition were recorded, and the changes in systolic function were evaluated by Tei index including TeiS, TeiRL, TeiM and TeiT. Results The mean values of LVEF in the normal and the experimental group were both above 60%. FS, SV, and EDV were all in the normal range. While common indicant, the index of TDI or Tei was not statistically significant(P>0.05). The levels of TeiM, TeiRL and TieT in the groups that received a total dose of 200 mg/m2 anthracyclines and 250 mg/m2 were significantly different from that before treatment(P<0.05). Conclusion Tei index can be utilized as a sensitive indicator for early changes in left and right heart function after children with acute leukemia are exposed to anthracyclines.
2024, 45(2): 123-130.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240217
Abstract:
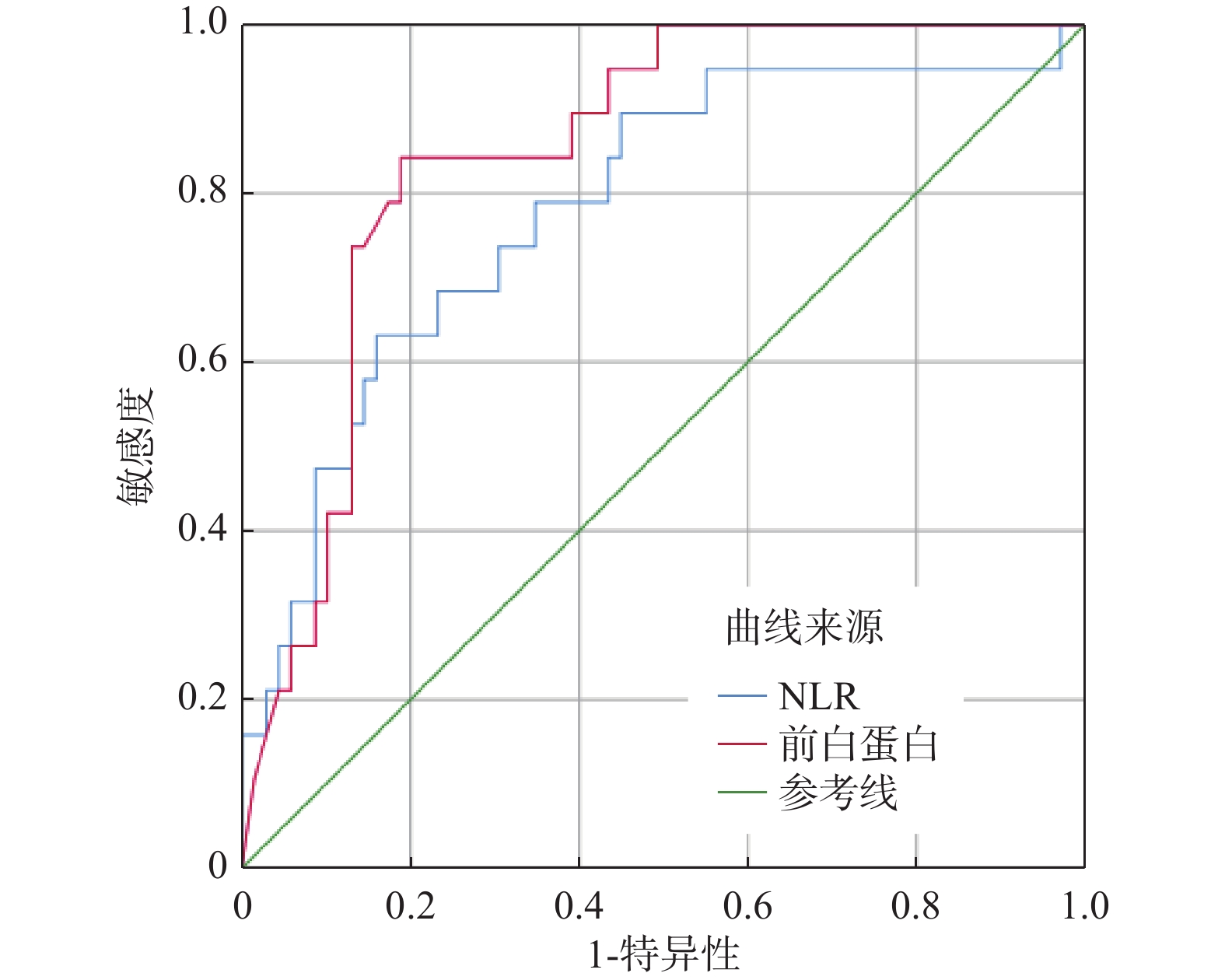
Objective To explore the clinical characteristics and risk factors of death during hospitalization in patients with community-acquired pneumonia(CAP) complicated with diabetes mellitus(DM). Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on 566 patients with CAP hospitalized in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2018 to January 2022. The patients were divided into simple CAP group(n=478) and CAP combined with diabetes(CAP+DM) group(n=88) according to whether they had diabetes, and then CAP+DM group(n=88) was divided into survival group(n=69) and death group(n =19) according to whether the patients died during hospitalization. The clinical data and laboratory test indicators of patients in different groups were compared. Cox regression analysis was used to screen the risk factors of death during hospitalization in the CAP+DM group. Receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve was plotted to evaluate the predictive value of independent risk factors on hospitalization death. Results Compared with the simple CAP group, the CAP+DM group had significant differences in age, concomitant hypertension, coronary heart disease, CURB-65 score, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio(NLR), C-reactive protein(CRP), procalcitonin(PCT), albumin(ALB), prealbumin(PA), glucose(GLU), serum potassium(K), calcium(Ca), phosphorus(P), magnesium(Mg), lactic acid(Lac), non-invasive ventilation time, ICU occupancy rate and mortality rate(P < 0.05); Compared with the survival group, there were statistically significant differences in CURB-65 score, NLR, CRP, PCT, GIU, ALB, PA, serum iron(Fe), Ca, non-invasive ventilation time, and ICU admission rate among the death group patients(P < 0.05). Cox regression analysis showed that the increase of NLR level and the decrease in PA level were the risk factors for in-hospital death in patients with CAP complicated with diabetes(P < 0.05). When the PA cutoff value was 91 mg/L, the AUC, sensitivity, and specificity for predicting in-hospital death of CAP patients with diabetes were 0.849, 84.2% and 81.2%, respectively. Conclusion Patients with CAP combined with diabetes are more serious and have worse prognosis than those with CAP alone. PA has a good predictive value for the prognosis of these patients. Early detection and active intervention should be carried out to reduce the in-hospital mortality of patients.
2024, 45(2): 131-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240218
Abstract:
Objective To compare the diagnostic value of smear acid-fast staining, TB-DNA, X-pert MTB/RIF and culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Methods Four methods were used to detect the perifocal pus of the patients with bone destruction in orthopaedics department within one year, and the results were analyzed statistically, the indexes included sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value. Results The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and Youden index were 31.75%, 100.00%, 100.00%, 53.74% and 0.32 respectively. TB-DNA had a sensitivity of 88.89%, a specificity of 98.00%, a positive predictive value of 98.25%, a negative predictive value of 87.50%, and a Youden Index of 0.87. Xpert MTB/Rif had a sensitivity of 95.23%, a specificity of 68.00%, and a positive predictive value of 78.95%, the negative predictive value was 91.90%, the Youden index was 0.63. The sensitivity, the specificity, the positive predictive value, the negative predictive value and the Youden index were 41.27%, 100.00%, 100.00%, 57.47% and 0.41 respectively, (χ2 = 77.354, P <0.005) . Conclusion Among the four methods, TB-DNA has a good Sensitivity and specificity, Xpert mtbrif has a good sensitivity, TB-DNA and Xpert mtbrif ha a good authenticity, and both positive and negative predictive values are high, it has good value in the diagnosis of bone tuberculosis.
2024, 45(2): 136-140.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240219
Abstract:
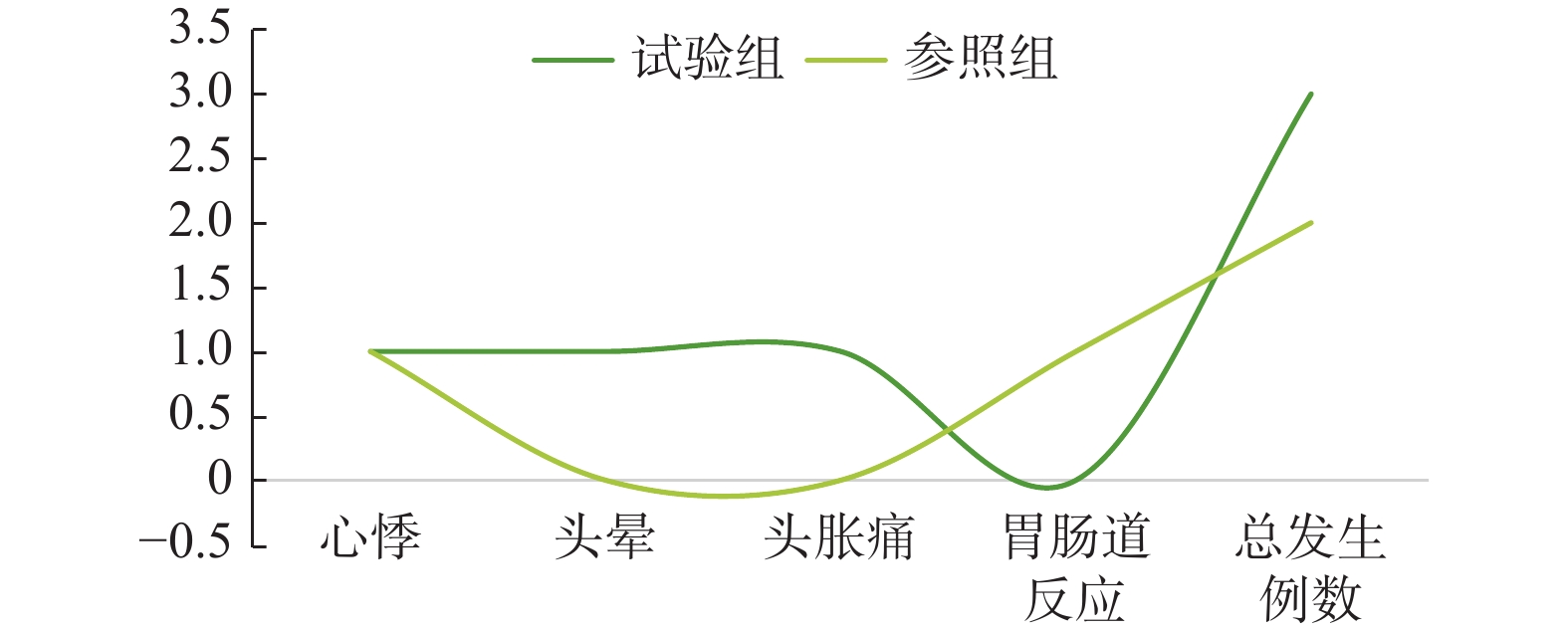
Objective To investigate the effects of treatment with nicorandil after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) in patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) on inflammation-related markers, and to assess its effects on vascular endothelial function. Methods Sixty-six ACS patients who underwent PCI in the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University from August 2022 to January 2023 were used as the study sample, and were divided into the control group and the experimental group according to the method of completely randomized design, with 33 cases in each group. The control group was treated with conventional therapy, and the experimental group was treated with nicorandil. Inflammatory indexes, homocysteine (Hcy) and adverse reactions in serum were compared between the two groups. Results After nicorandil treatment, the levels of postoperative inflammation-related factors in the control group were higher than that in the experimental group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05); The levels of Hcy after nicorandil treatment were lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.05); and the rate of adverse reactions in the experimental group was higher than that in the control group, and there was no statistical difference ( P > 0.05). Conclusion Nicorandil application in elderly ACS patients after PCI has a definite efficacy, can optimize the vascular-related inflammatory indexes, reduce homocysteine levels to improve coronary vascular endothelial function, and is suitable for further promotion.
2024, 45(2): 141-147.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240220
Abstract:
Objective To compare the efficacy of three different methods in the prevention of adhesion after the HEOS system for different degrees of intrauterine adhesions. Methods 284 patients with mild, moderate and severe intrauterine adhesions, who were treated with the HEOS system, were divided into three groups, the intrauterine device with sodium hyaluronate gel was placed in Group A, Foley water capsule tube with sodium hyaluronate gel was placed in Group B, and sodium hyaluronate gel was placed in Group C only. The recovery of uterine adhesion, improvement of menstruation, endometrial thickness, and adverse reactions were compared among the three groups. Results The mild intrauterine adhesions group showed statistical differences among the three groups(P<0.05). Group A had a higher menstrual improvement rate than Group C(P<0.017), and there was no significant difference in other therapeutic indicators(P>0.017). However, the adverse reaction rate in Group A was also higher than that in Group C(P<0.017). In the moderate intrauterine group, there was a significant difference in the improvement rate of intrauterine adhesions between Group B and the other two groups(P<0.017).Group A and B were higher than Group C in terms of menstrual status, endometrial thickness, and adverse reactions(P<0.017). In severe intrauterine adhesions, Group A had higher efficacy indicators than other groups(P<0.017). Conclusions The curative effect index and adverse reaction rate were analyzed, after operation. For the light, moderate, and severe intrauterine adhesions, sodium hyaluronate gel, Foley water capsule tube with sodium hyaluronate gel, and intrauterine device with sodium hyaluronate gel were the best choice for adhesion. Individual and hierarchical management can achieve good clinical effects, which is worth popularizing.
2024, 45(2): 148-152.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240221
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effects of different virulence types of Helicobacter pylori on pepsin and inflammatory factors. Methods 110 patients admitted from December 2021 to March 2023 were collected and divided into HP positive group(n=79) and HP negative group(n=31) according to 13 carbon breath test results. The HP positive group was divided into type I group(n=52), type II group(n=11) and undetermined group(n=16) according to the Helicobacter pylori antibody typing. The HP negative group was selected and divided into blank control group(n=12). Gastric juice pH value, sodion(Na+), potassium(K+), chloridion(Cl-), IL-6, IL-8, gastrin 17(G-17), pepsinogen Ⅰ(PG Ⅰ) and pepsinogen Ⅱ(PG Ⅱ) were detected in all patients. Results There was no difference in pH, Na+, Cl-, K+ between Hp positive group and Hp negative group(P > 0.05). The content of Cl- in HP-positive group was lower than that in HP-negative group( P < 0.05). The levels of IL-6, IL-8, G-17, PG Ⅰ and PG Ⅱ in HP-positive group were significantly higher than those in HP-negative group( P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in pH, Na + and K+ between type I group and type II group, undetermined group and blank control group(P > 0.05). The content of Cl - in type I group and undetermined group was lower than that in blank control group(P < 0.05). The levels of IL-6, IL-8 and PG Ⅰ in type I group were higher than those in type II group, undetermined group and blank control group( P < 0.05). There was a significant difference in PG Ⅱ between the blank control group and the other groups( P < 0.05). There was no difference in G-17 content between type I group and undetermined group( P > 0.05). The level of G-17 in type I group was higher than that in type II group and blank control group( P < 0.05). Conclusion Type I Hp infection may cause gastric mucosal injury by increasing the expression of IL-6, IL-8 and G-17, and then lead to abnormal digestive function.
2024, 45(2): 153-159.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240222
Abstract:
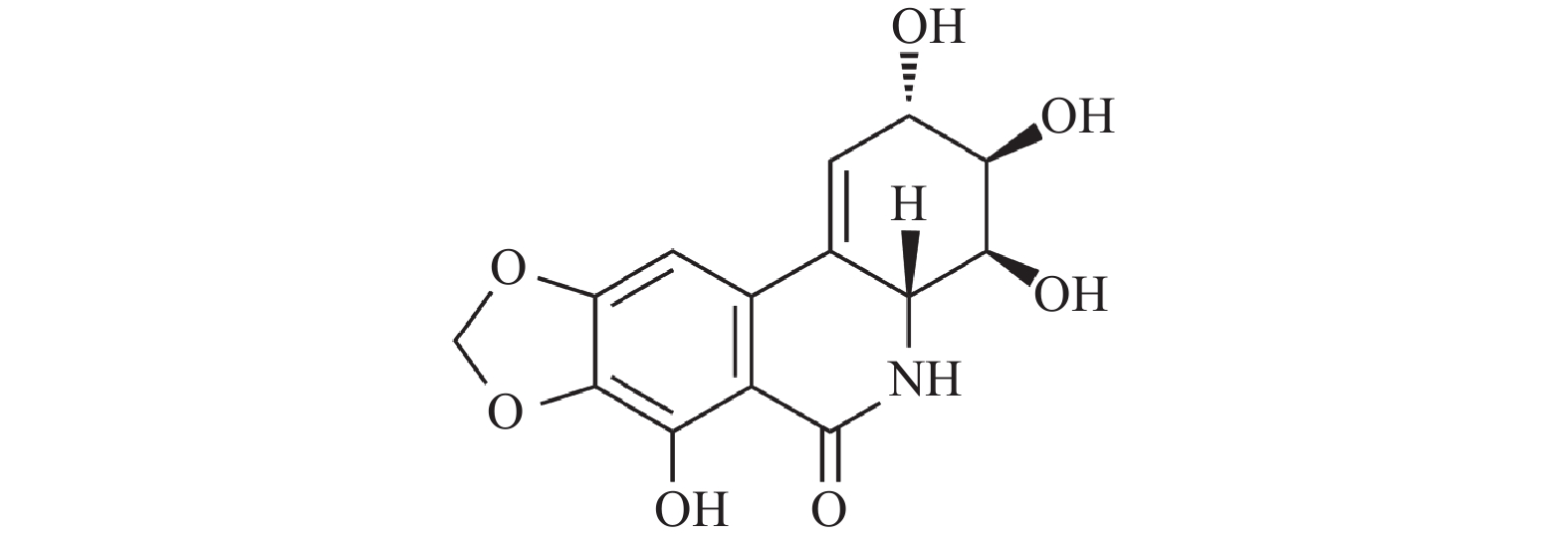
Narciclasine(NCS), a hymenocallis littoralis alkaloid extracted from the bulbs of the genus Narcissus in the Lycoriaceae family, has been proven to have significant anti-tumor activity against a variety of tumor cells. The antitumor mechanisms of NCS are diverse and NCS exhibits antitumor effects through different pathways, which adapts to the current trend of developing multi-target anti-tumor drugs. This review introduces the research progress of the anti-tumor activity and mechanism of NCS in recent years based on the inhibitory effect of NCS on gastric cancer cells, oral cancer cells, polymorphous glioblastoma cells, colon cancer cells, breast cancer cells, melanoma cells and primary exudative lymphoma cells, aiming to provide ideas and references for the research and development, and design of NCS type anti-tumor drugs in the future.
Narciclasine(NCS), a hymenocallis littoralis alkaloid extracted from the bulbs of the genus Narcissus in the Lycoriaceae family, has been proven to have significant anti-tumor activity against a variety of tumor cells. The antitumor mechanisms of NCS are diverse and NCS exhibits antitumor effects through different pathways, which adapts to the current trend of developing multi-target anti-tumor drugs. This review introduces the research progress of the anti-tumor activity and mechanism of NCS in recent years based on the inhibitory effect of NCS on gastric cancer cells, oral cancer cells, polymorphous glioblastoma cells, colon cancer cells, breast cancer cells, melanoma cells and primary exudative lymphoma cells, aiming to provide ideas and references for the research and development, and design of NCS type anti-tumor drugs in the future.
2024, 45(2): 160-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240223
Abstract:
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) is a class of genetically related diseases caused by multiple genes and environmental factors that accelerate the disturbance of the immune-gut-microbiome axis. Lesions often involve multiple organs and systems. Biological agents are an important means of treating IBD and its extraintestinal manifestations. Current studies suggest that biologics can bring benefits to patients, but paradoxical skin lesions, joint lesions, and ocular lesions appear during the treatment. Diseases, pulmonary lesions and other manifestations or lesions are easily ignored in clinical practice, thereby delaying the patient's condition and affecting the patient's quality of life. Therefore, by summarizing the clinical characteristics and diagnosis and treatment experience of contradictory extraintestinal manifestations in the current application of biological agents, this review aims to improve the understanding of clinicians, identify this clinical manifestation early, and avoid delaying the patient's condition.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) is a class of genetically related diseases caused by multiple genes and environmental factors that accelerate the disturbance of the immune-gut-microbiome axis. Lesions often involve multiple organs and systems. Biological agents are an important means of treating IBD and its extraintestinal manifestations. Current studies suggest that biologics can bring benefits to patients, but paradoxical skin lesions, joint lesions, and ocular lesions appear during the treatment. Diseases, pulmonary lesions and other manifestations or lesions are easily ignored in clinical practice, thereby delaying the patient's condition and affecting the patient's quality of life. Therefore, by summarizing the clinical characteristics and diagnosis and treatment experience of contradictory extraintestinal manifestations in the current application of biological agents, this review aims to improve the understanding of clinicians, identify this clinical manifestation early, and avoid delaying the patient's condition.
2024, 45(2): 166-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240224
Abstract:
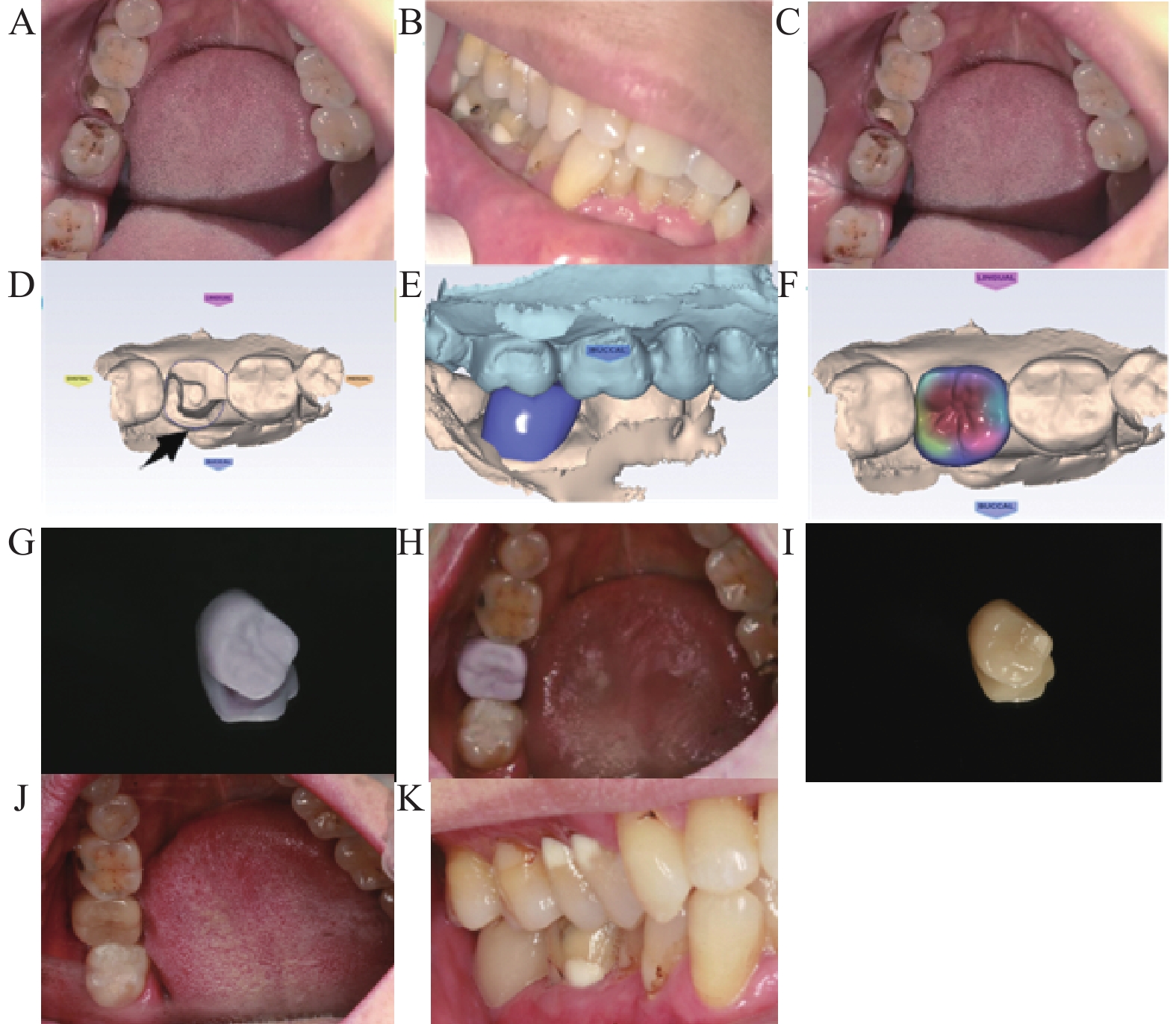
Objective To study the application value of CAD/CAM technology in the teaching of inlay manufacturing. Methods A total of 60 undergraduates interned in the Department of Stomatology, Yan’ an Hospital, Kunming Medical University were randomly divided into an experimental group (n=30) and a control group (n=30). We selected appropriate clinical cases for students to prepare for mandibular molar’ s proximal occlusal inlays. The instructor guided the results of the first preparation in different ways, and the students made the second modification and preparation, and the assessment team scored and evaluated the five aspects of the final preparation, the shape of the preparation, the shape of the occlusal surface, the dovetail retention, and the adjacent surface. Results The scores of all detection indexes in the experimental group were higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). Conclusion The application of CAD/CAM technology in inlay manufacturing teaching can effectively improve students' clinical hands-on ability and achieve better teaching effects than traditional teaching methods.
2024, 45(2): 170-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240225
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the health education needs of patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation and to provide a basis for the formulation of targeted health education programs. Methods A self-designed questionnaire on the health education needs of patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing radiofrequency ablation was designed based on the Kano model. A total of 190 patients with atrial fibrillation who underwent radiofrequency ablation in Grade 3A Hospital of Yunnan Province from February to July 2023 were investigated, and their health education needs were determined according to the Kano model. Results A total of 190 questionnaires were sent out, 180 valid questionnaires were recovered, and the effective recovery rate was 94.74%. Among the 32 health education needs of patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation, including 6 necessary needs, 13 expected needs, 11 charismatic needs, and 2 undifferentiated needs, no reverse demand was found. The importance-satisfaction matrix diagram shows that 12 items are located in the dominant area, 11 items in the area to be improved, 7 items in the maintenance area, and 2 items in the secondary improvement area. Conclusion The Kano model can analyze the health education needs of patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation in multiple dimensions, and provide a reference for doctors and nurses to further develop the content and form of patient-oriented health education.
2024, 45(2): 177-183.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240226
Abstract:
0bjective To explore the effectiveness of caregivers based on health education under the guidance of timing theory in the nursing of elderly patients after hip replacement. Methods By convenient sampling method, eighty elderly patients undergoing hip replacement were divided into control group and observation group, 40 cases in each group. The control group was given routine orthopedic care, and the observation group was based on health management under the guidance of the timing theory (total hip replacement, TIR) based on routine orthopedic care. The Harris Hip Score, Activities of Daily Living Scale (Barthel index), Caregiver Burden Inventory and Family Caregiver Task Inventory were used to compare and evaluate the application effect of health education of two groups of caregivers in the nursing of elderly patients after hip replacement. Results The patients were observed one month and three months after discharge, the Harris score and Barthel index of the observation group were significantly higher than those of the control group (P < 0.01). At discharge, 1 month after discharge and 3 months after discharge, the FCTI score (P < 0.01) and CBI score (P < 0.01) of family caregivers in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group. Conclusion Caregivers based on health education under the guidance of timing theory can effectively reduce the care burden of caregivers, enhance the care ability of caregivers, improve the rehabilitation effect of patients, and ameliorative the quality of life of patients.
2024, 45(2): 184-190.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240227
Abstract:
Objective To explore the current situation of nurses’ emergency response ability of public health emergencies and analyze its influencing factors in Yunnan province, so as to provide empirical basis for the construction of emergency response ability training system in the future. Methods A total of 4821 clinical nurses from 43 hospitals in Yunnan province were selected by convenience sampling. A cross-sectional survey was conducted using the general information questionnaire, Nurses' Public Health Emergency response Capacity Scale and Nurses’ Emergency attitude scale. The influencing factors were analyzed by stepwise multiple linear regression. Results The total score of public health emergency response ability of clinical nurses in Yunnan Province was(70.35±14.08), and the total score of public health emergency response attitude was(42.26±6.14). Gender, department, hospital level, working years, whether to participate in public health emergency training, whether to experience rescue activities in public health emergencies, and attitude towards public health emergencies were the influencing factors of nurses’ public health emergency response ability(P < 0.05), which explained 29.0% of the total variation. Conclusions The ability of clinical nurses to respond to public health emergencies in Yunnan Province is generally above the medium level, but there is still a significant shortage in emergency knowledge. Targeted training is needed. Nursing management should build targeted layered training programs combined with influencing factors to enhance nurses’ ability to respond to public health emergencies.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS