2021 Vol. 42, No. 7
2021, 42(7): 1-6.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210701
Abstract:
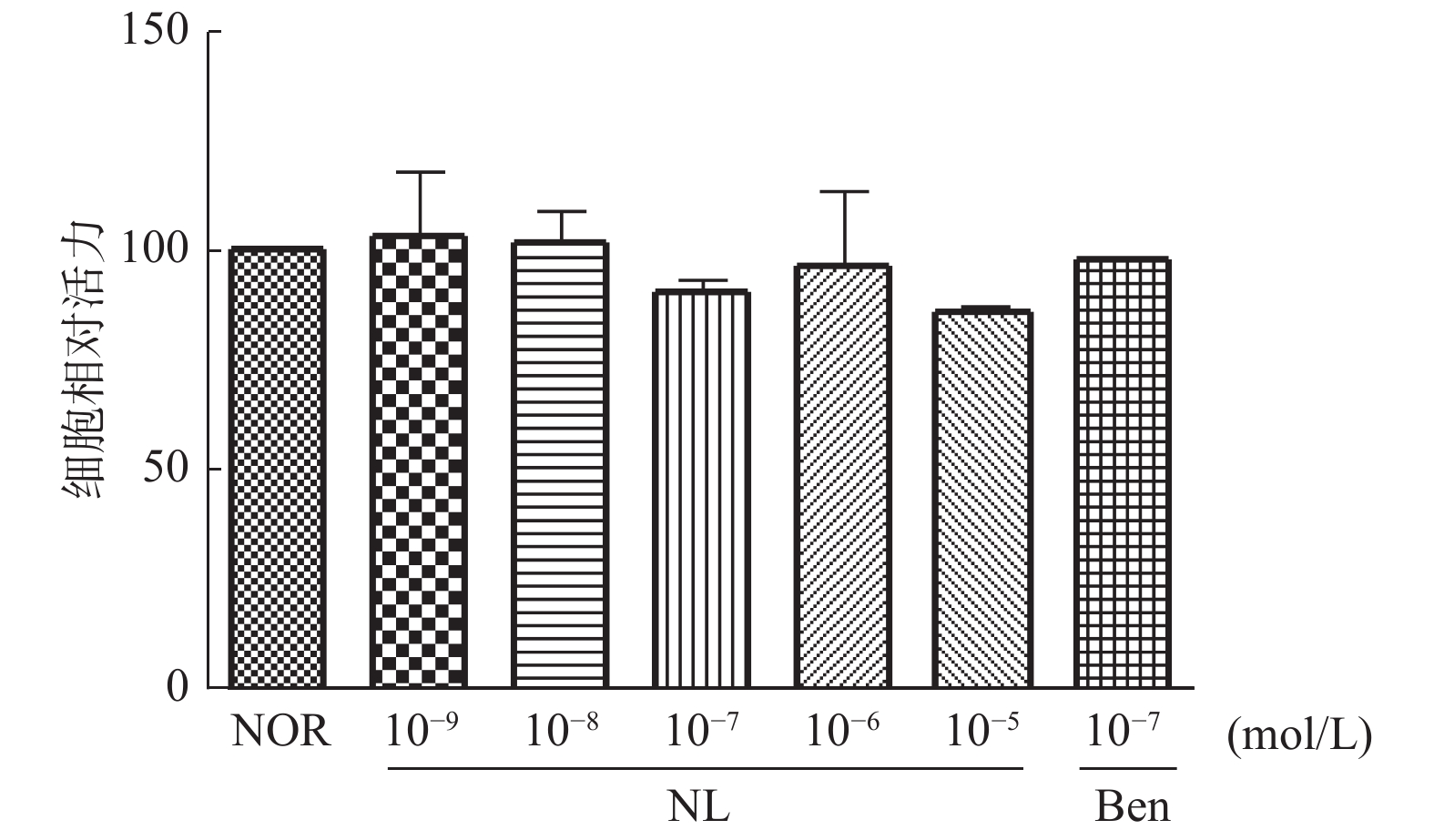
Objective To study the effects of norathyriol on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of HK-2 cells induced by TGF-β1. Methods MTT assay was used to detect the effect of norathyriol on HK-2 cell viability. The HK-2 cells were divided into normal group, model group, norathyriol (10-8, 10-7, 10-6 mol·L-1) groups and positive control (benzbromarone, 10-7 mol/L) group. The norathyriol and benzbromarone were incubated for 4 h before HK-2 cells were treated by TGF-β1 (10 ng/mL) to induce EMT. Then, the HK-2 cells were cultured for another 24 h or 48 h. Scratch assay was used to detect the migration motility of HK-2 cells. Transwell invasion assay was used to detect invasion ability of HK-2 cells. The proteins expression of fibronectin (FN) and collagen type Ⅰ (ColⅠ) were detected by western blot. Results (1) The norathyriol (10-9-10-5 mol/L)has no effects on the HK-2 cell viability, compared with the normal group (P > 0.05). (2) Compared with the normal group, the cells morphology of the model group changed from the original cobblestone shape to a long fusiform shape, the migration rate and the invasive ability of the model group was significantly increased ( P < 0.01). The protein expression of Col and FN in the model group was significantly increased. Compared with the model group, the cells morphology of norathyriol (10 -8, 10-7, 10-6 mol/L) and benzbromarone (10-7 mol/L) groups maintain thecobblestone shape partly, the migration rate (10-8, 10-7, 10-6 mol/L) and the invasive ability (10-6 mol/L) of norathyriol were significantly decreased (P < 0.01); The protein expression of Col and FN were significantly down-regulated in the norathyriol (10 -6 mol/L) group and the benzbromarone group (P < 0.05, 0.01). Conclusion Norathyriol can inhibit the migration and invasion of HK-2 cells induced by TGF-β1 and down-regulate the protein expression of fibronectin (FN) and collagen type Ⅰ (ColⅠ).
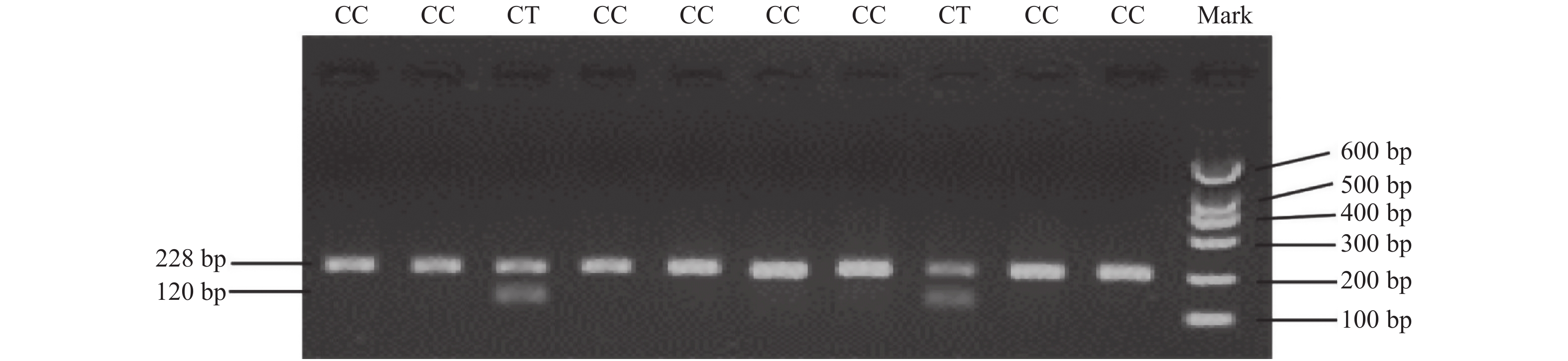
2021, 42(7): 7-12.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210702
Abstract:
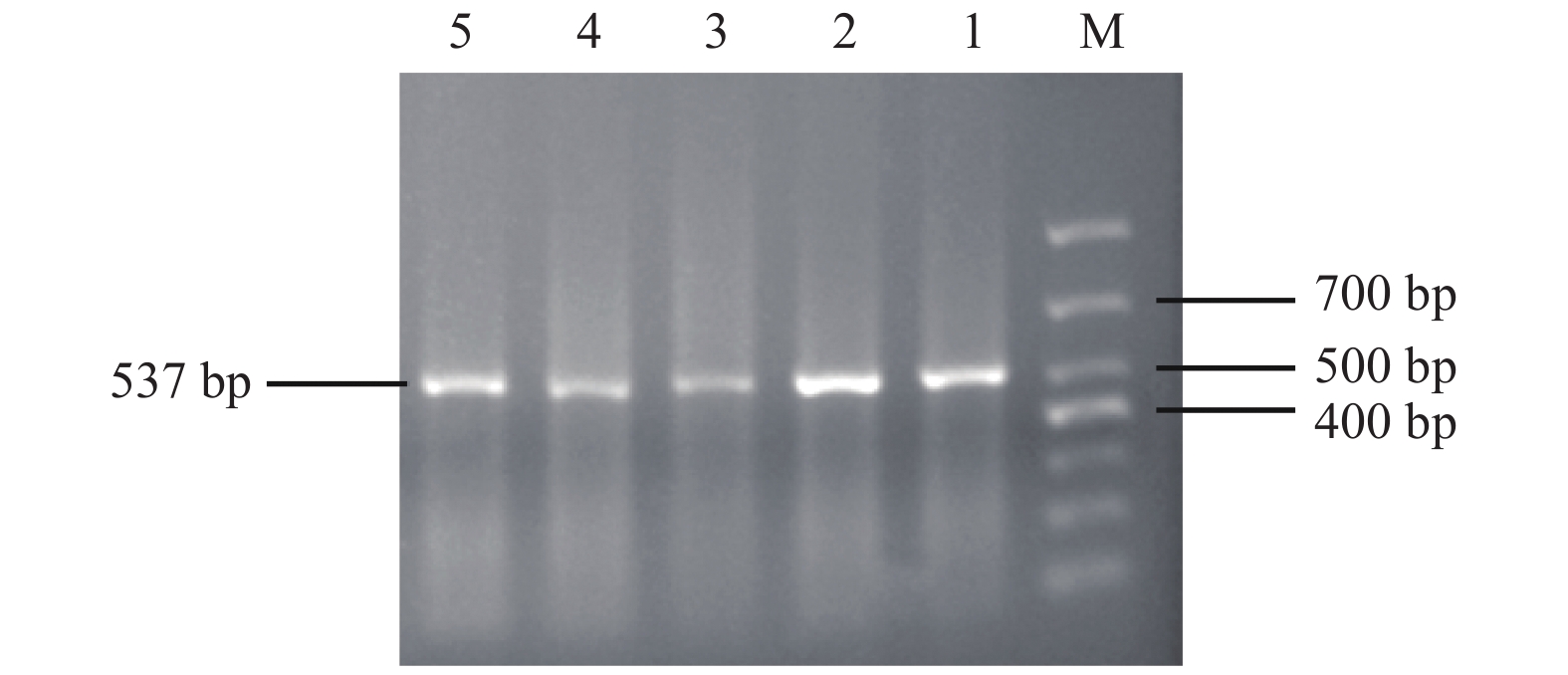
Objective To investigate the correlation between CYP11B2 gene -344C/T polymorphism and essential hypertension in Yi people of Yunnan Shuanghe Township. Methods We collected peripheral blood of 308 Yi residents of Shuanghe township, Jinning county, Yunnan province, including 132 patients with essential hypertension (EH group) and 176 control group members. The target fragment was amplified by PCR and restriction endonuclease enzymes were used. Identify the genotype, calculate genotype frequency and allele frequency, and perform correlation analysis. Results The genotype frequency of TT in the EH group/control group was 64.39%/60.23%, CT was 29.55%/32.95%, CC was 6.06%/6.81%, and the allele T frequency was 79.17% /76.70%, the frequency of allele C was 20.83% /23.30%, but there was no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05), however, the TT genotype frequency in female patients (70.00%) was higher than that in control group (56.44%) ( P < 0.05). In EH group, the genotype frequency TT of male /female patients was 55.77%/70.00%, CT was 32.69%/27.50%, CC was 11.54%/2.50%, and allele T frequency was 72.12%/83.75%. The frequency of allele C was 27.88%/16.25%, and the genotype frequency of TT, CC and allele frequency of the two groups were significantly different ( P < 0.05). Conclusion The distribution of CYP11B2 gene -344C/T polymorphism in Yi people with essential hypertension has gender differences, but it may not be related to essential hypertension in Yi people of Yunnan Shuanghe township.
2021, 42(7): 13-19.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210703
Abstract:
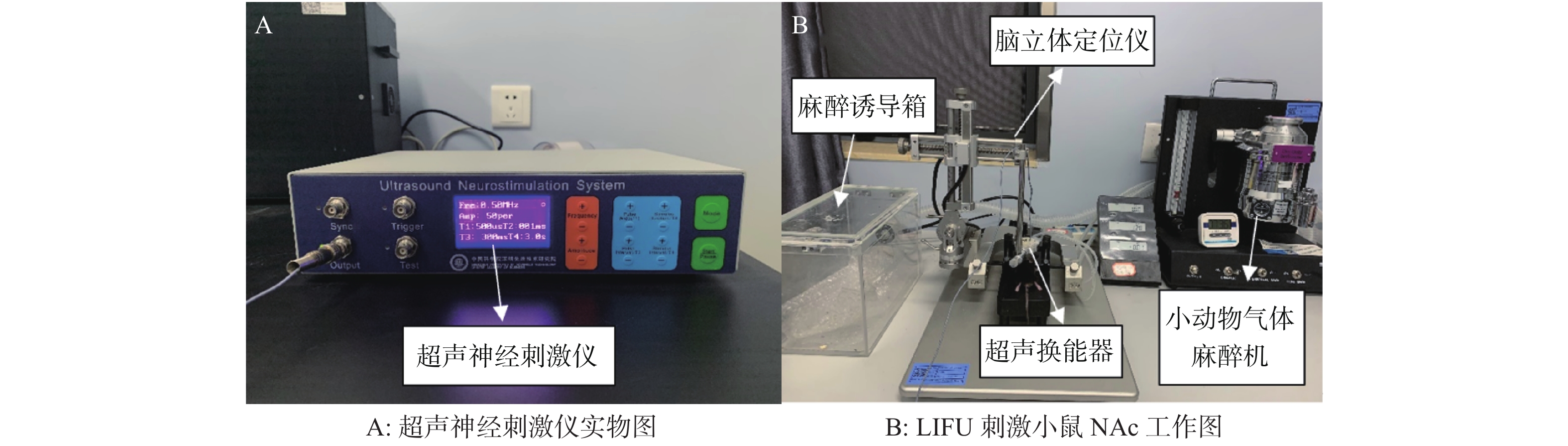
Objective To investigate the effectiveness of ultrasound stimulation for neural regulation from the aspects of behavioral pathology and neurobiochemistry by using low intensity focused ultrasound to stimulate the nucleus accumbens of normal mice. Methods 100 C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into experimental group and control group with 50 mice in each group. The control group was given sham stimulation, and the experimental group was given transcranial low-intensity focused ultrasound to stimulate the NAc, twice a day, 10 min each time, for 7 consecutive days. After the intervention, 30 mice were randomly assigned to behavioral assessment (forced swimming, open field, and water maze), 10 mice were assigned to electron microscopy (EM), and 10 mice were assigned to neurotransmitter test.The depression, anxiety and learning and memory ability of the mice were evaluated by forced swimming, open field and water maze tests.The ultrastructural changes of neurons in the NAcof mice were observed by transmission electron microscopy. The contents of monoamine neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, dopamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine) in NAc of mice were determined by ELISA. Results 1. Behavioral evaluation results: Compared with the control group, the immobile time in the ultrasonic stimulation group was significantly longer (P < 0.01), the total distance travelled, the average speed travelled, the distancetravelled of the central area, the time of the central area and the number of exits from the central area in the open field all decreased significantly ( P < 0.05, P < 0.01), In the water maze experiment, the avoidance latency time was significantly longer, the number of crossing the platform was significantly reduced, and the residence time in the target quadrant was significantly shorter ( P < 0.05, P < 0.01). 2. Electron microscopy results: The ultrastructure ofNAc neurons in the control group was basically normal. In the ultrasound stimulation group, the neurons were swelling, nerve fiber dissolution and necrosis, mitochondrial vacuolation, endoplasmic reticulum dilation, and intracytoplasmic organelles were reduced or disappeared.3. Measurement results of neurotransmitters: Compared with the control group, the contents of NAc monoamine neurotransmitters NE, DA and 5-HT were significantly decreased in the ultrasonic stimulation group ( P < 0.05). Conclusion Low intensity focused ultrasound can induce inhibitory neuroregulation in mice, and cause morphological and neurobiochemical changes in NAC neurons, which may be one of the mechanisms of ultrasound neuromodulation.
2021, 42(7): 20-24.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210704
Abstract:
Objective To explore the signal pathway of vein graft failure in coronary artery bypass grafting. Methods 40 rabbits were randomly divided into two groups. Group A was sham operation group; Group B was model group in which rabbit model of CABG was established. The jugular vein in group A and the graft vein group B was removed 2 days and 2 weeks after the vein grafting, and pathological section was used to quantify lumen stenosis, immunohistochemistry was used to detect the phosphorylated p38, and the indexes were comared. Results Compared with group A, the degree of luminal stenosis of group B were significantly higher in 2 weeks after vein graft (P < 0.05). The expression of p-p38 in vein graft tissue of group B were significantly higher than group A in 2 days and 2 weeks after vein grafting, p-p38 were significantly higher 2 days than 2 weeks after vein grafting in group B (P < 0.05). Conclusion The mechanism of vein graft failure in CABG might be related to the p38 MAPK signal pathway.
2021, 42(7): 25-30.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210705
Abstract:
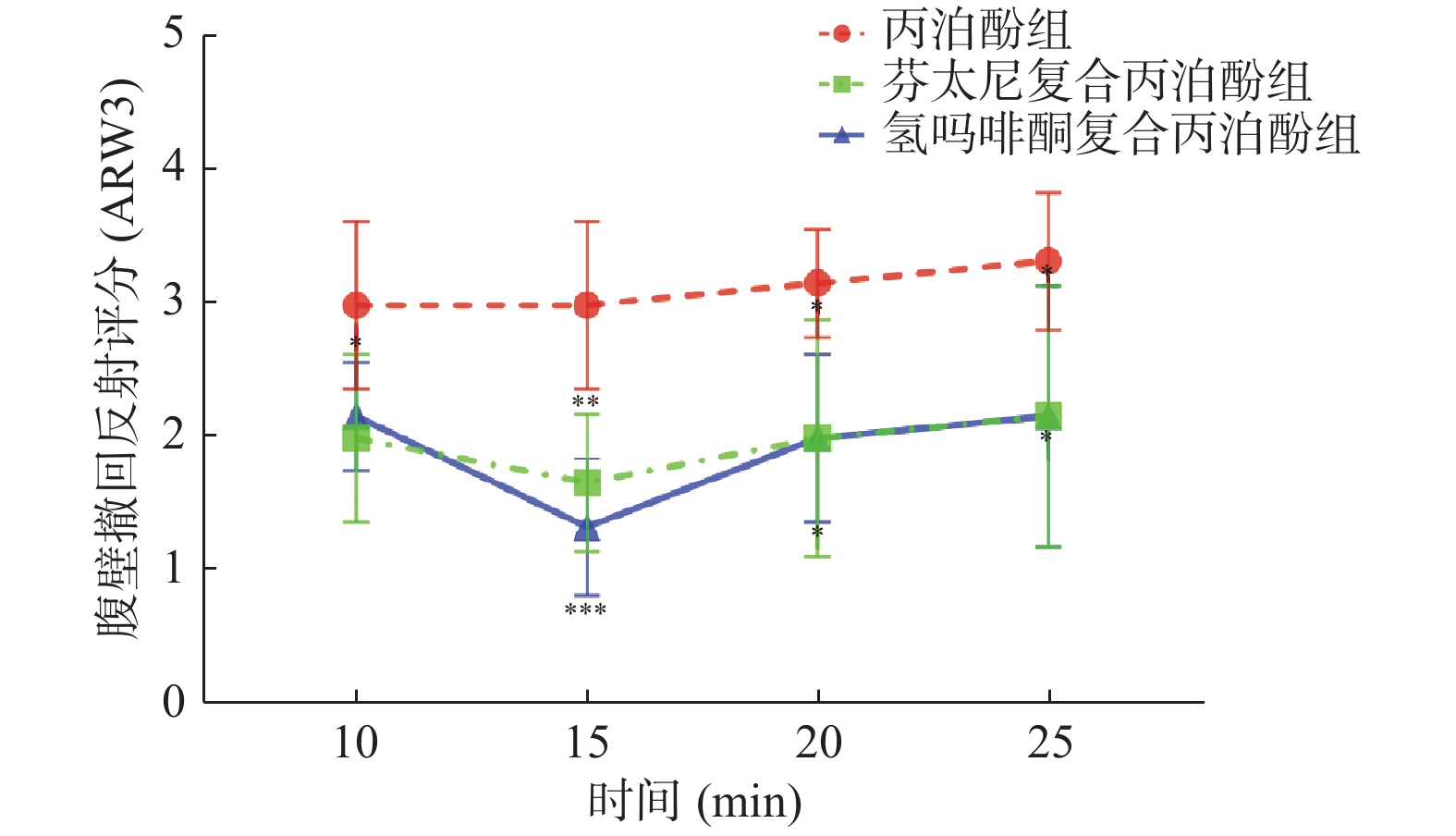
Objective To study the anesthetic effect of hydrocodone combined with propofol for painless colonoscopy and to investigate the mechanism of the analgesic effect produced by hydrocodone. Methods Clean grade male SD rats were randomly divided into four groups: normal group; propofol group; fentanyl combined with propofol group; hydromorphone combined with propofol group. After the model was anesthetized for 10 minutes, colorectal dilation was performed using a fully lubricated balloon for once per 5 min, each lasting 30 s. The abdominal wall withdrawal reflex (AWR3) scores of each group were recorded, and epinephrine and norepinephrine content were detected by ELISA. MAPK p38 expression changes were detected by western blot. Results (1) 10 minutes after abdominal administration of propofol, the AWR3 scores of the propofol group were significantly higher than those of the fentanyl combined with propofol group and the hydromorphone combined with propofol group (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001). The lowest AWR3 scores were reached 15 minutes after abdominal administration in all three groups. 20 minutes after abdominal administration, the AWR3 scores in the fentanyl combined with propofol group and the hydromorphone combined with propofol group were higher than those in the 10 and 15 minutes, but remained low. (2) The contents of epinephrine and norepinephrine in the fentanyl combined with propofol group and the hydromorphone combined with propofol group decreased significantly compared with those in the propofol group (epinephrine: P = 0.0023, P = 0.0002; norepinephrine: P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001). (3) The p-p38/p38 ratio was significantly reduced in the fentanyl combined with propofol group and the hydromorphone combined with propofol group (P < 0.0001, P < 0.0001) compared with the propofol group rats. Conclusion Hydromorphone combined with propofol can effectively inhibit the phosphorylation of p38MAPK, thereby relieving pain.
2021, 42(7): 49-56.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210708
Abstract:
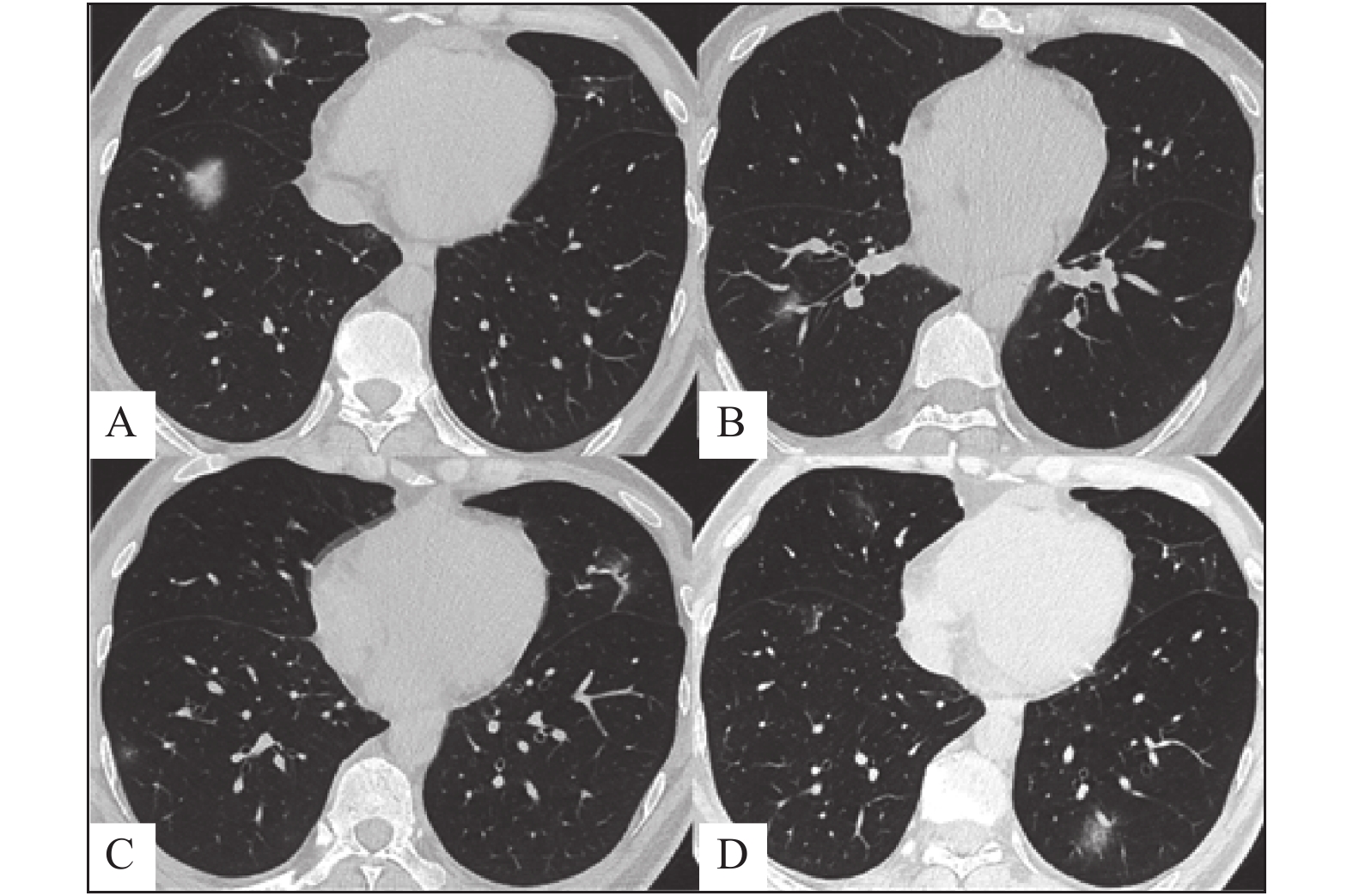
Objective To investigate the correlation between the imaging characteristics of the first diagnosis of imported novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19) and clinical severity grading. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical and imaging data of 116 imported COVID - 19 cases (aged 5 ~ 84 years, 59 males and 57 females) confirmed by nucleic acid test on January 21, 2020 (solstice, February 25, 2020) in Yunnan province.Differences in clinical data, laboratory examination and imaging characteristics of patients with different clinical types (light, normal, heavy and critical) were compared. Fisher’ s exact probability method was used for comparison of measurement data, z-test was used for comparison of ppairs, analysis of variance was used for comparison of quantitative data, and mann-whitney test was used for comparison of ppairs. Results There was no statistically significant difference in prevalence between male and female patients with 116 cases input COVID-19 (χ2 = 1.288, P = 0.808); There were statistically significant differences among different age groups (χ2 = 19.589, P = 0.006), The prevalence of 21-55 years old is high, about 44.83% (55/116), the second is 51 to 70 years old, about 36.21% (42/116), Severe pneumonia (6/42, 14.29%) was higher in patients aged from 51 to 70 than in patients aged 21 to 50 (3/52(5.17%) (P < 0.05).; Fever/chills (70.8%) and respiratory symptoms (58.4%) were the most common initial symptoms of new crown pneumonia.The average time from symptom onset to the first CT scan was 4.17±1.12 days. The longer the time, the heavier the clinical classification ( F = 2.688, P = 0.049). The differences in total number of leukocytes, total number of lymphocytes, percentage of lymphocytes, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and c-reactive protein in different clinical classifications were statistically significant (F = 3.486, 3.640, 5.154, 15.361, 8.195, all P < 0.05). The total number and percentage of lymphocytes of the severe and critical types were significantly lower than that of the light and normal types ( P < 0.05). There were 383 lesions in 116 patients, with an average score of 4.17±2.12 points in total involvement range, and the involvement range of the normal type was smaller than that of the critical type ( F = 62.137, P = 0.000). The lesions mostly involve both lungs, accounting for approximately70/116 (78.26%), The lower lobe 85/116 (37.12%) is more common than the middle lobe 70/116 (30.13%) and the upper lobe 75/116 (32.75%) (χ2 = 10.190, P = 0.021) The subpleural area87/229 (57.24%) is more common than the hilum area 29/229 (19.08%) and the middle lung zone36/229 (23.68%) (χ2 = 5.187, P = 0.018); Round and oval lesions were more common (χ2 = 43.922, P = 0.000), and banded and discoid lesions were more common in severe and critical patients (P < 0.05). Different types of patients have different pathological characteristics ( χ2 = 50.974, P = 0.000), vascular enlargement sign is the highest incidence in GGO, approximately 19.58%, next is cable strip shadow, approximately 13.71% and paving pattern, about13.61%. pure GGO, paving pattern, mixed density, air bronchogram and halo sign are more common in ordinary type (P < 0.05), GGO accompanied by thickening of bronchial wall, fiber cord, and deformation of bronchi were mostly seen in heavy and critical cases ( P < 0.05); Pleural thickening was the most common extrapulmonary lesion ( χ2 = 42.119, P = 0.000), about 73.12%, Heavy pleural effusion is more common than normal type and critical type (P < 0.05). Conclusion The clinical data, laboratory examination and imaging findings of input COVID-19 with different clinical typing have certain characteristics. HRCT can provide theoretical basis for early screening, diagnosis and clinical typing of COVID-19 with insufficient nucleic acid detection kits.
2021, 42(7): 83-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210713
Abstract:
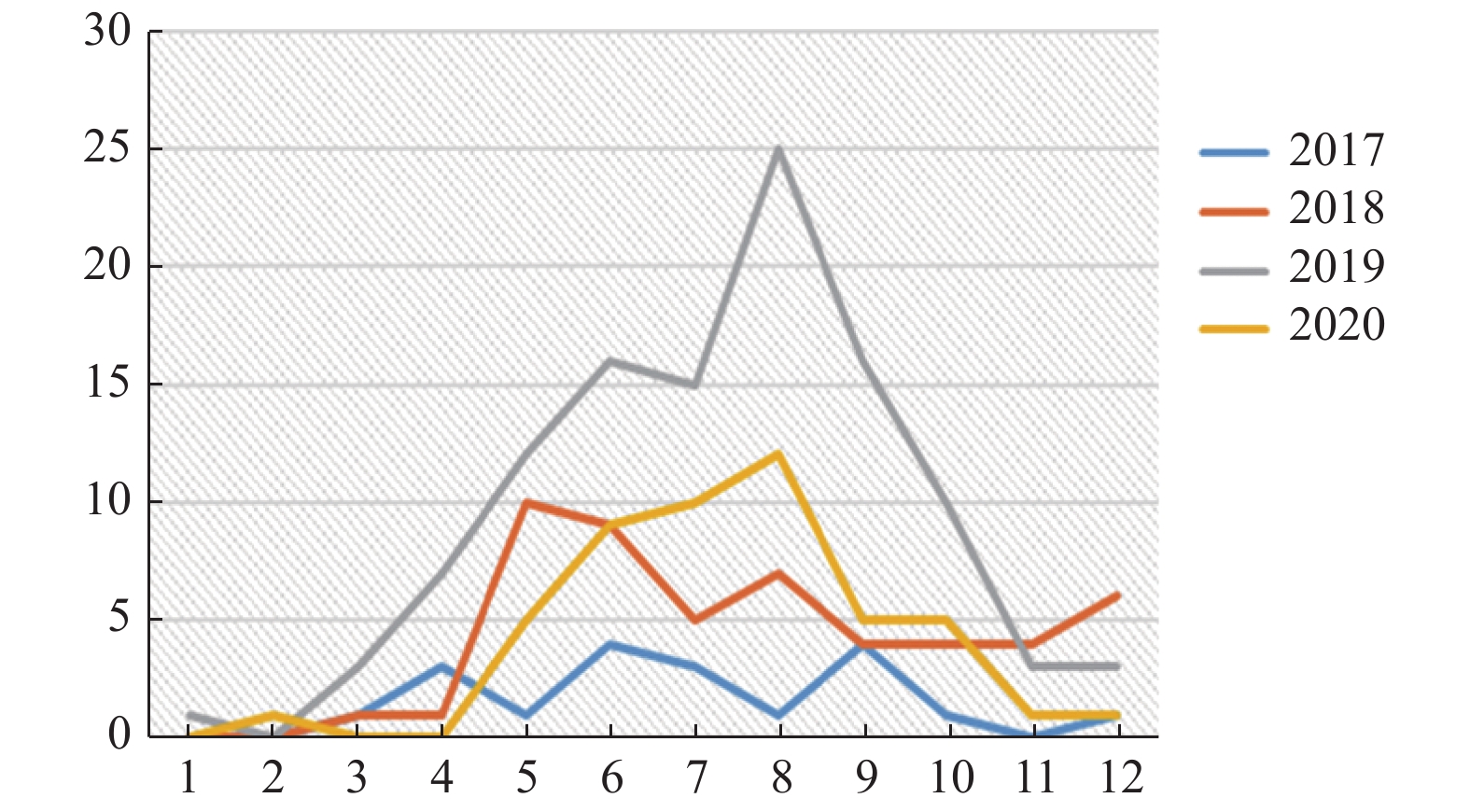
Objective To study the distribution and drug sensitivity of Salmonella and Shigella in bacterial infectious diarrhea in children in Kunming and provide reliable basis for clinical rational drug use. Methods Salmonella and Shigella were cultured from the fecal samples of children with diarrhea in Kunming children’ s Hospital from 2017 to 2020. The pathogens were identified by Vitek compact, an automatic bacterial analyzer, and their drug sensitivity was determined. The agglutination serotyping was completed. Finally, the original data were analyzed and statistically analyzed by WHONET 5.6 software. Results A total of 226 strains of Shigella and Salmonella were isolated from 29674 specimen in our hospital from 2017 to 2020, including 75 strains of Shigella (33.2%), 33 strains of Shigella flexneri (14.6%), 42 strains of Shigella sonnei (18.6%), and no Shigella dysentery and Shigella baumannii were detected. 151 strains (66.8%) of Salmonella were isolated and 5 serotypes were detected, including 106 strains (46.9%) of Salmonella typhimurium and 25 strains (11.1%) of Salmonella typhimurium. The main distribution of infectious diarrhea in Kunming children is from April to October, and the aggregation distribution is from May to October. 72.8% (110/151) of the population under 2 years old were susceptible to Salmonella infection. Diarrhea caused by Salmonella infection in children in Kunming is increasing year by year, and Salmonella typhimurium is the main Salmonella. This study showed that Shigella flexneri was the main Shigella species in 2017 and 2018, and changed to Shigella sonnei after 2019. In addition, amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (82%) was the first choice for children with infectious diarrhea caused by Salmonella in Kunming, while ceftazidime (97.6%) and amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (92.8%) were the first choice for Shigella sonnei. The sensitivity rates of Shigella flexneri to ceftazidime and cefepime were only 60% and 40%, which suggested that the susceptibility of Shigella serogroups to antibiotics is different. No imipenem resistance was found in Salmonella and Shigella. Conclusions Salmonella and Shigella are the main infectious diarrhea pathogen in children, while Salmonella shows an increasing trend year by year. The incidence of diarrhea is higher over 2 years old. Salmonella typhimurium is the main serotype. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid is the first choice for empirical use. The drug resistance of Shigella serotypes to antibiotics is different. Therefore, it is necessary to strengthen the monitoring of pathogenic bacteria and drug resistance in feces of diarrhea children, It is necessary to strengthen the surveillance of pathogens and drug resistance of stools in children with diarrhea so as to provide clinicians with targeted anti infective treatment according to the results of drug sensitivity.
2021, 42(7): 110-114.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210718
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the concentration and efficacy of rifampicin (RIF) in cerebrospinal fluid during intrathecal injection of RIF in the treatment of tuberculous meningitis. Methods Forty patients with tuberculous meningitis were randomly divided into two groups according to the admission criteria, and both groups were given HRZE regimen, A1 group was non-intrathecal injection control group, A2 group was given intrathecal injection of rifampicin 40 mg + dexamethasone 2.5 mg once a day, and the concentration of RIF in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (expressed by bCxh and cCxh) was monitored at 0 h, 4 h and 8 h, respectively. Results At the 0th hour, the value of RIF in cerebrospinal fluid in A2 group was significantly higher than that in A1 group, P < 0.01. The concentration of rifampicin in serum reached the peak at 4 h, and the concentration of rifampicin in cerebrospinal fluid was higher at 8 h (cC 8 h), 3.34 (1.03, 51.60) µg/mL, The results showed that there were significant differences in cC0 h, cC4 h and cC8 h (P < 0.01). Conclusions Intrathecal injection of RIF helps to increase the concentration of RIF in cerebrospinal fluid, and the curative effect is more significant. Intrathecal injection of Rifampin can keep the concentration of Rifampin at a high level at the 8th hour.
2021, 42(7): 31-42.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210706
Abstract:
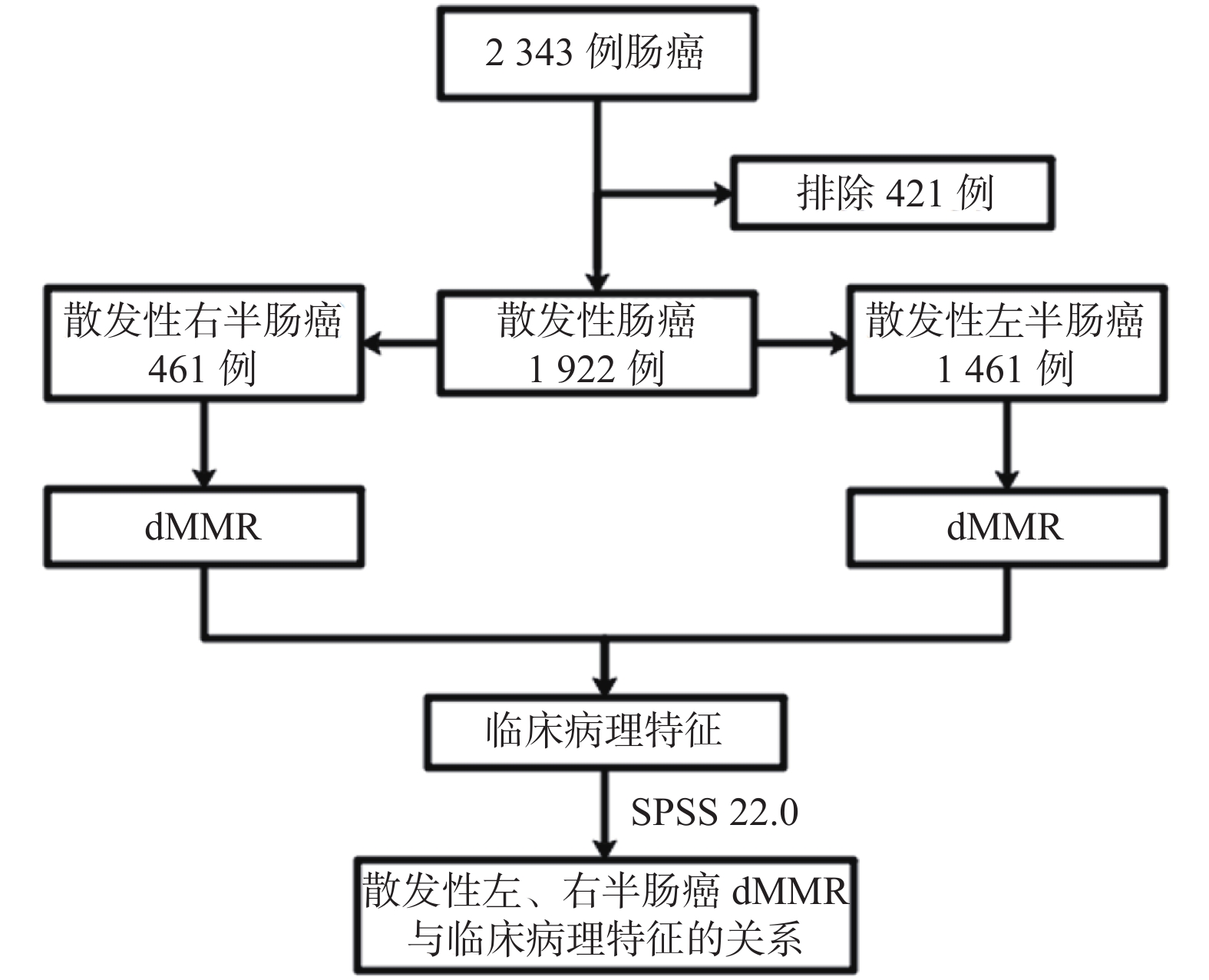
Objective To analyze the correlation between mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) and clinicopathological characteristics in left and right-side sporadic colorectal cancers. Methods The clinicopathological data of 1922 patients who were pathologically confirmed as adenocarcinoma from January 2014 to September 2019 in the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were collected, and the dMMR and gender, age, and body mass index (BMI), ethnicity, blood type, preoperative CEA level, pathological type, tumor differentiation, tumor diameter, T stage, N stage, number of lymph nodes detected, distant metastasis, UICC stage, vascular invasion, perineural invasion were analyzed in sporadic left and right colorectal cancers. Results A total of 1922 cases of sporadic colorectal cancer met the inclusion criteria. Patients with sporadic right-side colon cancer accounted for 23.99% (461/1922), and patients with sporadic left-side colorectal cancer accounted for 76.01% (1461/1 922). The dMMR rate of all patients with sporadic colorectal cancer was 23.47% (451/1922), the dMMR rate of sporadic right-side colon cancer was 38.83% (179/461), and the dMMR rate of sporadic left-side colorectal cancer was 18.62% (272/1461). Consistent with previous studies, the dMMR of all sporadic colorectal cancers in this study is more common in age < 62 years (OR = 1.551, P < 0.001), right-side colon (OR = 2.603, p < 0.001), tumor diameter≥4 cm (OR = 1.362, P = 0.009), the degree of pathological differentiation is moderate-poorly differentiated (OR = 1.538, P = 0.046), poorly differentiated (OR = 2.124, P = 0.013)and undifferentiated (OR = 1.850, P = 0.045)), UICC stages I~II (OR = 1.340, P = 0.014), and patients without perineural invasion (OR = 1.407, P = 0.004). In sporadic right colon cancer, dMMR is more common in patients younger than 62 years old (OR = 1.888, P = 0.001), pT1~T2 (OR = 3.778, P = 0.000)and tumor diameter≥4 cm (OR = 1.856, p = 0.012); in sporadic left-side colorectal cancer, dMMR is more common in age < 62 years (OR = 1.525, P = 0.002), tumor diameter ≥4 cm (OR = 1.391, P = 0.016), and no perineural invasion (OR = 1.454, P = 0.009). Conclusions Regardless of the primary site of intestinal tumors, dMMR is more common in patients younger than 62 years and tumor diameter≥4 cm, while no perineural invasion and pT1~T2 are more common in sporadic left-side and right-side colorectal cancers, respectively.
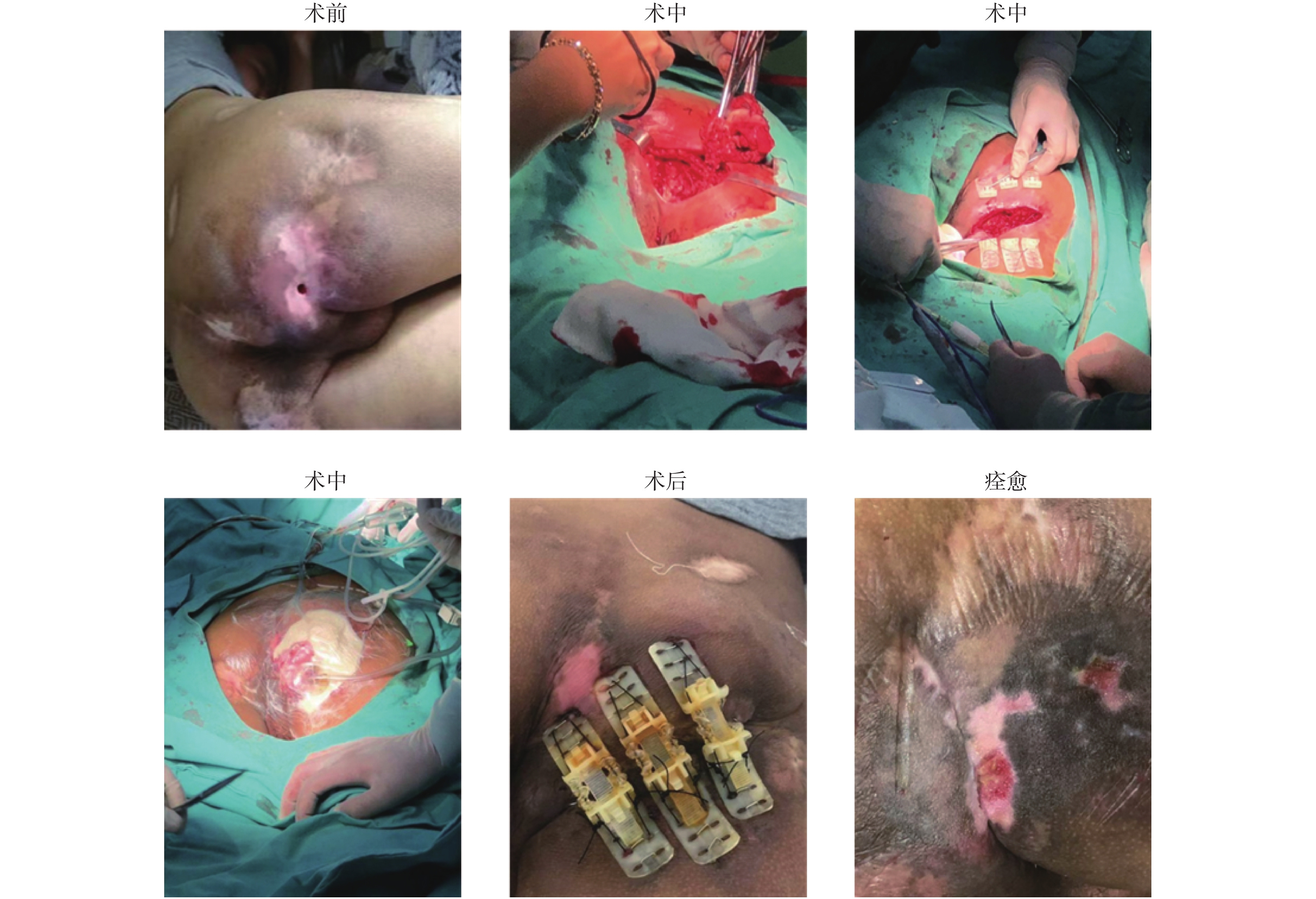
2021, 42(7): 43-48.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210707
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the clinical efficacy of Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy in the treatment of refractory wounds. Methods From August 2018 to July 2020, 36 patients with refractory wounds at different sites were selected from the Department of Gastroenterology and hernia surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University. We retrospectively analyzed the therapeutic effects of Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy. Results After 35 patients were treated with Top Closure skin traction occluder and oxygen-enriched adjustable negative pressure therapy, the wounds healed well and there was no malunion or nonunion. One patient died of severe cardiopulmonary failure after operation. Conclusion Top Closure tension-relief system combined with regulated oxygen-enriched negative pressure-assisted wound therapy in the treatment of refractory wounds is relatively simple, it can greatly reduce the difficulty of operation, and make the wound heal well after operation, so it can be used to treat refractory wounds.
2021, 42(7): 57-63.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210709
Abstract:
Objective To study the relationship between calcitonin receptor (CTR) gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes (T2DM) with osteoporosis in Kunming area, and to explore the genetic predisposing factors of T2DM with osteoporosis. Methods A total of 237 T2DM patients who were hospitalized in the Department of Endocrinology, Ganmei Hospital, the First People’ s Hospital of Kunming from June 2017 to January 2019 were collected. According to the results of bone mineral density, they were divided into T2DM without osteoporosis (group A), 61 cases, and T2DM combined with osteopenia (Group B), 111 cases, T2DM with osteoporosis group (Group C) 65 cases. By using polymerase chain reaction (PCR-RFLP) and restriction fragment length polymorphism technology, we analyzed the CTR gene polymorphism of the three groups of people, and compared the three groups of patients with gender, age, diabetes course, blood pressure, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), blood calcium, blood lipids, blood uric acid (UA), vitamins D concentration, estrogen, testosterone levels, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (Hs-CRP), fibrinogen (FIB), oral glucose tolerance (OGTT) -0 h, 2 h blood glucose, 0 h, 2 h insulin (INS) levels, insulin Resistance index(HOMA-IR)clinical indicators. We also compared the bone mineral density of different parts of the CTR genotype in 237 cases of T2DM and 65 cases of T2DM with osteoporosis, and compared the CTR genotype and the clinical indicators with statistical differences between the three groups Multivariate logistic regression analysis. Results (1) In patients with T2DM and T2DM with osteoporosis in Kunming area. The CTR genotype was mainly type CC. (2) There was no significant difference in the distribution frequency of CTR genotype between the three groups A, B and C (P > 0.05)). The distribution frequencies of CTR alleles C and T in the three groups were not statistically different (P > 0.05). (3) There was a statistically significant difference in the age, height, weight, and BMI of the three groups of patients (P < 0.05). And pairwise comparison, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.017). (4) In patients with T2DM and T2DM with osteoporosis, the difference in bone mineral density of different CTR genotypes at each site was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). (5) Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age was an independent risk factor for T2DM with osteoporosis in Kunming. Conclusions (1) In patients with T2DM and T2DM with osteoporosis in Kunming, the CTR gene distribution is mainly of type CC. (2) In patients with T2DM with normal bone mass, T2DM with osteopenia, and T2DM with osteoporosis, CTR has no significant difference in the frequency of genotype distribution and allele distribution frequency; In patients with T2DM and T2DM with osteoporosis, the bone density of different CTR genotypes did not differ at each site. The CTR genotype may have nothing with genetic susceptibility in T2DM and T2DM with bone in Kunming. (3) BMI is a protective factor for T2DM without osteoporosis in Kunming, and proper weight gain has a positive significance in preventing and treating T2DM with osteoporosis. (4) Age is an independent risk factors for T2DM with osteoporosis in Kunming.
2021, 42(7): 64-69.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210710
Abstract:
Objective To establish volume quantitative analysis and explore the value of MRI with synovial quantitative analysis for treatment evaluation of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). Methods Quantitative analysis model pretest and clinical prospective study were conducted. A total of 30 patients with JIA whom were treated regularly for 1 year were studied. The same joint was scanned before and after treatment for each patient and the corresponding for treatment synovial volume were measured by a self- designed software (The MRI software for synovial volume quantitative analysis, Kunming University of Science and Technology), as well as Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP) of studied patients were simultaneously measured. Results The volume quantitative analysis model has satisfactory results and accurate measurement. The synovial volume, ESR and CRP decreased significantly after treatment (P < 0.05). Synovial volume change is significantly correlated to those of ESR (r = 0.655) and CRP (r = 0.752). Conclusion Synovial volume quantitative analysis is an accurate measure for disease severity assessment and treatment effect evaluation.
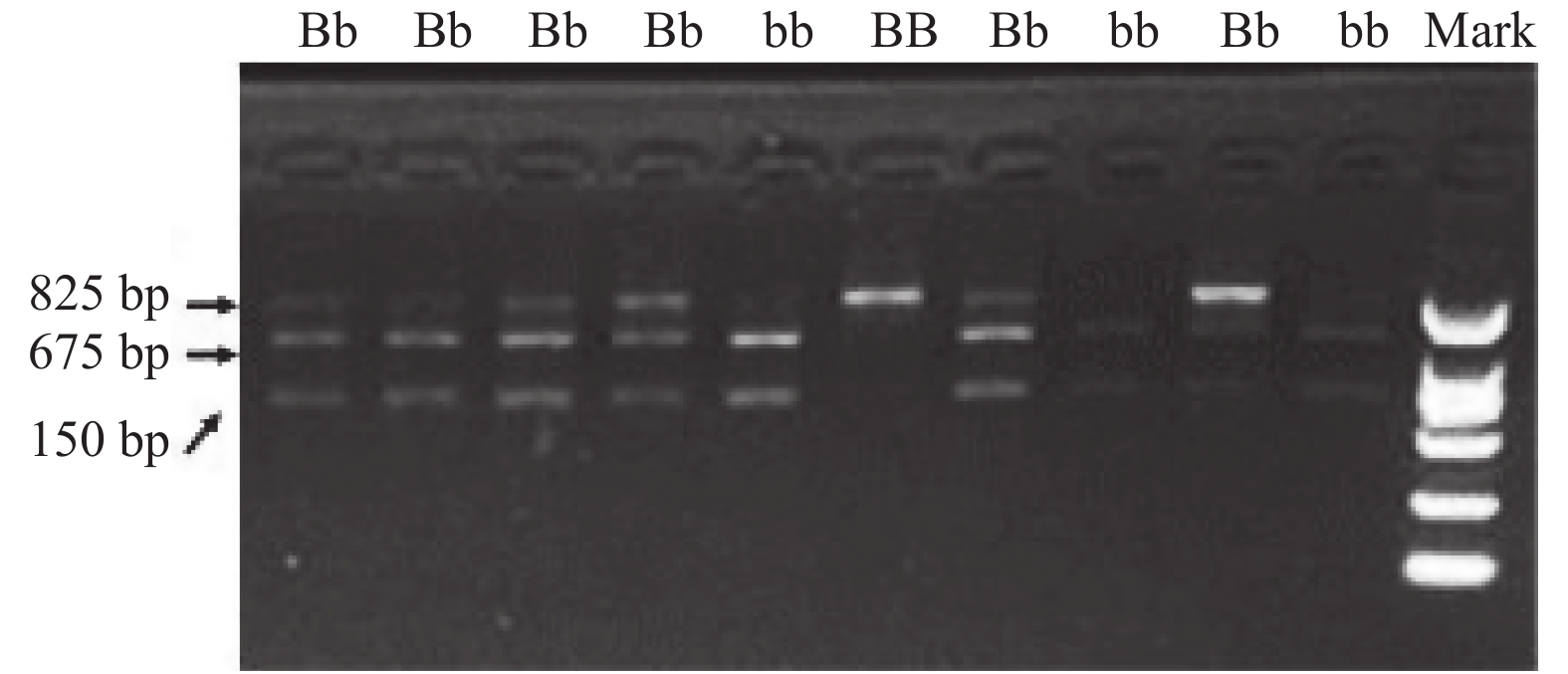
2021, 42(7): 70-76.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210711
Abstract:
Objective To study the relationship between vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) with osteoporosis in Kunming area, and to explore the genetic susceptibility factors of T2DM with osteoporosis. Methods We selected 237 diabetic patients in the department of endocrinology of First People’ s hospital of Kunming from June 2017 to January 2019. (1) The patients were divided into T2DM without osteoporosis group (61 cases), T2DM with osteopenia group (111 cases), and T2DM with osteoporosis group (65 cases) by bone mineral density results. PCR - RFLP technique was used to detect VDR genotypes, we compared the differences between the three groups of patients in following indicators: VDR genotype and allele frequency, sex, age, duration of diabetes, blood pressure, height, weight, body mass index (BMI), fasting plasma glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), blood calcium, blood lipids, blood uric acid (UA), the concentration of vitamin D, estrogen and testosterone levels, allergic C - reactive protein (Hs - CRP), fibrinogen (FIB), oral glucose tolerance (OGTT) -0 h, 2 h; 0 h, 2 h-insulin (INS) level and insulin resistance index (HOMA-IR). (2) The differences in the bone mineral density was compared between different genotypes. (3) The VDR genotypes and the indicators with statistical differences between groups were analyzed by multivariate logistic regression. Results (1) VDR genotype was given priority to with a Bb, accounting for 77.6% in patients with T2DM in kunming area. (2) VDR genotype frequency and allele frequency differences between the three groups had no statistical significance (P > 0.05). (3) There was no significant difference in BMD between the three genotypes of VDR (P > 0.05) (P > 0.05). (4) Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that age and smoking could enter the regression equation, but VDR genotype did not. Conclusions (1) The main VDR genotype of T2DM patients in Kunming was Bb (2) Age and smoking were independent risk factors of T2DM patients with osteoporosis in Kunming. VDR (BSMI) genotype was not associated with the genetic susceptibility of T2DM patients with osteoporosis in Kunming.
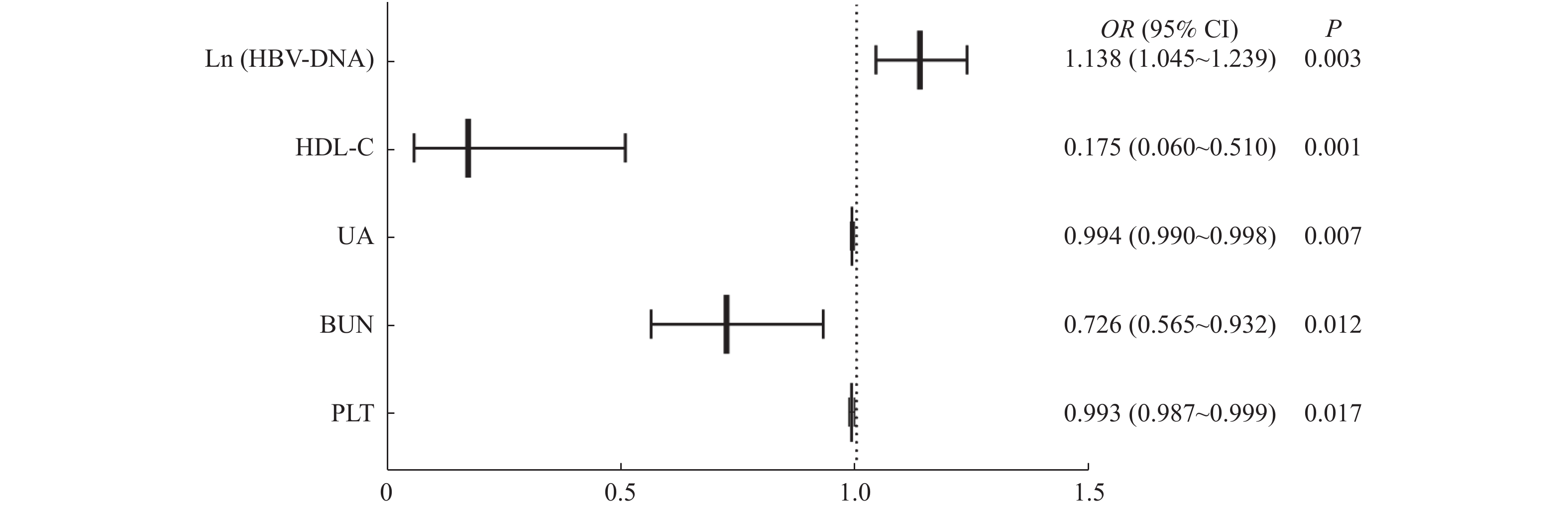
2021, 42(7): 77-82.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210712
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the influencing factors of liver injury in patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Methods The clinical data of 225 patients with CHB complicated with NAFLD admitted to the Third People’ s Hospital of Kunming from January 1st, 2020 to December 30th, 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. According to the liver function, they were divided into group A (120 cases, no liver injury or mild liver injury) and group B (105 cases, moderate or severe liver injury). The basic information, metabolism biomarkers, routine blood, renal functions and etiology markers of hepatitis B were used to perform an unifactor analysis. To explore the influencing factors of moderate or severe liver injury, binary logistic regression analysis were further performed. Results 1. There were significant differences in gender[group A vs. group B (the same as following): proportion of males = 76.67% vs. 87.62%], HBeAg (+/-) [(HBeAg positive) = 49.17% vs. 53.91%], CHOL[(4.89±0.95) mmol/L vs.(4.23±1.17) mmol/L], HDL-C[1.10 (0.94~1.28) mmol/L vs. 0.90 (0.53~1.18) mmol/L], LDL-C[3.03 (2.52~3.60)mmol/L vs. 2.70 (2.05~3.19) mmol/L], PLT[(202.47±60.79)*109/L vs.(173.37±60.89)*109/L], BUN[4.51 (3.83~5.41) mmol/L vs. 3.92 (3.37~5.02) mmol/L], UA[369.00 (314.00~421.00) μmol/L vs. 338.50 (292.00~397.25) μmol/L], Ln (HBV-DNA) [12.79 (7.82~17.31) IU/mL vs. 15.44 (12.64~17.76) IU/mL] between two groups (P < 0.05). 2. Binary Logisitic regression analysis showed that PLT[OR (95%CI) = 0.993 (0.987~0.999)], BUN[OR (95%CI) = 0.726 (0.565~0.932)], UA[OR (95%CI) = 0.994 (0.990~0.998)], HDL-C[OR (95%CI) = 0.175 (0.060~0.510)] were protective factors, with 1 unit decrease of which, the probability of moderate and severe liver injury increased by 0.7%, 27.4%, 0.6% and 82.5%, respectively; ; and HBV-DNA [OR (95%CI)=1.138 (1.045~1.239)] was a risk factor, the probability of moderate to severe liver damage increased by 13.8% with 1 unit increase of Ln (HBV-DNA). Conclusion HBV-DNA, HDL-C, BUN, UA and PLT are influencing factors for moderate or severe liver injury in CHB patients with NAFLD and a higher attention should to be paid.
2021, 42(7): 88-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210714
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between 25 (OH) D level and the occurrence of DPN. Methods A total of 138 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were selected as the study subjects. According to the clinical symptoms and neurogram results, there were 47 patients in the SDM group. And 91 patients in the DPN group were divided into 54 patients in the non-clinical group (DPN1 group) and 37 patients in the clinically symptomatic group (DPN2 group). The gender, age, treatment season, diabetes mellitus (DM) course, smoking history, SBP, DBP, BMI, 25 (OH) D, Ca, P, FPG, 2 hPG, HbA1c, FC, TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C and other indicators of all patients were collected. The group differences of the above indicators were compared, and the correlation between serum 25 (OH) D and the above indicators was analyzed. The occurrence risk factors of DPN were analyzed by binary Logistic regression. Results (1) The median serum 25 (OH) D in hospitalized T2DM patients was 16.25 (12.88, 19.90) ng/ml, and 97.10% of the patients were deficient (76.09%) and inadequate (21.01%) in 25 (OH) D. The proportion of serum 25 (OH) D deficiency in SDM group, DPN1 group and DPN2 group was 68.09%, 77.78% and 83.78%, 25 (OH) D inadequacy was 25.53%, 20.37% and 16.22%, and 25 (OH) D adequacy was 6.38%, 1.85%, and 0.00%, respectively. The difference between the groups was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). (2) Binary Logistic regression analysis showed that 25 (OH) D was a protective factor in the occurrence of DPN (OR = 0.238, 95%CI 0.074-0.764, P < 0.05). Conclusions (1) 25 (OH) D deficiency and inadequacy are common in hospitalized T2DM patients. (2) Serum 25 (OH) D may be a protective factor for the occurrence of DPN.
2021, 42(7): 94-97.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210715
Abstract:
Objective To compare the therapeutic effect and prognosis of Femostong and Honglilai combined with Duphaton in patients with intrauterine adhesions. Methods A total of 70 patients with intrauterine adhesions admitted to the first Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University from June 2019 to June 2020 were studied. Group A was given Femostong and group B was given Honglilai combined with Duphaton. After treatment, the menstrual improvement, uterine recovery, pregnancy rate and adverse reaction rate of the two groups were compared. Results Compared with preoperation, both groups A and B could effectively improve the menstrual improvement and uterine cavity recovery. Among them, group B achieved more significant results in restoring menstrual volume than group A (P < 0.05). There was no difference in the incidence of adverse reactions and pregnancy rate between the two groups (P > 0.05). Conclusion Honglilai combined with Duphaton can improve the prognosis of patients with intrauterine adhesion more effectively, and the safety is higher, which is worthy of clinical application.
2021, 42(7): 98-103.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210716
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of folic acid combined with alendronate sodium on bone metabolism, CCL4 and fibroblast growth factor levels in postmenopausal osteoporosis patients. Methods A total of 154 postmenopausal osteoporosis patients admitted to our hospital from January 2017 to January 2019 were selected as the research objects and randomly divided into observation group (77 cases) and control group (77 cases). The control group was given calcium combined with alendronate sodium treatment, and the observation group added oral folic acid tablets to the control group. The two groups of patients were treated continuously for 6 months. The total effective rate and fracture rate of the two groups were compared. The bone mineral density, 25-OHD, CTX, BALP, BGP, CCL4, FGF-21, FGF-23, VAS pain score and SF-36 quality of life score were compared between the two groups before and after treatment. Results The total effective rate and fracture rate in the observation group were 89.61% and 1.30%, respectively, and in the control group were 67.54% and 5.19%. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Before the treatment, there was no statistical difference between the two groups of L1-4, femoral neck, femoral tuberosity bone mineral density, 25-OHD, CTX, BALP, BGP, CCL4, FGF-21, FGF-23 levels, and VAS and SF-36 scores. (P > 0.05). After the treatment, the two groups of L1-4, femoral neck, femoral tuberosity bone mineral density, 25-OHD levels and SF-36 score increased, while CTX, BALP, BGP, CCL4, FGF-21, FGF-23 levels and VAS score decreased (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the observation group had higher L1-4, femoral neck, femoral tuberosity bone mineral density, 25-OHD level and SF-36 score, while CTX, BALP, BGP, CCL4, FGF-21, FGF-23 level and VAS score were lower (P < 0.05). Conclusion Folic acid combined with alendronate sodium has a significant clinical effect in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis patients, and can improve the bone mineral density, bone metabolism, CCL4 and fibroblast growth factor levels.
2021, 42(7): 104-109.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210717
Abstract:
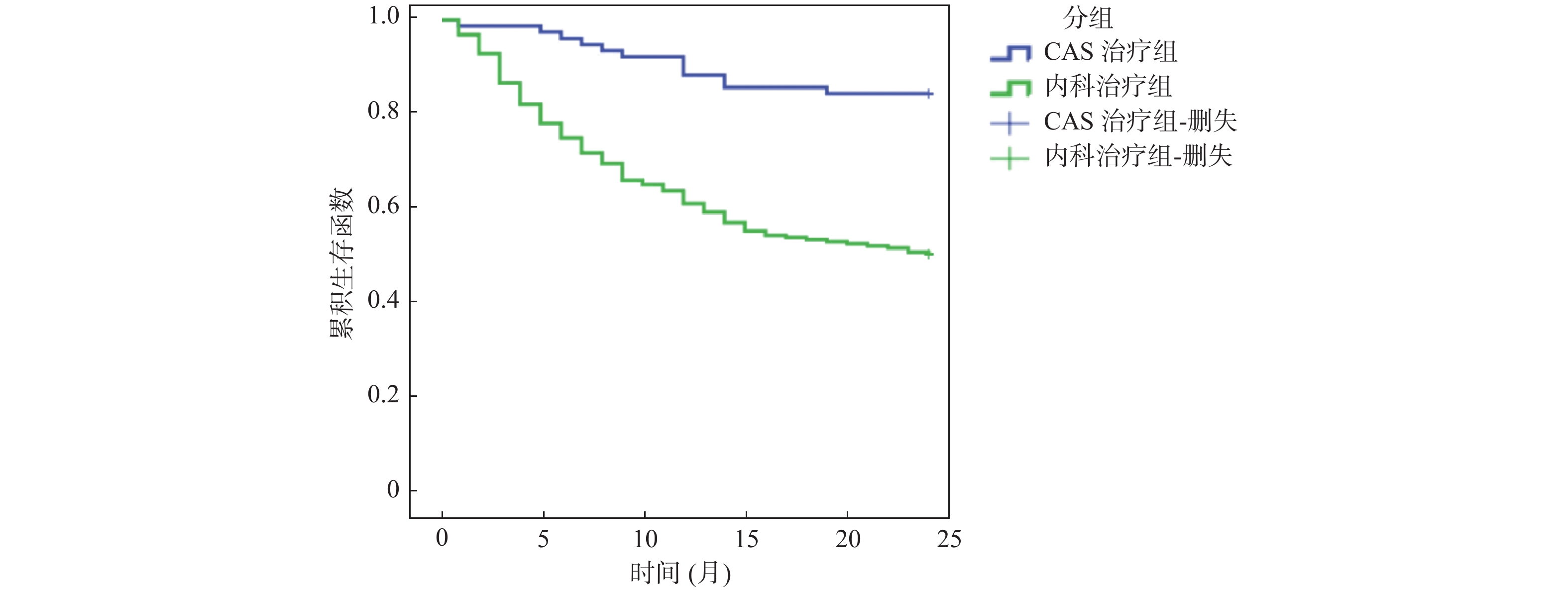
Objective To study the related influencing factors of adverse events of symptomatic carotid stenosis, and to explore the effect of stenting on adverse events of symptomatic carotid stenosis and the value of event-related evoked potentials in the diagnosis of adverse events. Methods 302 patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis in our hospital were divided into normal group and adverse event group according to the adverse events. The age, gender, hemoglobin, platelet count, blood glucose, total cholesterol, TG, treatment, event-related potentials and the degree of carotid artery stenosis were collected and analyzed statistically. Results Carotid balloon dilatation and stenting were protective factors for adverse events of symptomatic carotid stenosis. Event-related evoked potentials, degree of carotid stenosis and total cholesterol were risk factors for adverse events of symptomatic carotid stenosis. The sensitivity and specificity of event-related evoked potentials in the diagnosis of symptomatic carotid stenosis were 0.70 and 0.78, respectively. Carotid balloon dilatation and stenting are superior to medical treatment in reducing the incidence of adverse events. Conclusions Carotid balloon dilatation and stenting can reduce the occurrence of adverse events of symptomatic carotid stenosis. Event-related evoked potentials have certain guiding significance in judging the prognosis of symptomatic carotid stenosis.
2021, 42(7): 115-120.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210719
Abstract:
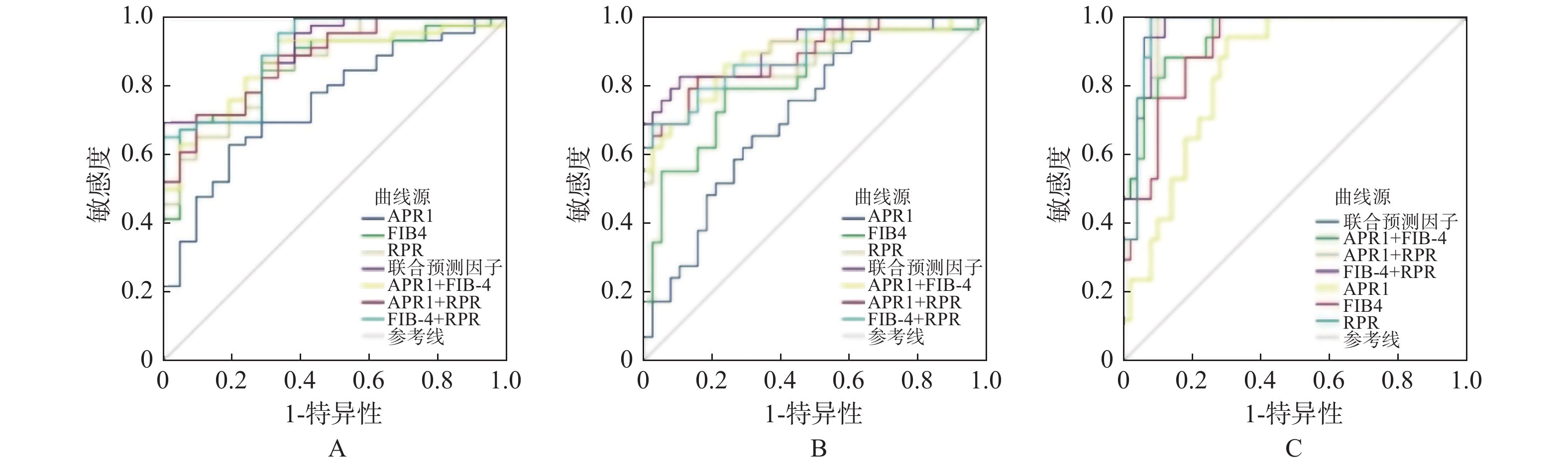
Objective To investigate the diagnostic value of APRI, FIB-4, Forns, GPR, S-index, King, RPR non-invasive models in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic liver disease. Methods The clinical data of 67 patients with chronic liver disease who received liver biopsy in Ganmei Hospital Affiliated to Kunming Medical University from January 2016 to December 2020 were retrospectively collected. The scores of different models were calculated and compared with the pathological stages of liver biopsy for statistical analysis. Results Among the 7 non-invasive models, the correlation between GPR and liver fibrosis stage was the weakest (r = 0.259), while RPR was the strongest (r = 0.769). The value of RPR in the diagnosis of liver fibrosis was the highest, and the AUROC of significant liver fibrosis (≥S2), advanced liver fibrosis (≥S3) and cirrhosis (S4) were 0.866, 0.883 and 0.967, respectively. The combined predictor RPR + FIB-4 + APRI was established to improve the ability to diagnose significant liver fibrosis, advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis (Auroc = 0.896, 0.919, 0.973). Conclusion The diagnostic performance of RPP is the best among the seven non-invasive models, and the combined diagnosis of non-invasive model can improve the accuracy of the diagnosis of liver fibrosis.
2021, 42(7): 121-125.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210720
Abstract:
Objective To study the effects of different doses of Ulinastatin on postoperative cognitive function and HMBG1 in elderly patients. Methods From May 2020 to September 2020, 60 elderly patients older than 60 years of age were selected for elective surgery in our hospital, 36 males and 24 females, aged 60-84 years, weight 46-74 kg, ASA classification Ⅰ -Level Ⅲ. According to the random number table method, they were randomly divided into experimental group (group U1, 2, 3) and control group (group C), 15 cases in each group. The experimental group was intravenously infused with ulinastatin 5,000 U/kg, 10,000 U/kg, 15,000 U/kg before anesthesia induction, and the control group was given the same dose of normal saline intravenously. We recorded the patient’ s age, education, length of stay, postoperative VAS score and other general information, and collected the patient’ s venous blood 5 minutes after entering the room (T1), 5 minutes before leaving the PACU (T2), 1 day (T3) and 3 days (T4) after the operation. The double antibody sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to monitor the concentration of HMGB1 in patients; the simple intelligent state check scale method was used to evaluate patients before operation (T1), postoperative 1 (T2), 3 (T3), 5 (T4), 7 (T5)Day cognitive function status. Results The concentration of HMGB1 in each group of patients was increased at T2, T3, and T4 as compared to T1 (P < 0.05), but T4 was slightly lower than T3 (P < 0.05). At the end of the operation, the HMGB1 in the 15,000 U/kg UTI group did not rise significantly as compared to the blank group (P < 0.05). On the first day after the operation, the HMGB1 concentration in the 10,000 U/kg and 15,000 U/kg dose groups was obvious lower than the control group (P < 0.05). There was no statistical difference in the basic MMSE value of patients in each group. The MMSE scores of the different doses of UTI group showed a downward trend at 1 and 3 days after surgery (P < 0.05), and there was a statistically significant difference between 5 and 7 days after surgery and 1 day after surgery (P < 0.05). On day 1 and day 3, the MMSE score of the control group was significantly lower than that of the 15,000 U/kg Ulinastatin group (P < 0.05). Conclusion 15,000 U/kg Ulinastatin can reduce the incidence of POCD in elderly patients undergoing elective laparoscopic surgery under general anesthesia, and its mechanism may be related to the reduction of HMGB1 in circulating blood.
2021, 42(7): 161-165.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210727
Abstract:
Objective To study the effect of modified position pad on reducing the occurrence of stress injury in prone position of neurosurgery. Methods From September 2017 to March 2019, 58 patients diagnosed as posterior fossa tumor in the first Department of Neurosurgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University were selected as the research objects. According to the exclusion criteria, 14 patients who did not meet the research principles were excluded, and 44 patients were included as the research objects. From September 2017 to June 2018, 21 patients with posterior fossa tumor resection in prone position were selected as the control group. They were treated in traditional prone position, and their heads were fixed with three nails. From June 2018 to March 2019, 23 patients with posterior fossa tumor resection who were operated in prone position were selected as the experimental group. On the basis of the control group, the experimental group used the improved body position pad to turn over in prone position. The number of cases, the incidence, the number of parts (the number of patients with PI) and the degree of stress injury were compared between the two groups. Results In the observation group, there were 9 cases of PI, the incidence rate was 42.85%, and the number of occurrence parts was 54, of which 18 cases were concentrated in the anterior chest wall area, and 1 case was > NPUAP stage I; in the experimental group, there were 2 cases of PI, the incidence rate was 8.69%, the occurrence site was 11, and 0 case was > NPUAP stage Ⅰ. Conclusion The improved body position pad uses a silk like synthetic fabric technology to significantly reduce the incidence of pressure injury, which is worthy of clinical application.
2021, 42(7): 166-169.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210728
Abstract:
Objective To explore the effect of standardized nutrition management on the quality of life of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma after radiotherapy. Methods 160 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma who received radiotherapy in a 3A tumor hospital were randomly divided into control group and observation group, 80 cases in each group. The control group received routine nursing, while the observation group received standardized nutrition management on the basis of routine nursing. Hb, PA, ALB and quality of life were compared between the two groups (FACT-H & N Scale). Results The nutritional index of the observation group was higher than that of the control group after standardized nutrition management, and the study was statistically significant (P < 0.05); The total score of the patients in the observation group was higher than that of the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Standardized nutrition management can effectively maintain the normal nutritional indicators and improve the quality of life of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma during radiotherapy.
2021, 42(7): 170-175.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210729
Abstract:
Objective To understand the influence of perioperative comprehensive structural nutrition intervention for cochlear implant patients on the complications, medical costs and satisfaction of cochlear implant patients, so as to provide reference for exploring the management mode of cochlear implant patients. Methods Self-assessment questionnaires were used to investigate the subjects from January1 2018 to November 30 2020. The comprehensive structural nutrition intervention mode was used in the intervention group, and the traditional conventional mode was used in the control group. The information such as auditory behavior classification, speech intelligibility classification, complications, medical expenses and satisfaction degree of the patients under the unmanaged mode from January 1 2018 to November 30 2020. Results The difference between the intervention group and the control group was not statistically significant in the auditory behavior grading and speech intelligibility grading at admission, 3 months and 6 months after operation (P > 0.05). There was statistically significant differences in the complications (χ2 = 4.406, P = 0.036), medical expenses (t = -17.131, P < 0.001), satisfaction score (t = 3.489, P = 0.007) between the intervention group and the control group. The multivariate analysis showed that patients with comprehensive nutrition intervention, increased body mass index, and improved satisfaction were less likely to have postoperative complications. Conclusions Comprehensive intervention of structural nutrition can effectively improve the clinical outcome of cochlear implant patients, reduce medical costs of the patients, and improve the satisfaction on the patients family members. Therefore, it is necessary to implement the comprehensive intervention management model of structural nutrition in cochlear implant patients.
2021, 42(7): 176-180.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210730
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effect of multiple preoperative visiting patterns on psychological stress in patients with cardiac valve replacement. Methods A total of 100 patients with simple valve replacement admitted to our department from May 2019 to April 2020 were selected. The control group of 50 cases received the traditional routine preoperative vising, the intervention group of 50 patients were treated with multiple preoperative visiting. Plasma corticotrophin (ACTH) and cortisol (Cor) concentrations were compared between the two groups one day before surgery, before anesthesia-induction after visiting, the heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP) and anxiety (SAS) and depression (SDS) self-rating scales were also monitored. Results There were no significant changes in HR MAP and SDS in the two groups before and after visiting. The values of ACTH, Cor and SAS in the intervention group were significantly lower after visiting than before (P < 0.05). And the values of the above three indexes after visiting in the intervention group were lower than the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion Diversified preoperative visiting mode can improve patients’ awareness of preoperative knowledge of the disease, relieve patients’ bad emotions, effectively reduce psychological stress response, thus make patients actively cooperate with surgical treatment and nursing, improve patient satisfaction and the quality of nursing.
2021, 42(7): 126-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210721
Abstract:
Objective To understand the treatment status and effect of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis in Kunming city in 2019. The proportion of the 28-day course completed and the influencing factors. It provides a reference for the wide application of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis. Methods Descriptive analysis was carried out on the data of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis in kunming city in 2019. Logistic analysis of factors affecting the completion of 28 days of treatment. Results The average age of 872 patients of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis was 32 (26, 36) years. Men accounted for 81.99%. Only 10.09% of people identified the infection source person with HIV. The proportion of patients with treatment FTC + DTG/RAL was 78.56%. The proportion of patients within 2 h was 2.87%, the proportion of patients within 2 h to 24 h was 63.88%. 78.56% completed the 28-day course. Unemployed, inactive and student patients were less likely to complete the 28-day course (OR = 1.668, P = 0.012); It is clear that patients who knew the infection source person with HIV infection are more likely to complete a 28-day course of treatment (OR = 0.166, P < 0.001). Only one of the 544 people who had test results or called then tested positive for HIV. Conclusion HIV post-exposure prophylaxis treatment is predominantly male, most do not know if the infection source person with HIV. Increasing economic income and identifying infection status are beneficial to increasing drug completion rate. At the same time, publicity and education should be strenghened to improve the timeliness and effectiveness of medical treatment.
2021, 42(7): 130-136.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210722
Abstract:
Objective To observe the efficacy and safety of SofosbuvirVelpatasvir in the treatment to chronic hepatitis C combining with HCV/HIV. Methods 419 patients with chronic hepatitis C and 56 patients with HCV/HIV that were admitted to Kunming Third People’ s Hospital were selected for this study. All kind of indicators such as virological response (SVR), biochemical responses, and liver Fibrosis have been continuously monitored during the treatment of 4 weeks, 12 weeks, as well as additional 12th week follow-up after treatment termination. Results After 12-week treatment the genotype 1 patient solely with HCV has SVR12 of 97.56%; the genotype 2 patient has SVR12 of 98.97%; the genotype 3 patients has SVR12 of 97.54% while the genotype 6 has SVR12 of 97.85%, P = 0.870. In contrast, the patients with HCV/HIV co-infection were treated with SofosbuvirVelpatasvir besides their HIV treatment. After 12 weeks of the treatment, the genotype 1 patient showed SVR12 of 85.71%; the genotype 3 showed SVR12 of 92.11%; the genotype 6 shows SVR12 of 90.91%, P = 0.862. Also, after antiretroviral therapy both patients show the significant improvement in the biochemical indictors, AST, ALT and ALB as well as the renal function. The hepatic fibrosis index from both decreases significantly after the treatment. For the adverse reactions, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and fatigue were found in GT3 genotype patients, while fatigue and headache were the most common in other genotypes patients and HCV/HIV co-infected patients. Conclusion Sofosbuvir and Vipatavir have high efficacy and good safety in the treatment to the patient with chronic hepatitis C and HCV/HIV co-infection.
2021, 42(7): 137-142.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210723
Abstract:
GPR88 is an orphan receptor of the Class A rhodopsin family, belonging to the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) family. Existing studies have shown that it is involved in the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, and at the same time as a potential therapeutic target has aroused widespread interest of researchers. This article reviews the recent research progress of GPR88 receptors in hypertension, alcohol use disorder, anxiety, schizophrenia, movement disorders and other related diseases and agonists, and aims to provide a deeper level of research on GPR88protein Theoretical basis.
GPR88 is an orphan receptor of the Class A rhodopsin family, belonging to the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) family. Existing studies have shown that it is involved in the occurrence and development of a variety of diseases, and at the same time as a potential therapeutic target has aroused widespread interest of researchers. This article reviews the recent research progress of GPR88 receptors in hypertension, alcohol use disorder, anxiety, schizophrenia, movement disorders and other related diseases and agonists, and aims to provide a deeper level of research on GPR88protein Theoretical basis.
2021, 42(7): 143-149.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210724
Abstract:
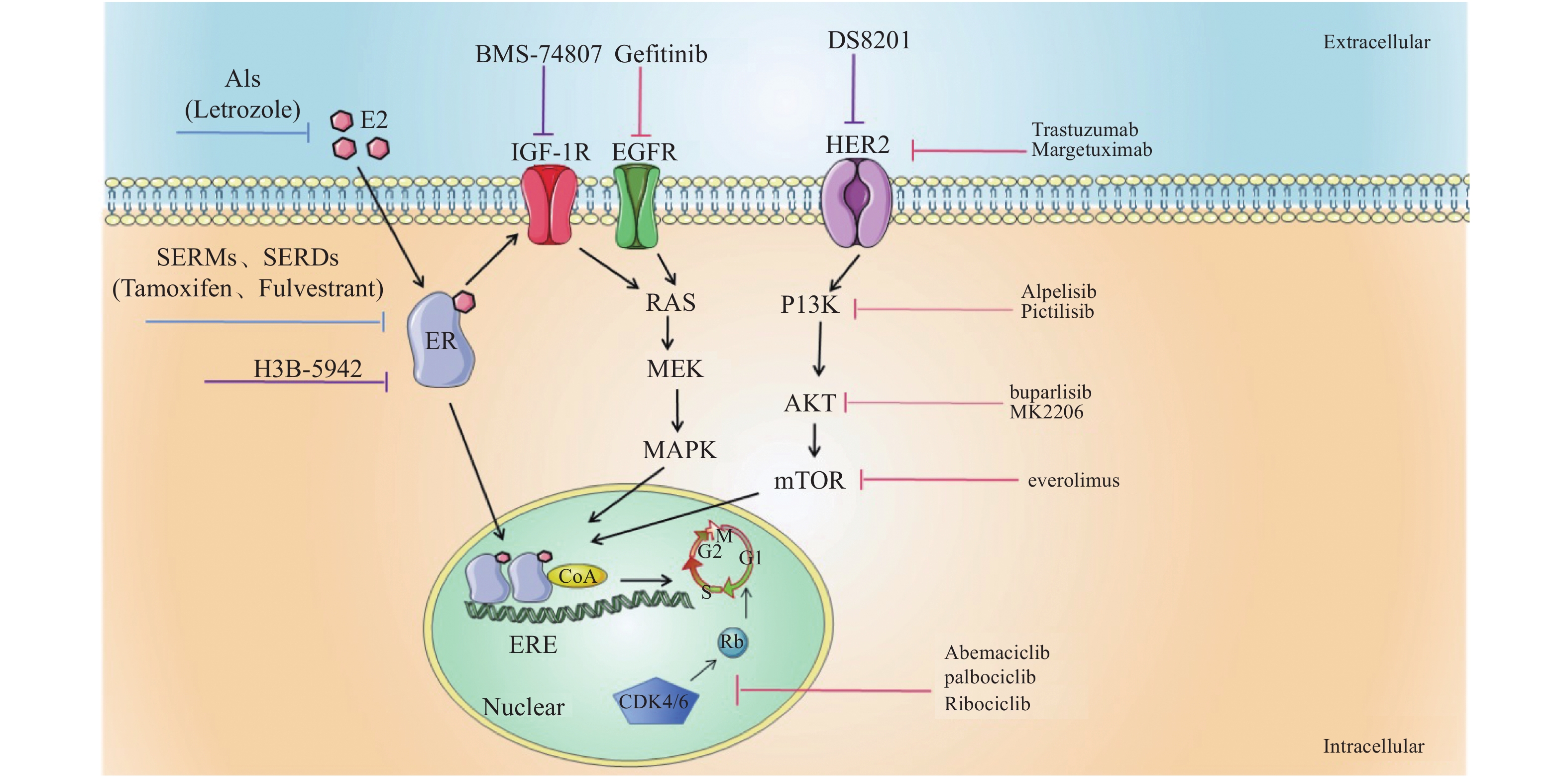
In the initial stage of clinical treatment of hormone receptor positive HR + breast cancer, good prognosis is often achieved by endocrine therapy. Once recurrence and metastasis occur, the overall prognosis is not ideal. Therefore, the efficacy of endocrine therapy is limited by the emergence of drug resistance these years. The reversal of endocrine resistance is considered to be a new method and hope for early hormone receptor positive breast cancer to return to chronic disease treatment. The strategy of delaying and reversing endocrine drug resistance has been paid close attention by clinical and scientific research work. This article will review the research progress and strategies of delaying and reversing endocrine therapy.
In the initial stage of clinical treatment of hormone receptor positive HR + breast cancer, good prognosis is often achieved by endocrine therapy. Once recurrence and metastasis occur, the overall prognosis is not ideal. Therefore, the efficacy of endocrine therapy is limited by the emergence of drug resistance these years. The reversal of endocrine resistance is considered to be a new method and hope for early hormone receptor positive breast cancer to return to chronic disease treatment. The strategy of delaying and reversing endocrine drug resistance has been paid close attention by clinical and scientific research work. This article will review the research progress and strategies of delaying and reversing endocrine therapy.
2021, 42(7): 150-156.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210725
Abstract:
Dental plaque is the main factor leading to a variety of oral diseases. In oral diseases, periodontal disease, and pulp tissue, we can find plaque structures composed of a variety of bacteria. These plaque structures are extremely complex, with rich differences and a high degree of bacterial density, and we call them plaque biofilms. The bacteria in the plaque biofilm, like other organisms, can sense the living environment and interact with other bacteria, thereby improving the adaptability and virulence to the microenvironment. Bacterial interactions include: physical and nutritional synergies, inhibition of resistance, intercellular communication, and gene transfer. Here are the latest advances in bacterial interactions during caries.
Dental plaque is the main factor leading to a variety of oral diseases. In oral diseases, periodontal disease, and pulp tissue, we can find plaque structures composed of a variety of bacteria. These plaque structures are extremely complex, with rich differences and a high degree of bacterial density, and we call them plaque biofilms. The bacteria in the plaque biofilm, like other organisms, can sense the living environment and interact with other bacteria, thereby improving the adaptability and virulence to the microenvironment. Bacterial interactions include: physical and nutritional synergies, inhibition of resistance, intercellular communication, and gene transfer. Here are the latest advances in bacterial interactions during caries.
2021, 42(7): 157-160.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20210726
Abstract:
Objective To explore the application effects of team-based learning (TBL) and workshop teaching models (Workshop) in speech therapy teaching courses. Methods Sixty students in the same class of 2017 Rehabilitation Therapy in Dali University were divided into 3 groups. Three methods of conventional teaching, TBL teaching and Workshop teaching were carried out respectively in the 3 groups, and an average of 20 male and female students were randomly selected in each group. Results The students in the study group were intervened by TBL and Workshop teaching methods, and the evaluations of students’ theoretical knowledge and classroom satisfaction survey were higher than those of the control group, with significant differences within the group (P < 0.05). Conclusions The workshop and TBL teaching methods in the teaching of speech therapy courses are helpful to improve students’ theoretical academic performance. At the same time, the new teaching methods are more easily accepted by students, which can provide references for future exploration of new teaching models of speech therapy.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS