2023 Vol. 44, No. 7
2023, 44(7): 1-8.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230723
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of Euonymine on isolated cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), so as to elucidate the possible mechanism of Euonymine in prevention and treatment of ISR. Methods The effect of trypan blue assay on the viability of HUVECs. MTT assay was used to observe the effect of Euonymine on the proliferation of normal HUVECs and VSMCs. A wound healing assay was performed to detect the effect of Euonymine on the migration of VSMCs. Results The MTT results showed that the absorbance of HUVECs and VSMCs decreased after the Euonymine intervention. In addition, the IC50 of Euonymine on HUVECs after 24 hours and on VSMCs after 48 hours were 28.6 µg/mL and 33.92 µg/mL, respectively. Flow cytometry results showed that Euonymine (25 μg/mL) arrested the cell cycle of both HUVECs and VSMCs at the G0/G1 phase, while Euonymine (100 μg/mL) blocked the mitosis of VSMCs at both the G0/G1 and G2/M phases. Conclusion Euonymine affects the cell cycle mainly by inhibiting the proliferation and migration of VSMCs and has potential value of clinical applications in inhibiting neointima hyperplasia after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
2023, 44(7): 9-15.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230710
Abstract:
Objective To evaluate the clinical application value of nanopore sequencing in tumor patients with concurrent infectious diseases and to provide a new detection method for rapid and sensitive diagnosis of infectious diseases in tumor patients. Methods Samples of inpatients with suspected infections from July to August 2022 at Yunnan Cancer Hospital were collected, and pathogenic microorganisms in the samples were identified using nanopore sequencing. Results Forty-six samples from 36 patients with suspected infection were collected. Nanopore sequencing detected 72.22% of bacteria, 31.48% of fungi, and 42.59% of viruses. Both bacterial and fungal detection rates were significantly higher (χ2 = 23.19 , P < 0.0001; χ2 = 13.14 , P = 0.0003) than the results by microbiological culture method (23.91% and 10.87%). The nanopore sequencing results showed significantly more bacterial and fungal species detected compared to microbial culture results. Conclusions Nanopore sequencing for the identification of pathogenic microorganisms has the advantages of high detection rate, wide detection of pathogenic genera, and rapid diagnosis. It has potential clinical application in the diagnosis of tumor-associated infectious diseases.
2023, 44(7): 16-21.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230702
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the screening results and genotype distribution characteristics of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency among Dai people in Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province, and to provide a scientific theoretical basis for its prevention and treatment. Methods The G6PD enzyme activity was quantitatively detected in 416 samples of gestational age population of Dai nationality in Yingjiang County by fluorescent spot test (FST), and the G6PD genotype was detected by next-generation gene sequencing (NGS) technology. The genotype and clinical phenotype were statistically analyzed. Results The G6PD enzyme activity was detected in 416 samples, and the positive rate was 22.12%, of which 27.42% were male and 17.83% were female, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Eight common gene mutation types were identified: c.1311C > T, c.487G > A, c.1388G > A, c.392G > T, c.1376G > T, c.143T > C, c.1024C > T. The carrier rate of c.1311C > T mutation in Yingjiang area was 33.17%. The positive rates of NGS and FST were 53.13% and 22.12%, respectively, and the results of the two methods were poorly consistent (Kappa = 0.280). The enzyme activity of the c.1311C > T mutation is mostly normal. If the c.1311C > T mutation is not considered, the results of the two methods are more consistent for male samples (Kappa = 0.658) than for females (Kappa = 0.233). Conclusions The carrier rate of G6PD deficiency is high in the Dai population in Yingjiang County, Yunnan Province. The gene mutations are mainly c.1311C > T, c.487G > A, c.1388G > A, c.392G > T, and c.1376G > T. c.1311C > T mutation and G6PD enzyme activity are mostly normal. The second-generation sequencing technology can simultaneously detect the common mutation types of the Dai people in Yingjiang County, Dehong Prefecture, and significantly improve the positive rate of detection. The fluorescent spot method may miss both female heterozygous and compound heterozygous mutations, and has a higher detection rate for male hemizygous mutations.
2023, 44(7): 22-28.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230711
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the relationship between endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidases (ERAP) gene polymorphisms and serum polio antibodies induced by sequential polio vaccine immunization. Methods A total of 243 Zhuang individuals were selected from the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region who received two doses of inactivated polio vaccine and one dose of bivalent oral polio vaccine. Polio-neutralizing antibodies types I, II and III were tested from pre-immunization and 28 days after immunizations, and six ERAP1 and two ERAP2 SNPs were genotyped using TaqMan probe genotyping. The allele frequency and genotype frequency were calculated for each SNP, and the association between the SNPs and the polio antibody response was analyzed. Results It was found that individuals carrying the rs2549782-G andrs2248374-A allele of the ERAP1 gene had lower levels of type I polio-neutralizing antibodies compared to those carrying the T and G alleles, respectively (both of 11.590±1.979 vs 11.950±1.895, Padj = 0.031). In addition, it was observed that GT and AG genotypes of rs2549782 of rs2248374 exhibited lower GMT type I polio-neutralizing antibodies than those of TT and GG genotypes (both of 11.741±0.141 vs 12.378±0.157, Padj = 0.045). Conclusion Polio vaccine-induced antibody responses may be associated with ERAP2 gene polymorphism.
2023, 44(7): 29-33.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230717
Abstract:
Objective To explore the relationship between DNA damage and urinary arsenic metabolism in four genes of EGFR, PTEN, Kras and PIK3CA in workers exposed to arsenic in arsenic factories. Methods A total of 78 first-line occupational arsenic exposure workers in an arsenic factory in Yunnan were selected as the exposure group and 24 people without history of arsenic exposure were included as the control group. The DNA damage of EGFR, PTEN, Kras and PIK3CA genes in peripheral blood lymphocytes was detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, and the contents of inorganic arsenic, monomethyl arsine acid and dimethylamine in the urine of all workers were detected and the percentages were calculated. Results The DNA damage and mean damage of the four genes in the occupational arsenic exposure group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). The mean damage of the four genes was positively correlated with inorganic arsenic, monomethyl arsine acid, dimethylamine acid, and the percentage of monomethyl arsine in urine and negatively correlated with the percentage of dimethylamine (P < 0.05). Conclusion The damage of important genes caused by arsenic exposure and the average damage of four genes have the potential to be used as markers of damage assessment.
2023, 44(7): 34-39.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230701
Abstract:
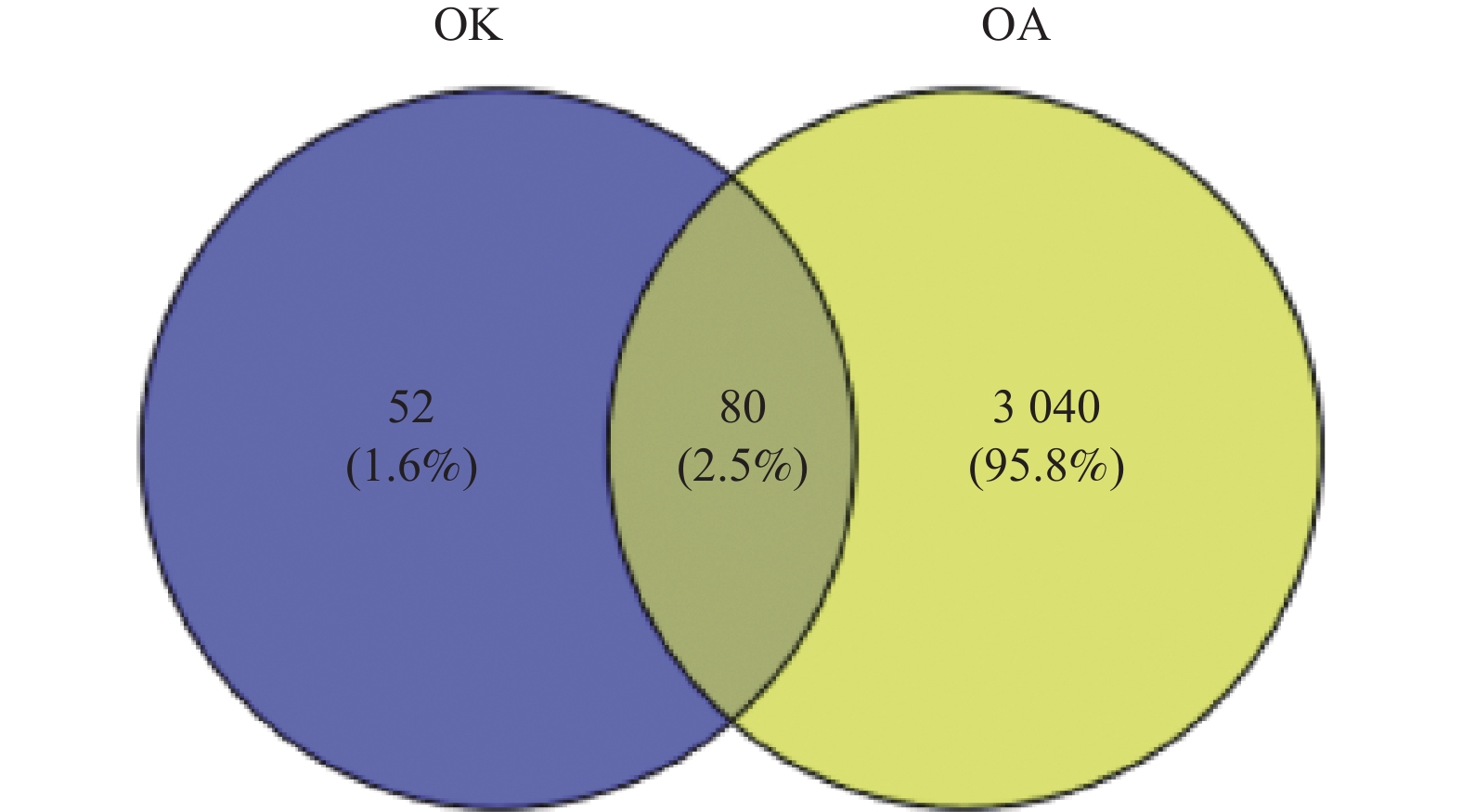
Objective To explore the potential mechanism of Osteoking (OK) in the treatment of Osteoarthritis (OA) and preliminarily verify it with DMM rats. Methods TCMSP database was used to collect potential targets of OK, GeneCards database and OMIM were used to screen target genes related to OA, and Cytoscape 3.8.2 software was used to establish a regulatory network for interaction between OK Active ingredient and OA target genes. The STRING database was used to construct protein interaction maps and GO and KECG were analyzed. In addition, OA rats were constructed using medial meniscus instability surgery (DMM) to observe knee joint cartilage lesions, and ELISA was used to detect inflammation and oxidative stress levels after OK treatment. Results Network pharmacology results showed that 80 core genes were involved in OK therapy for OA, including serum albumin (ALB) and interleukin-6 (IL6), mainly involving biological processes such as immunity, inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and metabolism. Animal experiments showed that compared with the model group, the surface structure of the articular cartilage in the OK group of rats tended to be normal, with less detachment of chondrocytes; OK reduced serum inflammatory factors IL-6 (P < 0.01), VEGF (P < 0.01), and oxidative stress factor MDA (P < 0.05), improved ALB levels and SOD activity (P < 0.01). Conclusion OK can alleviate OA cartilage tissue damage, enhance immunity, and inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress reactions, preliminarily verifying the results of network pharmacology.
2023, 44(7): 40-46.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230704
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the self-rated health status of elderly hypertensive patients in rural areas of Yi people, Yunnan province, and explore the influencing factors. Methods A convenience sample of 980 elderly hypertensive patients from rural areas where Yi ethnic groups gather in Yunnan Province was selected and their basic information, self-management and self-rated health level were investigated through a questionnaire survey. The relationship between self-management and self-rated health level was explored by Pearson correlation analysis. Finally, the influencing factors of the self-rated health level of elderly hypertensive patients were explored by multiple linear regression analysis. Results The participants reported low levels of self-rated health and self-management behavior. There was no significant difference in self-rated health scores between Han and Yi hypertensive elders (t = 1.458, P = 0.145). However, Han hypertensive elders had significantly higher self-management scores than Yi hypertensive elders (t = 2.577, P = 0.010). Accepted education (b = 10.408, P < 0.001), good economic situation (b = 8.309, P < 0.001), and high self-management score (b = 1.911, P < 0.001) were protective factors for self-rated health, while living alone (b = -7.052, P = 0.039), having a disease in the past two weeks (b = -5.950, P = 0.049), being physically disabled (b = -17.445, P < 0.001), and having other chronic diseases (b = -14.014, P < 0.001) were risk factors for self-rated health. Conclusions The findings suggest that elderly hypertensive patients in rural Yi areas have poor self-rated health. Interventions are recommended to enhance their self-management skills and to address their specific needs, especially for those who live alone or have poor physical condition.
2023, 44(7): 47-51.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230706
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the prognosis of surgical resection in patients with nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (NF-pNENs). Methods The clinical and follow-up data of 45 patients who were pathologically confirmed NF-pNENs in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from January 2011 to December 2020 were retrospectively analyzed. Results The follow-up time was 6 to 112 months, and the median follow-up time was 47 months. A total of 43 patients were followed up. Postoperative recurrence occurred in 1 case, distant metastasis in 2 cases, 40 cases survived, and 3 cases died, one well-differentiated G2 patient died 83 months after surgery due to multiple systemic metastasis, and two poorly differentiated G3 patients died 6 months after surgery. The 5-year postoperative survival rate of patients with NF-pNENs was 95.3%. Univariate analysis showed that the tumor WHO grade and lymph node metastasis were related to the prognosis of NF-pNENs patients, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Multivariate analysis did not suggest independent factors affecting the prognosis of NF-pNENs. Conclusions Surgery is the only cure for pNENs currently, which is available in specialized pancreatic centers. Preoperative identification of WHO grade and lymph node metastasis is conducive to the choice of surgical mode. Standard intraoperative lymph node dissection is required to obtain a sufficient number of lymph nodes to clarify the metastasis, so as to better guide the prognostic evaluation.
2023, 44(7): 52-56.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230718
Abstract:
Objective To determine the characteristics of Tibetan patients with orthodontic treatment in Shangri-la of Diqing prefecture, and provide scientific evidence for dentists. Methods 249 Tibetan orthodontic patients (90 males and 136 females) between the ages of 12-20 were selected in Diqing Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture People’s Hospital. By analyzing and evaluating case data, information on gender, age, oral health status, bad habits, Angle’s classification, clinical presentation classification, and reasons for seeking treatment were organized and recorded. The data obtained were statistically analyzed using SPSS 25.0 software. Results The results showed that among the Tibetan orthodontic patients who sought treatment, females aged 11 to 18 were the majority. The highest occurrence of dental caries was observed in oral health. Mouth breathing was the most common bad habit. Angle’s Class I malocclusion was the most common, while Class III was the least common. The most common clinical presentations were crowded teeth, deep overbite, and deep overjet. The main reasons for seeking treatment were aesthetic requirements and parental demands. There was no statistically significant difference between males and females (P > 0.05). Conclusions There was a certain characteristic in Tibetan patients with orthodontic treatment in Shangri-la of Diqin prefecture. Dentists can take this as scientific evidence to obtain better therapeutic effects, in addition, it is necessary to increase the intensity of oral health publicity and education and input of medical resources.
2023, 44(7): 57-63.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230713
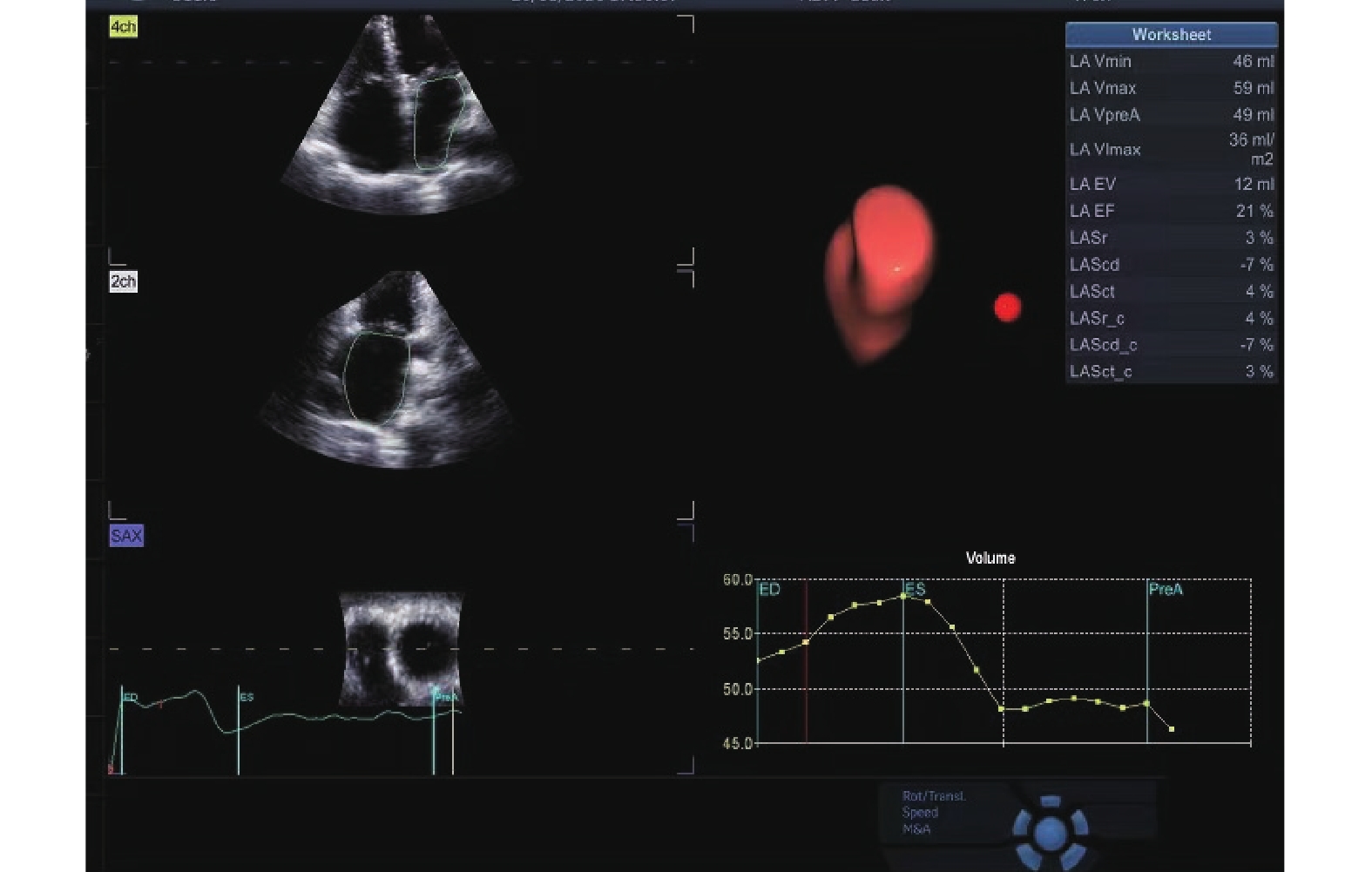
Abstract:
Objective To explore the role of four-dimensional left atrial automatic quantitative technology in evaluating the volume and function of the left atrium in non-selective continuous patients, and to preliminarily explore its accuracy and repeatability. Methods Foure-dimensional left atrial full-volume dynamic images of 187 consecutive patients were collected, 44 patients who failed the analysis were excluded, and 143 were successfully analyzed. Using Simpson’s biplane method as the reference standard, the 4D Auto LAQ technology was used to evaluate the left atrial end-diastolic volume (LAVmax), left atrial end-systolic volume (LAVmin), left atrial maximum volume index (LAVImax), and left atrial global ejection fraction. (LAEF) accuracy and repeatability. Results In all patients who were successfully analyzed, the inter-technique comparisons showed good correlations (R-values: LAVmax 0.91, LAVmin 0.89, LAVI 0.90, LAEF 0.54; all P < 0.01), small biases ( LAVmax 10.1 mL, LAVmin 3.1 mL, LAVI 6.4 mL, LAEF 10.0%; Concordance interval: LAVmax (-30.7-50.9) mL, LAVmin (-32.2-38.4) mL, LAVI (-21.2-34.1) mL, LAEF (-19.8-39.8)%] for all measurements in all patients. 4D Auto LAQ technology showed good correlation between the parameters of different cardiac cycles (r value: LAVmax 0.99, LAVmin 0.98, LAVImax 0.99, LAEF 0.92; all P < 0.01), and the average measurement difference did not exceed two measurement units (1 mL/volume, 1%/LAEF), the consistency interval is also narrow [LAVmax (-8.9-7.9) mL, LAVmin (-7.9-10.8) mL, LAVI (-7.9-10.8) mL/m2, LAEF (-14.8-9.1)%. The intra- and inter-observer repeatability of each parameter of 4D Auto LAQ technology was good (within-group correlation coefficients were all > 0.8, 0.81-0.99, and coefficients of variation were all < 10%), and it was better than Simpson’s biplane method. Compared with Simpson’s biplane method, the time of 4D Auto LAQ quantitative technology was significantly reduced, which were (30.87±5.05)s and (60.20±5.05)s respectively (P < 0.05). Conclusions Since4D Auto LAQ technology can be widely used in clinical practice as a feasible and objective ultrasound technique.
2023, 44(7): 64-68.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230727
Abstract:
Objective To analyze the clinical risk factors in idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism patients (IHH). Methods We selected 120 patients with hypogonadism from the Endocrinology Department of the First People's Hospital of Yunnan Province from January 2008 to December 2021 (82 males, 38 females, including 25 Kalman syndrome patients; 22.43 ± 6.08 years) as the case group. We also selected 95 healthy patients with normal gonadal function (75 males and 20 females21.47±2.67 years) as the control group. General clinical data of patients in the case group and control group were collected, excluding the patients with some missing data. We analyzed whether the indicators were statistically different between the case and control groups by multivariate analysis. The data on the bone mineral density of 48 IHH patients, including 31 patients with reduced bone mineral density (22 males, 9 Females) and 17 patients with normal bone mineral density (6 males, 11 females), were collected in the case group. The risk factors leading to abnormal BMD were analyzed in IHH patients. Results There were significant differences in age, weight, E2, Testo, LH, FSH, CHOL and blood glucose (P < 0.05), and no significant differences in gender, height, TSH, T3, T4, FT3, FT4, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C (P > 0.05). Unordered binary Logistic regression analysis showed that E2 and Testo were the protective factors for IHH patients (P < 0.05). Comparison between the IHH patients for the reduced BMD group and the IHH patients for the normal BMD group: there were significant differences in sex and age (P < 0.05), while E2, Prog, Testo, PRL, LH, L H, FSH was not significant. Disordered binary Logistic regression analysis showed that age was the risk factor for BMD in IHH patients, and sex was the protective factor for BMD in IHH patients (P < 0.05). Conclusions IHH can lead to decrease of blood glucose, lipid and bone density. E2 and T are the protective factors for IHH, age is the risk factor for decreased bone density in IHH patients, and gender is the protective factor.
2023, 44(7): 69-77.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230724
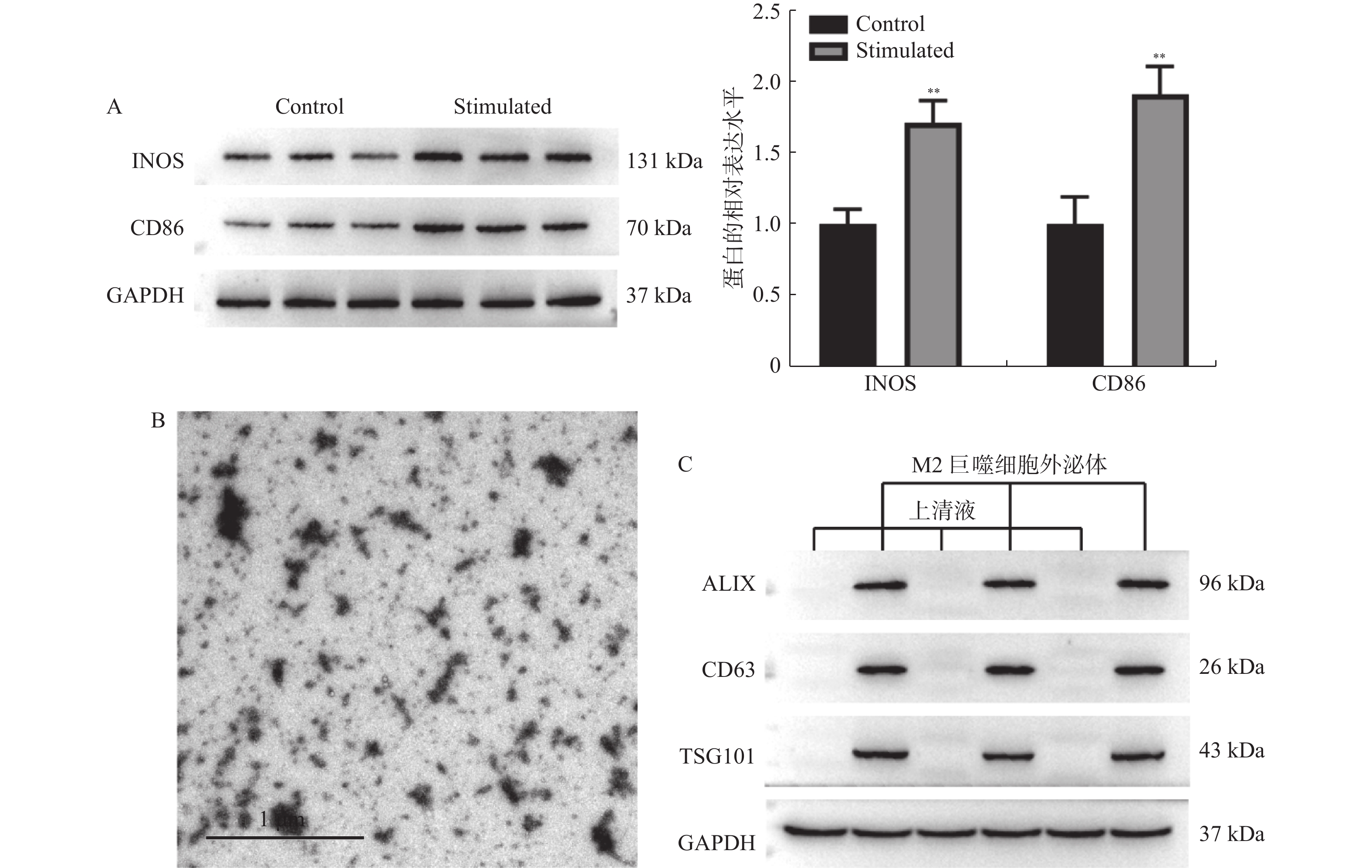
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of M2 macrophage-derived exosome miR-1246 on the proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of AGS cells. Methods After induction of M2 macrophages using LPS and IFN-γ, their exosomes were isolated and identified by transmission electron microscopy and western blot. After M2 macrophages were transfected with NC inhibitor and miR-1246 inhibitor respectively, the corresponding exosomes were isolated and co-cultured with AGS cells, and proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion of AGS cells were detected by CCK-8, Annexin V-FITC/PI and Transwell, respectively. TargetScan database predicted miR-1246 downstream targets and the targeting relationship between miR-1246 and GSK3B was validated by dual-luciferase reporter gene assays. Results The exosomes isolated from M2 macrophages were 30-150 nm in size and expressed ALIX, CD63 and TSG101. M2 macrophage-derived exosomes increased the viability and invasive cell count of AGS cells and decreased their apoptotic ratio. Phenotypic changes in AGS cells were reverted by knocking down the expression of miR-1246 in exosomes. Exosome miR-1246 targets GSK3B and upregulated the expression of β-catenin and c-Myc. Conclusion M2 macrophage-derived exosome miR-1246 mediates Wnt pathway activation to promote proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells and inhibit their apoptosis via targeting GSK3B.
2023, 44(7): 78-87.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230716
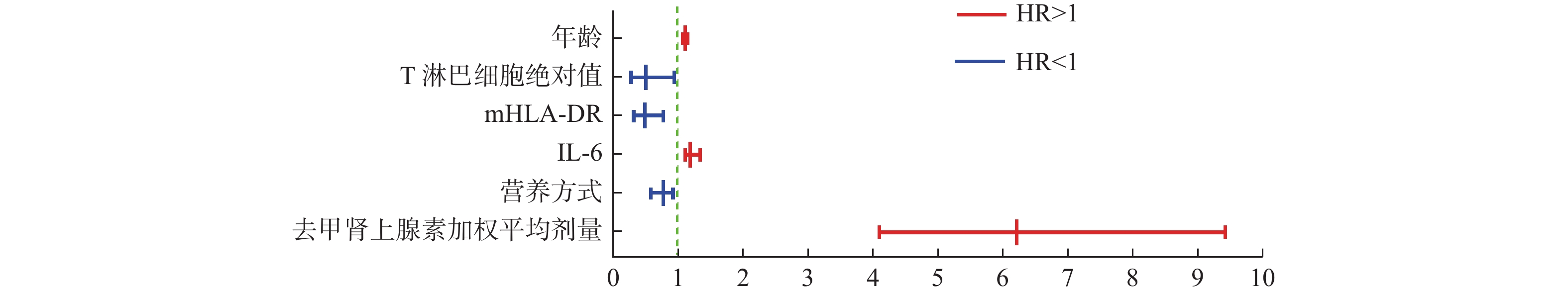
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the prognostic risk factors of patients with septic shock based on circulatory and cellular immune effects, to accurately regulate the noradrenaline dose, alleviate immune function suppression, and improve the success rate of septic shock treatment. Methods This is an observational, retrospective, cohort study. According to the inclusion and exculusion criteria, 160 patients with septic shock treated in ICU of the first affiliated hospital of Kunming medical university from May 2021 to December 2022 were collected, and all of them were given standard cluster treatment. At the same time, according to 28d survival outcome in patients with septic shock was divided into death group (n = 89) and survival group (n = 71), statistics of two groups of patients admitted to the hospital within 24h baseline data, test indicators, the weighted average dose of noradrenaline, blood gas index, microcirculation index, cellular immunity and early treatment of clinical data in 72h. Meaningful indicators were identified by single-factor analysis, and a multivariate COX proportional risk regression model was applied to screen out independent risk factors affecting the prognosis of patients with septic shock. Results Multivariate COX regression model analysis results showed that: age (HR = 1.05, 95%CI: 1.09~1.12, P = 0.036), nutritional mode (HR = 0.74, 95%CI: 0.56~0.90, P = 0.037), the weighted average dose of norepinephrine (HR = 6.21, 95%CI: 4.09~9.43, P < 0.001), IL-6 (HR = 1.16, 95%CI: 1.09~1.31, P = 0.012), absolute value of T lymphocytes (HR = 0.47, 95%CI: 0.24~0.91, P = 0.025), mHLA-DR (HR = 0.46, 95%CI: 0.28~0.75, P = 0.002).Six factors were independent risk factors affecting the outcome of patients with septic shock to visualize the forest plots presented. Conclusions The age, the weighted average dose of norepinephrine and IL-6 are the dangerous factors affecting the prognosis of patients with septic shock. The hazard ratio is greater than 1. Nutrition, T-lymphocyte absolute value and mHLA-DR are the protection factors affecting the prognosis of patients with septic shock. The hazard ratio is less than 1.
2023, 44(7): 88-93.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230707
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the correlation between pulmonary function and respiratory muscle strength in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) patients compared to healthy subjects of the same age, and to investigate the correlation between the size of the scoliosis angle and the type of scoliosis with pulmonary function and respiratory muscle strength in AIS patients. Methods We analyzed the lung function indicators of 50 patients with AIS (Cobb=29.720±11.875) and 50 healthy adolescents treated at the Department of Orthopedics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Kunming Medical University from June to December 2022. Pulmonary function indicators included forced vital capacity (FVC) as a percentage of predicted value (FVC pred%), and forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1). (FEV1 pred%), maximum expiratory flow volume (PEF pred%), and the maximum expiratory rate in one second (FEV1/FVC). Respiratory muscle function indicators included maximum expiratory pressure (MEP) and maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP). Results There were no statistical differences in FEV1/FVC and PEF pred% between the AIS group and healthy controls, and FVC pred%, FEV1 pred% (P < 0.01), inspiratory muscle strength, and expiratory muscle strength were worse in the AIS group than in the healthy group. There was no correlation between pulmonary function parameters, respiratory muscle strength, and Cobb’s angle, and no difference in pulmonary function and respiratory muscle strength between patients with different scoliosis types. Conclusions Patients with AIS have poorer FVC pred% and FEV1 pred%, and respiratory muscle strength than healthy subjects of the same age. Different types of lateral bending and the size of Cobb angle are not correlated with restricted lung function.
2023, 44(7): 94-99.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230709
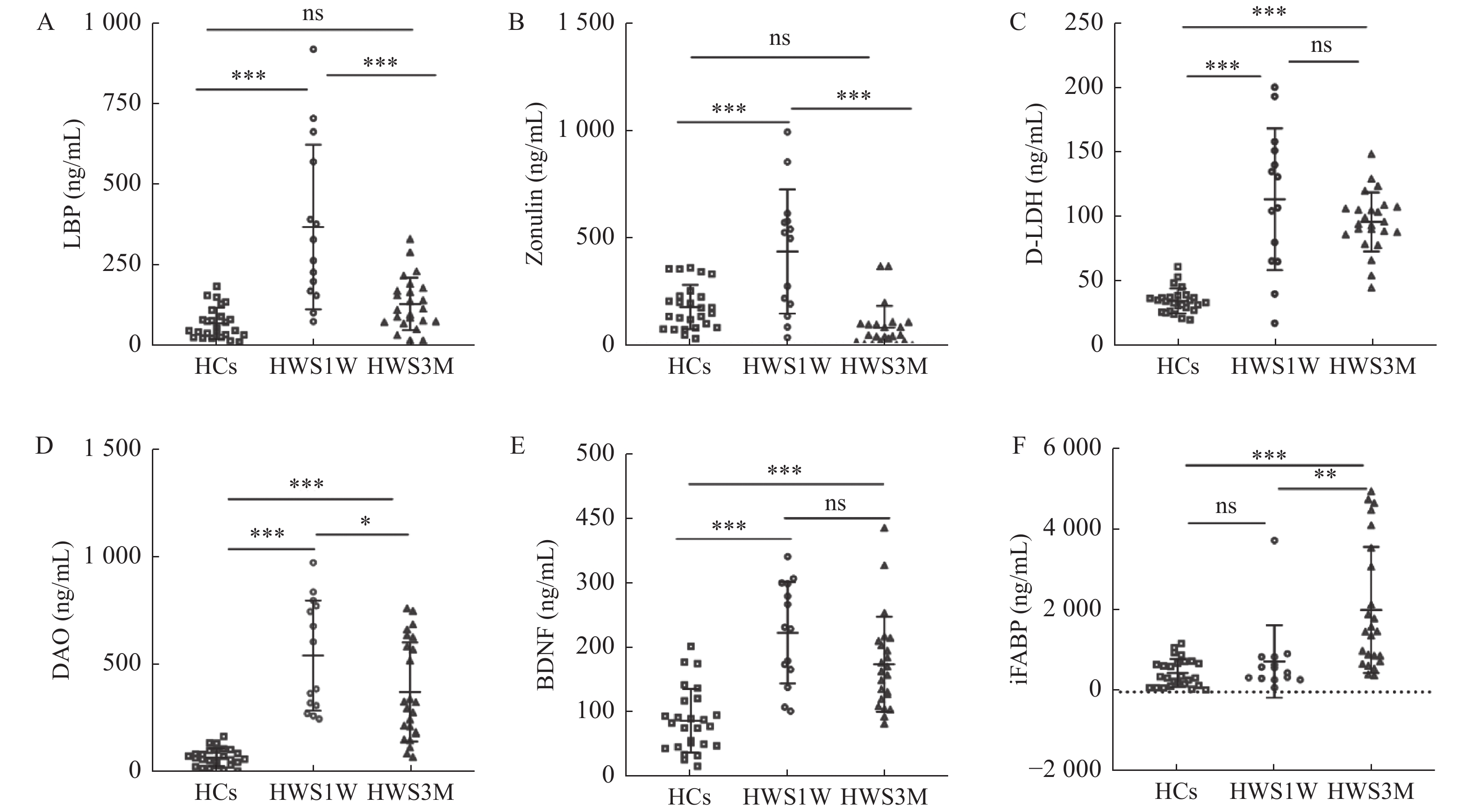
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the mechanisms of intestinal barrier damage after heroin withdrawal by analyzing changes in markers of intestinal barrier damage at different withdrawal times, providing a new direction for the relationship between altered psychiatric symptoms and the intestinal barrier after heroin withdrawal. Methods 14 1-week heroin withdrawal subjects (HWS1W), 24 3-months heroin withdrawal subjects (HWS3M) and 26 healthy controls (HCs) were recruited, and serum iFABP, D-LDH, iFABP, DAO, LBP, Zonulin, BDNF and D-LDH were determined by ELISA. Results Serum D-LDH, DAO, LBP, Zonulin and BDNF levels in HWS1W group were significantly higher than those in HCs (P < 0.001). Serum iFABP, D-LDH, DAO, and BDNF in HWS3M group were significantly higher than those in HCs group (P < 0.001). DAO increased significantly at 1 week of heroin withdrawal and decreased significantly at 3 months, but was still higher than the healthy control group (P < 0.001). iFABP showed no change in the acute withdrawal period (1 week), but increased at about 3 months of withdrawal. LBP and Zonulin increased significantly in the heroin abstention group for about one week, but there was no significant difference between the HWS3M group and the HCs group (P > 0.05). The levels of D-LDH and BDNF were significantly increased in HWS1W and HWS3M groups (P < 0.001). Conclusions The present study showed that intestinal barrier dysfunction occurred both 1 week and 3 months after heroin withdrawal. After 1 week of abstinence, intestinal barrier damage may be associated with intestinal flora disorder, changes in tight junction proteins, intestinal inflammation and intestinal epithelial integrity damage. After 3 months of abstinence, intestinal barrier damage is more likely to result from persistent damage to the intestinal barrier epithelium.
2023, 44(7): 100-104.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230725
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the pharmacokinetics of dexmedetomidine in burn patients with different degrees in order to improve the quality of anesthesia in burn patients. Methods Forty-five burn patients undergoing elective surgery were selected in this study. Among them, patients undergoing scar excision and skin grafting were included in group A, and patients with moderate and severe burns were respectively included in group B and group C, with 15 cases in each group. Patients in the three groups were respectively pumped dexmedetomidine 1µg/kg intravenously at a constant rate 10min before anesthesia induction. Before dexmedetomidine administration, during the administration of 1 (TCI1), 3 (TCI3), 5 (TCI5) and 10 (TCI10)min, after discontinuation of 2 (T2), 5 (T5), 10 (T10), 15 (T15), 20 (T20), 25 (T25), 30 (T30), 45 (T45), 60 (T60), 90 (T90), 120 (T120) min, we collected the arterial blood, and determined the plasma drug concentration (Cm) of dexmedetomidine. At last, we calculated the pharmacokinetic parameters. Results The Vd CL, K12, and K10 in group C were all higher than those in group A, the Vd, CL in group C were higher than those in group B, and the Vd in group B was higher than that in group A. Conclusions In severe burn patients, the Vd, CL, K12, and K10 of dexmedetomidine are increased, and Cm is decreased. The dose of dexmedetomidine can be appropriately increased to improve the quality of anesthesia and reduce complications.
2023, 44(7): 105-112.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230722
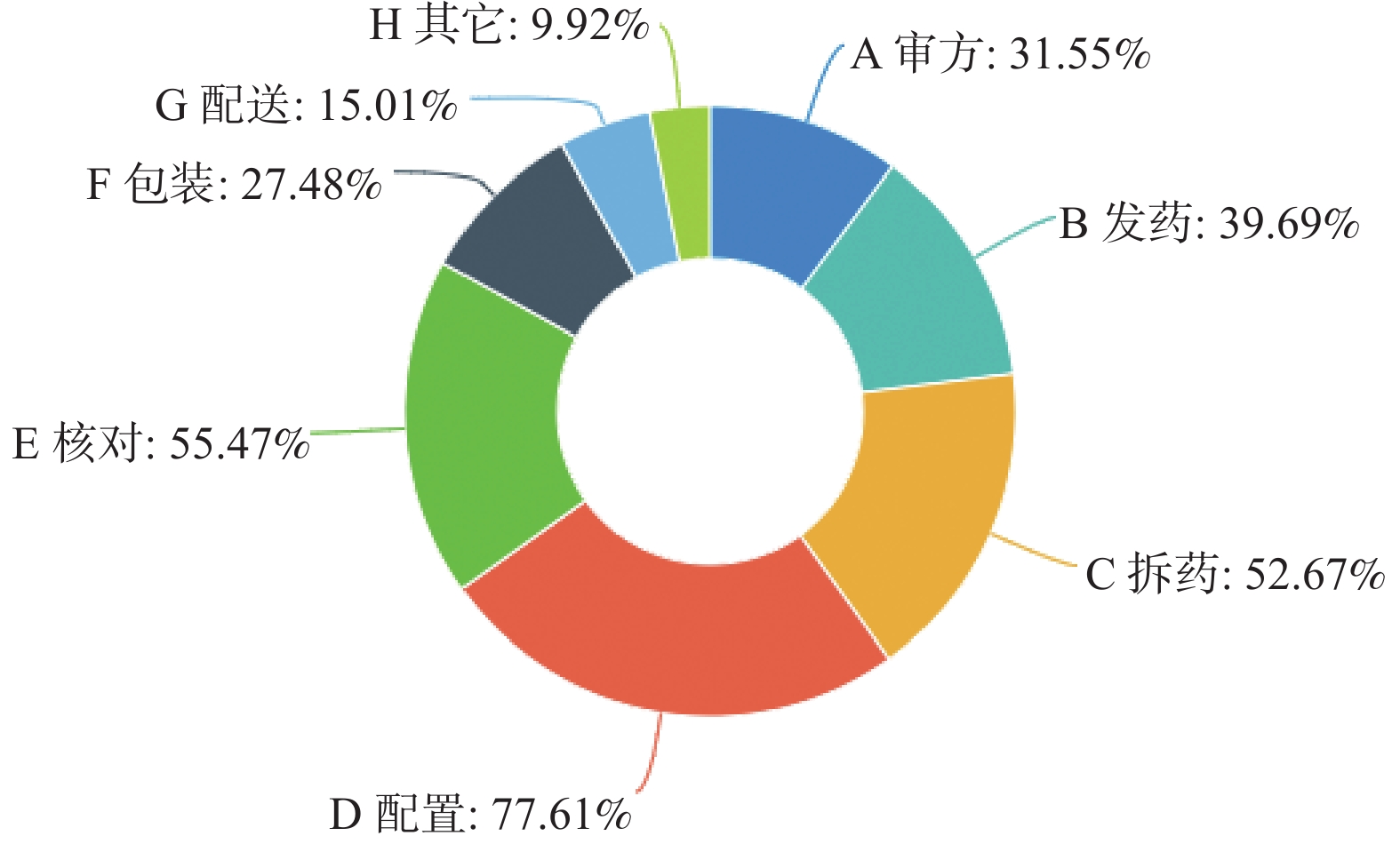
Abstract:
Objective To understand the occupational exposure situation of staff in the pharmacy intravenous admixture services (PIVAS) of Yunnan Province and identify the issues related to occupational protection in PIVAS staff. Methods Based on the “Quality Management Specification for Intravenous Dispensing of Cytotoxic Drugs in Medical Institutions” issued by the Chinese Pharmaceutical Association, a questionnaire survey was designed and tested using the Delphi method and reliability and validity analysis. The survey was conducted through “Wenjuanxing” in December 2021 among PIVAS staff in Yunnan Province hospitals. Results A total of 393 questionnaires were distributed and collected. After excluding invalid questionnaires based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, 382 valid questionnaires were obtained, with an effective response rate of 97.2%. The survey results showed that PIVAS staff in tertiary hospitals had more exposure to cytotoxic drugs and higher occupational exposure risks compared to staff in secondary hospitals. The hazards of cytotoxic drugs significantly increased with exposure time. There were issues with inadequate awareness of cytotoxic drug protection, improper handling of accidental exposure, and incomplete protection systems. Conclusions Occupational exposure is an important threat to the health of healthcare workers. It is necessary to establish and improve occupational protection management systems, enhance the awareness of occupational protection among healthcare workers, and implement effective occupational protection measures in order to reduce the hazards of occupational exposure.
2023, 44(7): 113-118.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230721
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the effects of combined subanesthetic doses of esketamine and propofol anesthesia in three-dimensional after loading treatment of cervical cancer. Methods One hundred patients who received three-dimensional afterloading treatment for cervical cancer in our hospital between February 2022 and January 2023 were randomly divided into two groups, with 50 cases in each group. Patients in the control S group received Sulfentany combined with propofol for anesthesia, while those in the experimental E group received esketamine together with propofol. The duration of surgery, wake-up time, the incidence of intraoperative respiratory adverse events, the incidence of postoperative adverse events, changes in vital signs at the same time point, and a self-reported satisfaction survey were recorded for both groups of patients. Results There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of operation time and wake-up time (P > 0.05). The effects of anesthetic and time on heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and oxygen saturation (SpO 2) were analyzed by two-way ANOVA. It was found that HR was higher in the E group than in the S group (F = 12.353, P = 0.001), and the HR differed significantly at different times (F = 6.637, P = 0.002). The MAP was also significantly higher in the E group compared with the S group (F = 11.245, P = 0.001), and also differed at different times (F = 17.023, P < 0.001), although there were no interactive effects between group and time ( F = 1.861, P = 0.159). Both group and time were observed to affect the SpO2, which was higher in the E group than in the S group (F = 4.960, P = 0.027) and also differed significantly at different times (F = 183.045, P < 0.001), although no interactive effects between group and time were observed ( F = 0.054, P = 0.947). No significant differences in the visual analog scale (VAS) scores were found between the two groups at different time points (P > 0.05), and both anesthesia methods had good analgesic effects. In terms of intraoperative adverse events, the incidence of hypotension (MAP ≤65 mmHg) or a decrease in blood pressure of ≥20% and requirements for vasoactive drug administration during surgery were lower in the E group than in the S group ( P < 0.05), while the incidence of psychiatric symptoms was higher in the E group than in the S group ( P < 0.05). As shown by the self-reported anesthesia satisfaction survey, all 100 patients were satisfied with the anesthesia, with no significant difference in the satisfaction rates between the two groups ( P > 0.05). Conclusions The combination of subanesthetic doses of esketamine and propofol anesthesia in the three-dimensional after loading treatment of cervical cancer resulted in stable hemodynamics, good analgesic effect, and patient satisfaction. However, the incidence of postoperative psychiatric symptoms was higher compared to the control group.
2023, 44(7): 119-124.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230703
Abstract:
Objective To observe the effects of rTMS on cognitive function in patients with traumatic brain injury. Methods A total of 160 patients with traumatic brain injury admitted to Yan’an Hospital of Kunming City from January 2021 to January 2022 were selected as the research objects and randomly divided according to the admission sequence number by random number table method. There were 80 cases in the treatment group and 80 cases in the control group. The control group was given sham rTMS stimulation on the basis of conventional drug treatment and cognitive training, while the treatment group was given true rTMS stimulation on the basis of conventional drug treatment and cognitive training, once a day, for a total of 4 weeks. Mini-Mental State Examination (Mini-mental State Examination) was performed before and 4 weeks after treatment. The cognitive function of the two groups was evaluated by MoCA, MMSE, RBMT. Results Intra-group comparison: the MMSE scores (orientation ability, memory ability, recall ability, calculation ability) of the treatment group were all improved compared with those before treatment (P < 0.05), while the MMSE scores (orientation ability, immediate memory ability) of the control group were only improved compared with those before treatment (P < 0.05). In the treatment group, the RBMT scores (remembering surname and given name, remembering artifact, remembering convention, picture recognition, immediate path memory, orientation) were all in- creased compared with those before treatment (P < 0.05), while in the control group, the RBMT scores (remembering surname and given name, remembering artifact, picture recognition, orientation) were only increased compared with those before treatment (P < 0.05). The MoCA scores (memory, language, calculation, orientation) in the treatment group were higher than those before treatment (P < 0.05), while the MoCA scores (memory, orientation) in the control group were only higher than those before treatment (P < 0.05). Comparison between groups: After treatment, the total scores of MMSE, RBMT and MoCA in the treatment group were higher than those in the control group (P < 0.05). Conclusion rTMS can effectively improve the cognitive function of patients with traumatic brain injury.
2023, 44(7): 125-129.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230720
Abstract:
Objective To study the growth factors and its contents in the concentrated growth factor (CGF) fibrin gel for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Methods T2DM patients who needed tooth extraction and implantation under insulin hypoglycemic were selected and grouped according to the hemoglobin A 1 c (HbA1c) results, peripheral blood was drawn and centrifuged to obtain CGF. In samples, TGF-β1, EGF, OPG, PDGF-BB, VEGF, IGF-1, BMP-2, Bfgf, TNF-αand IL-1βwere tested by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Results The CGF gels from insulin-controlled T2DM patients contained the same 10 growth factors as those from healthy controls. There was no significant difference in the content of OPG in T2DM patients with good and moderate insulin control compared with the healthy control group (P > 0.05). There were significant differences from the poorly controlled groups (P < 0.05). The content of partial growth factors (TGF-1, EGF) of T2DM patients in different groups was lower than that of healthy controls (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in the contents of some growth factors (PDGF-BB, VEGF, IGF-1, BMP-2, bFGF, TNF-αand IL-1β) between the observation group and healthy control group (P > 0.05). Conclusion The CGF fibrin gel of insulin-controlled T2DM patients contains a variety of growth factors, which can stimulate cell proliferation, migration and differentiation, improve bone formation quality, and promote soft and hard tissue healing, with strong regeneration and repair potential functions.
2023, 44(7): 130-135.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230715
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the influencing factors of preeclampsia to provide basis for prediction and treatment of preeclampsia. Methods In Qujing Maternal and Child-care Hospital, 11679 pregnant women who were included in the prospective cohort of maternal during the period from January 1, 2021 to June 30, 2022 were selected as the study subjects, and the clinical medical records of pregnant women were collected and recorded, the final result is preeclampsia or not.The risk factors of preeclampsia were analyzed by univariate and multivariate Logistic regression analysis. Results The attack rate of preeclampsia in this research was 1.36%, univariate analysis showed that there were statistically significant differences between the two groups in age, gestational weeks, pre-pregnancy BMI, educational level, multiple pregnancy, assisted reproduction, gestational hypertension, gestational diabetes, uterine fibroids, and regular antenatal examination (P < 0.05). With the multivariate Logistic regression analysis, we found low educated degree (OR = 1.932), gestational hypertension (OR = 32.107), gestational diabetes (OR = 1.765)and without regular antenatal examination (OR = 1.503)were the risk factors for preeclampsia. Conclusions Preeclampsia is a pregnancy-induced hypertension caused by a variety of factors, and its occurrence is related to education level, pregnancy-induced hypertension, gestational diabetes, regular birth check-up and other factors. Early prediction of preeclampsia should be strengthened to reduce the occurrence of adverse pregnancy outcomes and improve maternal and child health.
2023, 44(7): 136-141.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230705
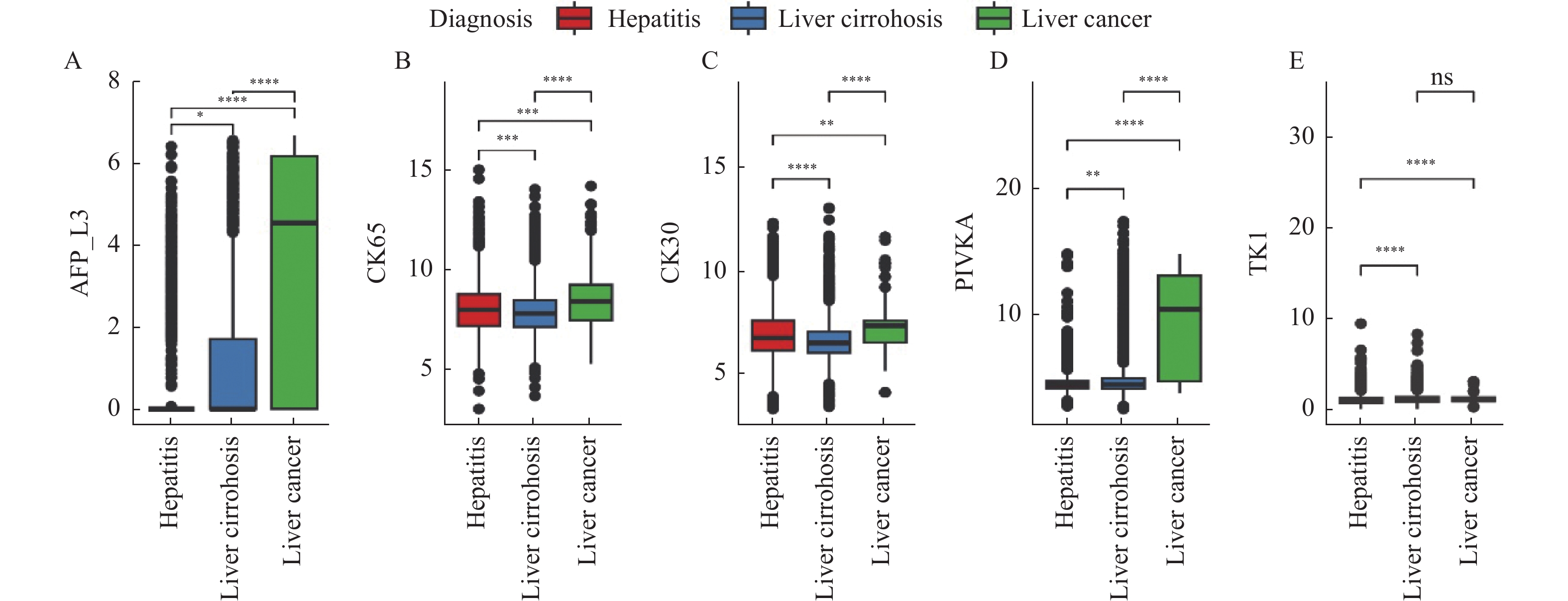
Abstract:
Objective To investigate the diagnostic value of AFP-L3 and PIVKAⅡ in liver cancer. Methods A total of 3066 patients with chronic liver disease who were admitted to Qingdao Sixth People’s Hospital from January 2019 to January 2022 were selected as objects of the research. The levels of AFP-L3, PIVKAⅡ, CK65, CK30, and TK1 in hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer were compared. The specificity and sensitivity were evaluated, and the ROC curve was used to evaluate the biomarkers and propose the optimal cutoff point. Results The expression of AFP-L3 and PIVKA in the liver cirrhosis group was higher than that in the hepatitis group (P < 0.0001), while the expression of CK65, CK30, and TK in liver cirrhosis group was lower than that in the hepatitis group (P < 0.001). The expression of AFP-L3, CK65, CK30 and PIVKA in the liver cancer group was significantly higher than that in the liver cirrhosis group (P < 0.0001), while the expression of TK in the liver cancer group was lower than that in the liver cirrhosis group (P > 0.05). Among the five biomarkers included in the study, AFP-L3 had the highest specificity (0.89) and PIVKAⅡ had the highest sensitivity (0.62), and the combined application of AFP-L3 and PIVKAⅡ had a sensitivity of 0.70 and a specificity of 0.81, which was better than a single marker. The analysis of ROC curve showed that PIVKAⅡ had a higher diagnostic value (24). Conclusion AFP-L3 is more specific than PIVKAⅡ in liver cancer screening, and the combination of AFP-L3 and PIVKAⅡ diagnosis may have diagnostic value in liver cancer.
2023, 44(7): 142-147.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230726
Abstract:
Objective To understand the psychological status of the elderly, through a survey of the elderly in Chengdu, to explore the correlation between the different psychological status of the elderly, to find the cut-in point for the related departments to establish the intervention strategy of the psychological status of the elderly in the early stage. Methods By using a multi-stage sampling method, the sampled communities were selected according to the east, west, south, north, and central. From March 5, 2022 to July 22, 2022, a self-designed questionnaire was used to conduct a field survey among the elderly in the community, collected basic information, cognitive status, depression status, anxiety status, psychotic symptoms of the elderly, etc. chi-square test and rank sum test were used to analyze the differences of psychological status among the elderly with different demographic characteristics, and Spearman correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation among the different psychological status of the elderly. Results It is based on the chi-square and rank sum test on the psychological status of the elderly with different demographic characteristics. There was statistically significant difference among the elderly in terms of social support (Z = -2.348, P = 0.019), anxiety (χ2 = 11.434, P = 0.001), and cognitive impairment (χ2 = 120.56 , P < 0.001). There was a statistically significant difference in cognitive impairment ( χ2 = 5.105, P = 0.024) among the elderly with different marital status. There were statistically significant differences in social support (H = 14.512 , P = 0.006), depression (χ2 = 7.033 , P = 0.008), and cognitive impairment (χ2 = 29.152, P < 0.001) among the elderly of different occupational types. There were statistically significant differences in social support ( H = 12.019, P = 0.017) and cognitive impairment (χ2 = 56.752, P < 0.001) among the elderly with different educational levels. There were significantly correlated with social support and depression ( r = -0.079, P = 0.011), social support and anxiety (r = -0.092, P = 0.003), cognitive impairment and depression (r = 0.117 , P < 0.001), and cognitive impairment and anxiety ( r = 0.179, P < 0.001), cognitive impairment and symptoms of mental illness ( r = 0.188 , P < 0.001), depression and anxiety ( r = 0.320 , P < 0.001), depression and symptoms of mental illness ( r = 0.103, P = 0.001), anxiety and symptoms of mental illness (r = 0.215, P < 0.001). Conclusions It is different in the psychological status of the elderly with different demographic characteristics, and there is a correlation between different psychological statuses. The relevant departments should formulate comprehensive intervention strategies according to the different demographic characteristics of the elderly, when a single mental state is found, it is necessary to carry out other related mental state investigations, which can effectively improve the mental state of the elderly and promote healthy aging.
2023, 44(7): 148-155.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230708
Abstract:
Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of pediatric chronic liver disease worldwide, and its incidence is gradually increasing with the global epidemic of obesity, but there is no standardized and effective treatment plan. At present, the pathogenesis of NAFLD has not been fully elucidated, Among many pathogenic factors, intestinal microflora disorder is the current research hotspot, which opens up a new direction for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of NAFLD. However, the treatment of NAFLD in children is still being explored. In this paper, the possible mechanism of intestinal flora and its metabolites mediating NAFLD in children in recent years was reviewed, as well as the diagnosis and treatment methods using intestinal flora as an intervention target, hoping to provide some new ideas and methods for the treatment of NAFLD in children.
Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of pediatric chronic liver disease worldwide, and its incidence is gradually increasing with the global epidemic of obesity, but there is no standardized and effective treatment plan. At present, the pathogenesis of NAFLD has not been fully elucidated, Among many pathogenic factors, intestinal microflora disorder is the current research hotspot, which opens up a new direction for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of NAFLD. However, the treatment of NAFLD in children is still being explored. In this paper, the possible mechanism of intestinal flora and its metabolites mediating NAFLD in children in recent years was reviewed, as well as the diagnosis and treatment methods using intestinal flora as an intervention target, hoping to provide some new ideas and methods for the treatment of NAFLD in children.
2023, 44(7): 156-161.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230719
Abstract:
Heart failure is one of the main causes of death in cardiovascular diseases. With the increasing prevalence of heart failure, it has become the main research direction to explore new therapeutic targets and further reduce the mortality of patients. This review provided a comprehensive overview of the different targets for heart failure therapy, including the G protein-coupled receptor family, Na+/H+ exchangers, deacetylase family, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines etc., by searching and collating studies related to heart failure therapeutic targets published in China and abroad. It provided new ideas for the treatment of heart failure and the development of new drugs.
Heart failure is one of the main causes of death in cardiovascular diseases. With the increasing prevalence of heart failure, it has become the main research direction to explore new therapeutic targets and further reduce the mortality of patients. This review provided a comprehensive overview of the different targets for heart failure therapy, including the G protein-coupled receptor family, Na+/H+ exchangers, deacetylase family, inflammatory cytokines and chemokines etc., by searching and collating studies related to heart failure therapeutic targets published in China and abroad. It provided new ideas for the treatment of heart failure and the development of new drugs.
2023, 44(7): 162-167.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230728
Abstract:
NASH is the characteristic pathological manifestation of the liver in MAFLD, which is a key turning point in the development of MAFLD from a relatively benign and reversible stage to liver injury and even cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent studies have shown that lipid deposition and oxidative stress run through MAFLD metabolic diseases, and improving hepatic lipid deposition and oxidative stress is the main intervention approach for the treatment and prevention of NASH disease. In general, promoting autophagy levels can reduce triglyceride (TG) accumulation and oxidative stress (OS) and promote hepatocyte survival, while blocking autophagy levels may accelerate the progression of NASH. However, the activation of autophagy levels is closely related to the activation of upstream signals AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 and the regulation of EI24. EI24, an essential autophagy protein closely related to the activation of AMPK and mTOR protein channels, can accelerate the activation of autophagy flow by promoting the degradation process of autophagy-lysosome. Meanwhile, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as ideal autophagy inducers have been widely studied for their excellent therapeutic effects in treating various inflammatory diseases such as NAFLD through the activation of AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Therefore, “drug-acting” mesenchymal stem cells should be used to regulate the activation of autophagy level of EI24/AMPK/mTOR to promote autophagy, inhibit adipogenesis and reduce lipid deposition, and effectively alleviate or reverse NASH liver injury, to provide a basis for elucidating the pathogenesis of NASH related diseases and developing new therapeutic strategies.
NASH is the characteristic pathological manifestation of the liver in MAFLD, which is a key turning point in the development of MAFLD from a relatively benign and reversible stage to liver injury and even cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent studies have shown that lipid deposition and oxidative stress run through MAFLD metabolic diseases, and improving hepatic lipid deposition and oxidative stress is the main intervention approach for the treatment and prevention of NASH disease. In general, promoting autophagy levels can reduce triglyceride (TG) accumulation and oxidative stress (OS) and promote hepatocyte survival, while blocking autophagy levels may accelerate the progression of NASH. However, the activation of autophagy levels is closely related to the activation of upstream signals AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 and the regulation of EI24. EI24, an essential autophagy protein closely related to the activation of AMPK and mTOR protein channels, can accelerate the activation of autophagy flow by promoting the degradation process of autophagy-lysosome. Meanwhile, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as ideal autophagy inducers have been widely studied for their excellent therapeutic effects in treating various inflammatory diseases such as NAFLD through the activation of AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy. Therefore, “drug-acting” mesenchymal stem cells should be used to regulate the activation of autophagy level of EI24/AMPK/mTOR to promote autophagy, inhibit adipogenesis and reduce lipid deposition, and effectively alleviate or reverse NASH liver injury, to provide a basis for elucidating the pathogenesis of NASH related diseases and developing new therapeutic strategies.
2023, 44(7): 168-172.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230714
Abstract:
Objective To understand the distribution of Kolb learning style of medical students and analyze its influencing factors, so as to provide a theoretical basis for the reform of medical teaching. Methods Kolb Learning style Scale and 10 related factors were used to investigate the learning style preferences and potential influencing factors of 416 medical students from 5 medical colleges in China. Results Among the Kolb learning styles of medical students, diverging, assimilating, converging and modulating styles accounted for 47.1%, 44.9%, 4.7% and 3.3%, respectively; The accommodating and converging types scored the highest in the process of active experimentation, while the diverging and assimilating types scored the highest in the process of reflective observation learning. The main factors influencing the learning style of medical students are their learning stage and their families’ attitude towards medical learning P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Conclusion The Kolb learning style of medical students is divergent, and has a strong ability to process information in the learning process.
2023, 44(7): 173-176.
doi: 10.12259/j.issn.2095-610X.S20230712
Abstract:
Objective To explore the role of case-based collaborative learning (CBCL) in the standardized training of residents. Methods All 64 residents included in this study were randomly divided into two groups: the experimental group (n = 32) and the control group (n = 32). The experimental group adopted CBCL teaching method and the control group adopted PBL teaching method. After 8 weeks of teaching, the two groups of residents were assessed and questionnaires were conducted to obtain the assessment scores of the two groups of residents and the evaluation scores of the residents on the two teaching methods. The scores difference between the two groups of residents were compared. Results The total scores of the experimental group were significantly higher than that of the control group (70.40±5.85 vs. 60.90±5.34, P < 0.05). The subitem scores of the experimental group (basic theoretical knowledge, case analysis knowledge, new progress knowledge and practice-related knowledge scores) were higher than those of the control group ( P < 0.05). The results of the questionnaire showed that the experimental group presented higher scores than the control group (general evaluation of teaching methods, P < 0.001; Evaluation of teaching methods stimulating interest in learning, P < 0.05; Evaluation of teaching methods improving practical ability, P = 0.008; Evaluation of teaching methods to improving diagnostic ability, P < 0.05; Evaluation of teaching methods to improving treatment, P < 0.05). Conclusion CBCL teaching method can be used in standardized training of residents.


 Email
Email RSS
RSS