2024 Vol. 45, No. 1
2024, 45(1): 1-7.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240101
Abstract:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease, with a global prevalence of approximately 30.05% to 32.4%. It is closely associated with various other diseases. In recent years, microRNAs(miRNAs) have played a crucial role as non-invasive biomarkers in understanding the pathogenesis and diagnosis of NAFLD. miRNAs play significant roles in both lipid metabolism and insulin resistance, exerting specific regulatory functions in the development and progression of NAFLD. miRNAs are small RNA molecules that regulate the gene expression and protein synthesis by controlling the transcription and translation of target genes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the roles and mechanisms of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, and the occurrence and development of NAFLD.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD) is the most common chronic liver disease, with a global prevalence of approximately 30.05% to 32.4%. It is closely associated with various other diseases. In recent years, microRNAs(miRNAs) have played a crucial role as non-invasive biomarkers in understanding the pathogenesis and diagnosis of NAFLD. miRNAs play significant roles in both lipid metabolism and insulin resistance, exerting specific regulatory functions in the development and progression of NAFLD. miRNAs are small RNA molecules that regulate the gene expression and protein synthesis by controlling the transcription and translation of target genes. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the roles and mechanisms of miRNAs in lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, and the occurrence and development of NAFLD.
2024, 45(1): 8-14.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240102
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between HLA-DM gene polymorphism and antibody response induced by poliomyelitis vaccine. Methods 355 healthy infants aged 2 to 3 months in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region were selected as the study objects, and 10 SNPs of DMA exon 3 and DMB exon 2/3 were genotyped by Sanger sequencing. The correlation between DMA and DMB genes and poliomyelitis vaccine-induced antibody response was analyzed at allele, genotype and haplotype levels. Results In the type I antibody response induced by polio vaccine, the frequencies of DMA*01:02, DMB*01:01, DMB*01:01/DMB*01:01 and DMA*01:02-DMB*01:01 were higher in the non-seroconversion group than in the seroconversion group(P < 0.05). In the polio type II antibody response, the frequencies of DMA*01:02, DMA*01:02/DMA*01:02, DMB*01:01/DMB*01:01 and DMA*01:02-DMB*01:01 were higher in the non-seroconversion group than in the seroconversion group( P < 0.05). Conclusion Alleles DMA*01:02 and DMB*01:01 may be associated with type I and type II antibody responses induced by poliomyelitis vaccine.
2024, 45(1): 15-21.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240103
Abstract:
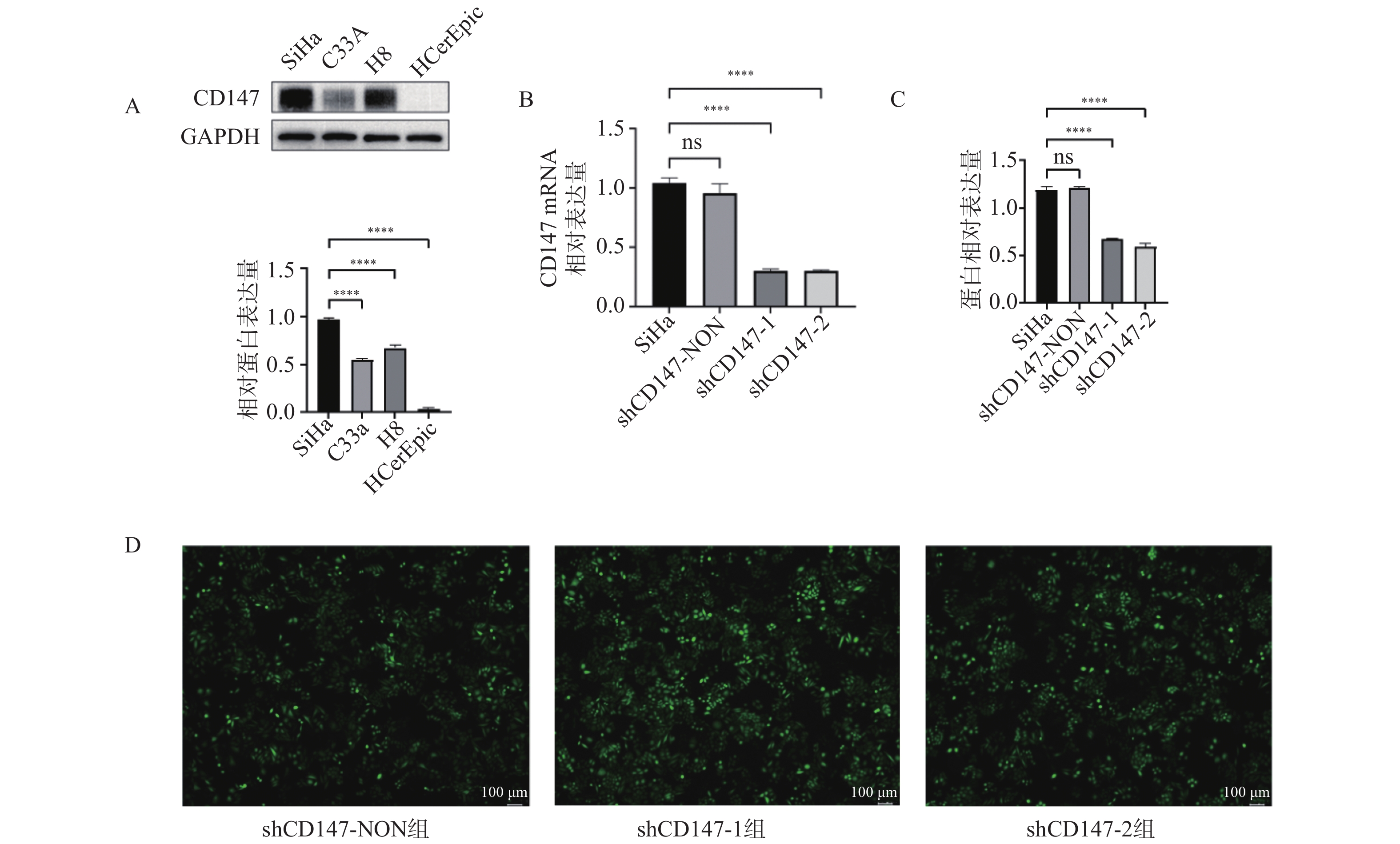
Objective To investigate the effect of transmembrane protein CD147 expression on AIM2 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis and proliferation of cervical cancer cells. Methods Western Blot was used to detect the expression of CD147 in cervical cancer cell lines SiHa(HPV+) and C33a(HPV-) and normal cervical epithelial cells H8(HPV+) and HCer Epic(HPV-). SiHa cells were transfected with lentivirus to down-regulate the expression of CD147. According to the different treatments, SiHa cells were divided into SiHa group, negative control group(shCD147-NON), knockdown group 1(shCD147-1) and knockdown group 2(shCD147-2). The transfection effect was verified by Western Blot, RT-qPCR and green fluorescence expression. The protein and mRNA expressions of AIM2, Caspase-1, IL-18 and GSDMD were detected by Western Blot and RT-qPCR. The lactate dehydrogenase(LDH) release was measured in the cell culture supernatant, and the cell morphology was observed under the fluorescence inverted microscope; the proliferation ability of cells was measured by CCK-8 and the colony formation ability was measured by cell cloning experiments. Results Western Blot results showed that CD147 protein expression in SiHa cells was the highest compared with that in HCerEpic cells. CD147 low expression lentivirus effectively down-regulated the expression of CD147 in SiHa cells. The results of Western Blot and RT-qPCR experiments showed that the expression of AIM 2, Caspase-1, IL-18, GSDMD protein and mRNA increased in shCD147-1 and shCD147-2 group(P < 0.05). Lactate dehydrogenase(LDH) release assay showed that compared with the SiHa group, the shCD147 group had a significant increase in LDH release(P < 0.05). Fluorescence inverted microscope showed that the shCD147 group had swelling and vacuolization, showing typical pyroptosis. Compared with the SiHa group, the shCD147-1 and shCD147-2 groups had significantly reduced the cell proliferation and colony formation ability(P < 0.05). Conclusion Low expression of CD147 effectively up-regulates the expression of AIM2 inflammation-related factors in cervical cancer SiHa cells, induces the pyroptosis, and inhibits the cell proliferation and cloning.
Metabolomics of Siha Supernatant in Cervical Cancer Cells with Down-regulated HPV16 E6/E7 Expression
2024, 45(1): 22-27.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240104
Abstract:
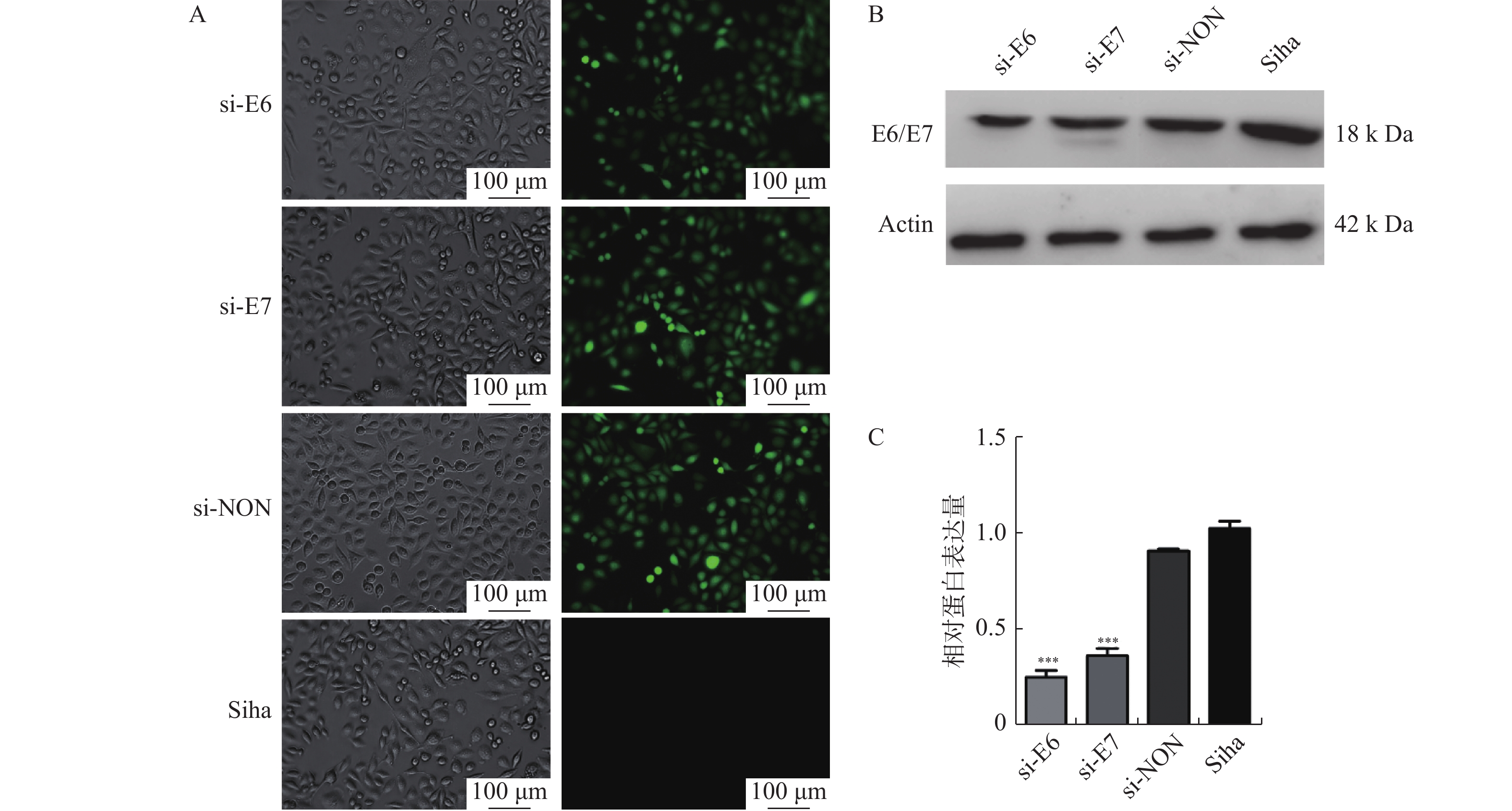
Objective To detecte the differential metabolites and related pathways in Siha cells of cervical cancer by screening the inhibition of HPV16 E6/E7 expression based on 1H NMR metabolomics so as to identify the key metabolic markers involved in the development of high-risk HPV16 cervical cancer. Methods Siha cells were transfected with RNAi fragments to down-regulate the expression of E6/E7, which were divided into the normal control group(Siha cells), no-load group(si-NON), si-E6 group and si-E7 group, and their transfection efficiency was verified. 1H NMR metabolomics was used to reveal the differential metabolites involved in interfering E6/E7 expression in Siha cells. Combined with MetaboAnalyst 5.0 online software, differential metabolites and related metabolic pathways were obtained. Results Fluorescence was observed by inverted fluorescence microscope. Western blotting results showed that compared with Siha group, the expression of E6/E7 in si-E6 group and si-E7 group was decreased(F=145.8, P < 0.001). After down-regulating the expression of E6/E7, 13 common differential metabolites, including Isoleucine, Leucine and valine, were detected. The results of MetaboAnalyst 5.0 online software analysis suggested that the above metabolites were mainly involved in the biochemical synthesis pathway of aminoacyl-trNA, biochemical synthesis pathway of isoleucine, Leucine and valine; There were 10 metabolic pathways of tyrosine, phenylalanine and tryptophan biochemical synthesis. Conclusion After HPV16 infection, changes of glucose and amino acid metabolism can promote the progression of cervical cancer, which provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and treatment of cervical cancer.
2024, 45(1): 28-34.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240105
Abstract:
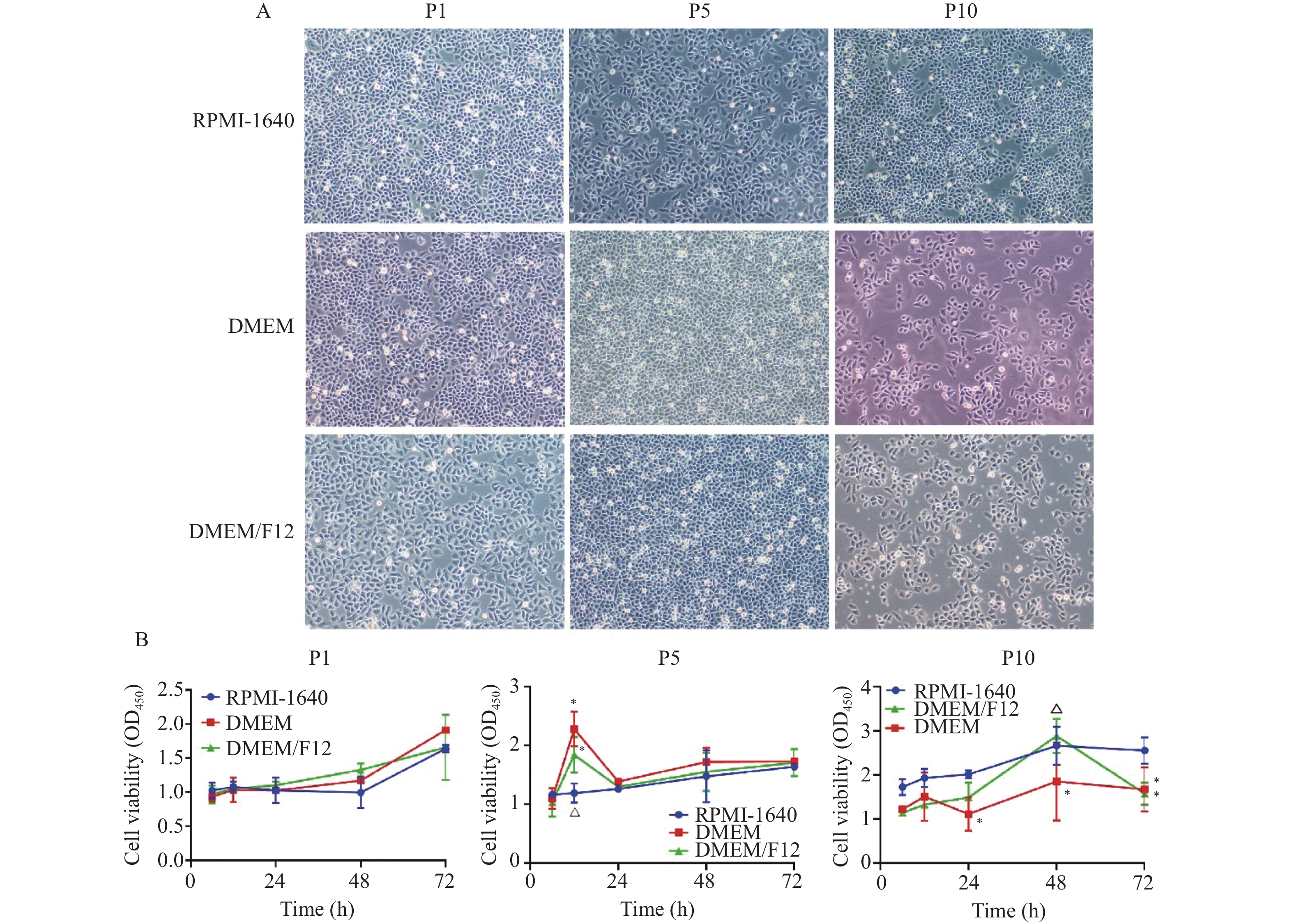
Objective To investigate the effects of different culture conditions(RPMI-1640, DMEM and DMEM/F12 medium) on the passage of MPM cells isolated from the tissues of Malignant pleural mesothelioma(MPM), and to study the effects of CDKN2B on the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of MPM cells. Methods MPM cells were isolated from MPM tissues and cultured in RPMI-1640, DMEM and DMEM/F12 medium, respectively. Cell proliferation was examined by CCK-8, and the nuclei and chromosomes were observed by Wright-Giemsa staining. Fluorescence intensities of Calretinin, CD141, CK5, EMA and WT-1 were conducted by immunofluorescence assay. The mRNA and protein expression of CDKN2B were detected by RT-qPCR and Western blot, respectively. Transwell was used to detect cell invasion and flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis. Results The established MPM cells showed good viability when passaged to the 10th generation in RPMI-1640, DMEM and DMEM/F12 cultures, and the MPM markers Calretinin, CD141, CK5, EMA and WT-1 were all expressed in the cells. The viability of MPM cells in RPMI-1640 culture medium was relatively stable. CDKN2B was downregulated in MPM cells(P < 0.05), and overexpression of CDKN2B significantly suppressed the proliferation(P < 0.05), invasion(P < 0.05) and epithelial interstitial transformation of MPM cells(P < 0.01), and promoted the apoptosis(P < 0.01). Conclusion The established MPM cells were stably passaged in RPMI-1640 culture medium, and CDKN2B may be a potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of MPM.
2024, 45(1): 35-40.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240112
Abstract:
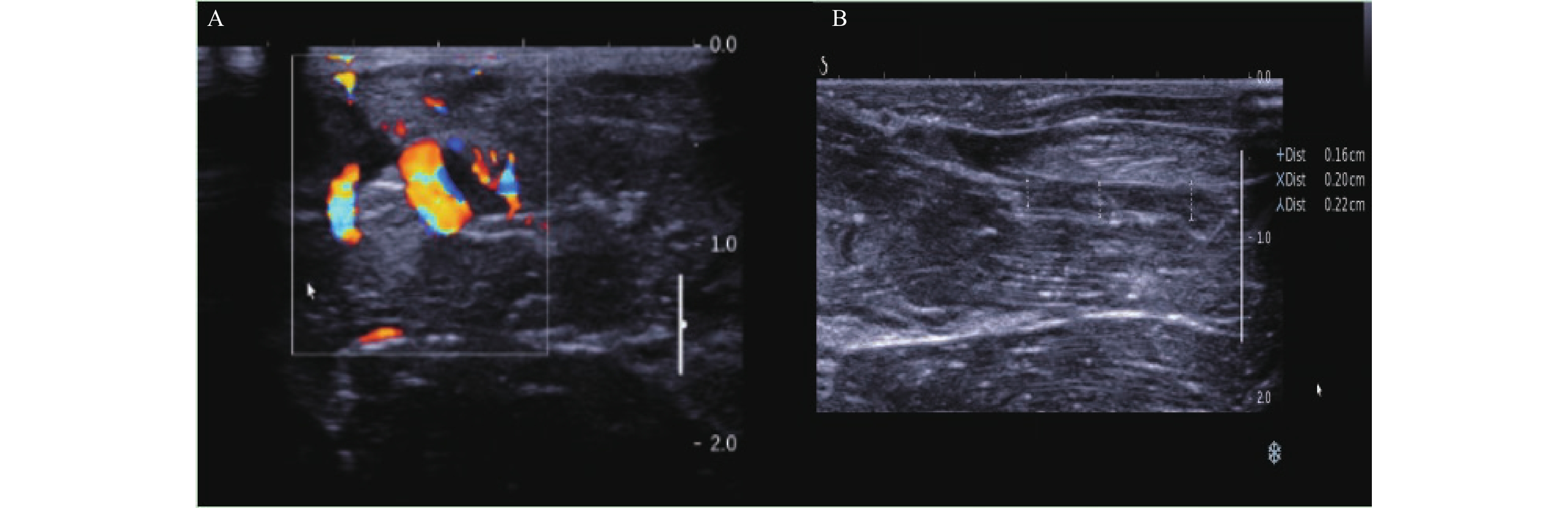
Objective Endothelial injury plays a crucial role in forming deep vein thrombosis. This study aims to compare the effectiveness of various methods for creating rabbit femoral vein thrombotic models after the endothelial injuryso as to provide a solid experimental foundation for further research on the endothelial injury and deep vein thrombosis. Methods Forty-five rabbits were randomly divided into three groups(A, B, C), with 15 cases in each group and subjected to the endothelial injury using the methods of simple clamping, combined complete ligation, and combined incomplete ligation, respectively. The intravascular ultrasonic manifestations and local endothelial pathological changes were compared at 1, 3, and 7 days after modeling. Results Significant differences in vascular diameter and Young’ s modulus values were observed after 7 days of modeling(P < 0.05). In pairwise comparisons between the groups, the Young’ s modulus values in group C were significantly higher than those in groups A and B after 7 days of modeling( P < 0.05). Pathological examination confirmed the presence of fibrinoid thrombus in the blood vessels of group C on the seventh day of modeling. Conclusion Combining simple clamping and incomplete ligation can produce a relatively stable endothelial injury and thrombus formation. This method provides a robust experimental model for further investigation into deep vein thrombosis after the endothelial injury.
2024, 45(1): 41-47.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240107
Abstract:
Objective The aim of this study is to analyze the prevalence of depression and anxiety symptoms and its relationship with the socio-economic position(SEP) among the elderly people in Dai rural areas of Jinggu County, Yunnan province. Methods A multi-stage stratified random sampling method was used to conduct a questionnaire survey among 1409 people aged 60 and over in Dai rural areas of Jinggu County, Yunnan Province. The individual SEP index was constructed using the principal component analysis. Results The prevalence of anxiety symptoms, depression symptoms, and mixed anxiety-depressive disorder symptoms was 4.8%, 52.0%, and 4.2% among them, 2.6%, 49.4%, and 2.3% among the males, and 6.8%, 54.5%, and 6.0% among the females respectively. Females had the higher prevalence of anxiety symptoms and mixed anxiety-depressive disorder symptoms than males(P<0.05). Elderly people with the higher level of education, annual per capita household income and SEP had the lower prevalence of anxiety symptoms and mixed anxiety-depressive disorder symptoms than their counterparts(bothP<0.05).The prevalence of depression symptoms increased with age(P<0.01). The difference in the prevelence of depression symptoms among the elderly people with the different numbers of chronic conditions was statistically significant(P<0.01). The results of multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the elderly people with lower SEP were more likely to suffer from the anxiety symptoms(OR=0.707, 95%CI: 0.566~0.883), depression symptoms(OR=0.492, 95%CI: 0.438~0.552), and mixed anxiety-depressive disorder symptoms(OR=0.602, 95%CI: 0.469~0.773). Conclusion There are significant socio-economic differences in the prevalence of anxiety symptoms and depression symptoms among the elderly people in Dai rural areas of Jinggu County, Yunnan province. Future mental health interventions should more focus on females, elderly people with advanced age, multiple chronic diseases and low SEP, so as to reduce the occurrence of depression symptoms and anxiety symptoms.
2024, 45(1): 48-54.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240108
Abstract:
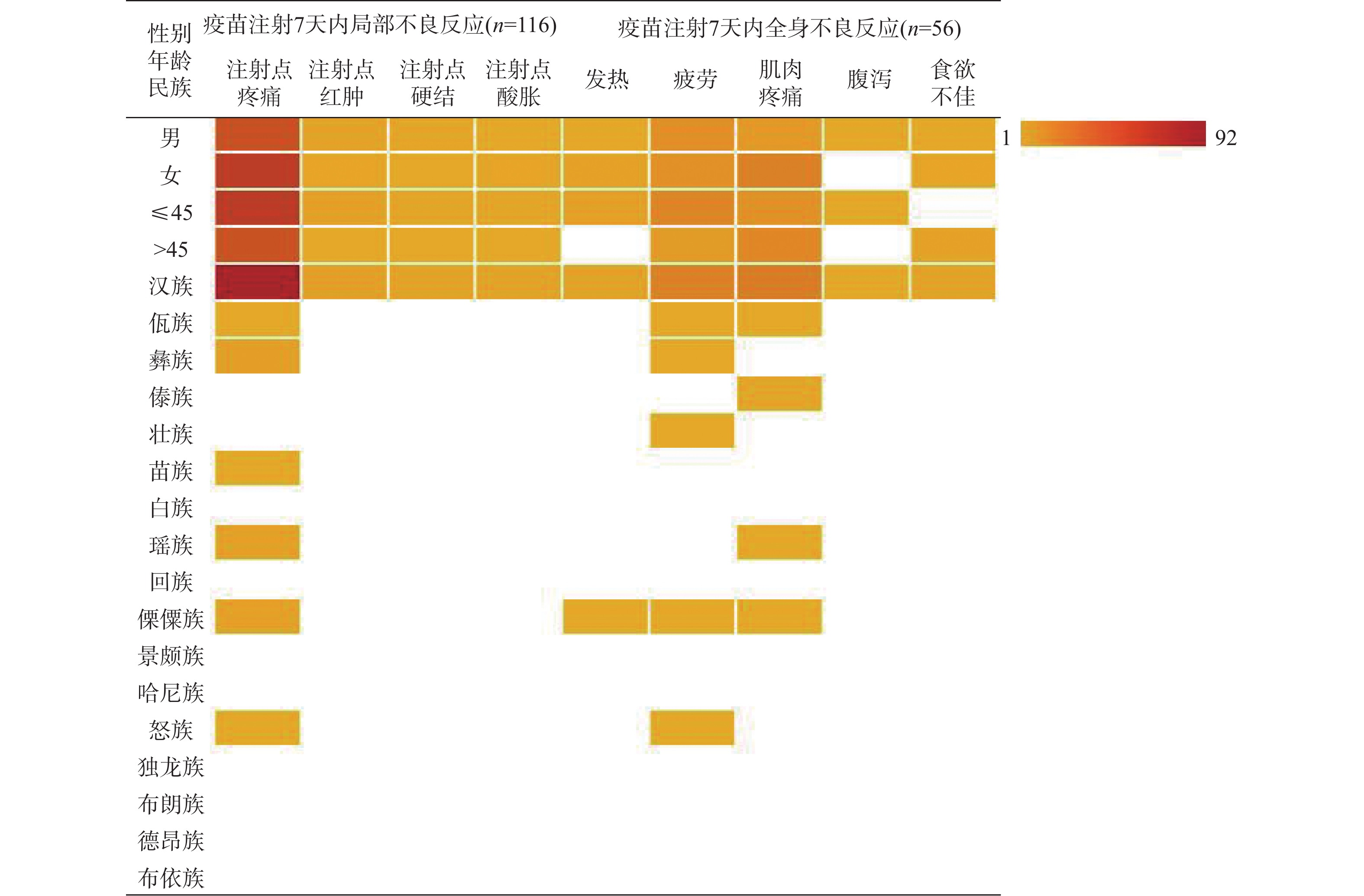
Methods From October 2021 to June 2022, a questionnaire survey was conducted among 2180 HIV/AIDS patients in Kunming, Qujing, Yuxi, Zhaotong, Puer, Baoshan, Lincang, Honghe, Wenshan, Xishuangbanna, Dali, Dehong and Nujiang prefectures. The questionnaire included age, sex, education, nationality, education level, vaccination, adverse reactions within 7 days after the vaccination, safety of COVID-19 vaccine, awareness of effectiveness, vaccination willingness and so on. Results Among the subjects, 2109 completed 3 injections, accounting for 96.74%, and 71 were not vaccinated, accounting for 3.26%. Within 7 days of inoculation, local adverse reactions occurred in 116 cases, accounting for 5.50%, and systemic adverse reactions occurred in 56 cases, accounting for 2.66%. Injection site pain, fatigue and muscle pain accounted for the highest proportion of adverse symptoms in different sex, age and the Han nationality, while the proportion of minority adverse reactions was very low, and there was no difference among the different sex and age (P > 0.05). The main reasons for the reluctance of HIV/AIDS population to be vaccinated were(recommended by doctors) that HIV/AIDS patients could not be vaccinated (67.61%) and may have serious adverse reactions after the vaccination (19.72%). The factors affecting the vaccination were found by logistic regression analysis, whether they were worried about infecting novel coronavirus (OR = 0.121, 95%CI = 0.083~0.640, P < 0.001) and how much they knew about COVID-19 vaccine (OR = 28.932, 95%CI = 15.469~54.115, P < 0.001), safety of vaccination(OR = 13.953, 95%CI = 4.819~40.404, P < 0.001) and belief in the preventive effect of vaccine (OR = 14.017, 95%CI = 4.752~41.348, P < 0.001) were significant factors affecting vaccination. Among the 13 prefectures and cities, Dehong (20), Zhaotong (21) and Lincang (14) had the largest number of unvaccinated people. Conclusion After the mass vaccination, the rate of adverse reaction in HIV/AIDS population is low, the symptoms are mild, the correct and scientific advice and guidance from doctors and the full understanding of the harmfulness of the disease, the safety, prevention and effectiveness of the vaccine are the key to complete vaccination and put an end to vaccine hesitancy.
Objective To investigate the vaccination status and vaccination willingness of novel coronavirus in HIV/AIDS population in Yunnan.
2024, 45(1): 55-60.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240109
Abstract:
Objective To understand the intention of the community diabetes management application and analyze the related factors. Methods Diabetes patients in the community were selected as the research objects, and the diabetes management application intention scale, diabetes electronic health literacy scale, diabetes self-management ability scale and general information questionnaire were randomly conducted for the investigation. Results The score of 286 cases of community diabetes management application intention was 44.38 ± 8.56, the qualification rate was 67.4%, the score of diabetes e-health literacy score was 22.38 ± 7.56, the qualification rate was 28.2%, and the score of diabetes self-management ability score was 43.41 ± 7.96. Through the analysis, it was found that diabetes management application intention, e-health literacy, and self-management ability were affected by patients' education, age, and income. The analysis of related factors showed that the intention to use the diabetes management application was positively related to the electronic health literacy and self-management ability of patients P < 0.05. Conclusion The intention to use community diabetes management application is affected by income, education level, age, e-health literacy and self-management ability. The overall level of e-health literacy and self-management ability of diabetes patients is low. It is necessary to improve the e-health literacy and self-management level of diabetes patients.
2024, 45(1): 61-66.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240110
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the relationship between the common clinical indicators and diabetic foot ulcer(DFU) in type 2 diabetes mellitus(T2DM) patients by using the cross-sectional study and to provide the reference indicators for clinical DFU monitoring and prognosis evaluation. Methods A total of 115 T2DM patients admitted to the Department of Endocrinology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from June 2021 to June 2023 were selected as the study objects and were divided into group A(with DFU) and group B(without DFU) according to whether they had DFU. Those in group A were then divided into group A1(Wagner0-1), group A2(Wagner2-3) and group A3(Wagner4) according to Wagner classification. The differences of general data, blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids and other common clinical indicators among all of the groups were compared, and the correlation between DFU and the above indicators was explored. Results Diabetes duration, D-dimer(DD), systolic blood pressure and other indexes in group A were higher than those in group B and there was a statistically significant difference(P < 0.05). DD was the main risk factor for DFU in T2DM patients. Diabetic course in patients with DFU was positively correlated with the age(r > 0, P < 0.05), and negatively correlated with fasting blood glucose(FPG) level and 2hPG level at 2 hours after meals(r < 0, P < 0.05). The levels of interleukin-6(IL-6) and C-reactive protein(CRP) in A1 and A2 groups were lower than those in A3 group, the levels of neutrophils and leukocytes in A1 group were lower than those in A3 group, and the high density lipoprotein cholesterol(HDL-C) in A1 group was higher than that in A2 group and there was a statistically significant difference(P < 0.05). Conclusion DD and systolic blood pressure are the main risk factors for DFU, and DD is closely related to DFU. The older the patients with T2DM, the later the onset of DFU. The worse the blood glucose control, the earlier the onset of DFU. HDL-C is a protective factor for peripheral vascular disease in T2DM patients.
2024, 45(1): 67-72.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240111
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical characteristics and risk factors of thyroid dysfunction(TD) in malignant tumor patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors(ICIs). Methods A total of 157 cancer patients who were hospitalized and received ICIs treatment in the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2019 to June 2022 were collected and divided into the normal thyroid function group and abnormal thyroid function group based on whether TD had occurred. Fifty-eight patients with the normal thyroid function and 58 patients with the abnormal thyroid function were selected, and 58 healthy adults who underwent the physical examination in our hospital were randomly selected as the control group. The baseline data on the gender, age, tumor and ICIs type, history of surgery before medication, history of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and the related indicators of liver and kidney function, blood lipids, thyroid hormone levels and so on were collected. The relevant indicators of the three groups were statistically analyzed, and the normal thyroid function group and abnormal thyroid function group were compared to evaluate the clinical characteristics and related risk factors of TD caused by ICIs. Results 1. Among 157 patients treated with ICIs, 58 cases(36.9%) had thyroid dysfunction, including 39 cases of hypothyroidism(including subclinical hypothyroidism), 9 cases of hyperthyroidism(including subclinical hyperthyroidism), and 10 cases of pure related antibody abnormality. 2. The analysis of the data of the normal thyroid function group, the abnormal thyroid function group and the control group showed that the age, thyroid stimulating hormone(TSH), and thyroid function of the three groups were significantly different. TSH) baseline level, free triiodothyronine(FT3) baseline level and aspartate transaminase(AST) baseline level were statistically different(P < 0.05). There were significant differences in TSH baseline and radiotherapy history between the normal thyroid function group and the abnormal thyroid function group(P < 0.05); Multivariate analysis showed that the radiotherapy history(OR=7.291, 95%CI= 1.579-33.663, P < .05), baseline TSH level(OR=3.917, 95%CI= 1.697-9.038, P < 0.05) were the independent risk factors for thyroid dysfunction in cancer patients after ICIs treatment. Conclusion Hypothyroidism is the most common type of TD caused by ICIs in cancer patients. The baseline TSH level and the history of radiotherapy are the independent risk factors for thyroid dysfunction.
2024, 45(1): 73-77.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240106
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the changes of sex hormone levels in polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS) in infertile population after the assisted reproductive technology treatment, and to provide an evidence for the choice of the treatment. Methods The medical data of patients admitted to the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2016 to June 2021 were collected and divided into PCOS group(103) and non-PCOS group(589) according to whether they were diagnosed with PCOS, and the sex hormone changes of the two groups were compared. Results The patients in PCOS group were younger and had the higher BMI, more sinus follicles, higher AMH value, and lower total Gn usage. The number of LH/FSH > 2 in PCOS group was higher than that in non-PCOS group( P < 0.05).After the treatment, LH in both groups decreased, FSH, E 2 and (P < 0.05) increased; The difference of LH and E 2 before and after the treatment in PCOS group was greater than that in non-PCOS group < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with non-PCOS infertile patients, the changes of sex hormone indexes in PCOS infertile patients before and after the treatment were more obvious. In order to obtain the better clinical effect in patients with polycystic ovaries, it is recommended to pay attention to the changes of related sex hormone levels in the course of subsequent treatment, and choose a reasonable treatment plan.
2024, 45(1): 78-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240113
Abstract:
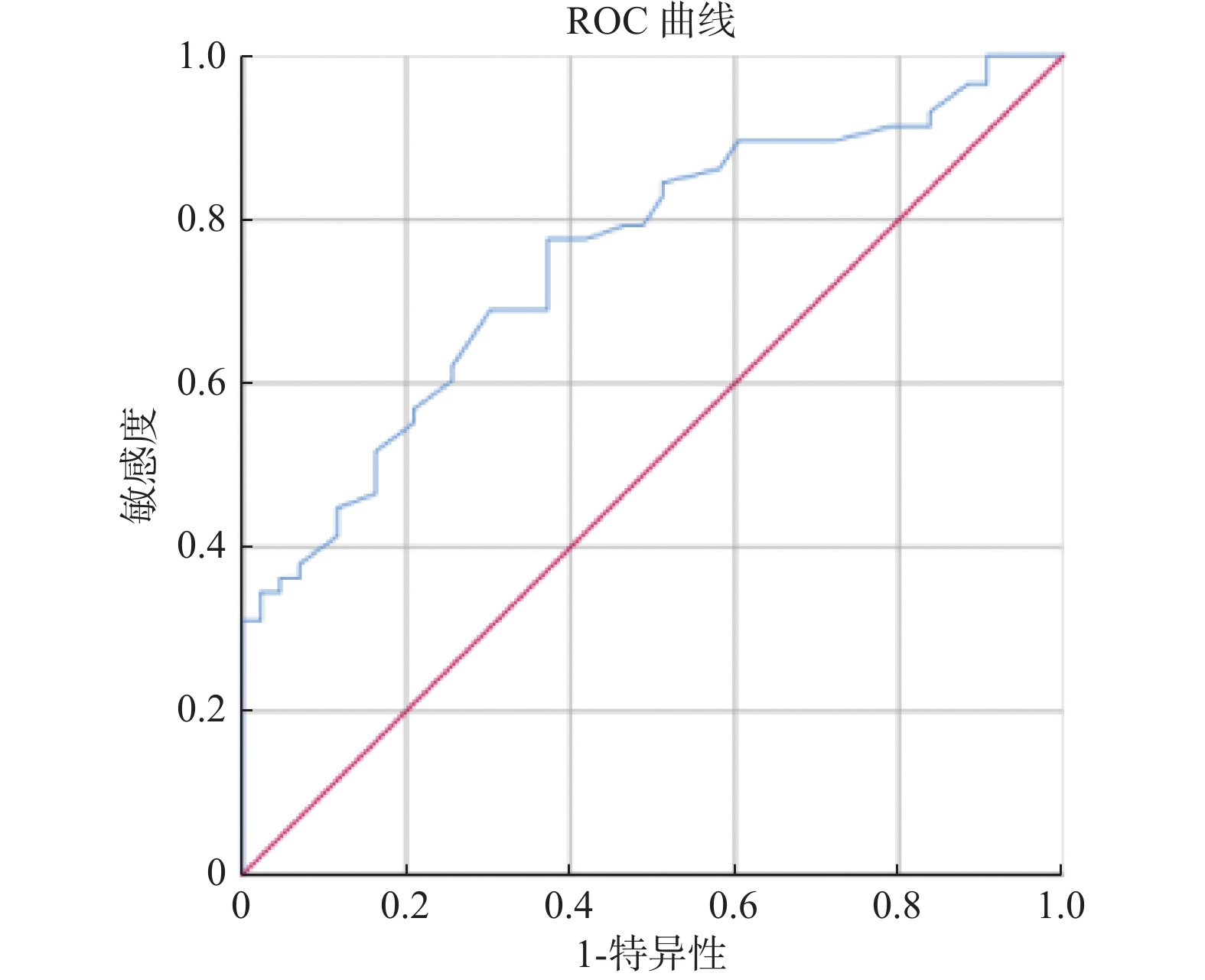
Objective To investigate the risk factors of relapse in patients with ischemic stroke using aspirin for single drug antiplatelet therapy. Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted on 200 patients with mild and medium ischemic stroke after 12 months of single drug treatment with aspirin, and the patients were divided into non-recurrence group and recurrence group according to the recurrence of stroke. Univariate analysis and multivariate logistic regression model were used to explore whether the related indicators were risk factors for recurrence.The ROC curve was used to predict the critical value of risk factors. Results Univariate analysis showed that platelet count, Hcy level and the A allele at rs12041331 site of PEAR1 gene were statistically significant risk factors(P < 0.05). Multifactor analysis showed that the independent risk factor for recurrence was homocysteine level [OR = 1.16(1.089-1.240), P < 0.001)]. The critical value of ROC prediction was 8.35 μmol/L (sensitivity 0.847, specificity 0.532). Conclusions The Hcy level, platelet count and A allele at rs12041331 site of PEAR1 gene are risk factors for recurrence in patients with ischemic stroke treated with aspirin for Single drug antiplatelet therapy.Hcy level is independent risk factor and can be used to predict the risk of recurrence.
Objective To investigate the risk factors of relapse in patients with ischemic stroke using aspirin for single drug antiplatelet therapy.
2024, 45(1): 83-86.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240114
Abstract:
Objective T o investigate the distributions of vitamin K1 and K2 in infants of different age groups by comparing the serum levels of vitamin K1 and K2 in them. Methods 1177 infants from 0 to 3 months were divided into 6 age groups. Those born/treated in the subject units(pediatrics, neonatology, child health care, obstetrics) were selected as the study subjects and grouped by age: 0~3 days(591 cases), 4~7 days(255 cases), 8~5 days(104 cases), 1 month(118 cases), 2 months(40 cases), and 3 months(69 cases). General data of the infants were collected, and the serum vitamin K1 and K2 levels were determined by HPLC-mass spectrometry(LC-MS) on a unified platform, and analyzed from the distribution of vitamin K1 and K2 at different ages. Results The distributions of vitamin K1 and K2 levels were statistically significant(P <0.001); newborns were highly vulnerable to vitamin K1 deficiency, and vitamin K2 deficiency was higher than vitamin K1 with age. Conclusion Maintaining the normal growth of vitamin K1 and K2 is crucial for the normal growth and development of infants of all ages, so we should pay close attention to the monitoring and supplement of vitamin K1 and K2.
2024, 45(1): 87-92.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240115
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the treatment strategy of the atrial septal defect in the surgical treatment of Ebstein’ s anomaly combined with the atrial septal defect and the short-term follow-up results of the treatment of Ebstein’ s anomaly. Methods A retrospective analysis of the clinical data and follow-up results of 20 patients with Ebstein’ s anomaly and atrial septal defect was conducted from September 2017 to February 2021. And the statistical analysis on the preoperative and postoperative echocardiography results of this group of patients was performed. Results Sixteen patients underwent the biventricular correction surgery, among whom two cases underwent the horizontal atrial tricuspid valvuloplasty(Danielsons procedure), four cases underwent the vertical atrial tricuspid valvuloplasty(Carpentier procedure), and ten cases underwent the conical reconstruction. Two patients were given a half ventricular correction surgery(tricuspid valve reconstruction combined with bidirectional Glenn surgery) and two patients underwent the bidirectional Glenn surgery. The combined atrial septal defects were closed in one stage during extracorporeal circulation for correction of deformitie in 20 patients. At 1, 3, 6, and 12 months after the surgery, the patient’ s right ventricular size significantly decreased compared to preoperative(P < 0.05), and cardiac function(left ventricular ejection fraction) significantly improved(P < 0.05). Conclusion The surgical treatment of Ebstein’ s anomaly combined with the atrial septal defect should follow the principle of individualized treatment. Biventricular correction is still the first choice for the treatment of Ebstein’ s anomaly, and the atrial septal defect should be closed at one stage, so as to obtain a good therapeutic effect.
2024, 45(1): 93-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240116
Abstract:
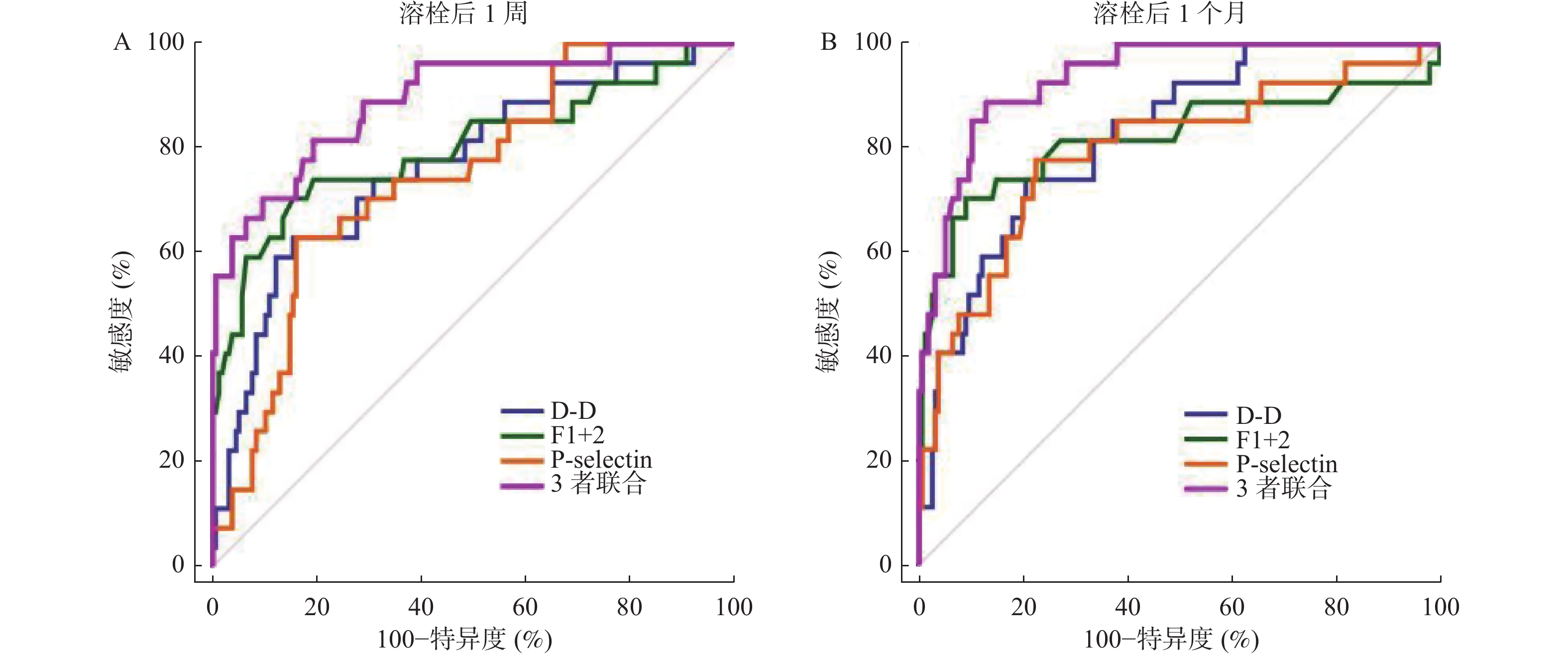
Objective To explore the changes and clinical significance of D-dimer(D-D), prothrombin fragment 1+2(F1+2) and P-selectin in patients with acute deep venous thrombosis of lower extremities(DVT) before and after catheterization and thrombolysis. Methods A total of 186 patients with acute DVT in the Third People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from March 2020 to March 2022 were selected as the study objects. And all of them underwent catheterization and hemolysis and were followed up in the outpatient form 12 months after the surgery. 4 cases were lost to follow-up, and a total of 182 cases completed postoperative follow-up. Postthrombotic syndrome(PTS) was divided into PTS group(n = 27) and non-PTS group(n = 155) according to whether post-thrombotic syndrome(PTS) occurred 12 months after the surgery. The general data of the two groups and the expression of D-D, F1+2, P-selectin in plasma before and after thrombolytic therapy were compared, and the influencing factors of PTS were analyzed by Logistic analysis. Receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC) and area under curve(AUC) were plotted to analyze the value of plasma D-D, F1+2, P-selectin in predicting the occurrence of PTS, and relative risk(RR) was used to analyze the influence of different plasma D-D, F1+2, P-selectin expression on PTS. Results Age, BMI, venous patency score, and plasma D-D, F1+2, P-selectin expression 1 week and 1 month after thrombolysis in PTS group were higher than those in non-PTS group(P < 0.05). Logistic showed that BMI and plasma D-D, F1+2 and P-selectin 1 week and 1 month after thrombolysis were the influential factors for PTS in acute DVT patients(P < 0.05). ROC curve showed that the combined efficacy of D-D, F1+2 and P-selectin 1 month after thrombolysis was significantly better than that of D-D, F1+2 and P-selectin 1 week after thrombolysis in predicting PTS. One month after thrombolysis, the risk of PTS in patients with high plasma D-D, F1+2, P-selectin expression was 4.211, 2.550 and 3.189 times higher than that in patients with low plasma D-D, F1+2, P-selectin expression. Conclusion The expression of D-D, F1+2 and P-selectin in plasma increases after thrombolysis in acute DVT patients, and the combination of D-D, F1+2 and P-selectin can predict the occurrence of PTS.
2024, 45(1): 100-106.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240117
Abstract:
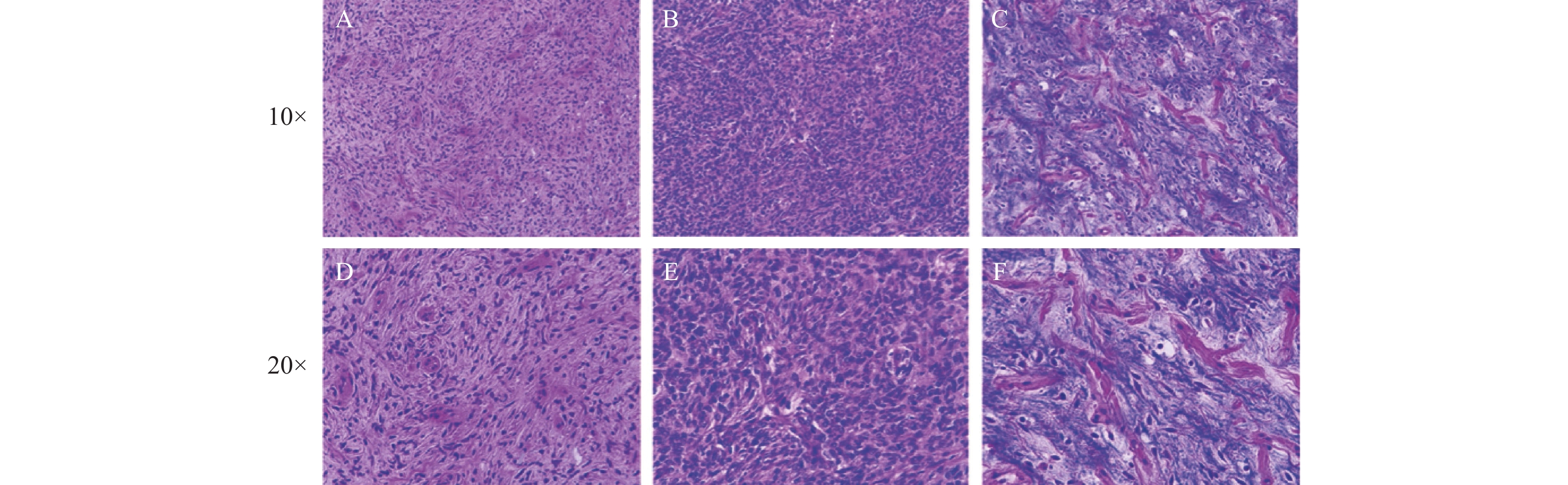
Objective To investigate the clinical and pathological characteristics of the extrapleural solitary fibrous tumor and the relevant differential diagnosis. Methods HE and immunohistochemical staining were performed on 26 samples of isolated fibrous tumors outside the pleura, and a comprehensive analysis was conducted based on the clinical and imaging data. Results The histological morphology of isolated fibrous tumors was diverse, with typical cases showing the irregular arrangement of oval or spindle shaped cells. In the stroma, thick collagen bands, antler like blood vessels, and peritubular transparent degeneration could be seen. The immunohistochemical staining demonstrated that the positive rates of STAT-6、CD34、Bcl-2、CD99、SMA were 96.2%、92.3%、92.3%、76.9% and 26.9%, respectively. Conclusion SFT commonly occurs in the pleura and can also occur in other areas. Its histological characteristics and immunohistochemical phenotype help to clarify the diagnosis. However, when it occurs in uncommon anatomical sites, it is necessary to carefully and meticulously distinguish and comprehensively judge the clinical prognosis of key diseases that need to be distinguished or excluded..
2024, 45(1): 107-115.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240118
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effects of bronchoalveolar lavage combined with microbiological rapid on-site evaluation in potential donor lung maintenance. Methods Brain death patients who met the inclusion criteria and were admitted to the Intensive Care Unit(ICU) of Calmette Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from September 2020 to December 2022 were selected for bronchoalveolar lavage(BAL) and(BAL) and the lavage fluid were collected for M-ROSE to compare the pathogen detection rate and initial diagnosis time. According to the positive results of the microbiological rapid on-site evaluation, patients with the brain death were treated with empirical anti-infective therapy, and the oxygenation index, chest X-ray score, and the infection index(WBC, CRP, PCT) of anti-infective treatment 48 hours were evaluated. Results 1.Comparison of the detection rate of pathogenic microorganisms: The results of M-ROSE were highly consistent with a routine microbiological smear(Kappa = 0.921, P < 0.001). 2.Comparison of diagnostic time: The initial diagnosis time of M-ROSE was significantly lower than routine microbiological smear time and microbial culture time(P < 0.001). 3.Comparison of therapeutic effects of anti-infective therapy for 48 hours: There was no significant difference in oxygenation index, white blood cells and hypersensitive C-reactive protein before and after the anti-infective treatment(P > 0.05). There were significant differences in procalcitonin and chest X-ray before and after the anti-infective treatment(P < 0.05). Conclusion Bronchoalveolar lavage combined with microbiological rapid on-site evaluation has the high timeliness in the diagnosis of potential donor pulmonary infection, which can provide a preliminary basis for the early anti-infective therapy of donor lung maintenance.
2024, 45(1): 116-121.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240119
Abstract:
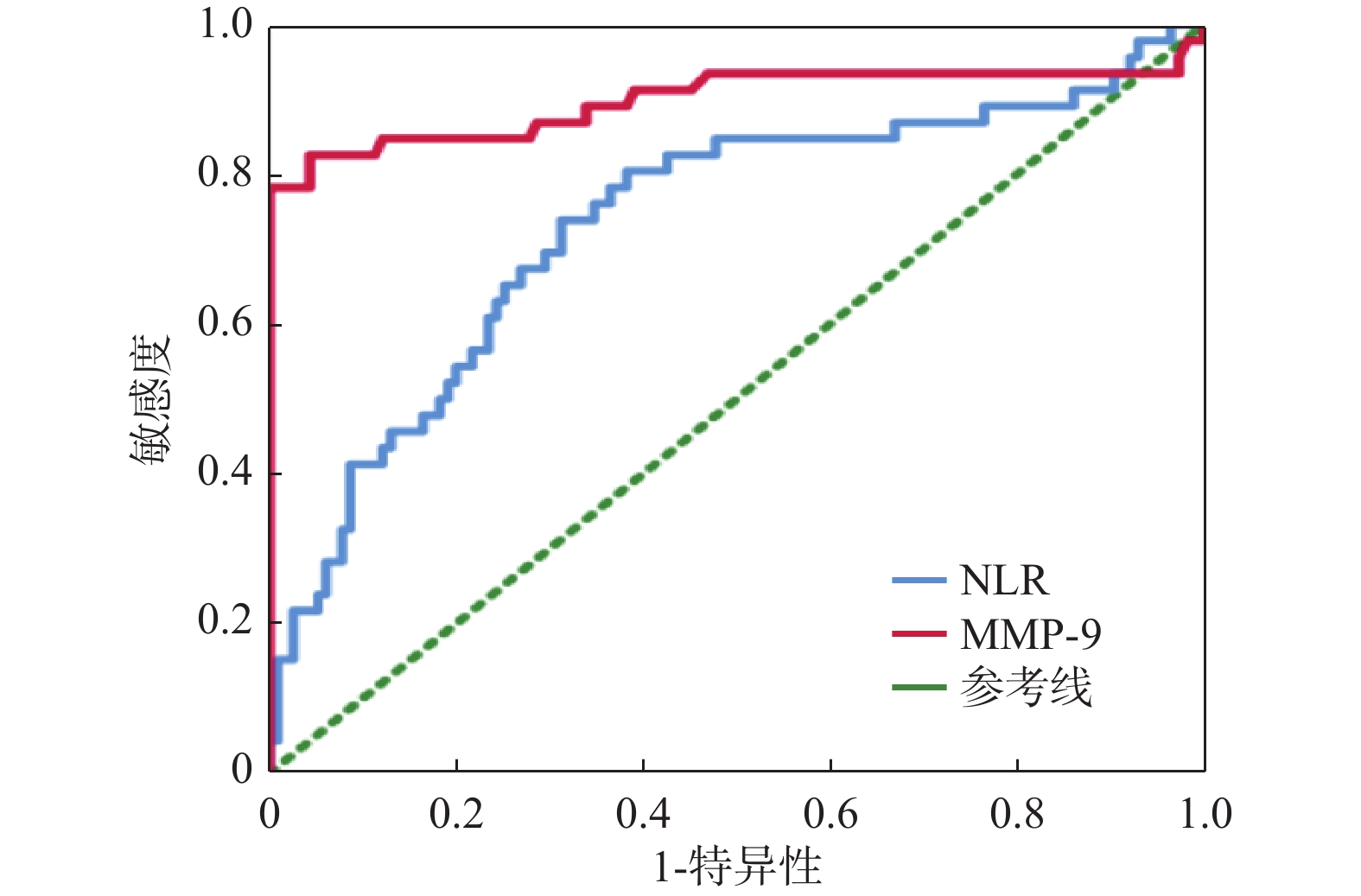
Objective To study the correlation between the changes of matrix metalloproteinase-9(MMP-9) and neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio(NLR) before and after the revascularization of acute ischemic stroke(AIS), so as to find biomarkers to predict the bleeding transformation risk of AIS patients. Methods From February 2022 to December 2022, 161 patients admitted to the Stroke Center of Qujing Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University with AIS werre divided in to the hemorrhagic transformation group and the non-hemorrhagic transformation groupand treated with revascularization(intravenous thrombolysis, endovascular treatment, combined the intravenous thrombolysis with endovascular treatment). Among them, there were 46 cases in the hemorrhagic transformation group and 115 cases in the non hemorrhagic transformation group. And the general data, NLR value and MMP-9 before and after the revascularization were compared between the two groups. Results There was no statistical difference in general data between the two groups(all P > 0.05) except for C-reactive protein in hemorrhagic transformation group and in non-hemorrhagic transformation group(P < 0.001). The white blood cells, neutrophils, neutrophil percentage, neutrophil absolute value, lymphocyte absolute value, NLR and MMP-9 value in hemorrhagic transformation group were significantly higher than those in non-hemorrhagic transformation group before the treatment and there was a statistical significance(P < 0.05).After revascularization, the indexes of blood routine and MMP-9 were significantly higher than those before the revascularization, and the increase in hemorrhagic transformation group was more obvious than that in non-hemorrhagic transformation group and there was a statistical significance(P < 0.001), The ROC curve showed that the area under the curve(AUC) of NLR and MMP-9 predicting bleeding transformation after AIS revascularization were 0.74 and 0.90. Conclusion NLR, MMP-9 are associated with the risk of bleeding transformation in AIS patients after the revascularization and can they can be used as the predictive factors for bleeding transformation risk.
2024, 45(1): 122-126.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240120
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the impact of not using drainage on clinical outcomes after arthroscopic autologous semitendinosus tendon reconstruction with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Methods From March 2022 to June 2023, 59 patients undergoing arthroscopic autologous semitendinosus tendon reconstruction with anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in Lincang People's Hospital were collected and randomly divided into the non-drainage group consisting of 29 cases(observation group) and the 24-hour drainage group consisting of 30 cases(control group). The pain levels of the two groups of patients were recorded on the 1st, 3rd, 7th, 14th, and 30th day after the surgery by using a visual analog scale. Additionally, the knee joint range of motion, length of hospital stay, and occurrence of postoperative complications were monitored. The circumference of the thigh was measured before and after the surgery, and the difference was calculated. Results Repeated measures analysis of variance revealed that there were statistically significant within-subject differences in pain ratings, thigh circumference, and knee joint range of motion(P < 0.05), but no statistically significant between-subject differences(P > 0.05). Independent samples t-tests showed that on the first day after the surgery, the observation group had lower pain ratings(P < 0.001), and higher thigh circumference and knee joint range of motion compared to the control group(P < 0.05). There were no statistically significant differences in pain ratings, knee joint range of motion, and thigh circumference between the two groups at the remaining follow-up times(P > 0.05); The observation group had a shorter hospital stay than the control group(P < 0.001); Both groups of patients had no complications such as lower limb nerve damage, deep vein thrombosis, knee joint infection, or hematomas requiring puncture and aspiration. Conclusion In the early postoperative period following arthroscopic autologous hamstring tendon reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament, the omission of drainage does not affect the clinical outcomes in terms of pain, knee joint mobility, and thigh circumference. Moreover, omitting drainage reduces the level of pain experienced by patients on the first day after the surgery, improves the knee joint mobility, and decreases the length of hospital stay. Therefore, in arthroscopic autologous hamstring tendon reconstruction of the anterior cruciate ligament, it is not recommended to routinely use drainage for preventive purposes.
2024, 45(1): 127-132.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240121
Abstract:
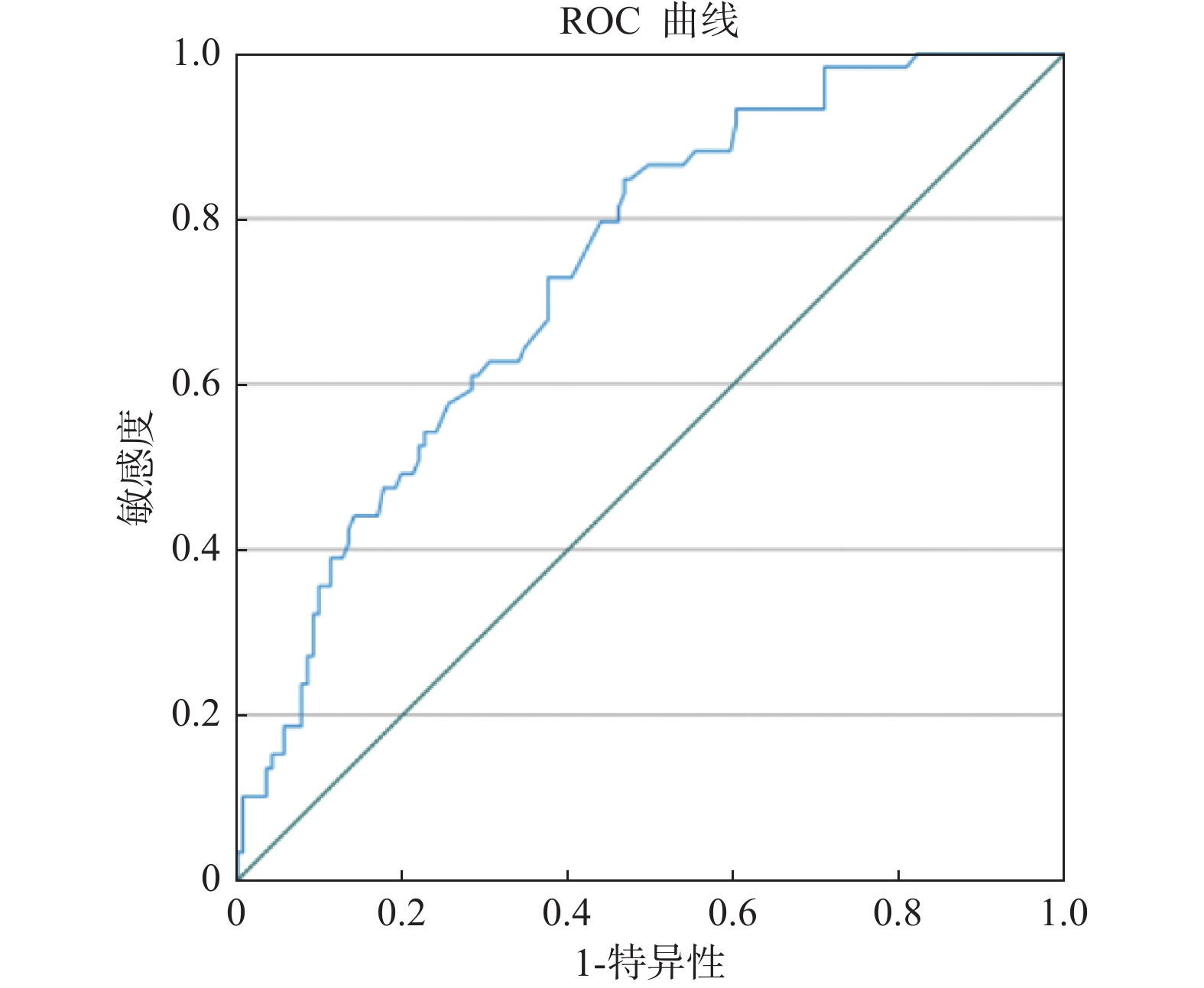
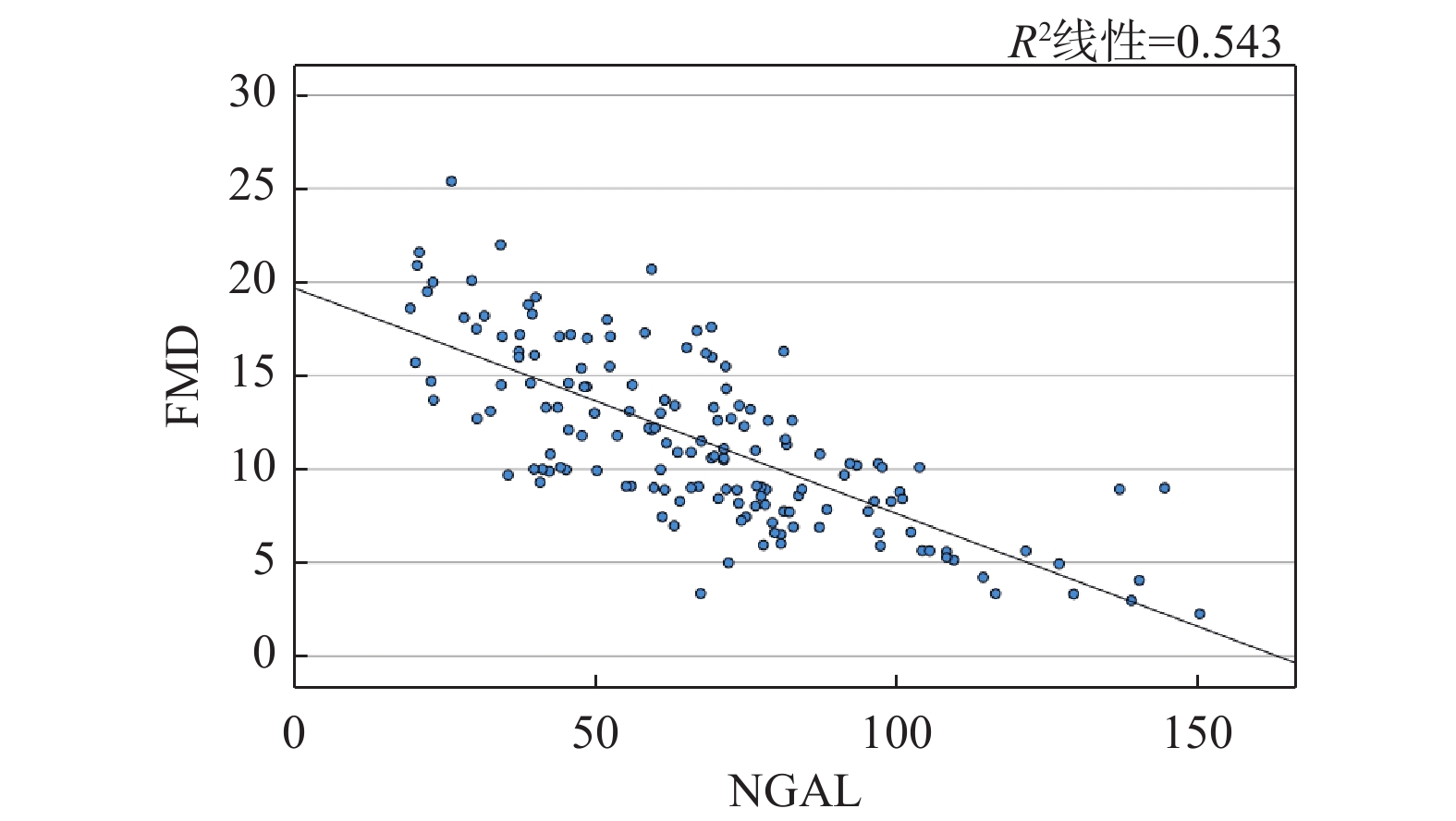
Objective To explore the correlation between the urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipid carrier protein(NGAL) and Brachial artery flow-mediated vasodilation(FMD) in Prehypertension. Methods 156 patients with Prehypertension found to have the normal high blood pressure during a health examination at the Luo Shi Road Community Health Service Center of Wuchang Hospital in Wuhan from September 2022 to September 2023 were included and divided into the normal endothelial function group and the endothelial dysfunction group with 89 cases and 67 cases respectively in each group according to whether the FMD was above 10%. The sex, age, smoking history, height, weight, SBP, DBP, FBG, Scr, eGFR, BUN, UA, Hcy, urine NGAL, FMD and other indicators were collected. The correlation between FMD and NGAL in prehypertension was analyzed by using independent samples t-test, Pearson linear correlation, multiple linear regression, binary logistic regression, and receiver operator characteristic(ROC) curves. Results There were no significant differences in gender, smoking history, SBP, FBG, TG, LDL-c, TC, BUN, Scr, UA, eGFR and Hcy(all P > 0.05).The age, BMI, DBP, HDL-c, and urine NGAL levels in the endothelial dysfunction group were significantly higher than those in the normal endothelial function group( P < 0.05). Pearson linear correlation analysis showed that urine NGAL levels were negative correlated with FMD( r = -0.632 P < 0.05). Multiple linear regression analysis: NGAL, DBP significantly affected FMD(all P < 0.05). NGAL and diastolic blood pressure were independent risk factors for FMD. The area under the curve of ROC curve analysis was 0.813, 0.895 and 0.906 respectively for urinary NGAL, DBP and urinary NGAL combined with DBP. DBP combined with urinary NGAL had the higher diagnostic efficacy. Conclusion Urinary NGAL and DBP are associated with the endothelial dysfunction, and urinary NGAL is expected to be a new biomarker for evaluating the vascular endothelial function loss and a target for the intervention of prehypertension
2024, 45(1): 133-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240122
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the changes of vitamin D in children with Henoch-Schonlein purpura(HSP). Methods 130 children with HSP from Kunming Children’ s Hospital between July 2022-July 2023 were selected as the study subjects and 100 healthy children were selected during the same period as the control group. The blood samples were collected from the children with HSP and the healthy children. The content of vitamin D was measured by Kunming Kingmed Institute for Clinical Laboratory. Results The content of 25(OH) D in children with HSP was lower than that in healthy children, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.01).The proportion of vitamin D insufficiency in children with HSP was higher than that in healthy children, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.01). Conclusion The children with HSP are prone to vitamin D insufficiency. Vitamin D supplementation may provide a new method for the treatment of HSP.
2024, 45(1): 136-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240123
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the effect of photo-activated disinfection(PAD) as a kind of adjuvant treatment on moderate to severe chronic periodontitis. Methods 21 patients with the chronic periodontitis(totally 218 selected sites) were randomly enrolled and divided into group A( minocycline hydrochloride), group B(PAD) , group C(PAD + minocycline hydrochloride ), and group D(no adjunctive therapy) for the adjunctive treatment after receiving the scaling and root planing(SRP). Periodontal indexs as probing depth(PD), bleeding on probing(BOP) and clinical attachment loss(CAL) were examined at the baseline , 6 and 12 weeks after the treatment. Meanwhile, periodontal pathogens as Porphyromonas gingivalis(Pg) and Tannerella forsythia(Tf) from subgingival plaque of group A, B and C were detected by Real-time PCR. Results Compared with the baseline, the periodontal inflammations of all groups were improved signiffcantly at 6 and 12 weeks after the treatment(P < 0.001), and group A, group B and group C were better than group D(P < 0.001), group C was better than group A(P < 0.001); Furthermore, the concentration of Pg and Tf was decreased significantly(P < 0.001), and there was no difference among the three groups with adjunctive therapy. Conclussion As the adjunctive treatment of SRP, PAD could achieve the same and even better effect than minocycline hydrochloride ointment.
2024, 45(1): 143-148.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240124
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of the laparoscopic surgery and open surgery on the postoperative intestinal function recovery time in elderly patients with colorectal cancer(CRC). Methods 66 elderly patients with CRC and treated in the 2nd People’ s Hospital of Kunming from January 2021to July 2022 were chosen and divided into the control group(n = 33) and the study group(n = 33) according to different operation ways. And the postoperative bowel function recovery time, radical, complications and surgical index were compared between the two groups. Results The recovery time of intestinal function in the study group was significantly shorter than that in the control group(P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference in radical indicators between the two groups(P > 0.05).The incidence of complications in the study group was lower than that in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). The operation time of the study group was longer than that of the control group and there was the statistically significant difference(P < 0.05), while the bleeding was less than that of the control group and there was the statistically significant difference(P < 0.05). Conclusion Compared with the open surgery, laparoscopic surgery can more effectively shorten the recovery time of postoperative intestinal function, reduce the incidence of complications and intraoperative blood loss in elderly patients with CRC. Although there is no significant difference between two kinds of operation mode in terms of radical, it should be considered when it is applied in the specific operation time and other factors.
2024, 45(1): 149-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240125
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics and the antimicrobial resistance of respiratory tract infection in children in Baoshan City, guide clinicians to rationally apply antibiotics, and improve the success rate of treatment. Methods Retrospective analysis of the distribution characteristics and drug sensitivity results of 1039 strains of pathogens detected in pediatric inpatients of hospitals from 2019 to 2022 was conducted. Results The main pathogens causing the respiratory infections in children in Baoshan area were Streptococcus pneumoniae, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Analysis of the drug sensitivity results of pathogenic bacteria with a detected quantity greater than 80 revealed that Streptococcus pneumoniae had a high resistance rate to erythromycin, clindamycin, and compound sulfamethoxazole. The resistance rates of penicillin, ceftriaxone, cefotaxime, and meropenem were P<0.05, and the difference was statistically significan. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) was11.1%; CTX/CRO-R-ECO, CTX/CRO-R-KPN, CR-ECO and CR-KPN were lower than the 2021 ISPED level; The P.aeruginosa drug resistance rate and H.influenzae’ s ampicillin and ampicillin/sulbactam were higher than the 2021 ISPED level. Conclusion The treatment of respiratory tract infections in pediatric patients faces great challenges.The non-standard use of empirical medication has led to the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, and the selection of anti infection treatment drugs is limited. Therefore, it is imperative to grasp the epidemic characteristics and drug resistance of pathogenic bacteria in the local area.
2024, 45(1): 156-162.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240126
Abstract:
Objective To summarize the experience of multi-disciplinary team(MDT) in the pediatric department of Qujing Maternal and Child Health Hospital, and to evaluate the effectiveness of MDT on neonatal brain injury. Methods The clinical data of children with brain injury and treated in the pediatrics department of Qujing Maternal and Child Health Hospital from November 2019 to April 2023 were collected. The children with brain injury and treated from October 2019 to June 2020 were regarded as the non-MDT group, and the children with brain injury and treated from July 2020 to April 2023 were regarded as the MDT group for comparative analysis. Chi-square test /t-test was used to compare and analyze the clinical data of the two groups. Results Among the 890 cases of pediatric brain injury, there were 519 males and 371 females. The median and quartiles of the age distribution for the two groups were as follows: MDT group 2.00 (0.82, 5.00) years and non-MDT group 1.00 (1.00, 4.00) years. Craniocerebral injury was the main type of brain injury in both groups, in addition, among children with craniocerebral injury and intracranial hemorrhage, the cure rate of MDT group was higher than that of non-MDT group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Among the 405 children in MDT group, 154(38.0%) underwent the surgery, while among the 485 children in non-MDT group, 121(24.9%) underwent the surgery. The difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). 23.2% of children in MDT group were in critical condition during the hospitalization, which was significantly lower than that in non-MDT group (30.5%), and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). The unhealed rate of MDT group(2.0%) was also significantly lower than that of non-MDT group (5.6%), the cure rate of MDT group (40.5%) was significantly higher than that of non-MDT group (34.4%), and there was a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05). The expense of treatment, medicine and sanitary materials in MDT group were lower than those in non-MDT group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The multivariate Logistic regression model analysis of the cure rate of children with brain injury showed that the MDT model could effectively improve the cure rate of children with brain injury (RR = 1.513, 95%CI = 1.134-2.020). The results of multiple linear regression model analysis showed that there was no statistical difference in the effect of MDT on the actual hospitalization days of children (P > 0.05). Conclusion Using MDT model to diagnose and treat children with brain injury is helpful to improve the cure rate, reduce the risk of children’ s disease aggravation, and achieve the significant therapeutic effects in children with brain injury. MDT model is worth popularizing and applying in children with brain injury.
2024, 45(1): 163-167.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240127
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of smoking on the semen quality in infertile men. Methods A total of 360 male infertility patients were enrolled and divided into the smoking group(\begin{document}$n $\end{document} \begin{document}$n $\end{document} \begin{document}$n $\end{document} \begin{document}$n $\end{document} \begin{document}$n $\end{document} Results There were significant differences in semen volume, liquefaction time, sperm motility, normal morphological rate and DNA fragmentation rate between the smoking group and the non-smoking group(P <0.05). The semen volume, sperm motility and normal morphological rate of the smoking group were lower than those in the non-smoking group, and the DNA fragmentation rate and semen liquefaction time were higher than those in the non-smoking group. And with the increase of smoking volume, sperm motility and normal morphological rate decreased, semen liquefaction time and DNA fragmentation rate increased, and there was no significant difference in the sperm concentration between the smoking group and non-smoking group(P >0.05). There was no significant difference in the semen volume between the three groups with different smoking amounts(P >0.05). Conclusion Smoking has a negative impact on the sperm quality parameters such as semen volume, sperm motility, normal morphological rate, sperm motility, liquefaction time and DNA fragmentation, and the effect of heavy smoking is particularly obvious. We should strengthen the comprehensive health education, promote the healthy lifestyles and reduce smoking.
2024, 45(1): 168-171.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240128
Abstract:
The preparation edge of the tooth in oral restoration has always been the hot concern for dentists, and the improper preparation edge may lead to such diseases as caries and periodontitis, and ultimately lead to the restoration failure. The application of biologically oriented preparation technique has been proven to restore good periodontal soft and hard tissue morphology, which is expected to replace the traditional dental preparation methods. This article aims to comprehensively discuss the application of biologically oriented preparation technique in veneers, full crown and implantation.
The preparation edge of the tooth in oral restoration has always been the hot concern for dentists, and the improper preparation edge may lead to such diseases as caries and periodontitis, and ultimately lead to the restoration failure. The application of biologically oriented preparation technique has been proven to restore good periodontal soft and hard tissue morphology, which is expected to replace the traditional dental preparation methods. This article aims to comprehensively discuss the application of biologically oriented preparation technique in veneers, full crown and implantation.
2024, 45(1): 172-178.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240129
Abstract:
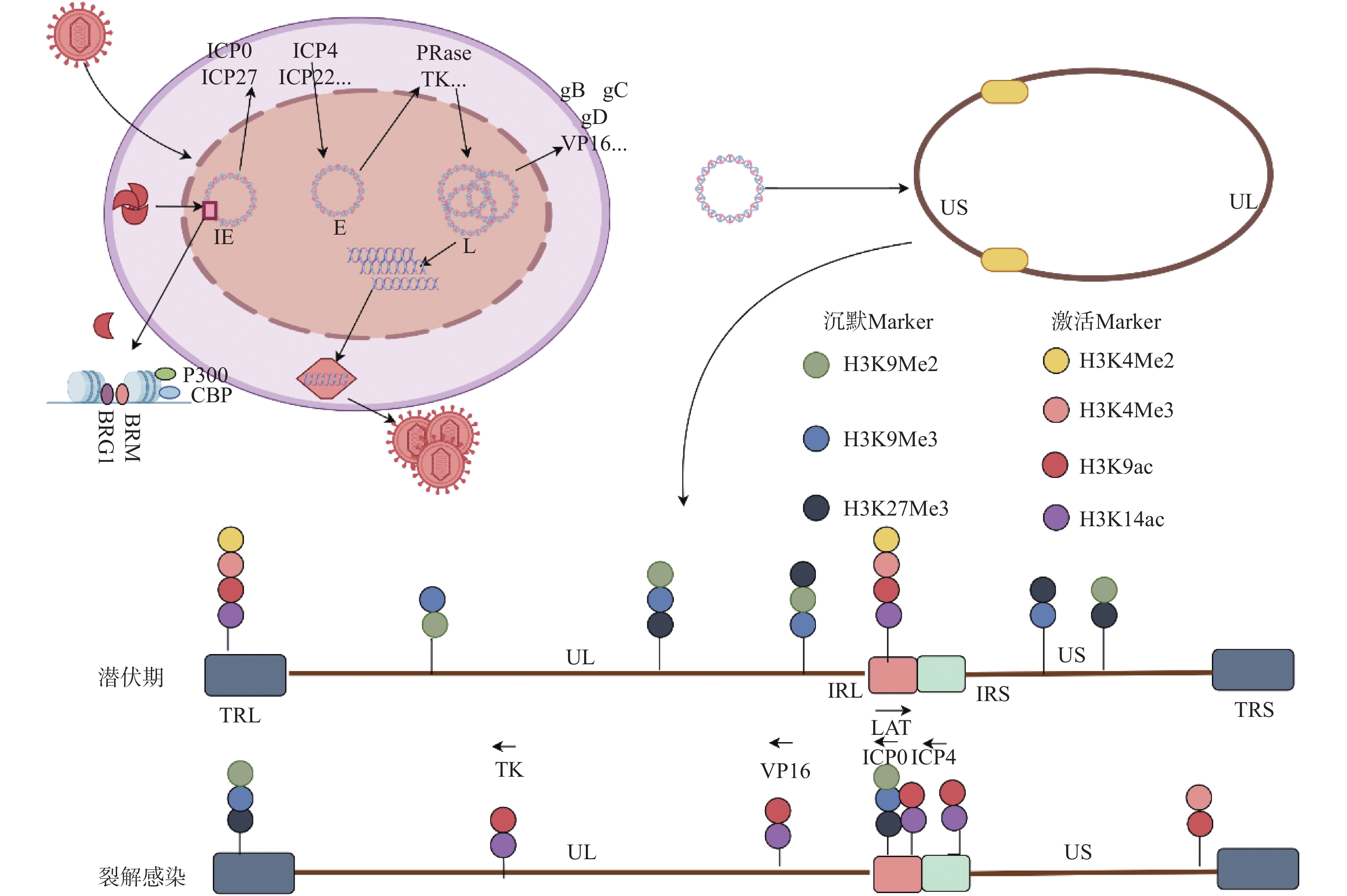
Herpes simplex viruses type 1(HSV1) is among the most ubiquitous human pathogens that cause a wide variety of disease states. The latent infection of the central nervous system and sporadically reactivation is the central part of HSV1 pathogenesis, which also brings challenges to antiviral therapies. At present, the mechanism of establishing, maintaining and reactivation of HSV1 has not been fully clarified, whereas it has been generally accepted that the epigenetic regulation may play an important role. Accumulating researches have also indicated that the lytic and latent viral genomes exhibit the different chromatin structures, and the accumulation of diverse post-translational modifies the histones endow viral genes with transcriptional activation or repression features. In addition, the latency-associate transcripts of virus may also participate in the genome epigenetic modification. In this review, we summarize the research progress of epigenetic regulation of HSV1 and highlight the critical role of chromatin remodeling in HSV1 lytic proliferation and establishment of latent infection.
Herpes simplex viruses type 1(HSV1) is among the most ubiquitous human pathogens that cause a wide variety of disease states. The latent infection of the central nervous system and sporadically reactivation is the central part of HSV1 pathogenesis, which also brings challenges to antiviral therapies. At present, the mechanism of establishing, maintaining and reactivation of HSV1 has not been fully clarified, whereas it has been generally accepted that the epigenetic regulation may play an important role. Accumulating researches have also indicated that the lytic and latent viral genomes exhibit the different chromatin structures, and the accumulation of diverse post-translational modifies the histones endow viral genes with transcriptional activation or repression features. In addition, the latency-associate transcripts of virus may also participate in the genome epigenetic modification. In this review, we summarize the research progress of epigenetic regulation of HSV1 and highlight the critical role of chromatin remodeling in HSV1 lytic proliferation and establishment of latent infection.
2024, 45(1): 179-186.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240130
Abstract:
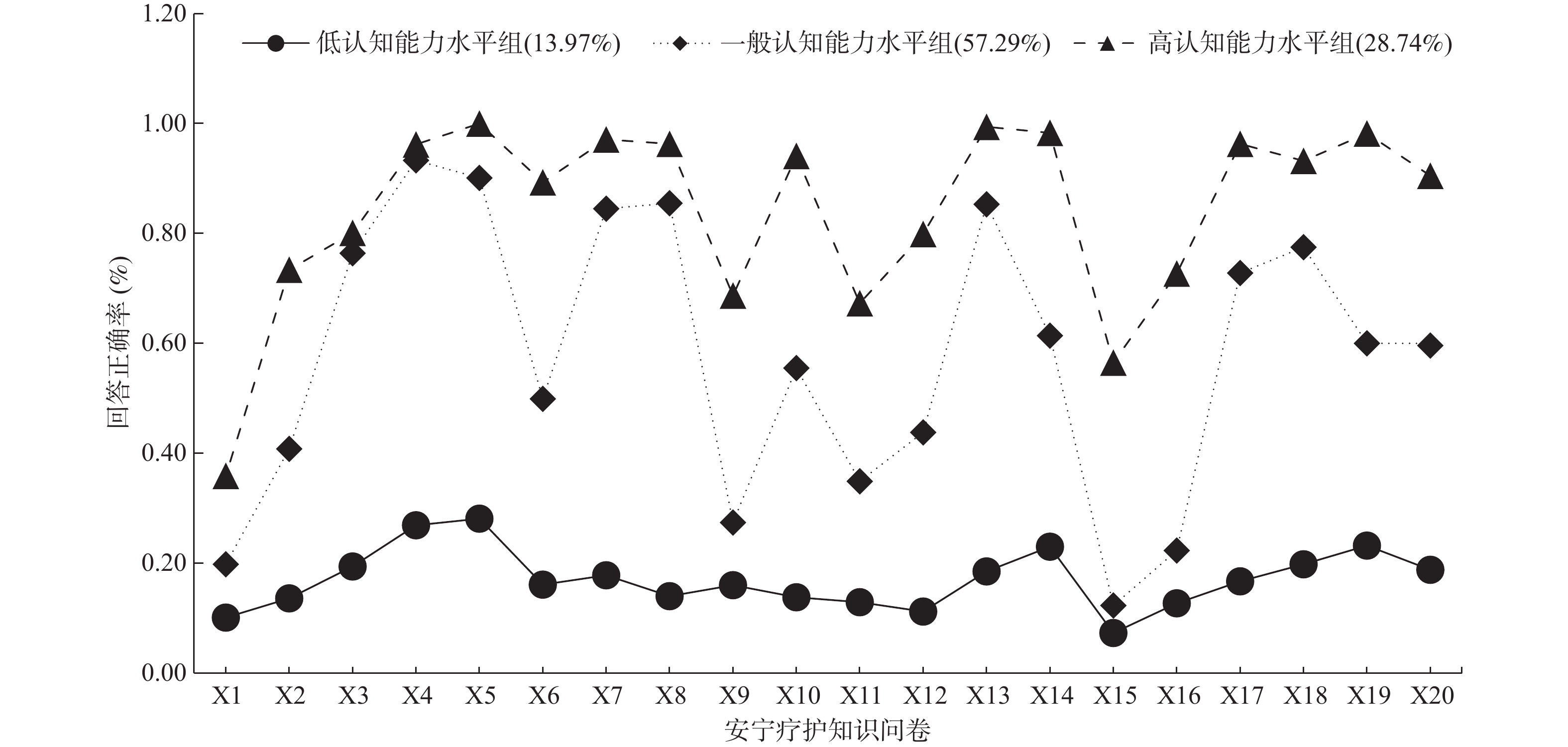
Objective To explore the different latent class and characteristics of the cognitive ability level of undergraduate nursing students in hospice care based on the individual-centered perspective, and analyze its influencing factors to provide the reference for the formulation of targeted nursing education. Methods Nursing students in a medical university in Yunnan Province were selected from March 2023 to June 2023. The general data questionnaire and hospice care knowledge questionnaire were used to conduct a cross-sectional survey. SPSS and Mplus were used for the data analysis. Results Three latent class of hospice care cognitive ability were identified, which were named as hospice care high cognitive ability group, general cognitive ability group, and low cognitive ability group, accounting for 28.74%, 57.29%, and 13.97%, respectively; Nursing students’ gender, nationality, place of residence, earning and practice experience of hospice care(whether they had the contact with end-stage cancer patients, whether they had received the hospice care related training), and whether they were willing to engage in the hospice care related work were the influencing factors of different potential categories of cognitive ability of hospice care among nursing students(P < 0.05). Conclusion There are three latent class of hospice care cognitive ability of nursing students. Male minority nursing students who have not been exposed to end-stage cancer patients and have not received the hospice care-related training, are unwilling to engage in the hospice care-related work. Male ethnic minority nursing students residing in rural areas have the weaker cognitive levels of hospice care. Scholars in the future can formulate targeted training strategies according to different latent class of hospice care cognitive ability to improve nursing students’ hospice care cognitive ability and reserve talents for hospice care teams.
2024, 45(1): 187-192.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20240131
Abstract:
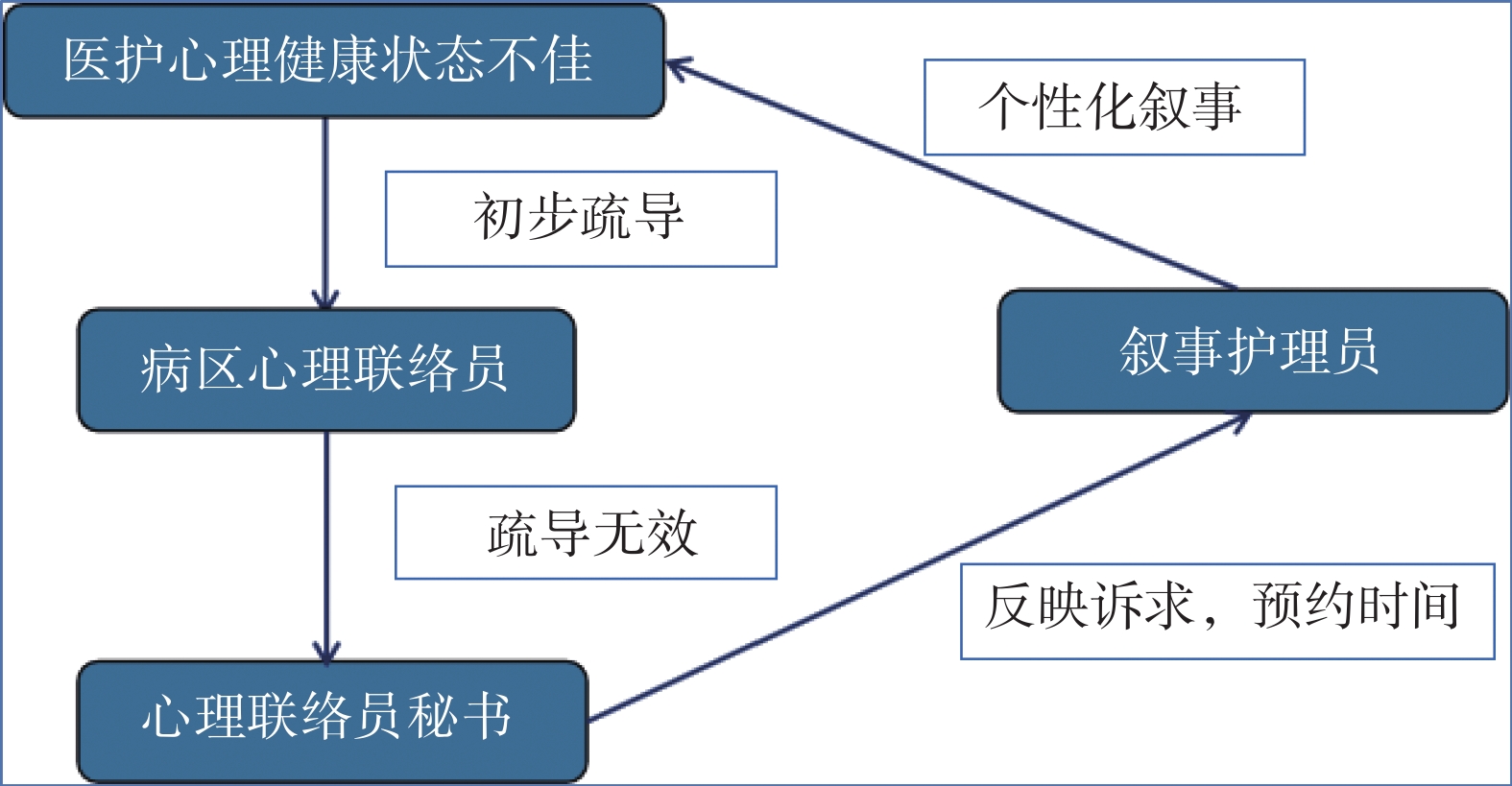
Objective To explore the impact of the three-level assistance model based on the narrative nursing theory on the mental health status of medical staff. Methods 140 medical staff working in a third class hospital in Xiangyang City were selected as the research object. The three-level assistance model based on narrative nursing theory was used to intervene them from September 2021 to July 2022. The symptom self-assessment scales before and after the intervention were compared. Results Before the intervention, the total score of SCL-90(156.37±32.56) points and the scores of various symptom factors of medical staff were higher; After the intervention, the total score of SCL-90(133.35±43.48) points and the scores of various symptom factors were lower than those before the intervention and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05). Conclusion The three-level assistance model based on narrative nursing theory can reduce the total score of SCL-90 and the scores of various symptom factors, improve the mental health status and mental health level.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS